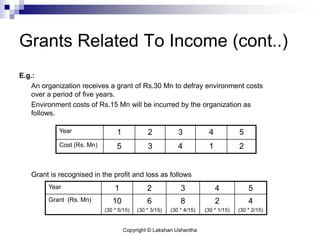
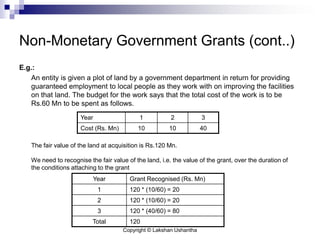
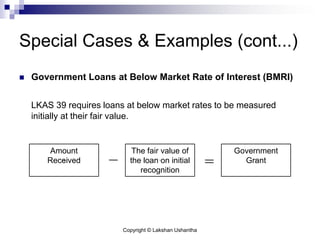
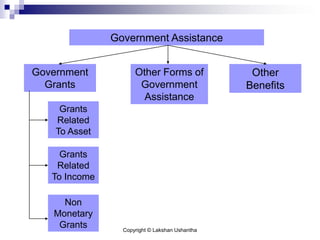
This document discusses Sri Lanka Accounting Standard LKAS 20 on accounting for government grants and disclosure of government assistance. It defines key terms like government grants and assistance, and outlines the standard's scope. It provides guidance on recognizing and measuring government grants related to assets and income, and addresses non-monetary grants, repayment of grants, and special cases. The document aims to help understand and apply the requirements of LKAS 20.








![Copyright © Lakshan Ushantha
Grants Related To Assets (cont..)
Government grants related to assets, including non-monetary grants
at fair value, shall be presented in the statement of financial position
either;
By setting up the grant as deferred income
By deducting the grant in arriving at the carrying amount
of the asset.
[Recognise in the profit and loss on a systematic basis over the
useful life of the asset]
OR
[Recognise in the profit and loss over a life of a depreciable assets as
a reduced depreciation expenses]
[Recognise in the profit and loss on a systematic basis over the
useful life of the asset]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lkas20-130717125509-phpapp01/85/Lkas20-10-320.jpg)