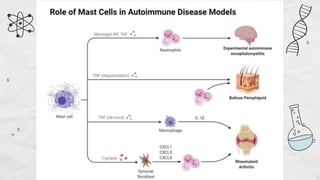
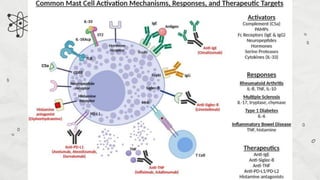
Mast cells are immune system cells that primarily reside in tissues rather than blood, playing a crucial role in the body's first response to external antigens. They originate from bone marrow and release various inflammatory mediators and pro-angiogenic factors essential for immune defense and maintaining homeostasis, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract. Mast cells also contribute to both innate and adaptive immunity, but their over-activation can lead to allergic reactions.