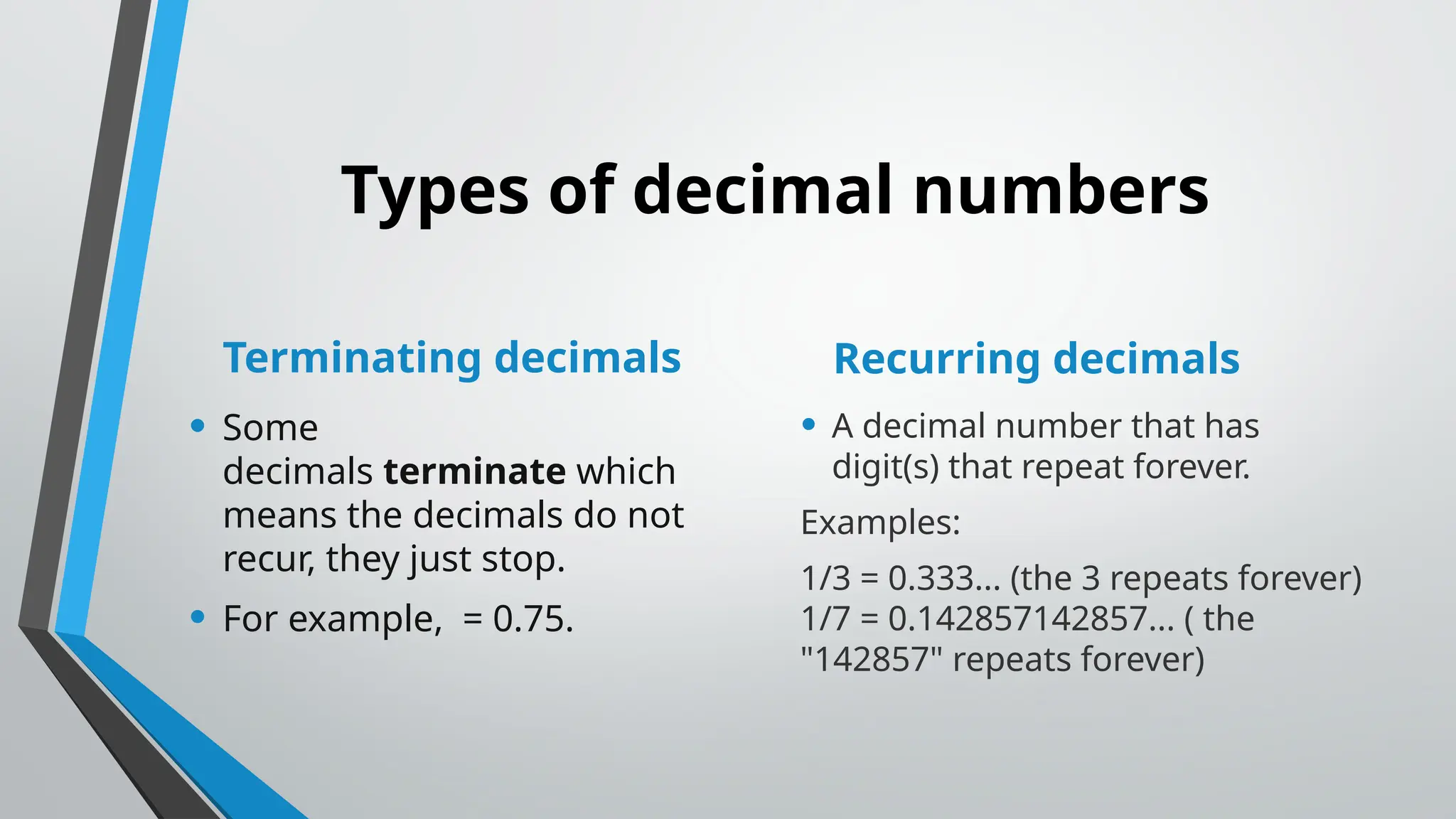
The document outlines the learning objectives for mastering fractions and decimals in mathematics for grade 8, including recognizing equivalent fractions and estimating mixed numbers. It explains the concepts of terminating and recurring decimals with examples, emphasizing the conversion of recurring decimals. Additionally, it addresses the use of arithmetic laws and order of operations when working with decimals and fractions.