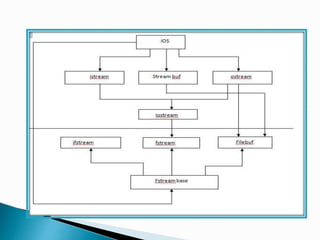
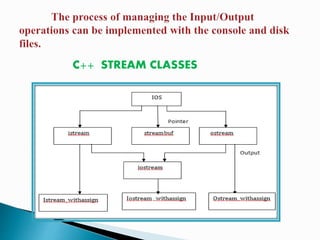
This document discusses C++ stream classes and file input/output. It covers the key stream classes like istream, ostream and iostream. It describes how to use stream manipulators and member functions to format console I/O. It also covers file streams like ifstream, ofstream and fstream for reading from and writing to files. Functions like open(), get(), put(), read(), write() are described for file I/O operations. Common file I/O tasks like displaying, modifying and deleting file contents are mentioned.




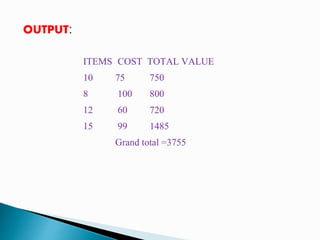
![#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int item[4] ={ 10,8,12,15};
int cost[4]={75,100,60,99};
cout.width(5);
cout<<”Items”;
cout.width(8);
cout<<”Cost”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingworking-170915124418/85/Managing-console-i-o-operation-working-with-files-6-320.jpg)
![cout.width(15);
cout<<”Total Value”<<”n”;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<4 ;i++)
{
cout.width(5);
cout<<items[i];
cout.width(8);
cout<<cost[i];
int value = items[i] * cost[i];
cout.width(15);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingworking-170915124418/85/Managing-console-i-o-operation-working-with-files-7-320.jpg)





![EXAMPLE:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int size=20;
char city[20];
cout<<”enter city name:n “;
cin>>city;
cout<<”city name:”<<city<<”nn”;
cout<<”enter city name again: n”;
cin.getline(city,size);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingworking-170915124418/85/Managing-console-i-o-operation-working-with-files-14-320.jpg)