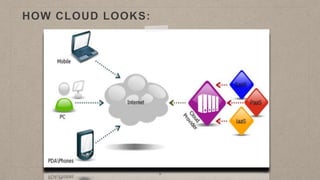
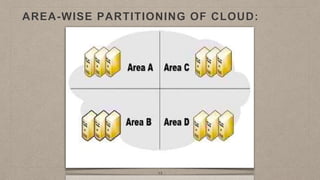
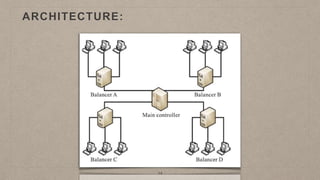
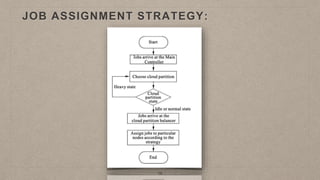
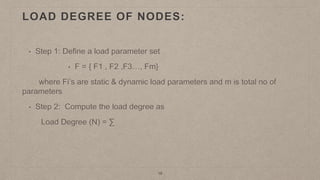
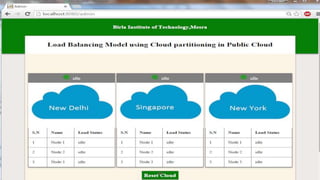
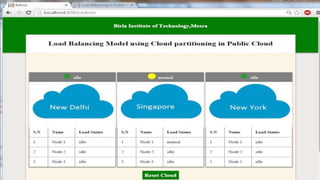
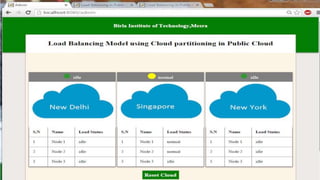
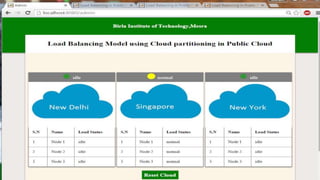
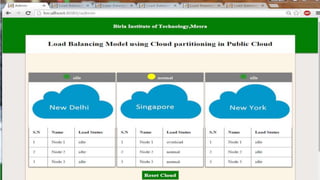
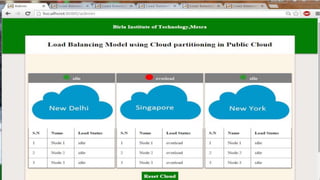
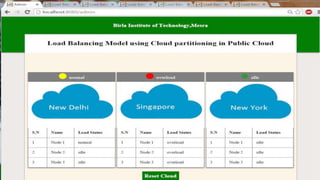
This document proposes a load balancing model for public clouds using cloud partitioning. It divides a large public cloud into partitions based on geographic location. When a job arrives, a main controller assigns it to the least loaded partition. Each partition uses algorithms like weighted round robin to further distribute jobs to nodes based on their calculated load degrees. The model aims to improve resource utilization and response times across the large, complex public cloud infrastructure.