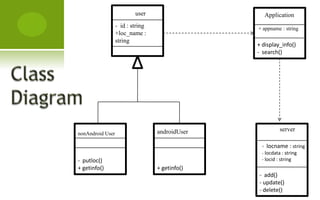
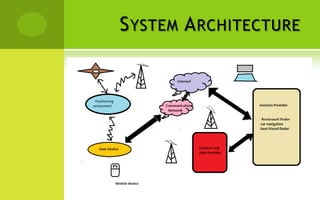
This document provides information about a proposed mobile application called "Info-Grabber" that would provide location-based advertisements and information to users. It would allow users to find their current location, popular nearby places, routes to locations, and details about selected locations. The application would use GPS for location services, MySQL for data storage, and protocols like HTTPS and FTP. It is intended to provide relevant ads and information to users based on their location in a simple interface. Potential benefits include speed, low cost, and ease of use, but privacy and spam concerns would need to be addressed.