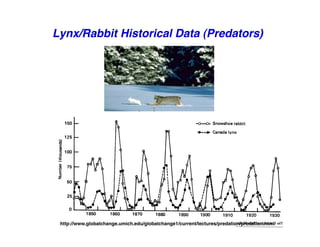
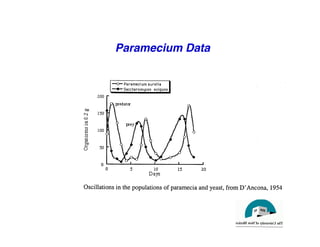
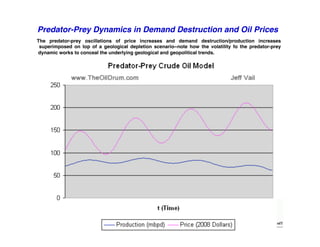
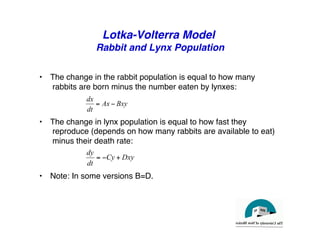
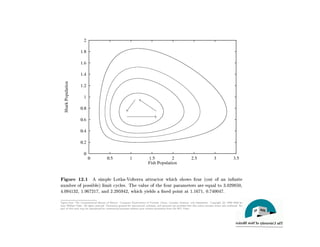
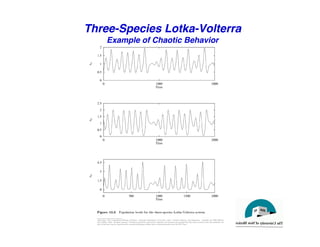
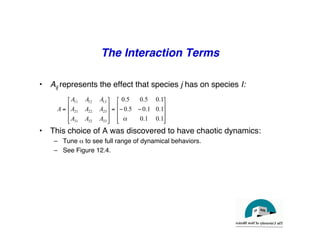
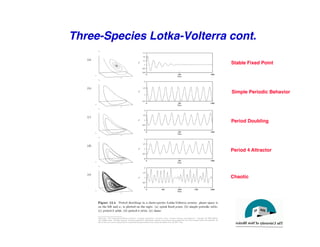
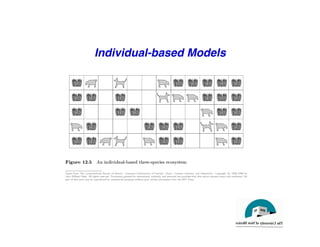
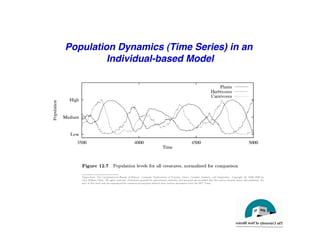
This document discusses predator-prey models including the classic Lotka-Volterra model and alternative agent-based models. The Lotka-Volterra model uses differential equations to model species populations over time, assuming homogeneous mixing and infinite population sizes. An agent-based model represents each individual explicitly on a grid and uses rules for local interactions, allowing for heterogeneity, finite populations, and spatial effects not captured by Lotka-Volterra. Both approaches can generate oscillating population dynamics resembling real predator-prey data, but the agent-based model provides a more individual-level perspective.




![Lynx Historical Data (Predators)
"
[D'Ancona, 1954]"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lotka-volterra-240406190944-d9b70430/85/Lotka-Volterra-model-Predator-prey-model-5-320.jpg)