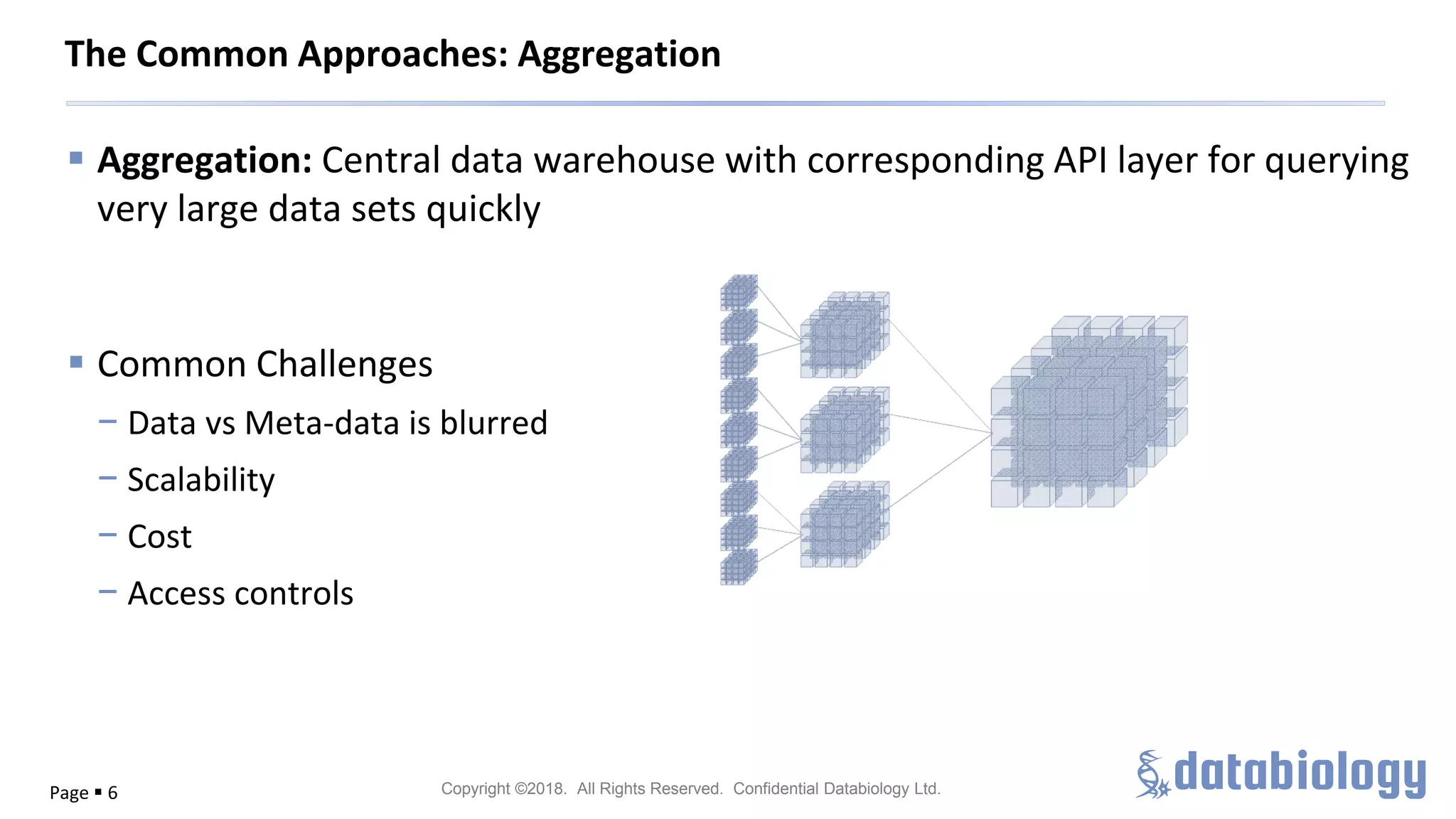
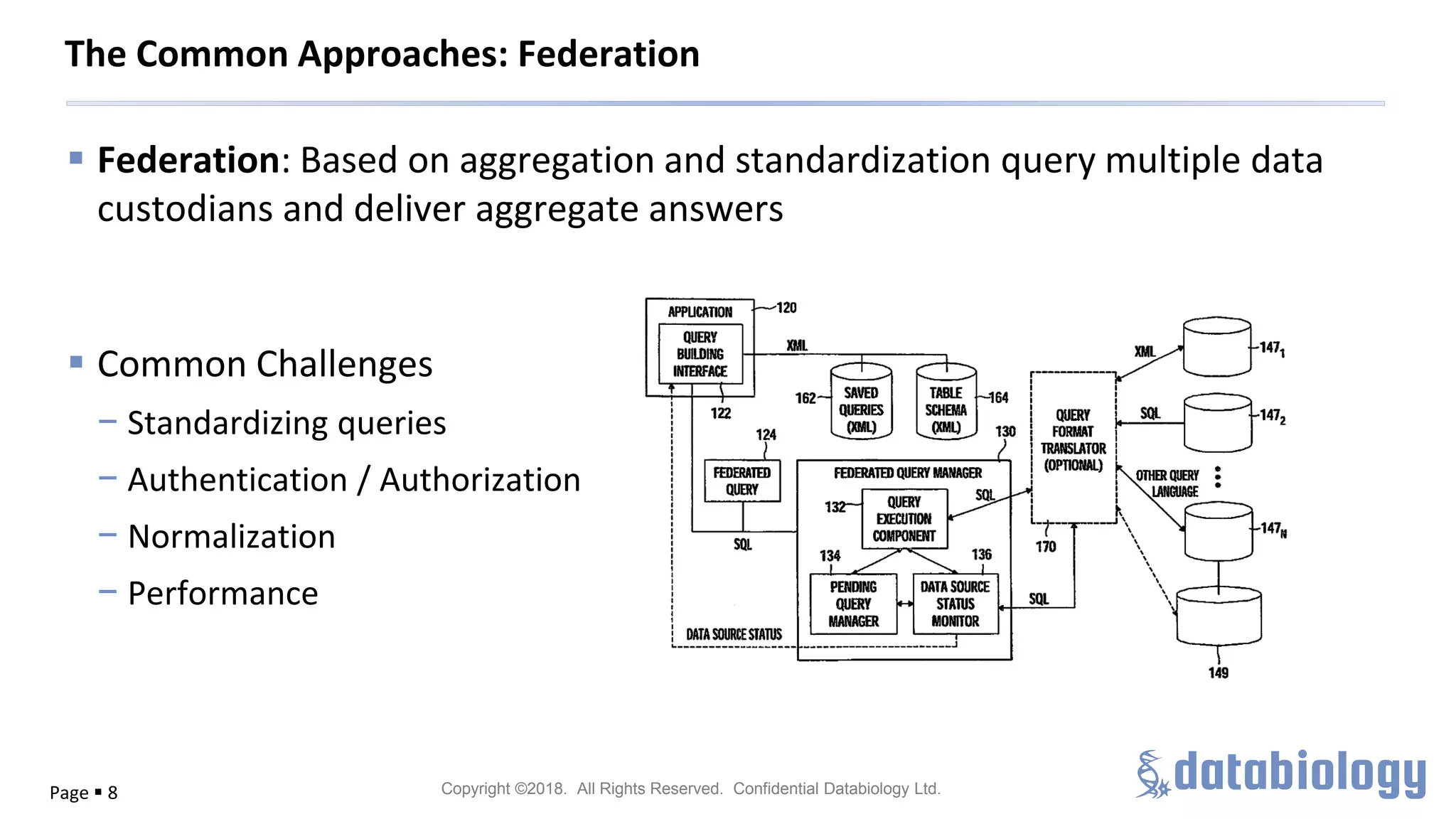
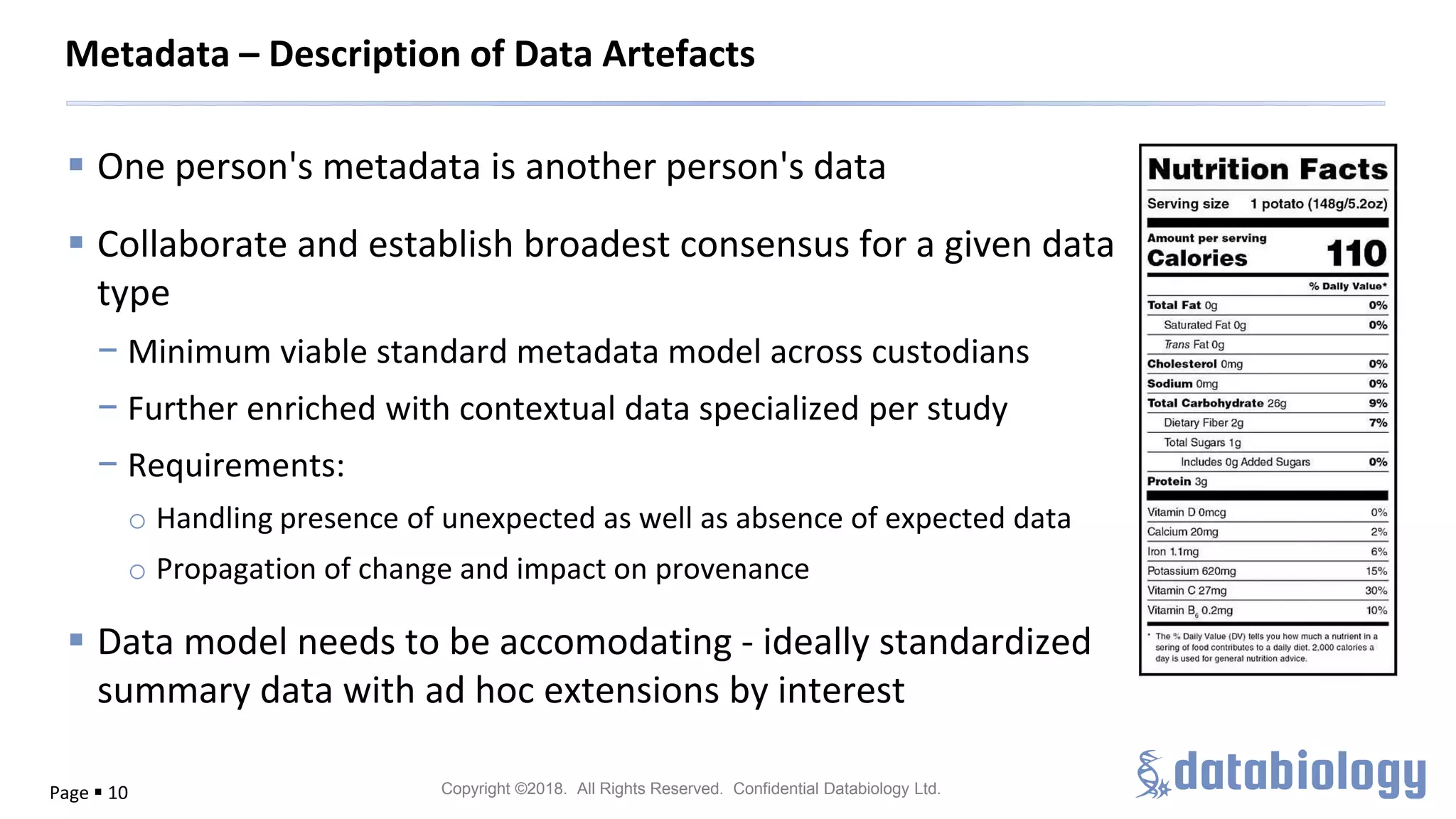
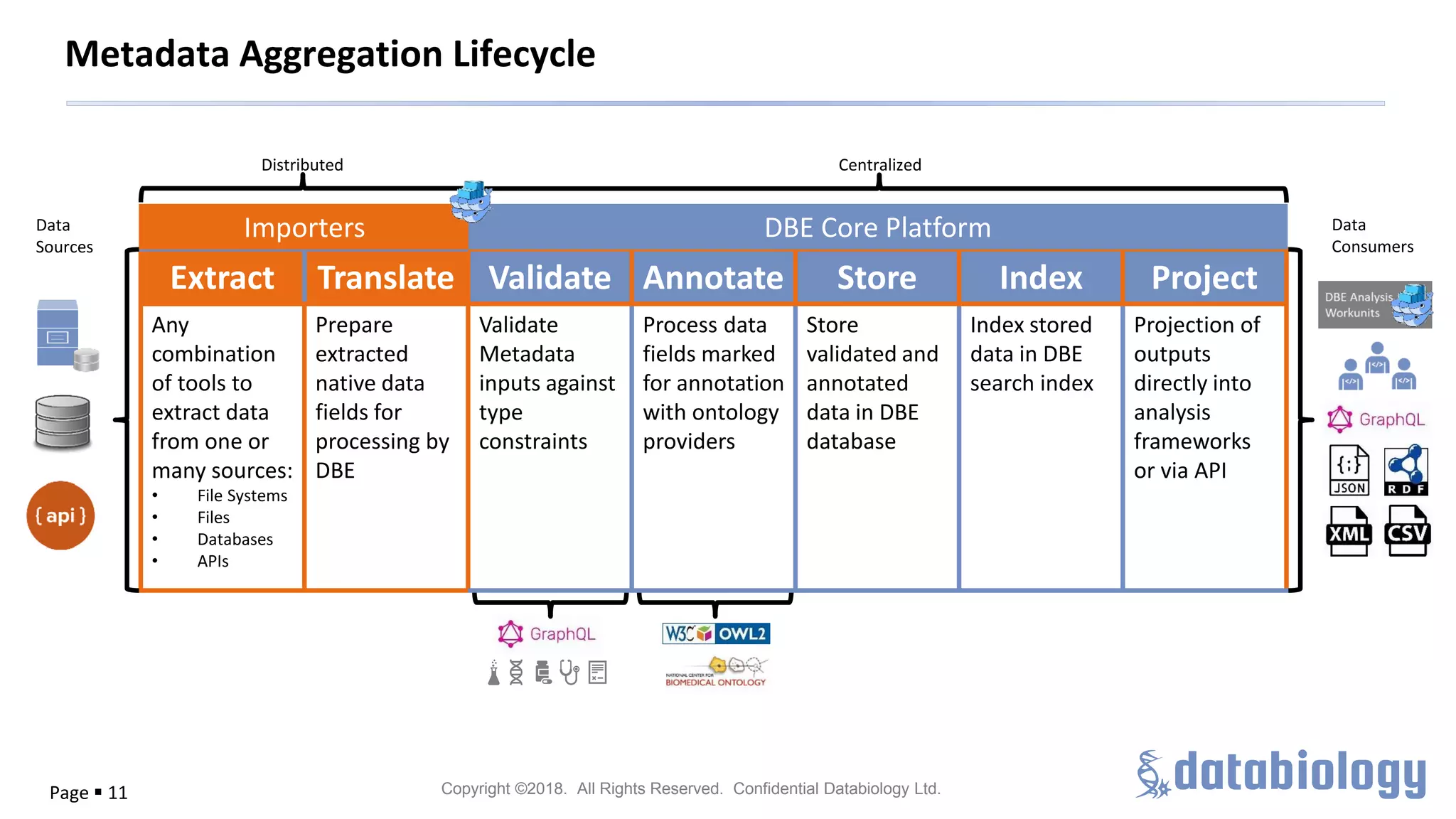
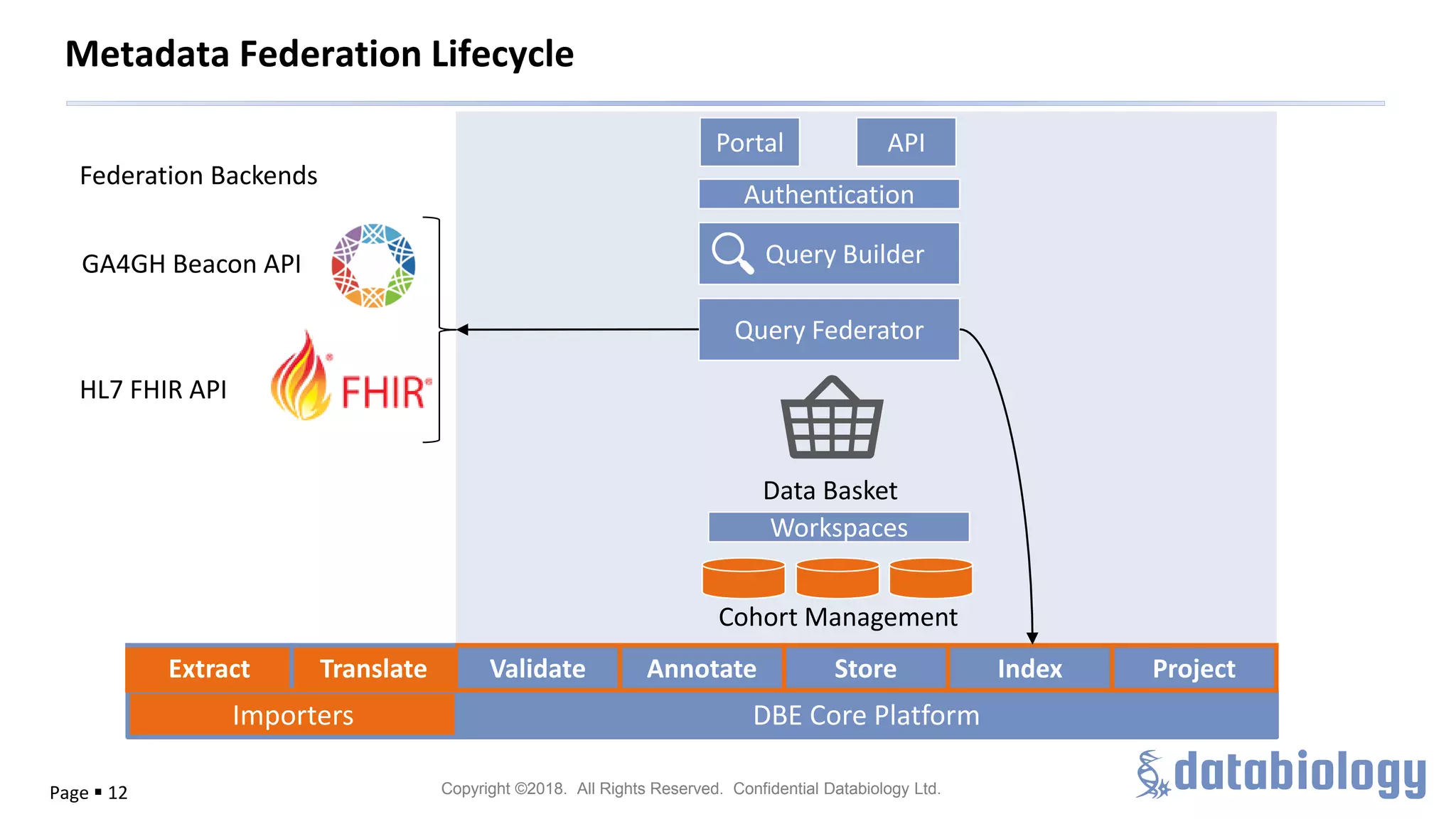
The document discusses the importance of metadata in managing biomedical data within large-scale collaborations, emphasizing that data is generated from various sources and that traditional data storage methods are becoming insufficient. It highlights challenges related to collaboration, such as data access, standardization, and the need for a unified approach to data management. The document also outlines metadata lifecycle processes, the significance of collaboration for establishing metadata standards, and the roles of various data custodians in facilitating data accessibility and usability.