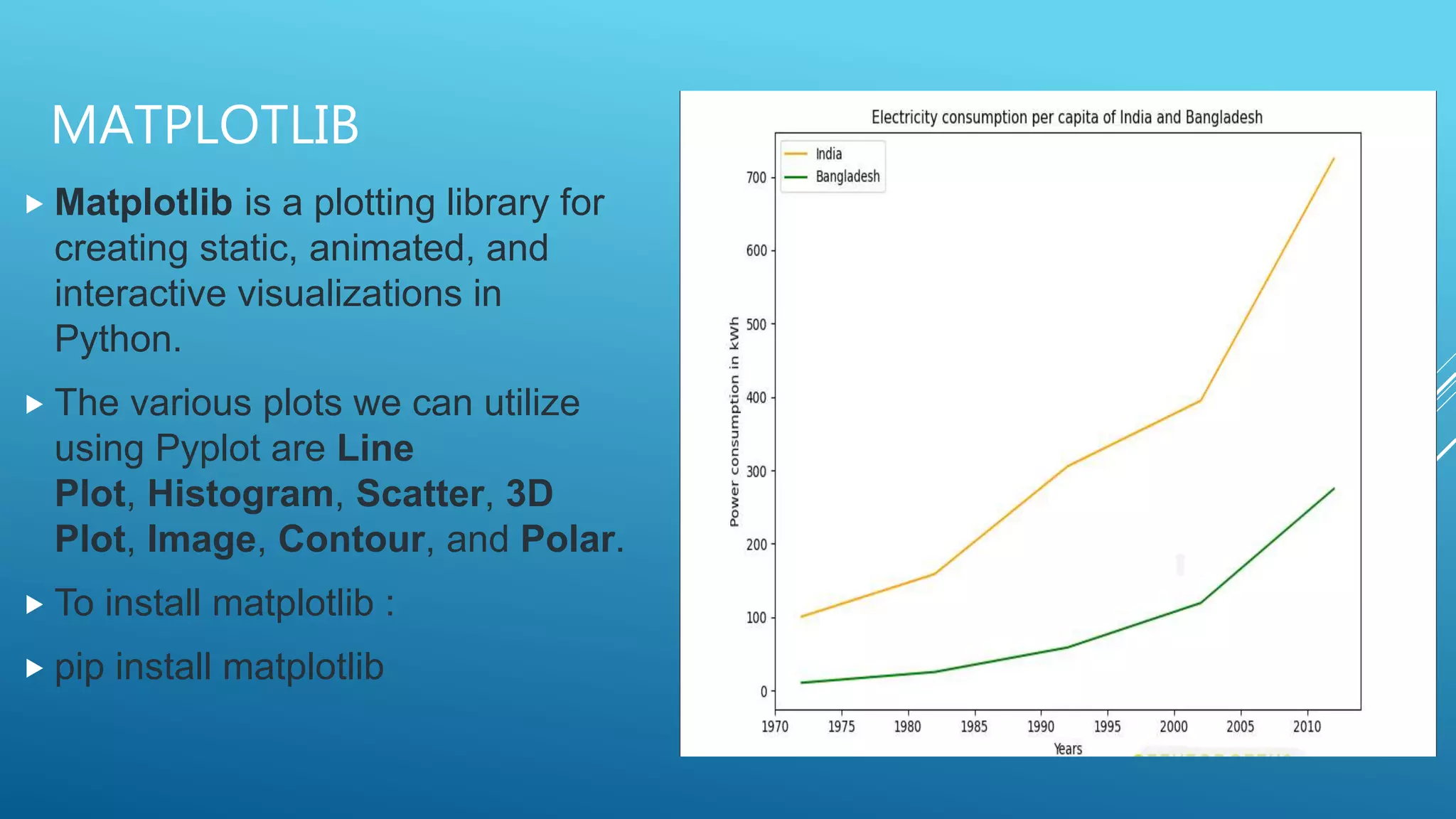
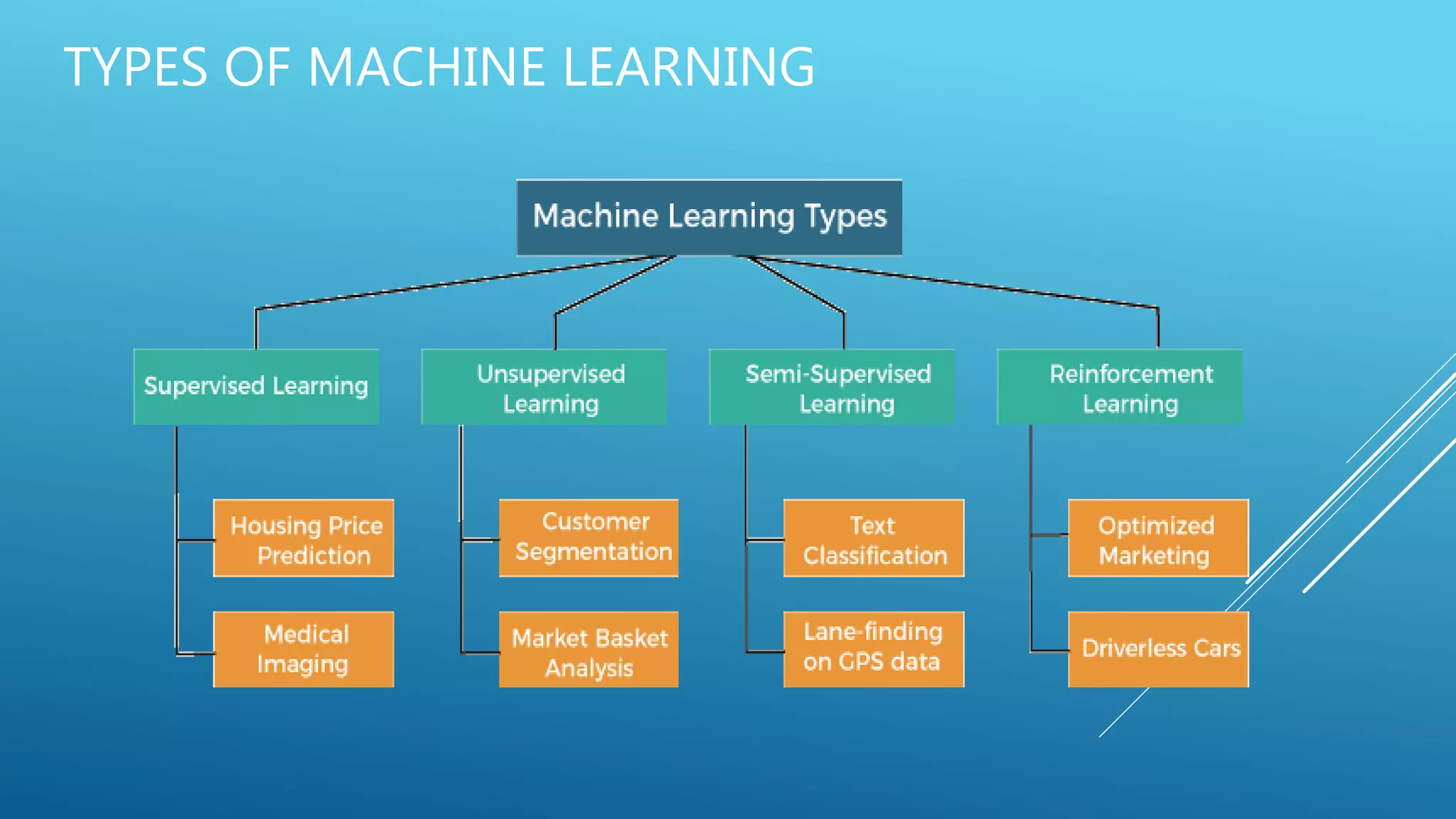
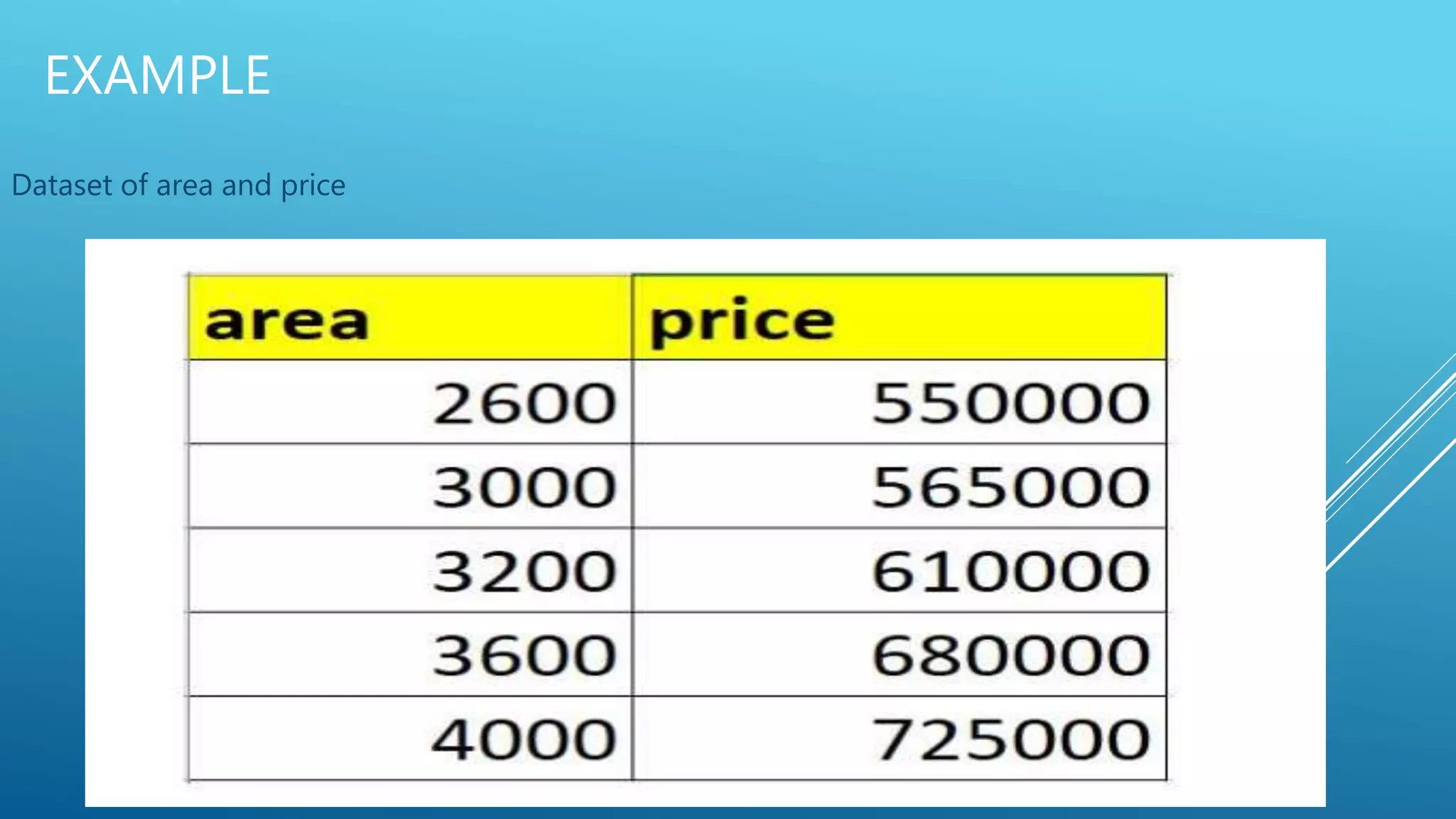
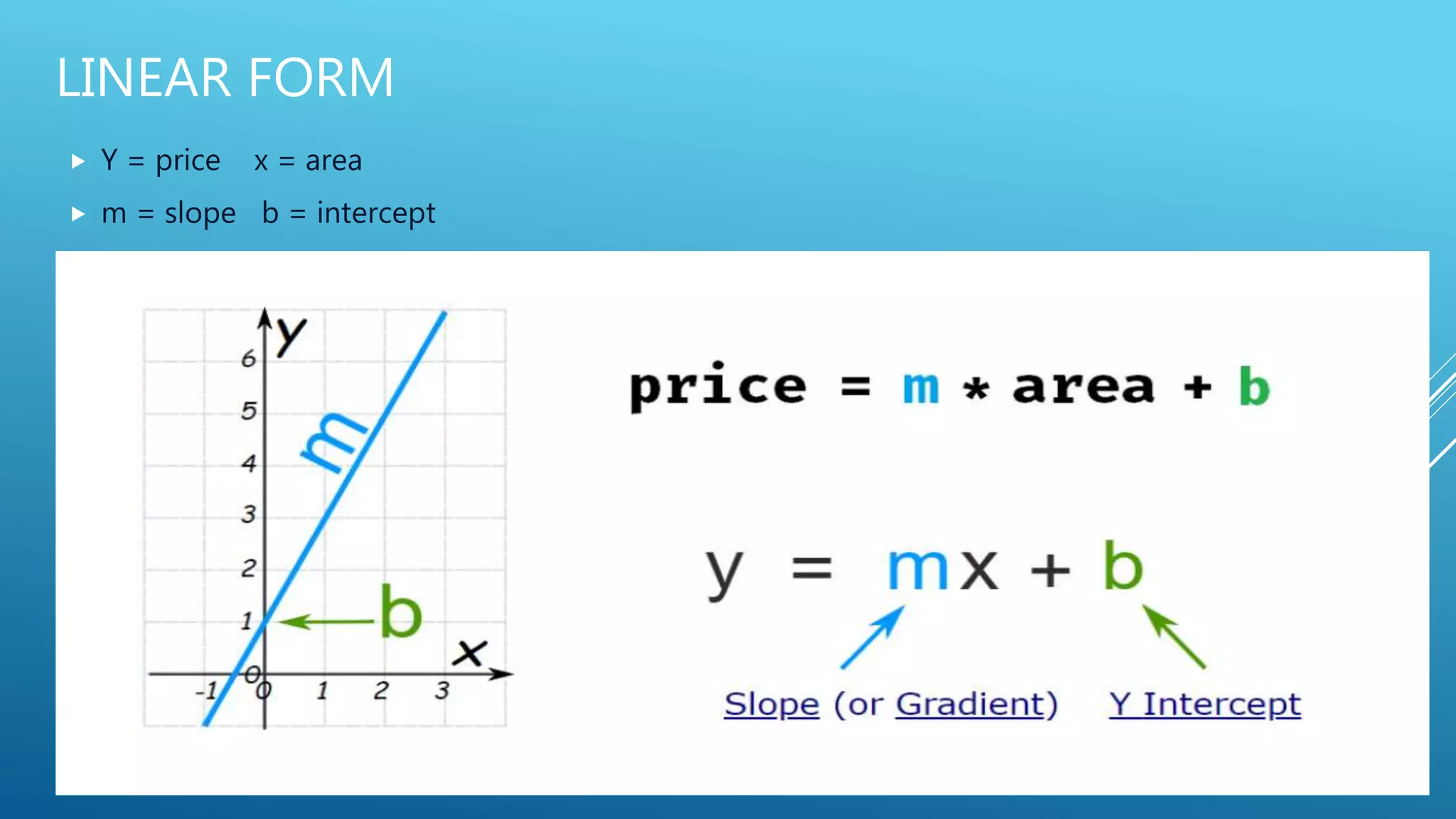
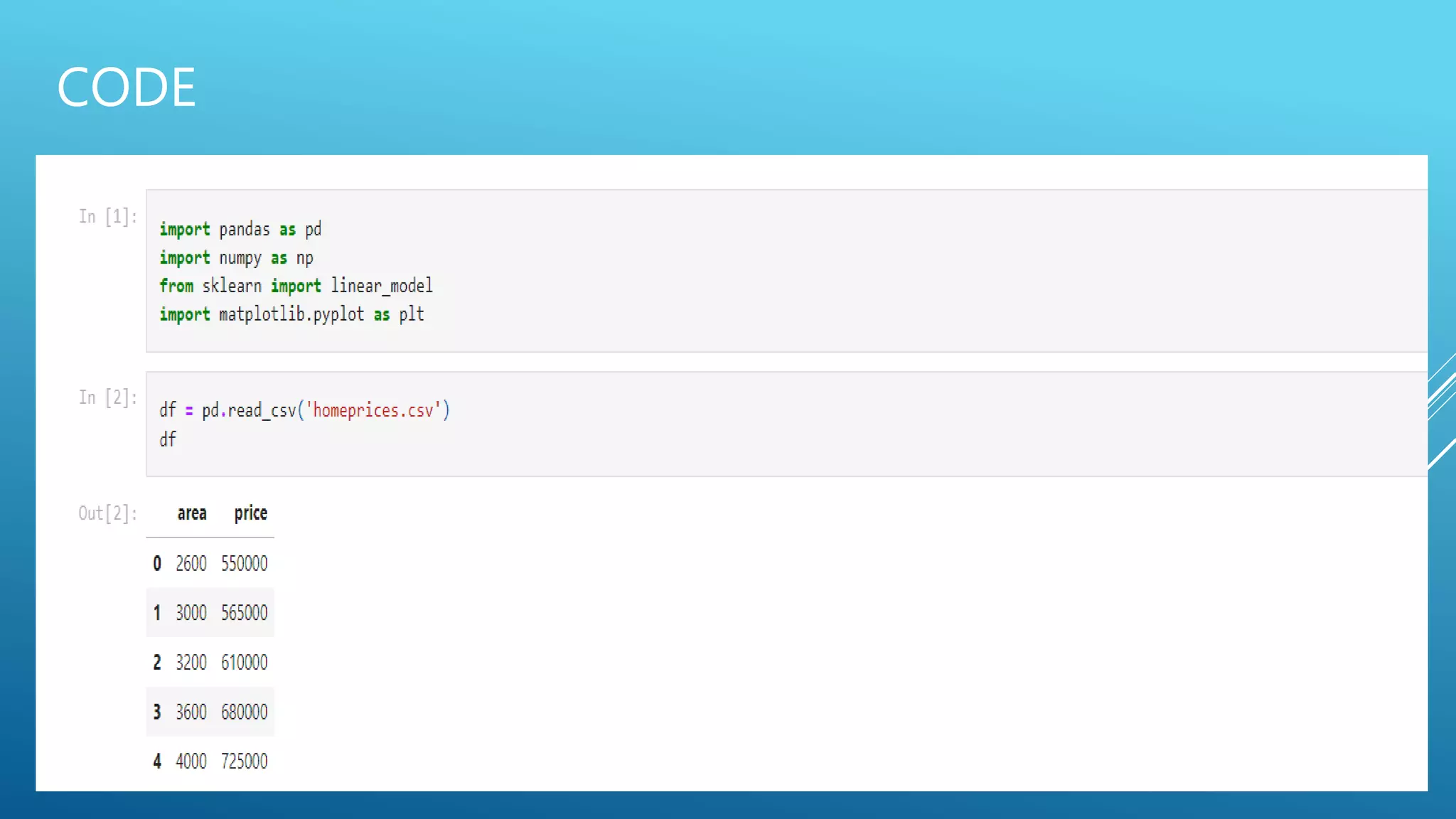
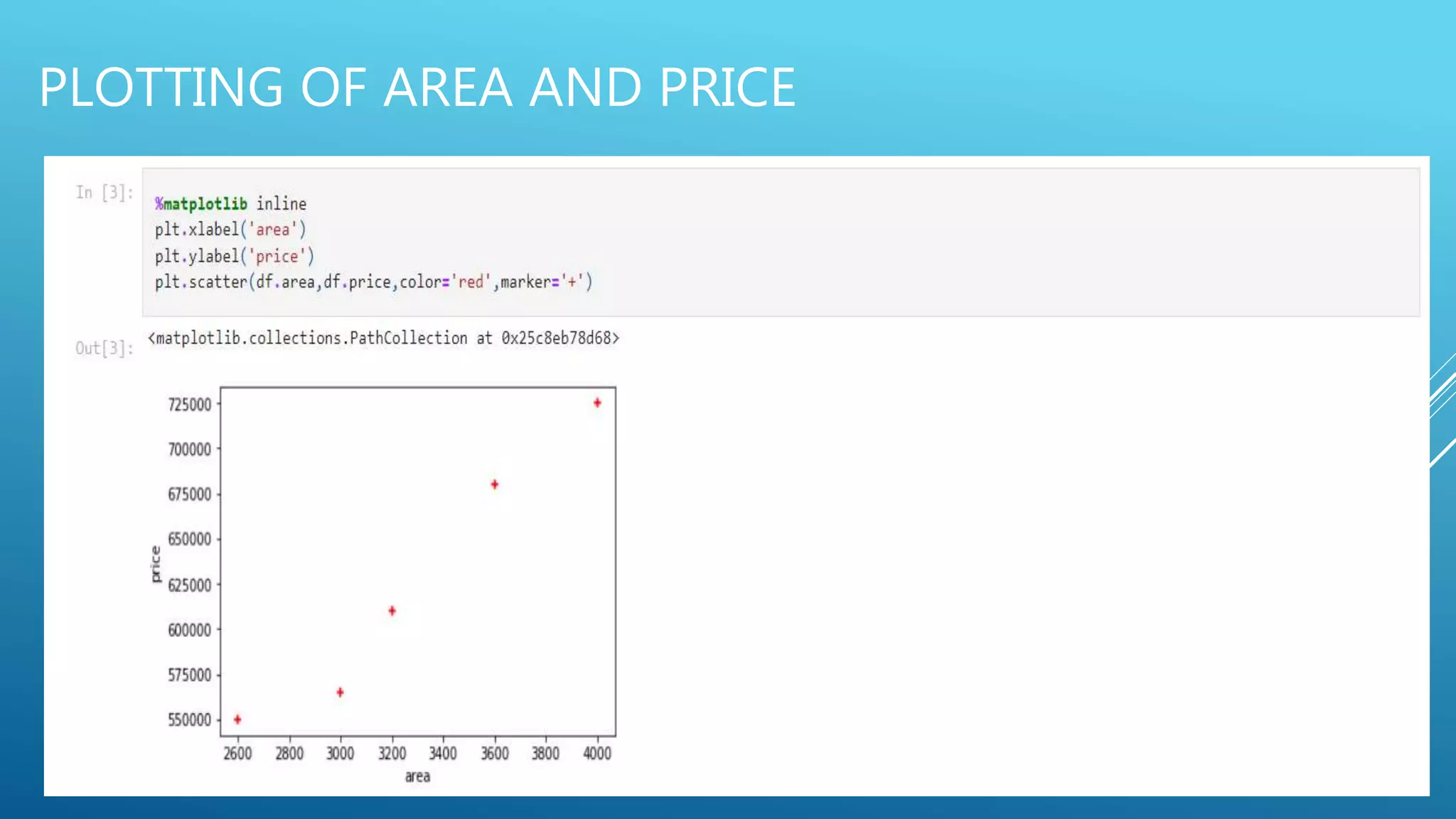
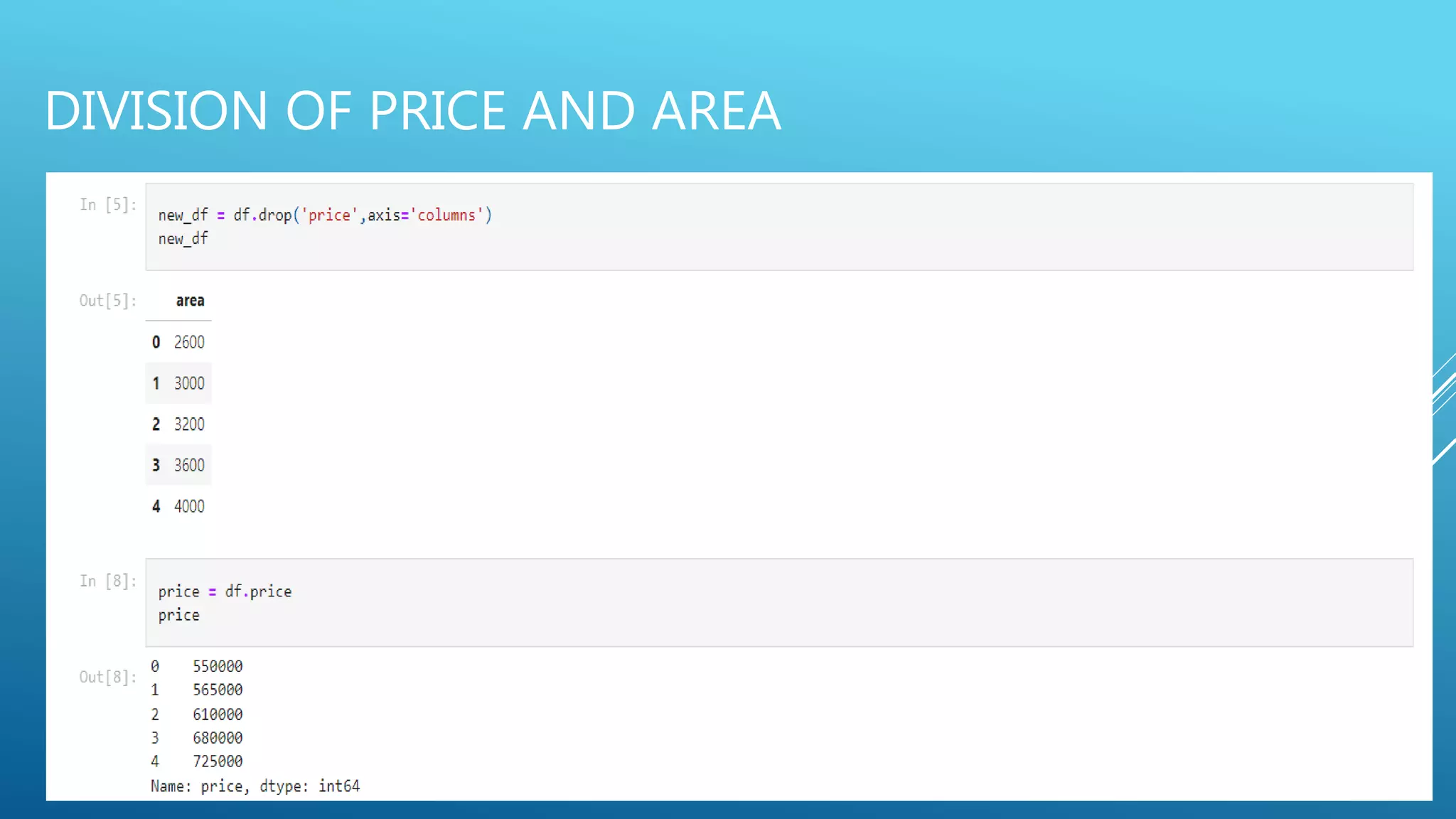
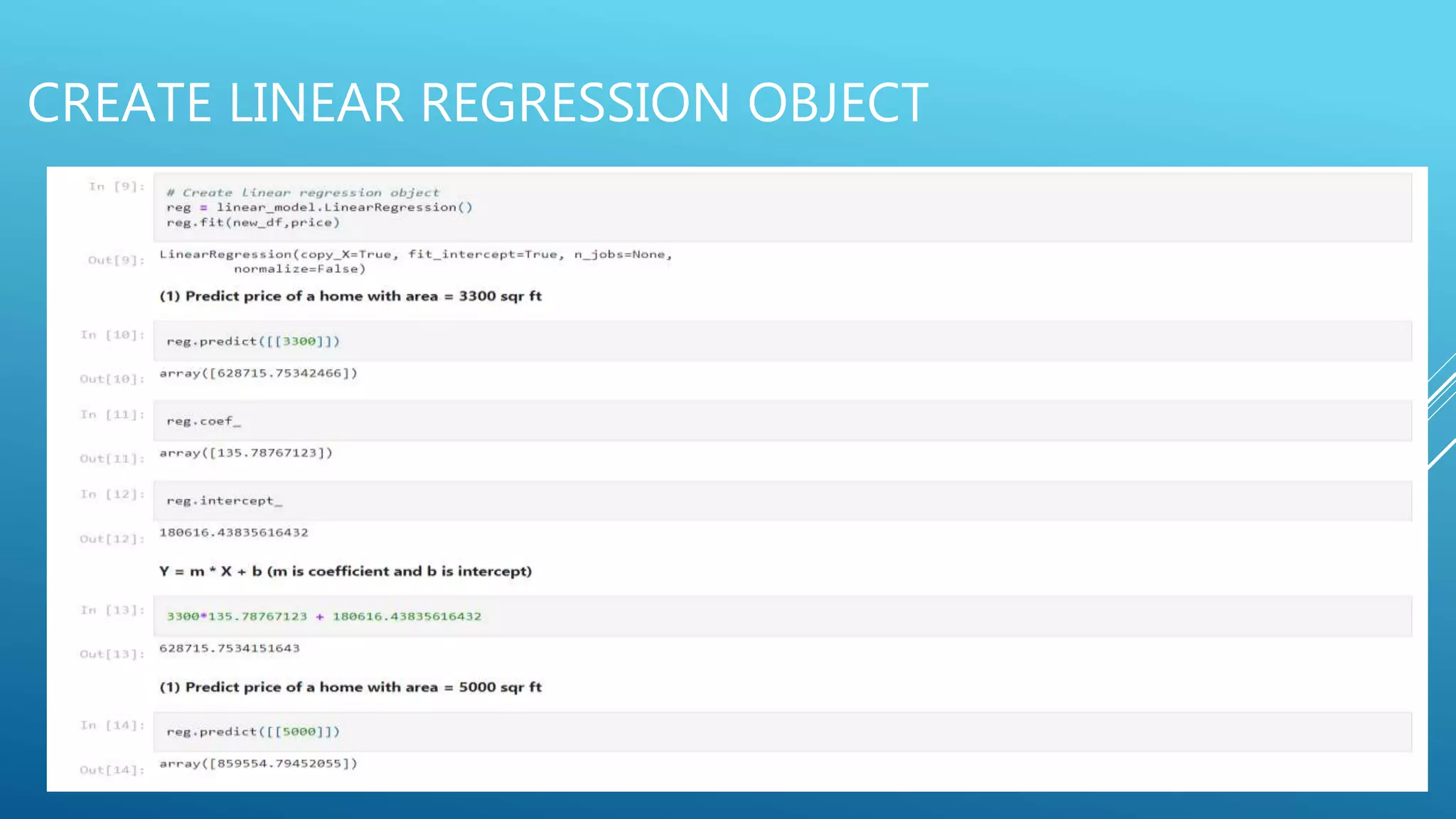
The document outlines an introduction to machine learning, including prerequisites such as Python programming and key libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and scikit-learn. It describes various types of machine learning, including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, along with their applications and advantages. Additionally, it addresses the benefits and challenges of machine learning, providing examples such as medical diagnosis and recommendation systems.