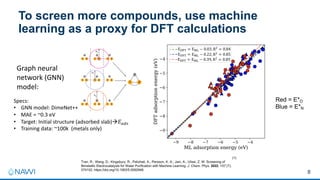
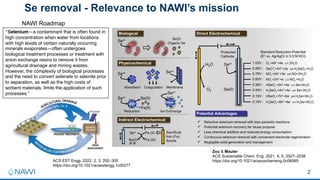
This document summarizes a presentation on developing an electrochemical system for selenium removal from water. The project aims to apply machine learning and automated synthesis techniques to accelerate materials development timelines. Initial calculations have reproduced experimental trends for nitrate reduction and screened candidate materials from databases. Procedures have also been established for electrode preparation, testing, and using robots to synthesize predicted candidates. While still early, progress has been made on computational screening, mitigating competing reactions, and testing baseline cathode materials for selenium removal performance and energy efficiency. The remainder of the first project year will focus on refining methods before demonstrating a commercially viable selenium removal system in years two and three.


![4
Project objectives
[1] DOI: 10.1021acscatal.9b02179
Autonomous
Precise
Resilient
Intensified
Modular
Electrified
Control voltage
Targets a single or a few solutes
Easily adjusted for variable water quality
No need for regeneration;
no brine to dispose
No high-pressure equipment;
no moving parts
Compatible with distributed DC power
• Background: New
advancements in machine
learning, theory, and
automated labs can accelerate
materials development
timelines
Can we apply these
techniques to water treatment?
• Our 3-year outcome:
demonstrate commercially
viable system for Se removal
Singh & Goldsmith ACS Catal. 2020, 10.
Werth et al. ACS ES&T Engg. 2021, 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nawipresentation-221128122839-f6c5eeb7/85/Machine-Learning-for-Catalyst-Design-4-320.jpg)

![6
Overview of computational approach
calculating the
adsorption and
activation energies
for monometallic systems
versus various
adsorbates
generating
linear scaling
relationships
estimating the
TOF and
selectivity from
microkinetic
modelling
plotting the TOF
volcano plot
from the
previous results
evaluating and
screening TOF
for calculated
bimetallic
materials
calculating
adsorption
energies for
bimetallic
materials
[1] DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.9b02179
[1]
[1] BM systems
metal oxides
more…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nawipresentation-221128122839-f6c5eeb7/85/Machine-Learning-for-Catalyst-Design-6-320.jpg)