1. Image compression reduces storage requirements by compressing images to reduce file sizes while retaining essential information.
2. Common image file formats include TIFF (uncompressed), JPEG (lossy compression), GIF (lossless compression suitable for web but limited colors), PNG (lossless compression for web that allows more colors than GIF), and RAW (unprocessed camera files).
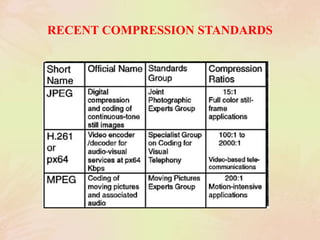
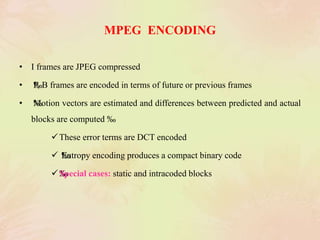
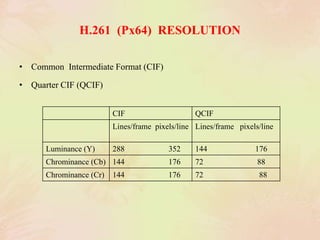
3. Standards like JPEG, MPEG, and H.261 were developed to compress images and video for efficient storage and transmission by applying techniques like the discrete cosine transform, quantization, and entropy encoding.