The document summarizes key concepts in macroeconomics including:
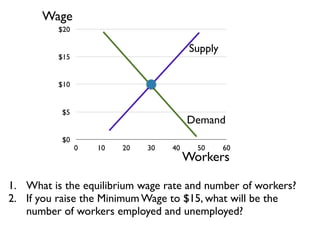
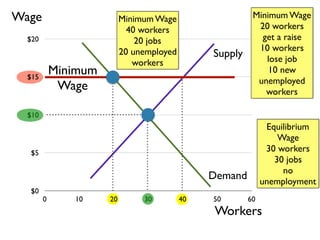
- Equilibrium models of supply, demand, and minimum wage rates and their impact on employment levels.
- The rule of 70s for calculating doubling time of values growing at a compound rate.
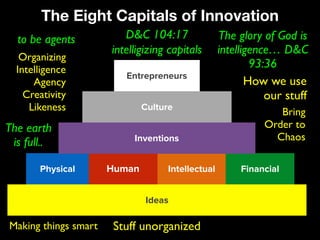
- Factors that influence innovation including incentives, creativity, and intellectual/physical/financial capital.
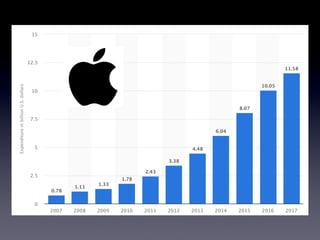
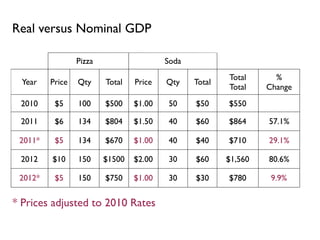
- Definitions and calculations for GDP, GDP per capita, nominal vs real GDP, GDP deflator, inflation rates, and using base years to adjust for inflation.