Embed presentation
Download to read offline

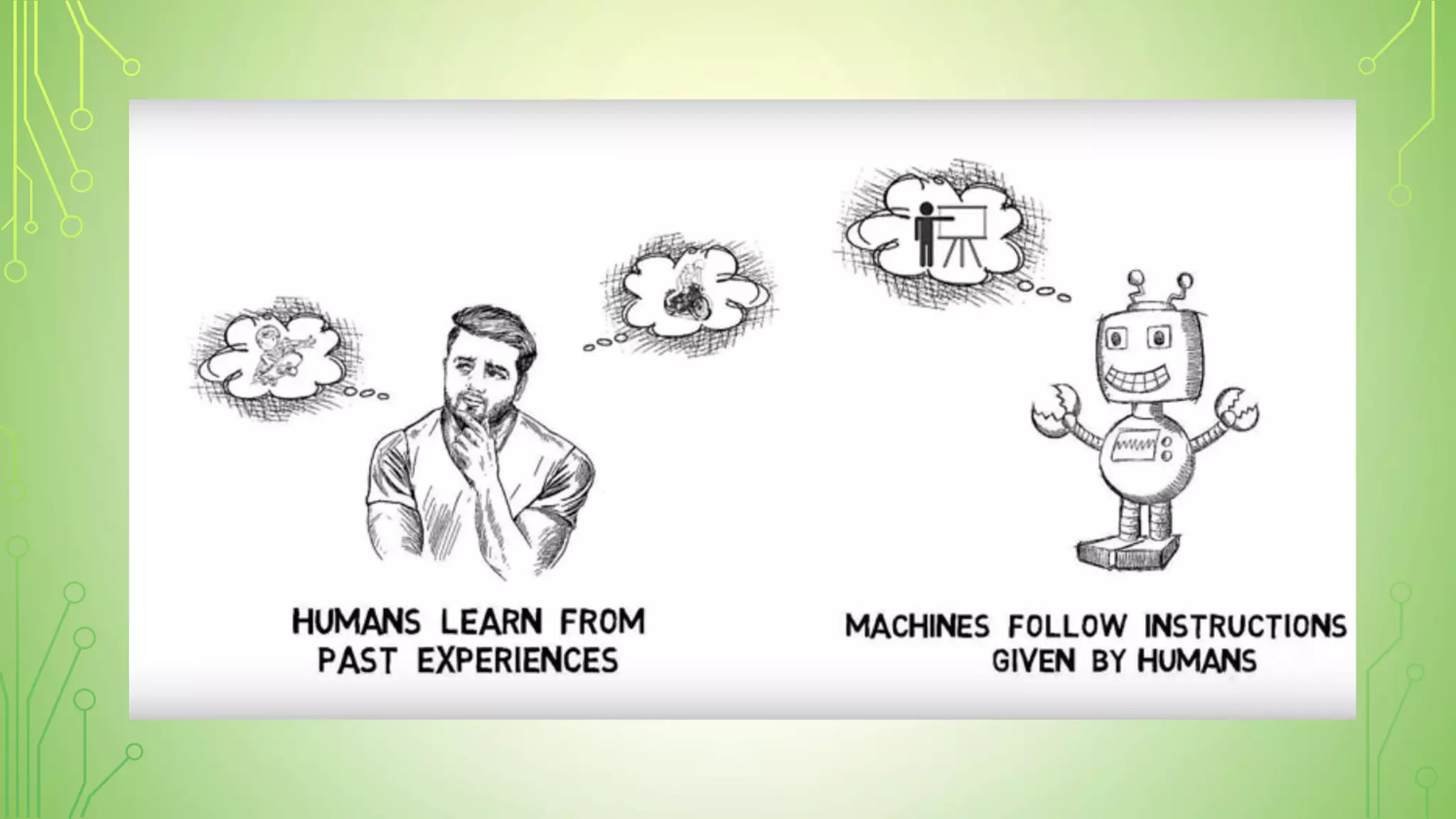
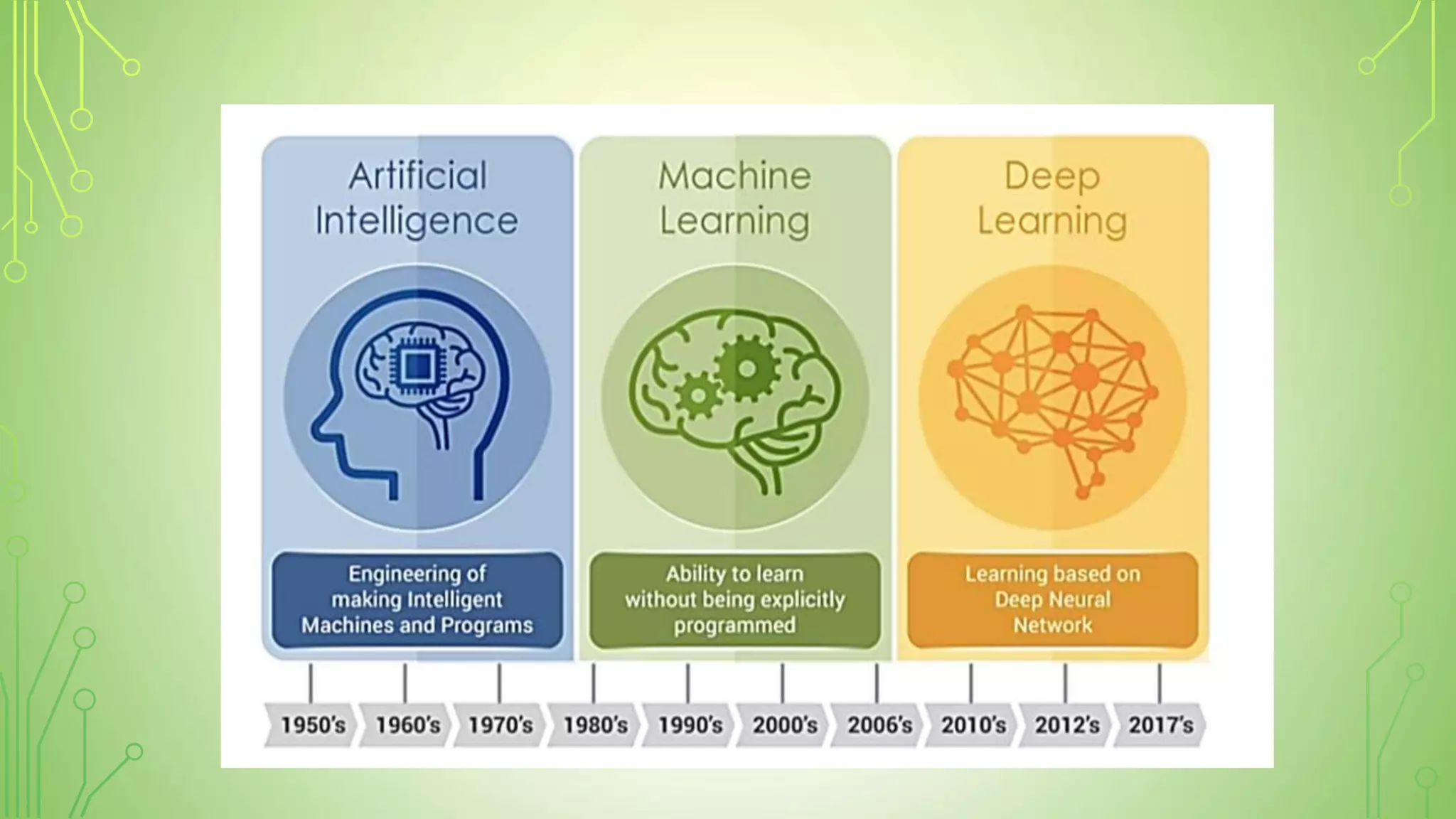
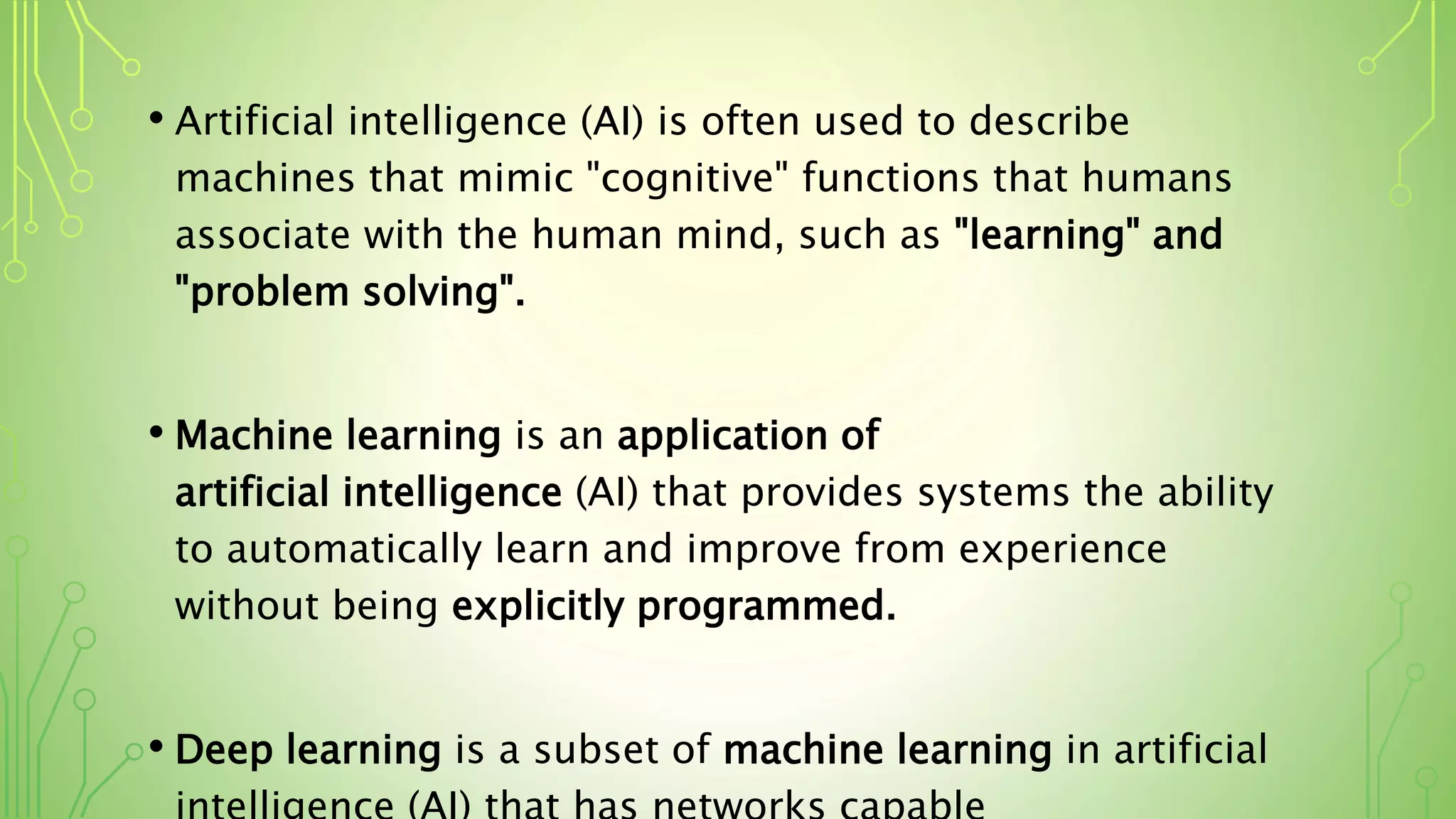
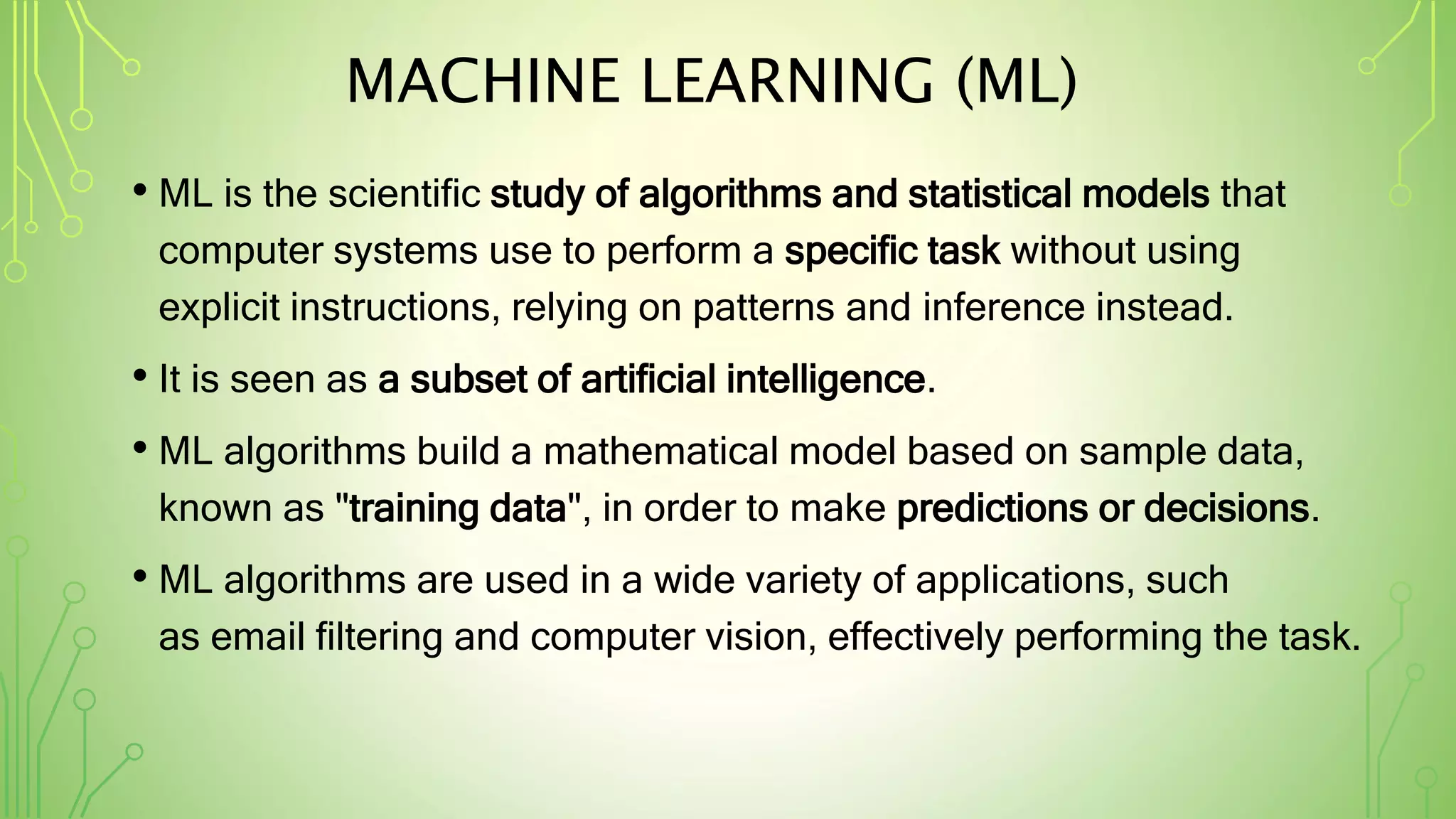
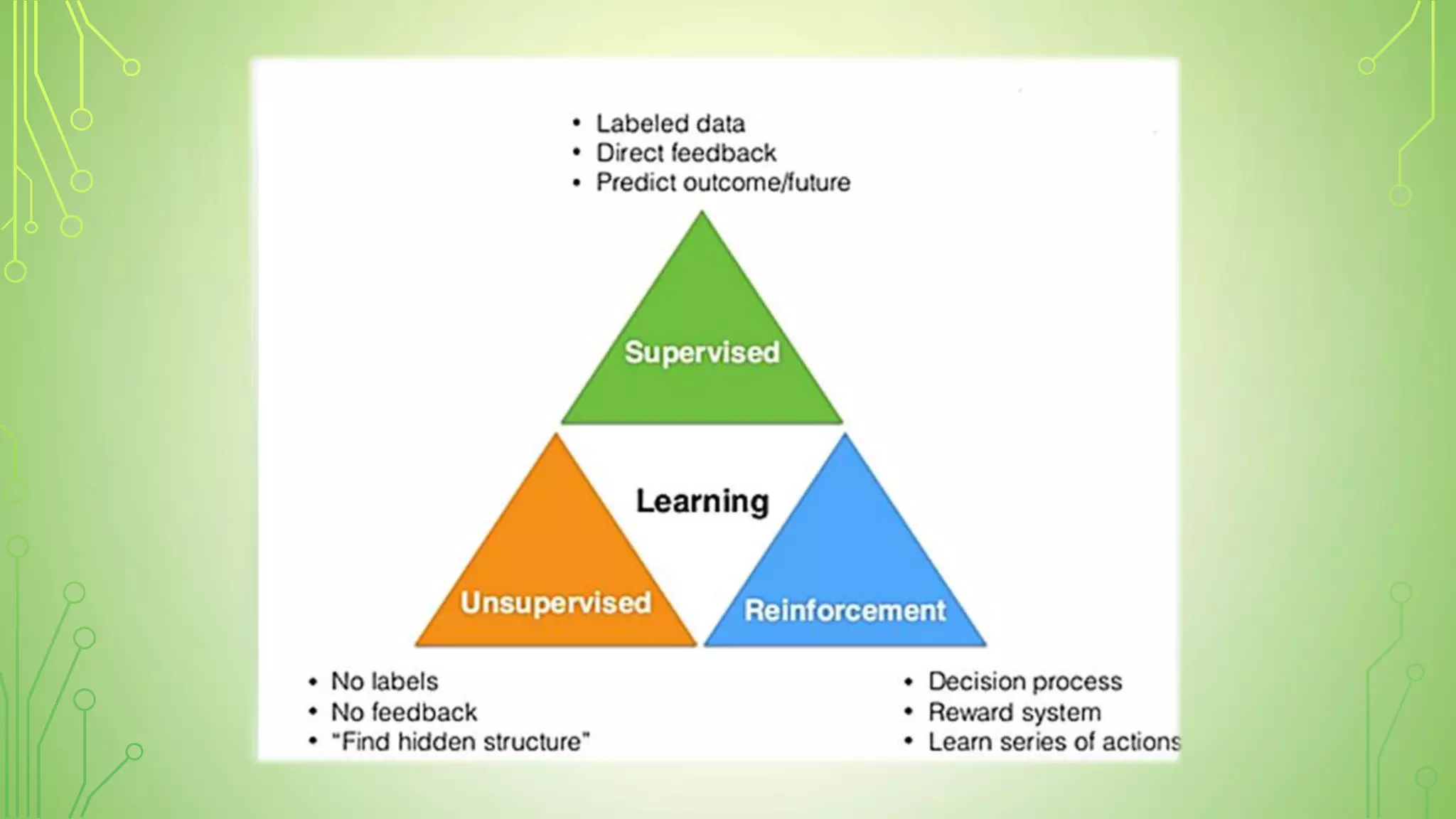
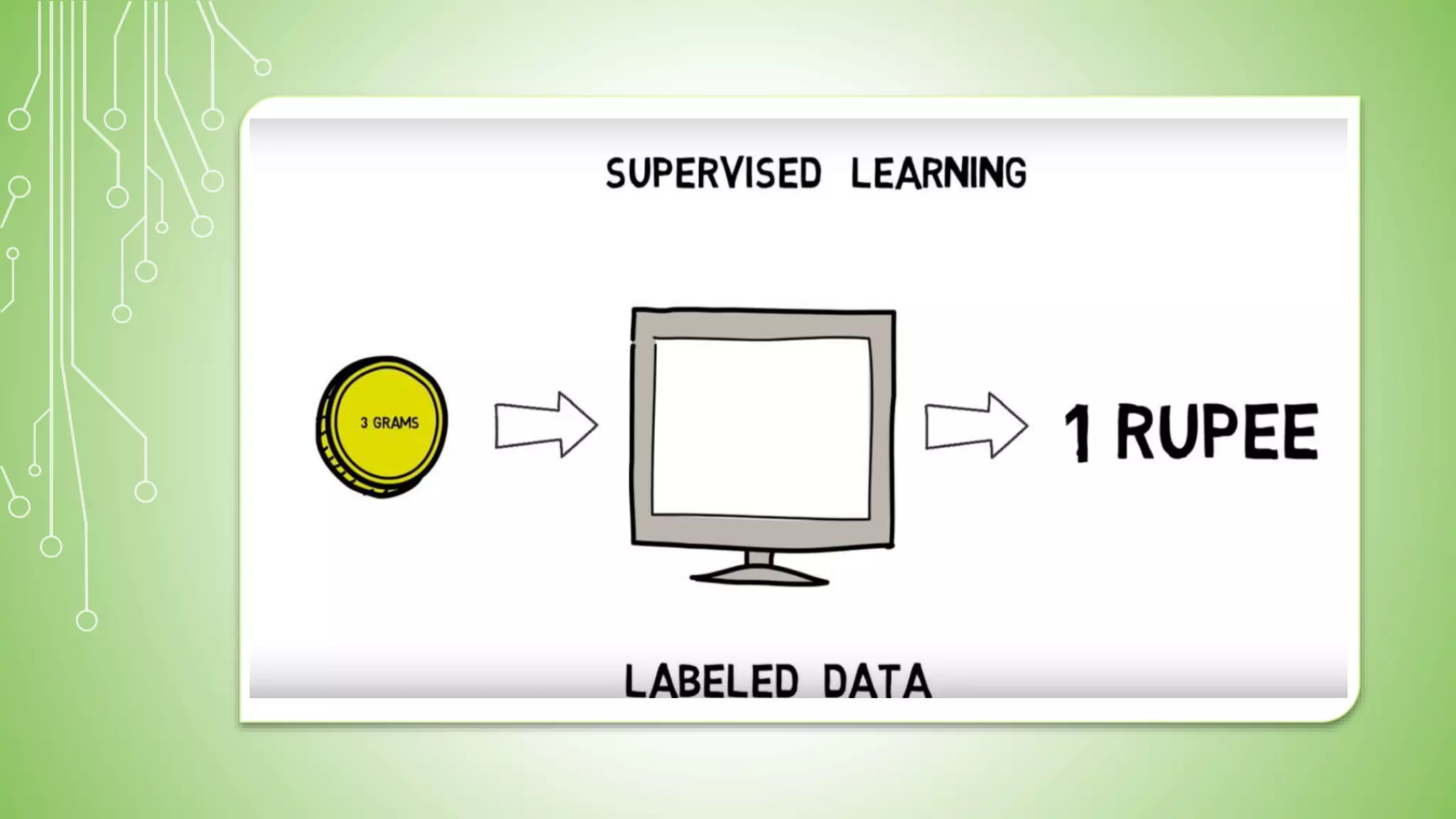
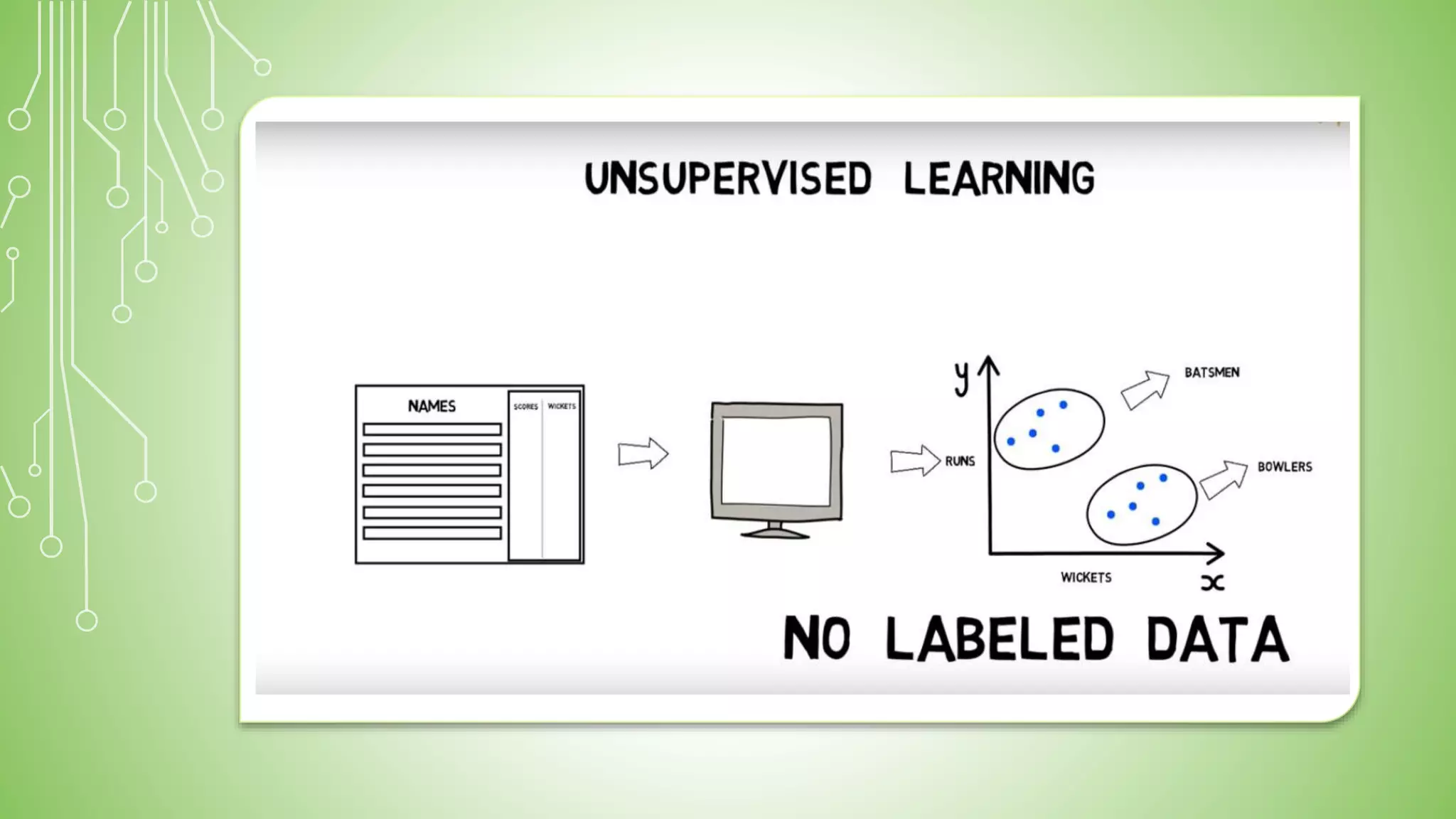
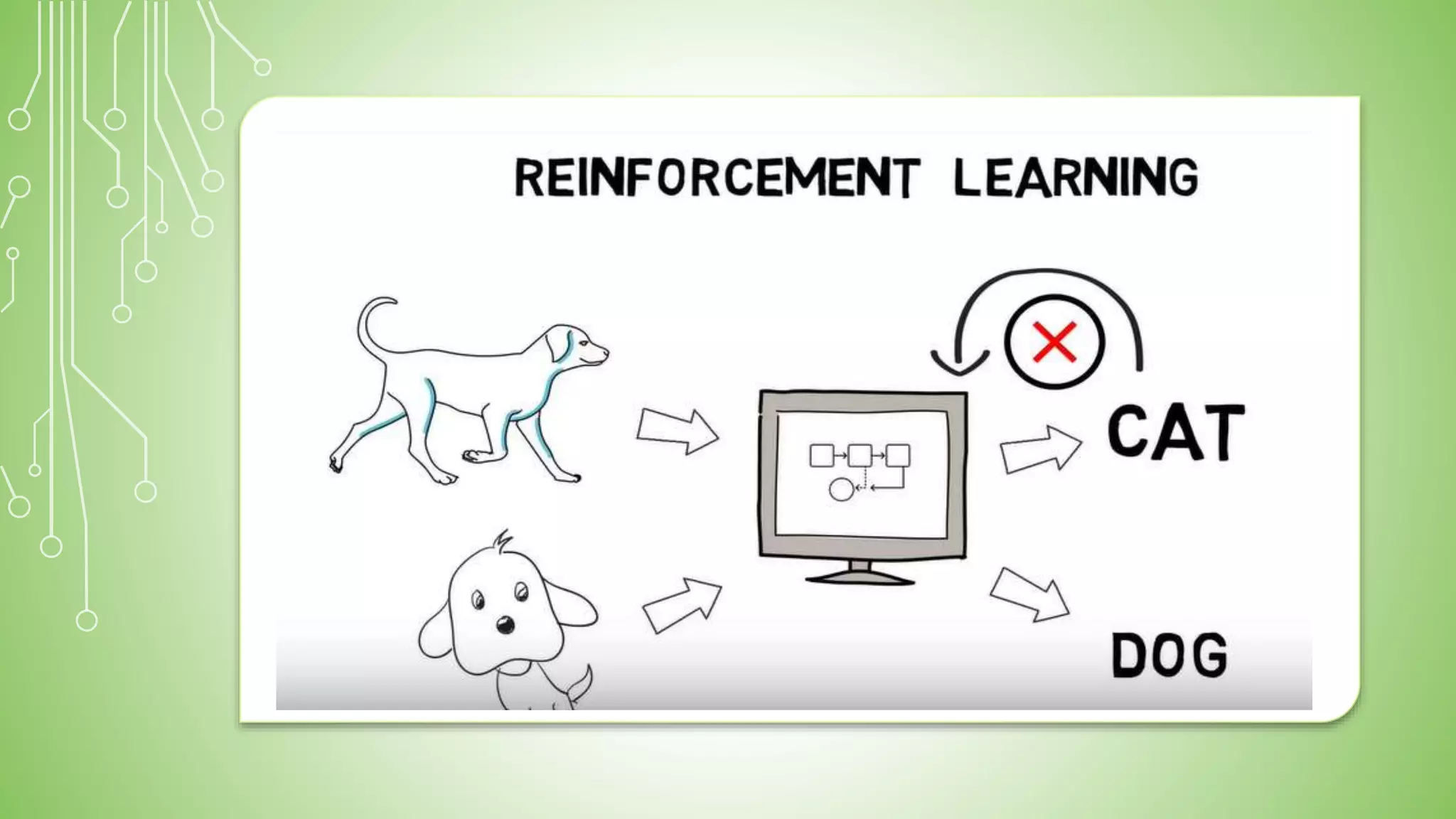
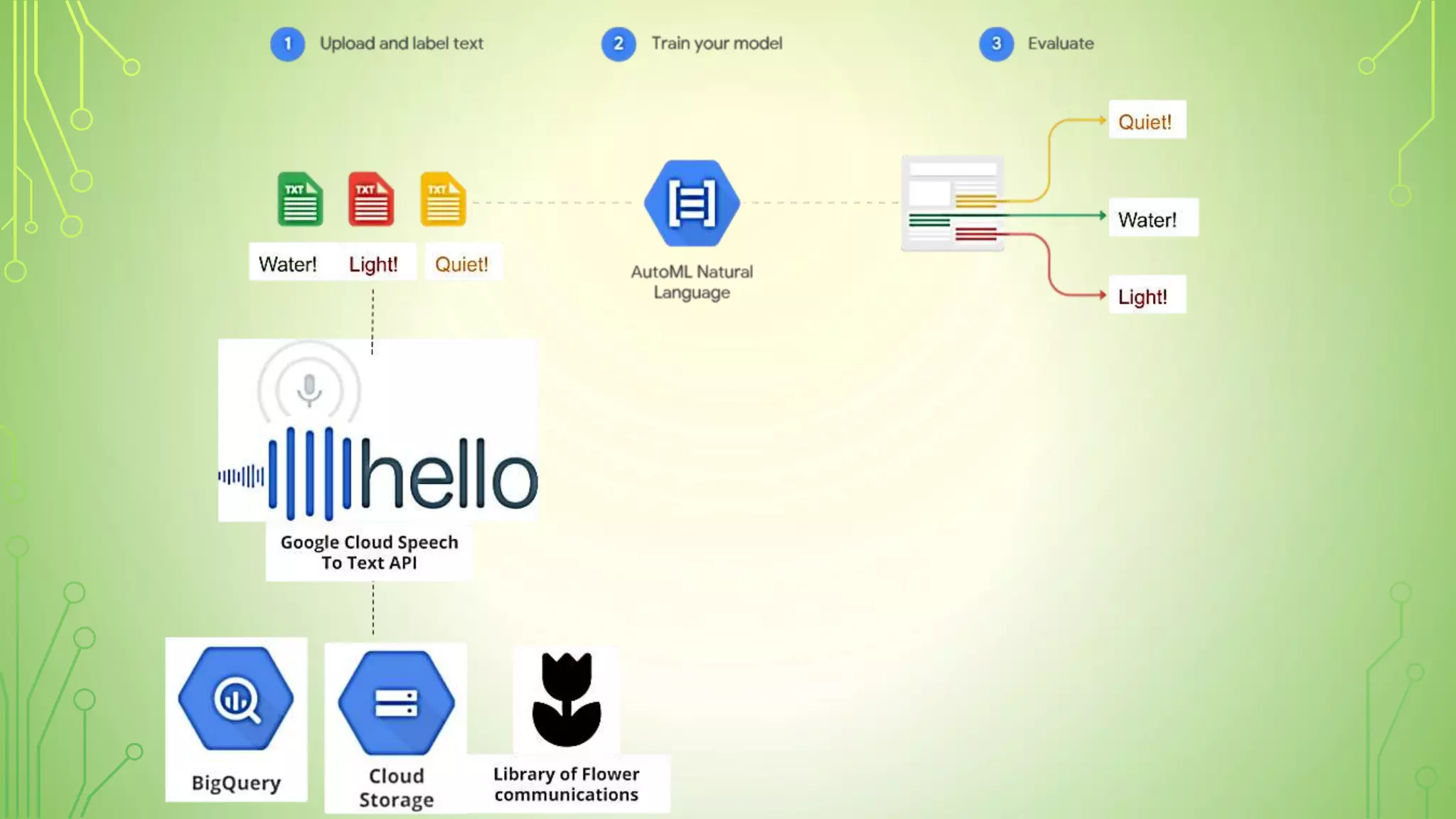

This document explains artificial intelligence (AI) and its subset, machine learning (ML), which allows systems to learn and improve from experience without explicit programming. It defines ML as the scientific study of algorithms and models that utilize training data for making predictions or decisions. Additionally, it mentions various applications of ML, such as email filtering and computer vision.










