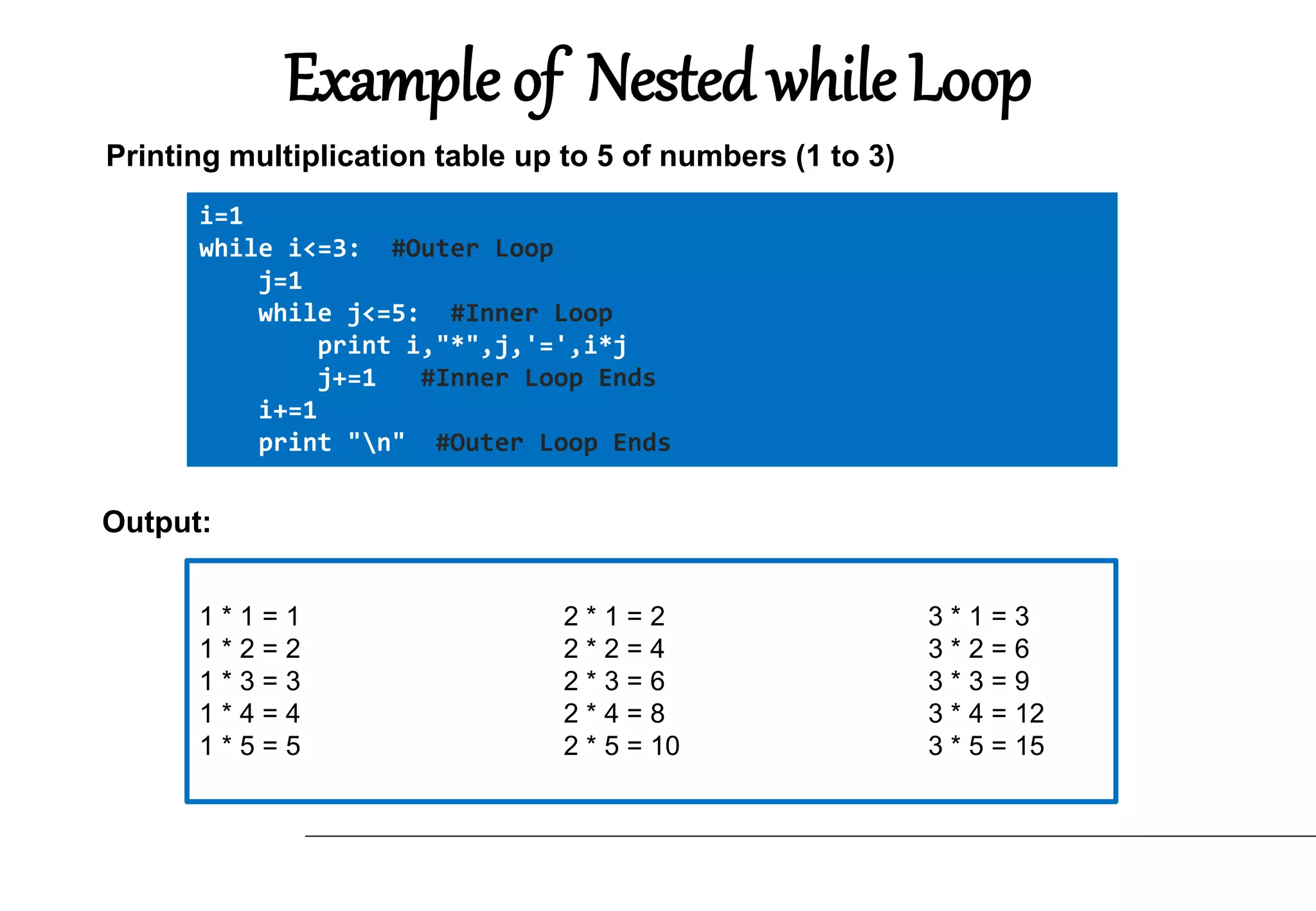
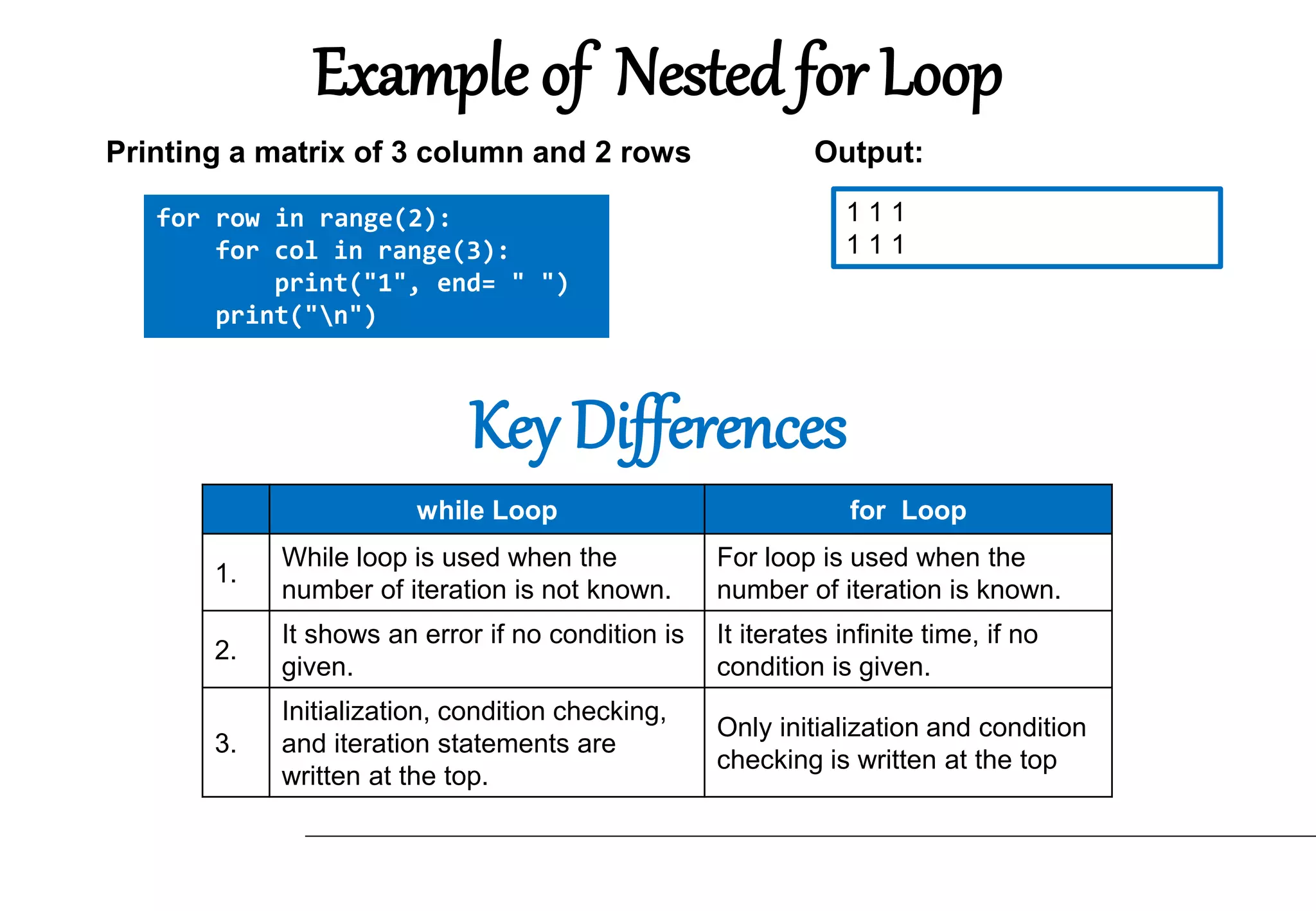
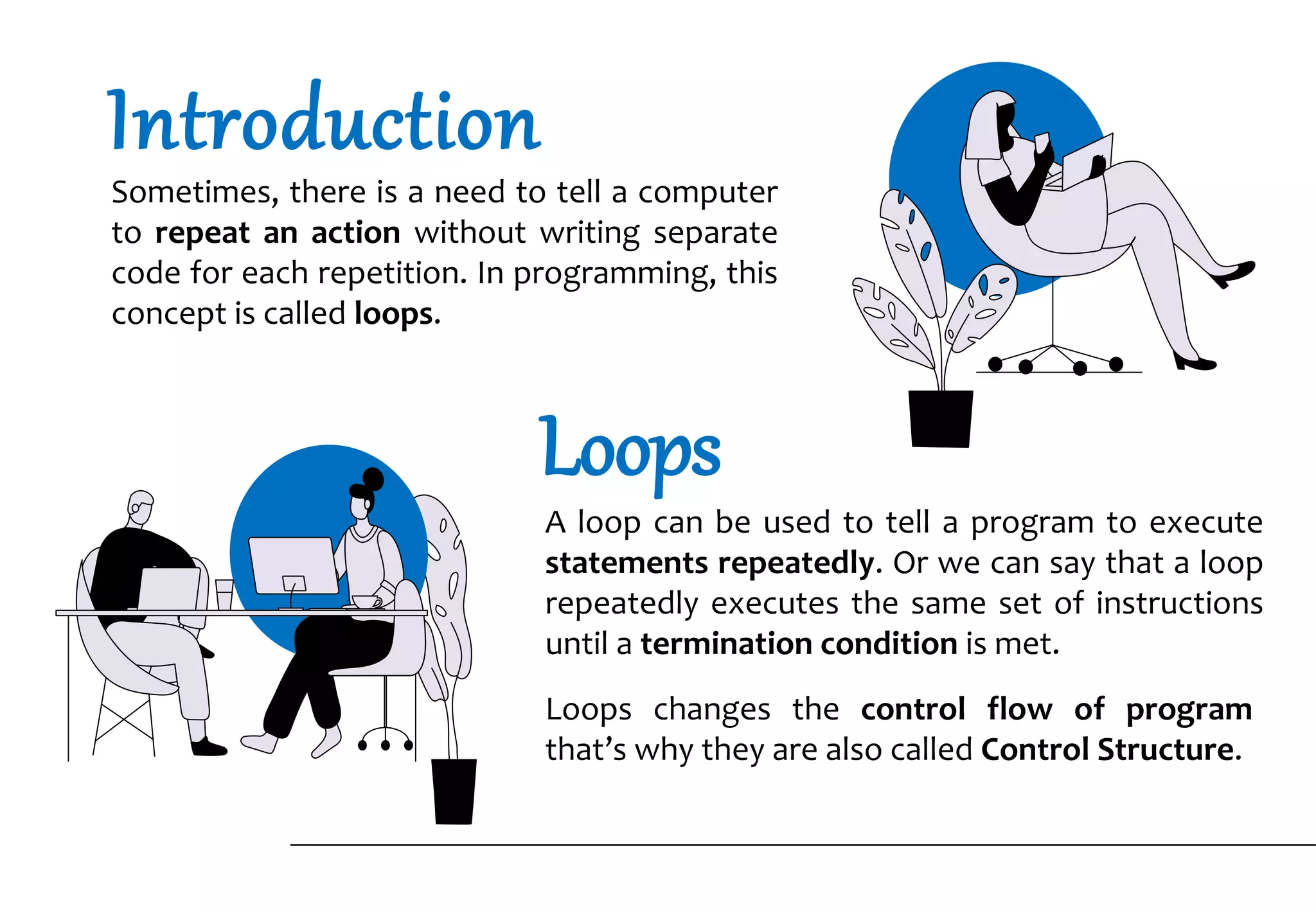
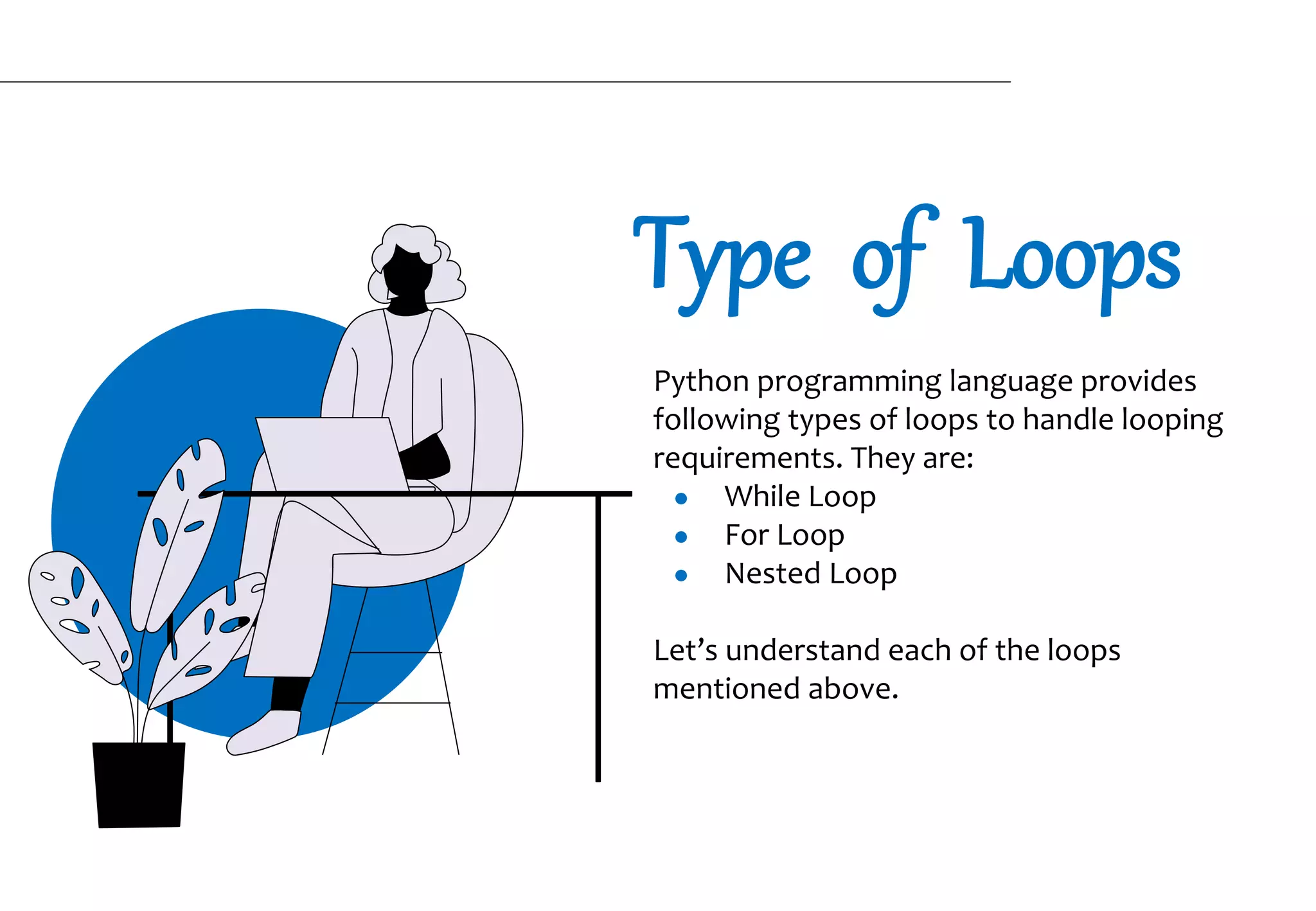
The document explains loops in Python, a programming concept used to repeat actions without writing separate code for each repetition. It covers the different types of loops: while loop, for loop, and nested loops, along with their syntax and examples. The importance of loops is highlighted through scenarios that illustrate their efficiency in executing repeated tasks.






![Example of for Loop
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
print(x)
LIST: Program to print each fruit in a fruit list:
apple
banana
cherry
Output:
for i in range(0,3):
print("Hello")
Range: Program to print “Hello” 3 times:
Hello
Hello
Hello
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/loopsinpython-2-230520083813-9a86fc17/75/Loops-in-Python-pptx-9-2048.jpg)