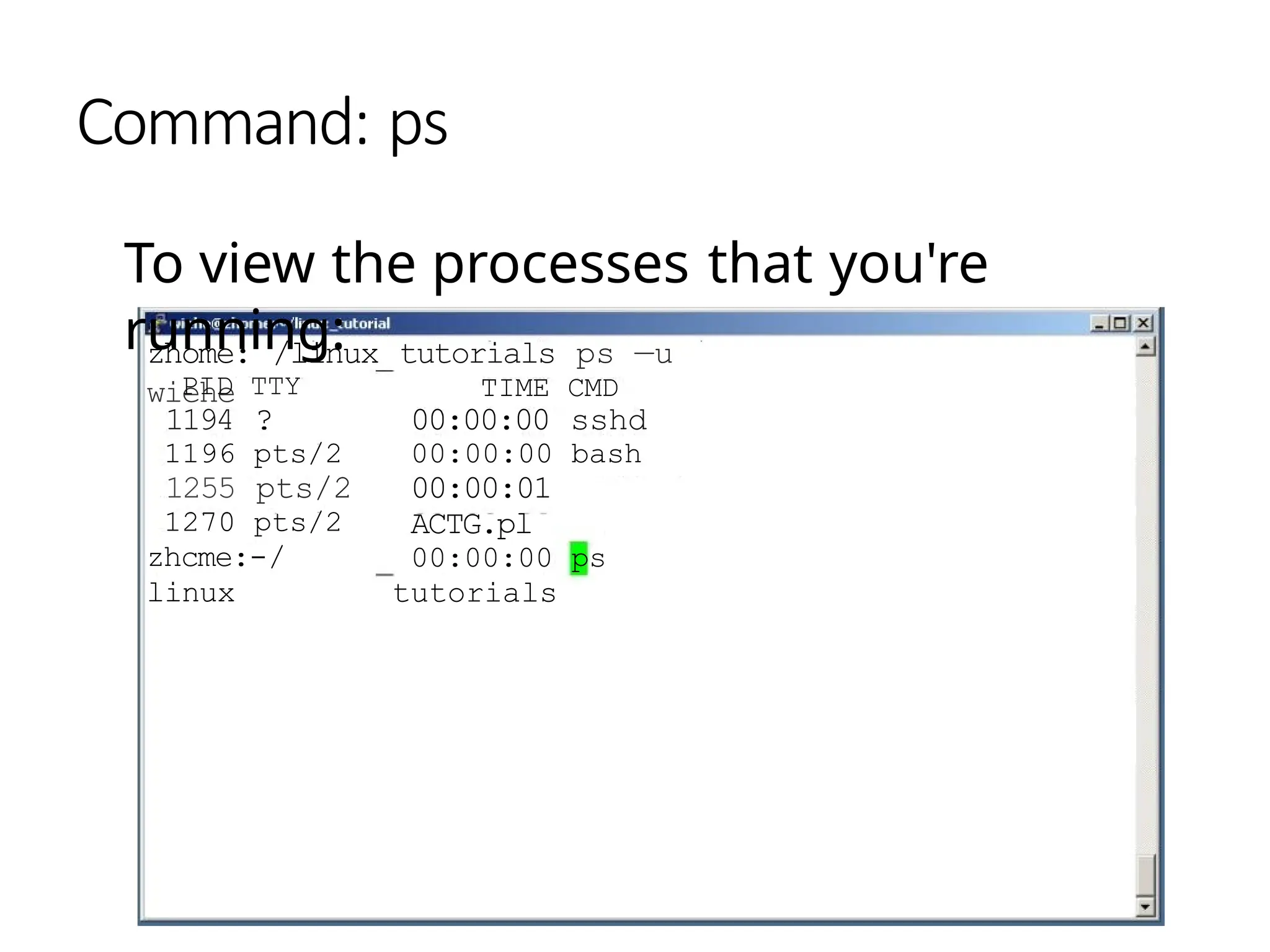
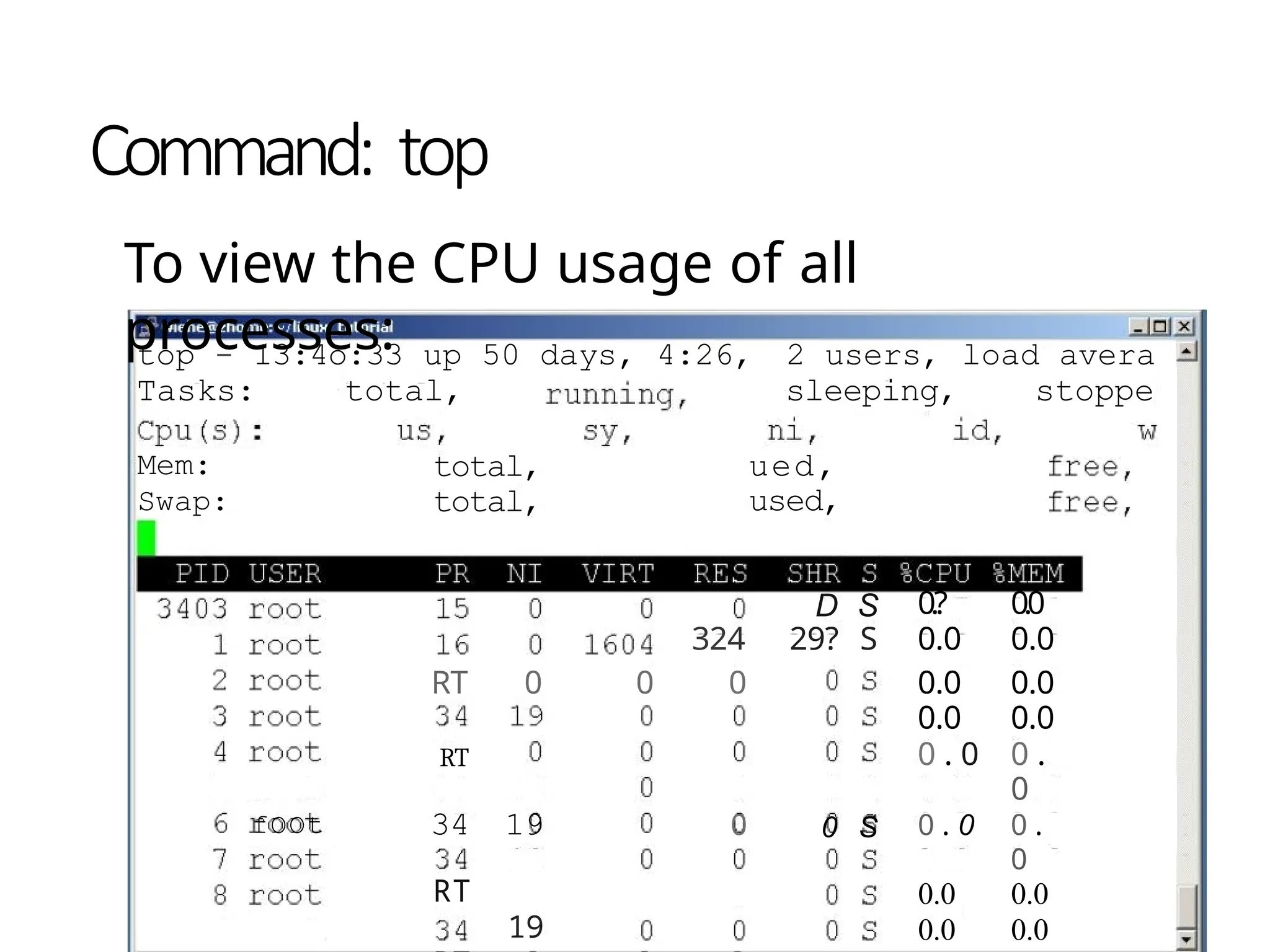
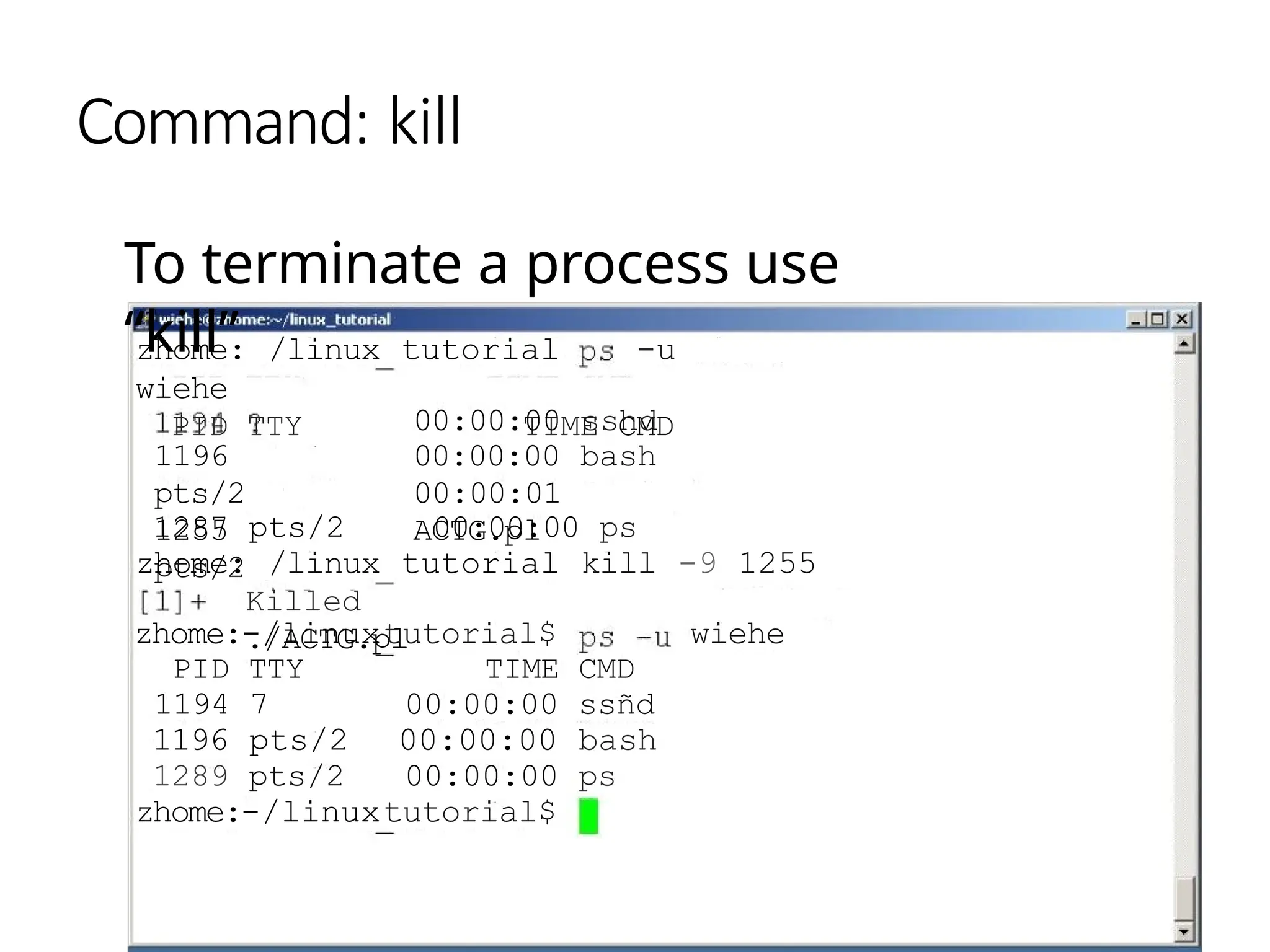
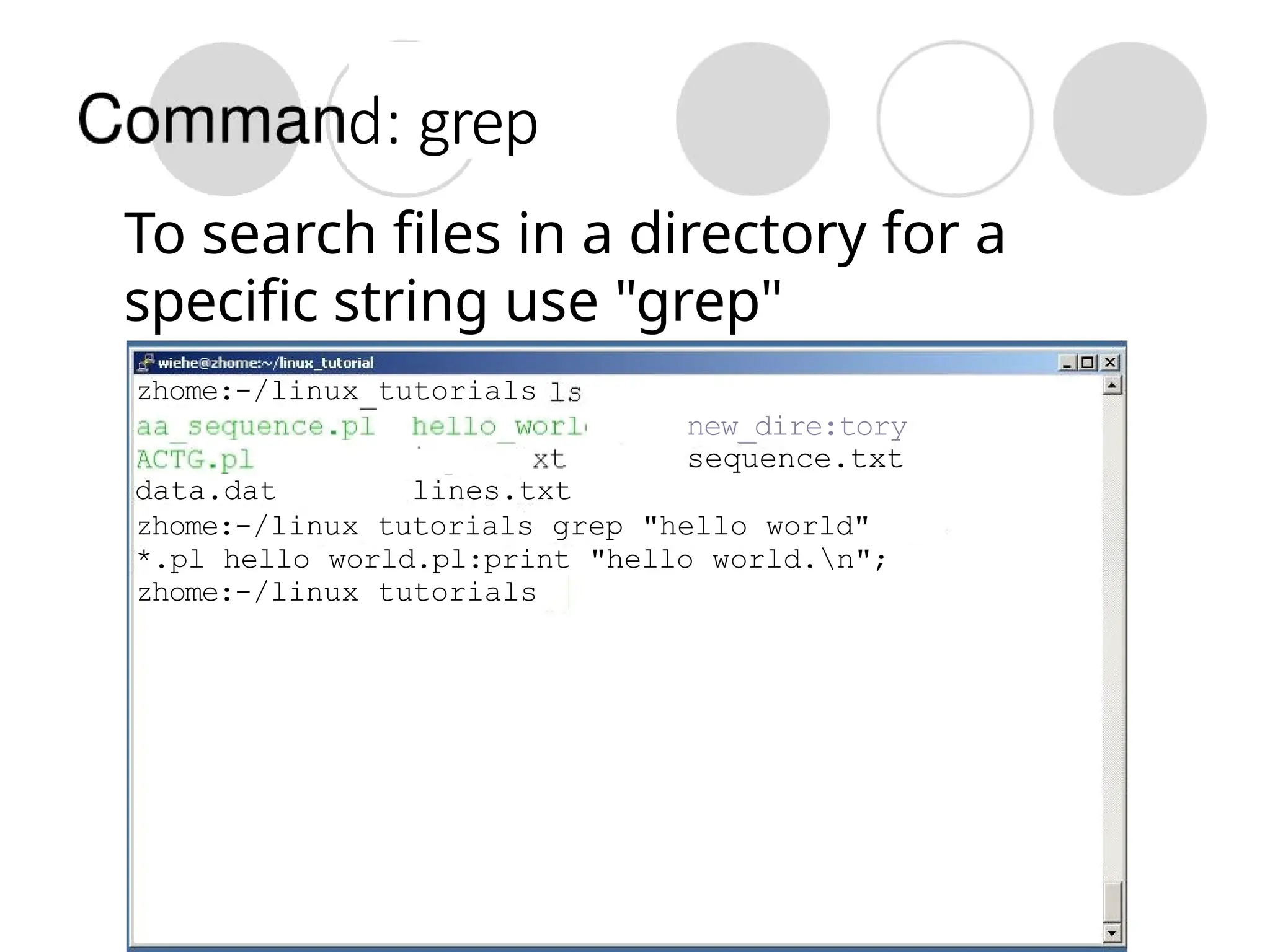
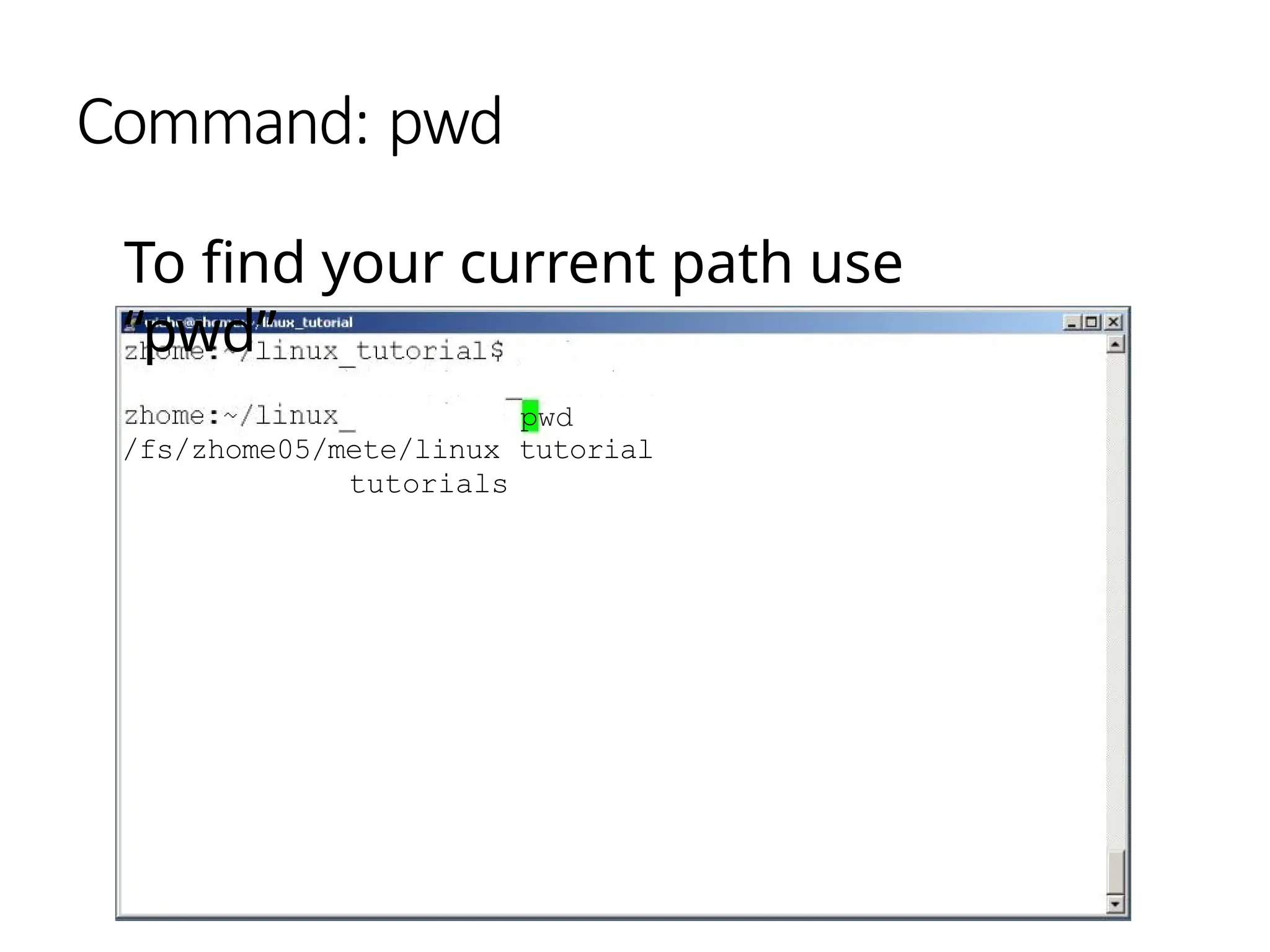
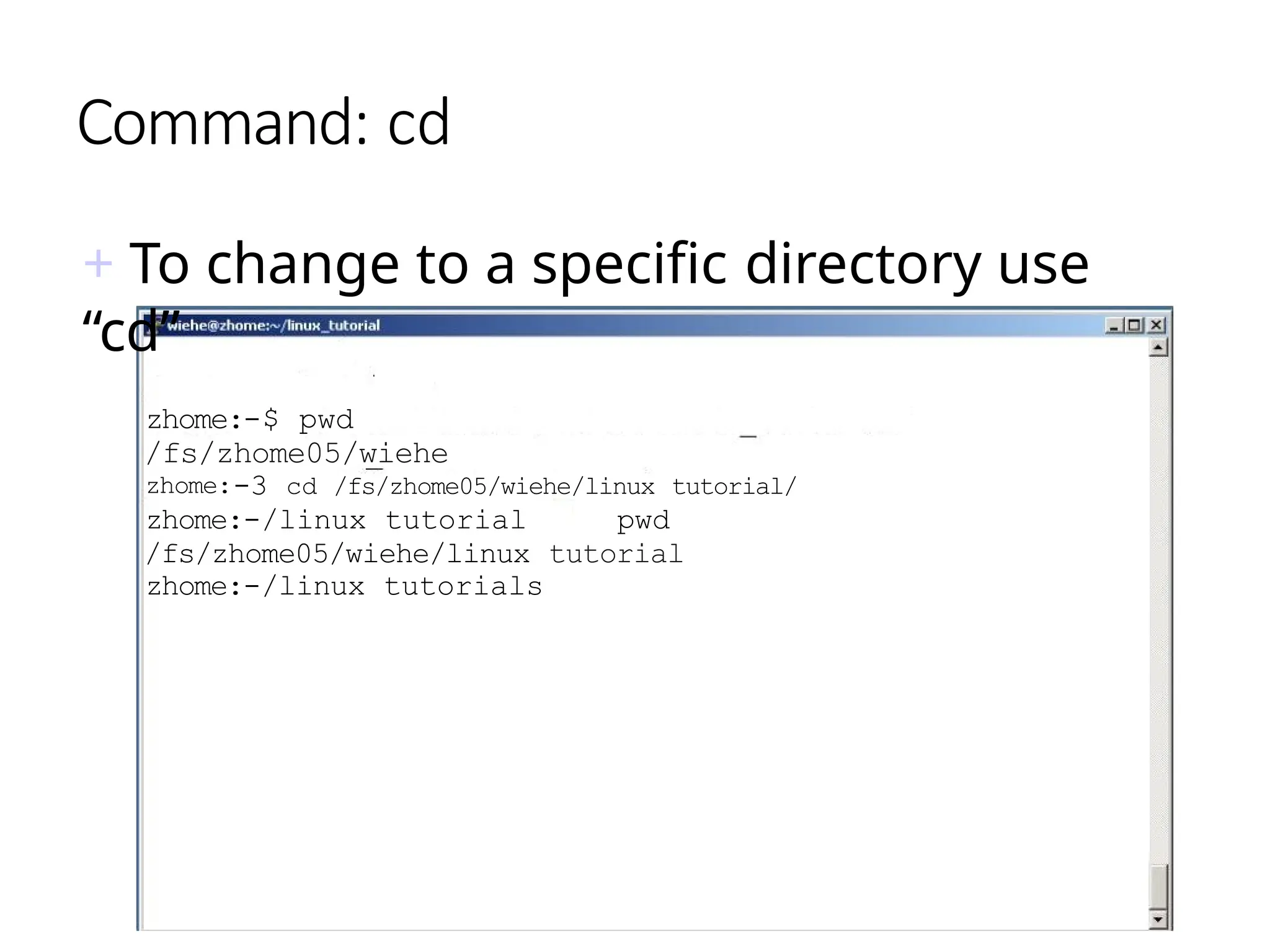
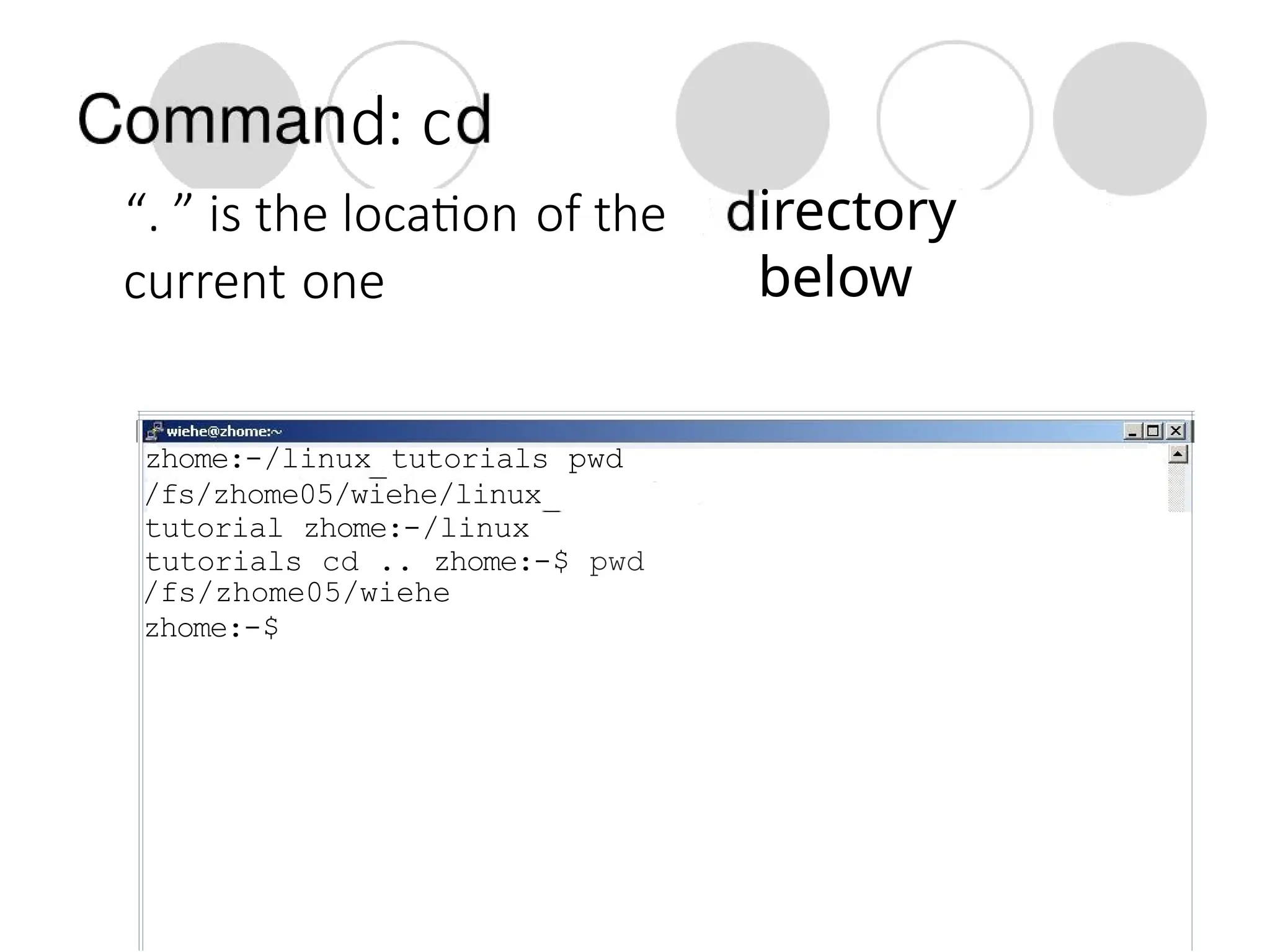
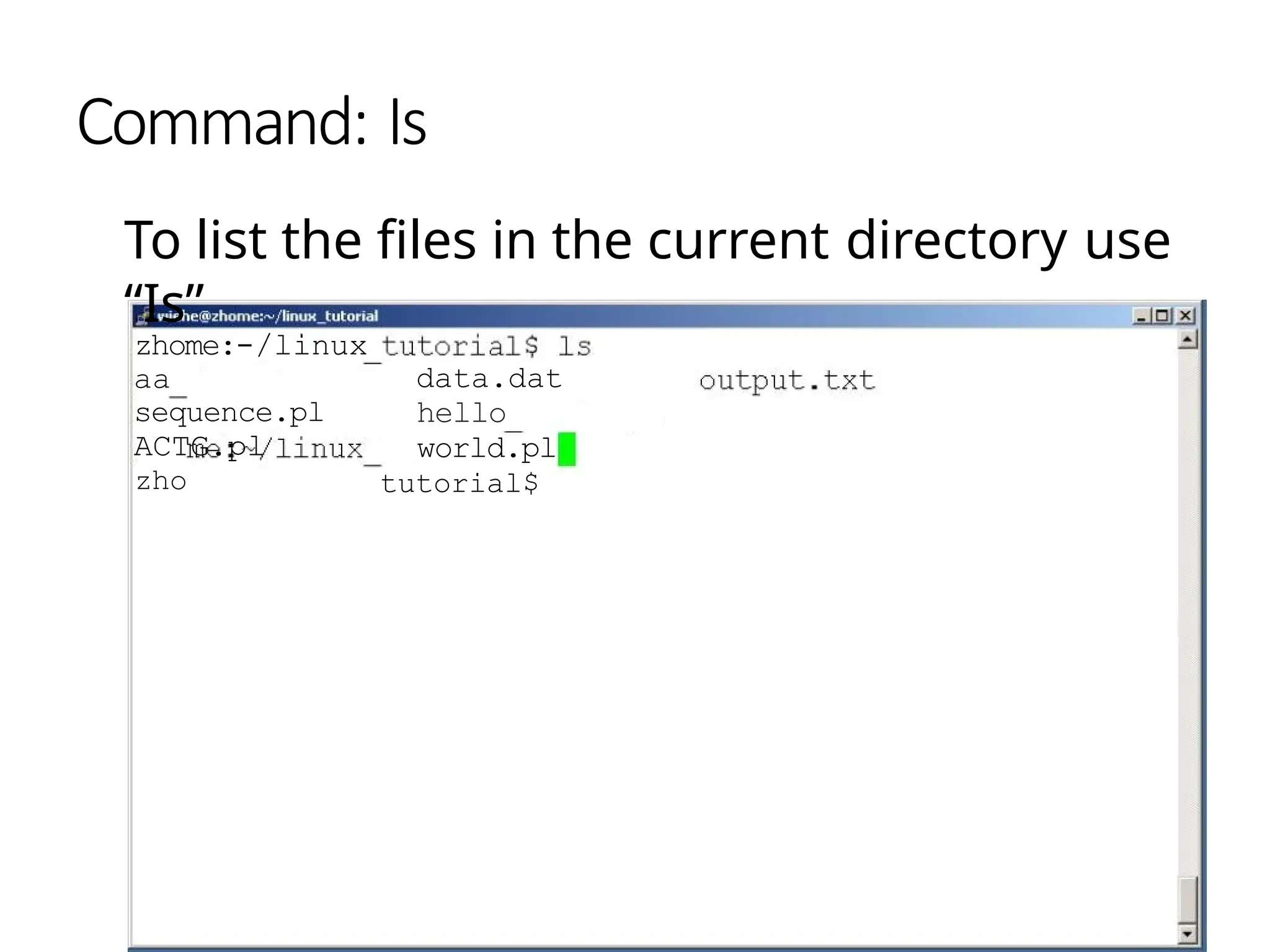
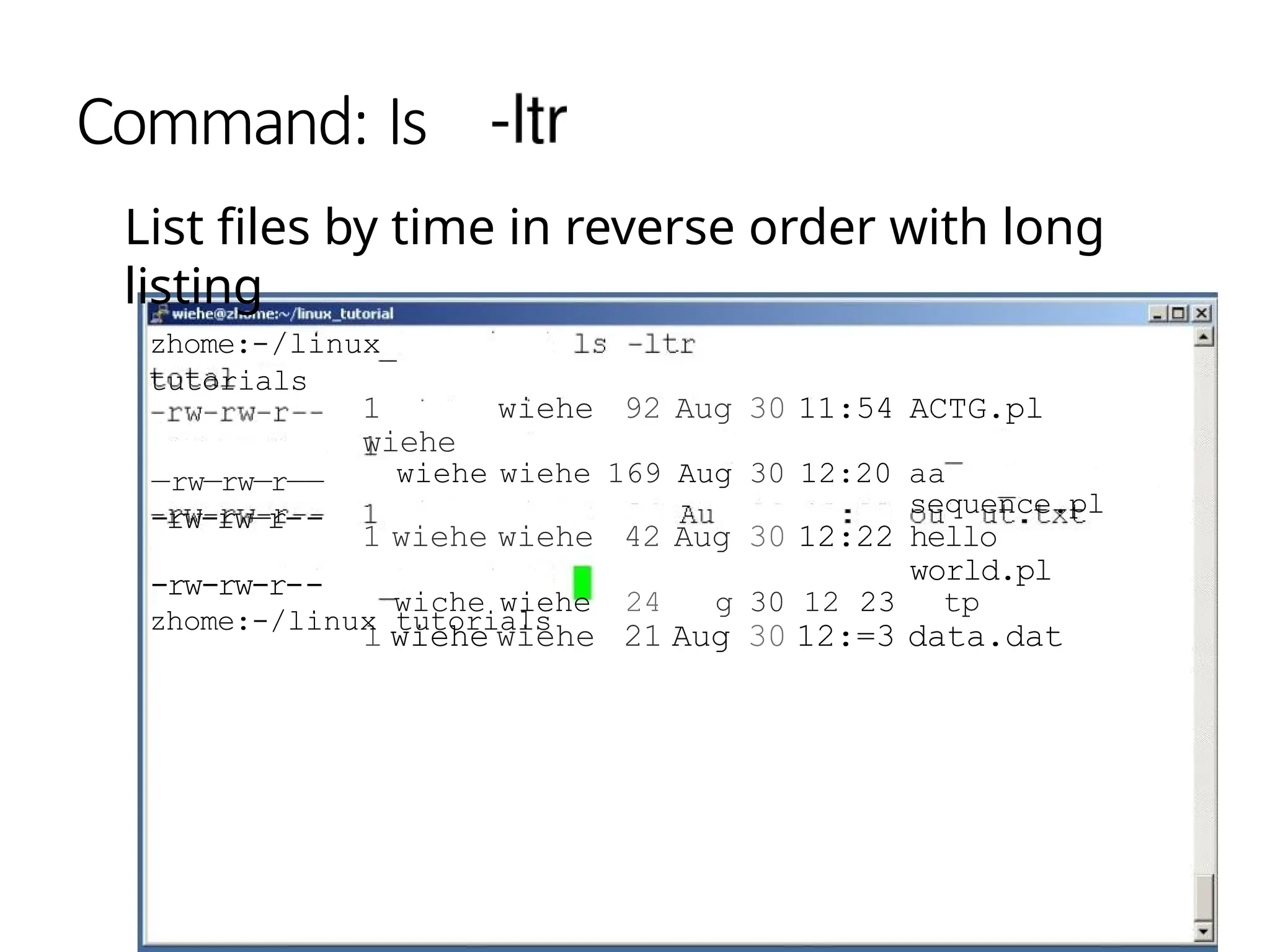
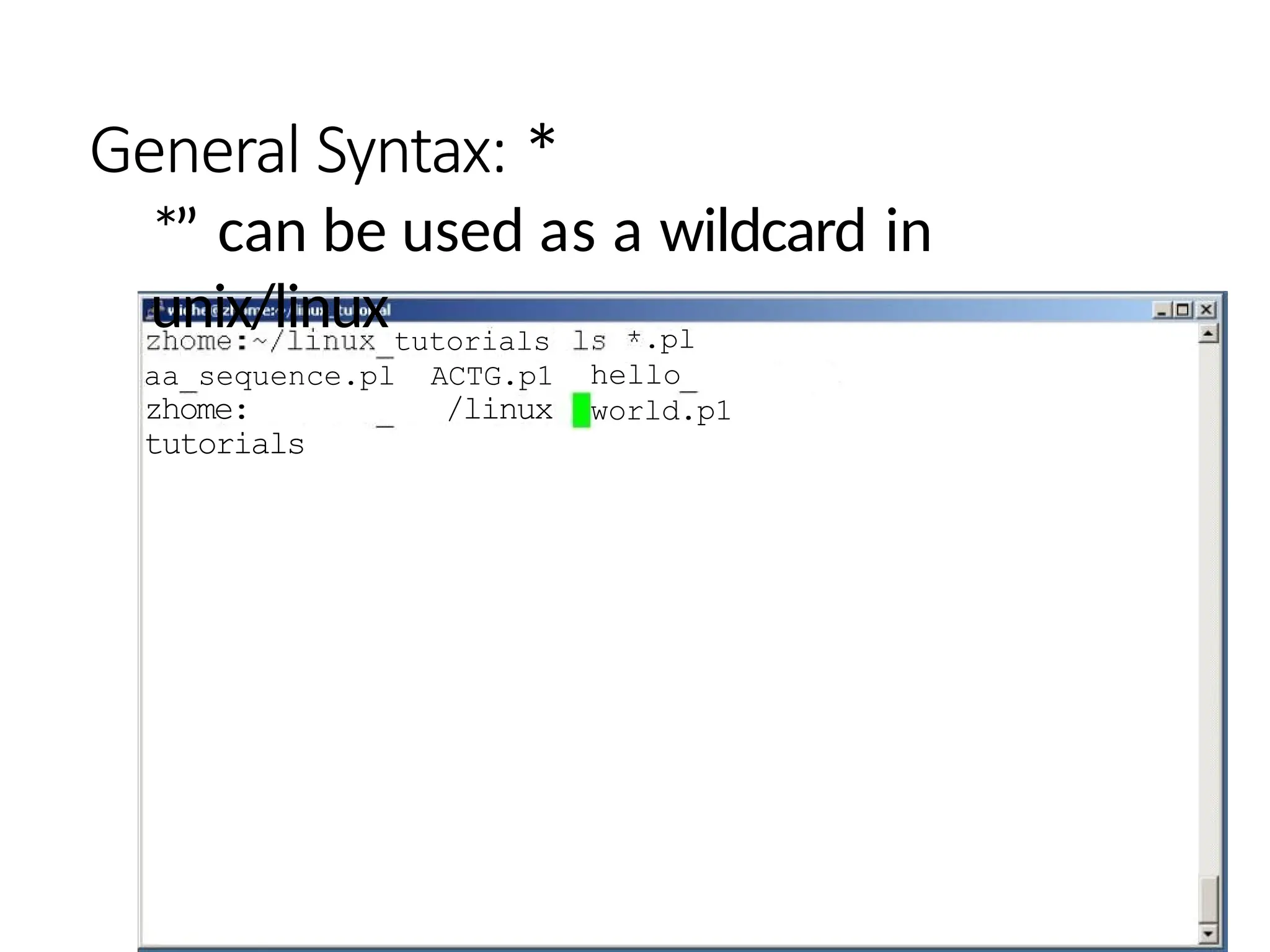
The document provides a detailed tutorial on connecting to and using a Unix/Linux system, focusing on command-line operations in the Bash shell. It covers essential commands for navigating directories, managing files (such as creating, copying, moving, and deleting), and understanding file permissions, along with basic file operations like viewing and searching content. Additionally, it introduces process management and command piping, offering examples and usage syntax for various commands.


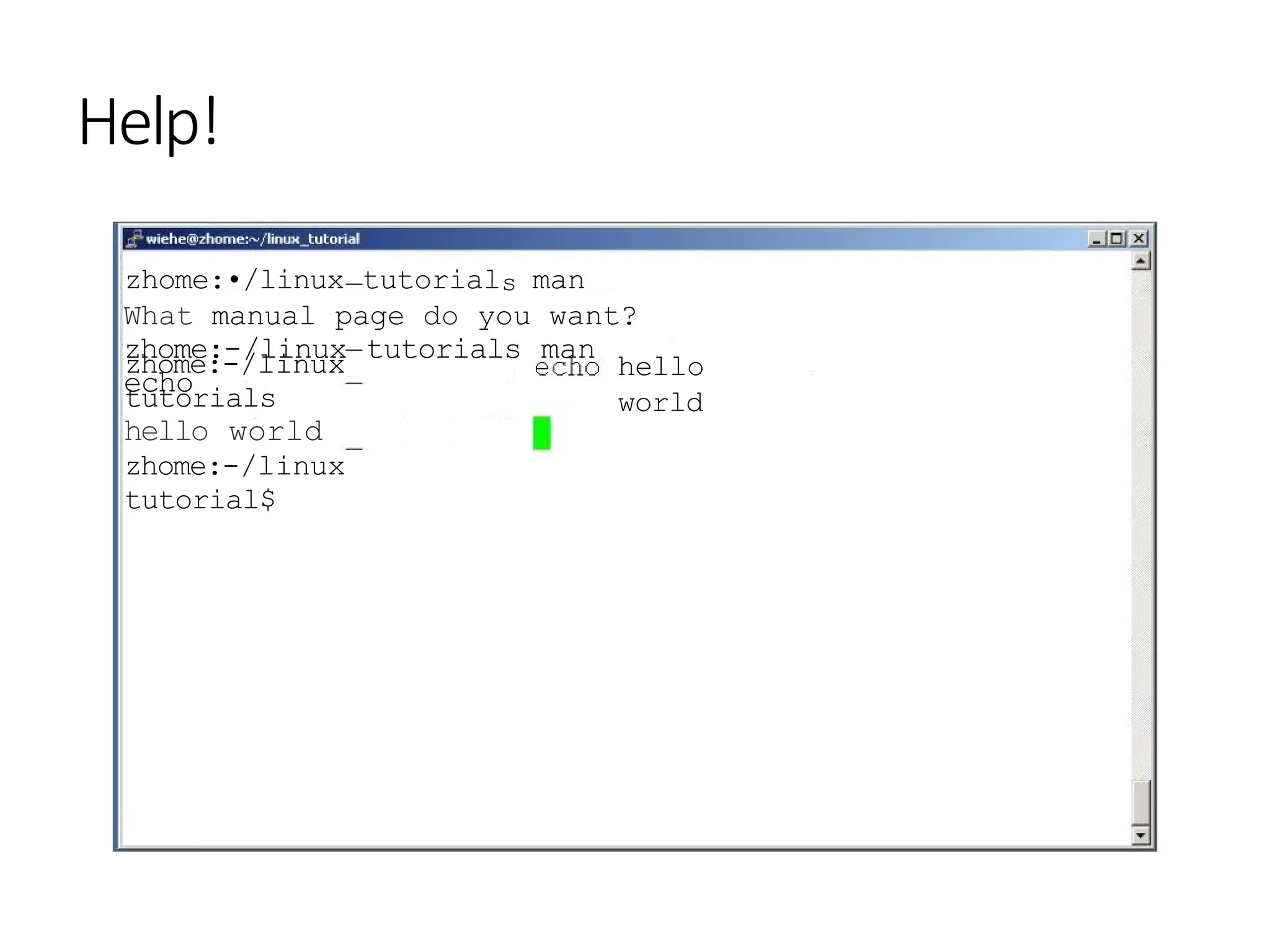
![ECHO ( 1) User Commands ECHO(1)
echo — display a line of text
SYNOPSIS
echo [OPTION]... [STRING]...
DESCRIPTION
NOTE: your shell may have its own version of
echo which will supercede the version described
here. Please refer to your shellas
documentation for details about the options it
supports.
Echo the STRING(s) to standard output.
do not output the trailing
newline
Help!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxcommandsppt-240909110404-df80bd67/75/LINUX_COMMANDS_FOR_BEGINNERS_POWERPOINTPRESENTATION-pptx-7-2048.jpg)


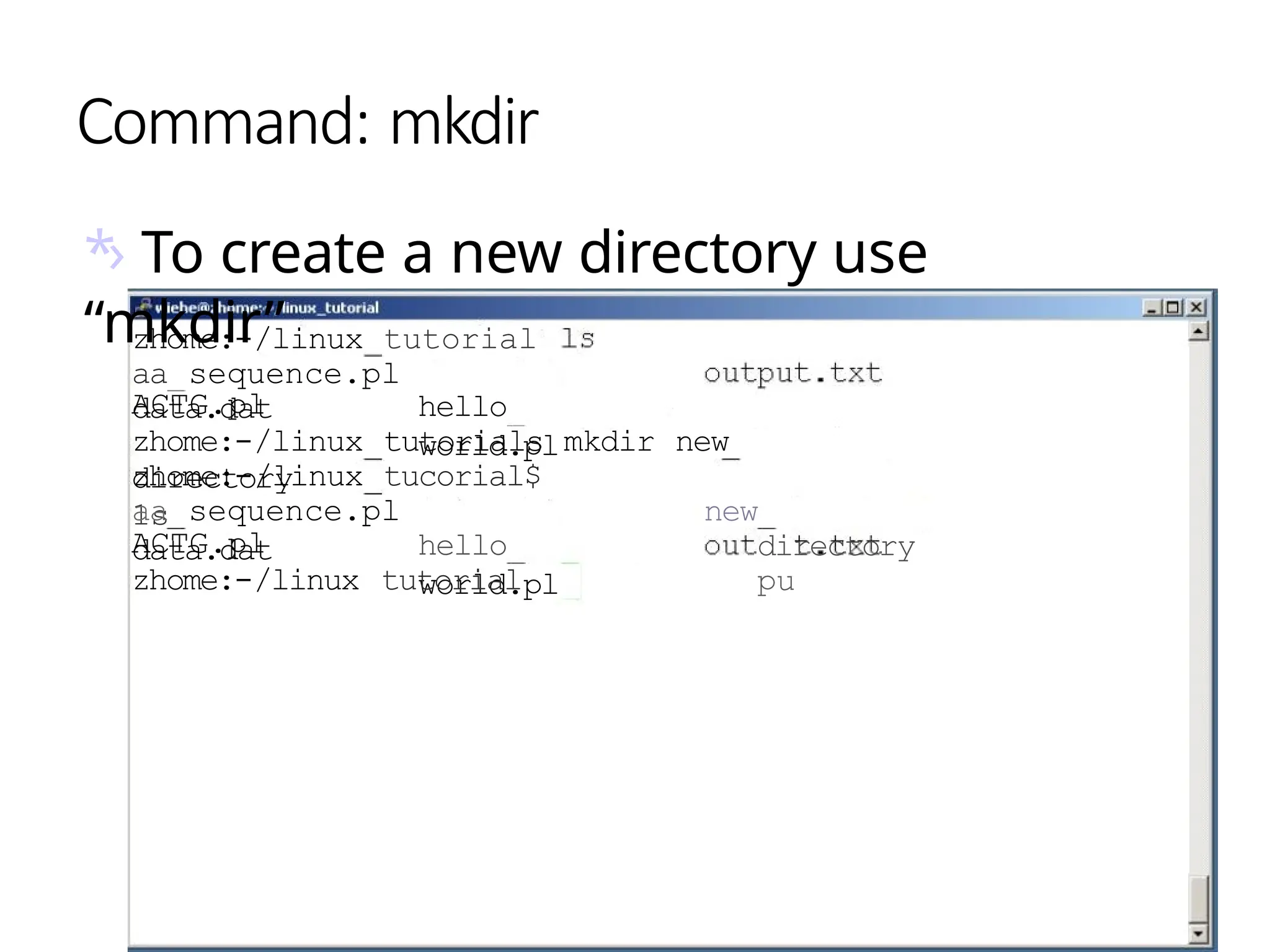


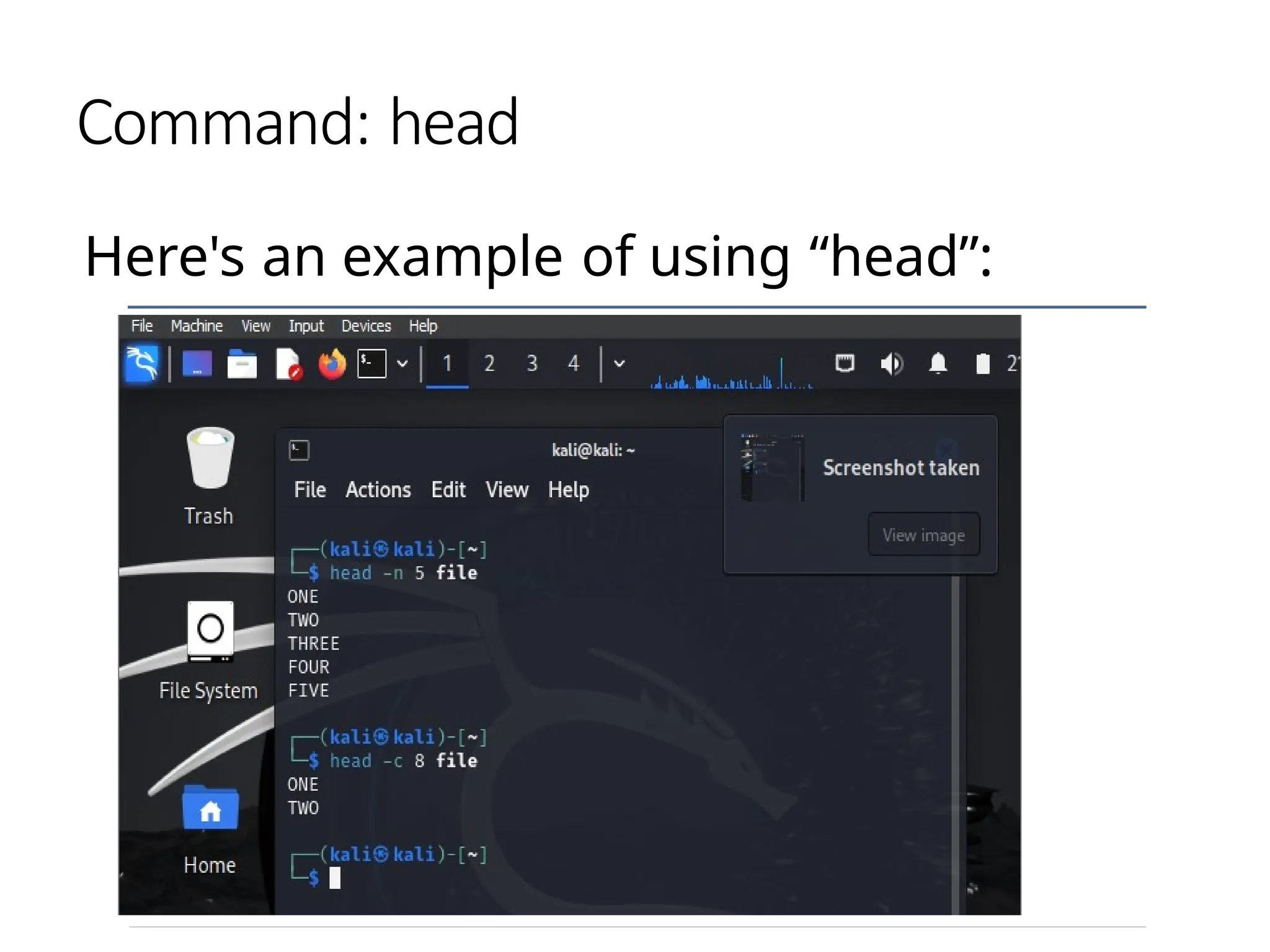
![Command: [head (option..) (file..)]
• The head command, as the name
implies, print the top N number
of data of the given input.
• By default, it prints the first 10
lines of the specified files. If more
than one file name is provided
then data from each file is
preceded by its file name.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxcommandsppt-240909110404-df80bd67/75/LINUX_COMMANDS_FOR_BEGINNERS_POWERPOINTPRESENTATION-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
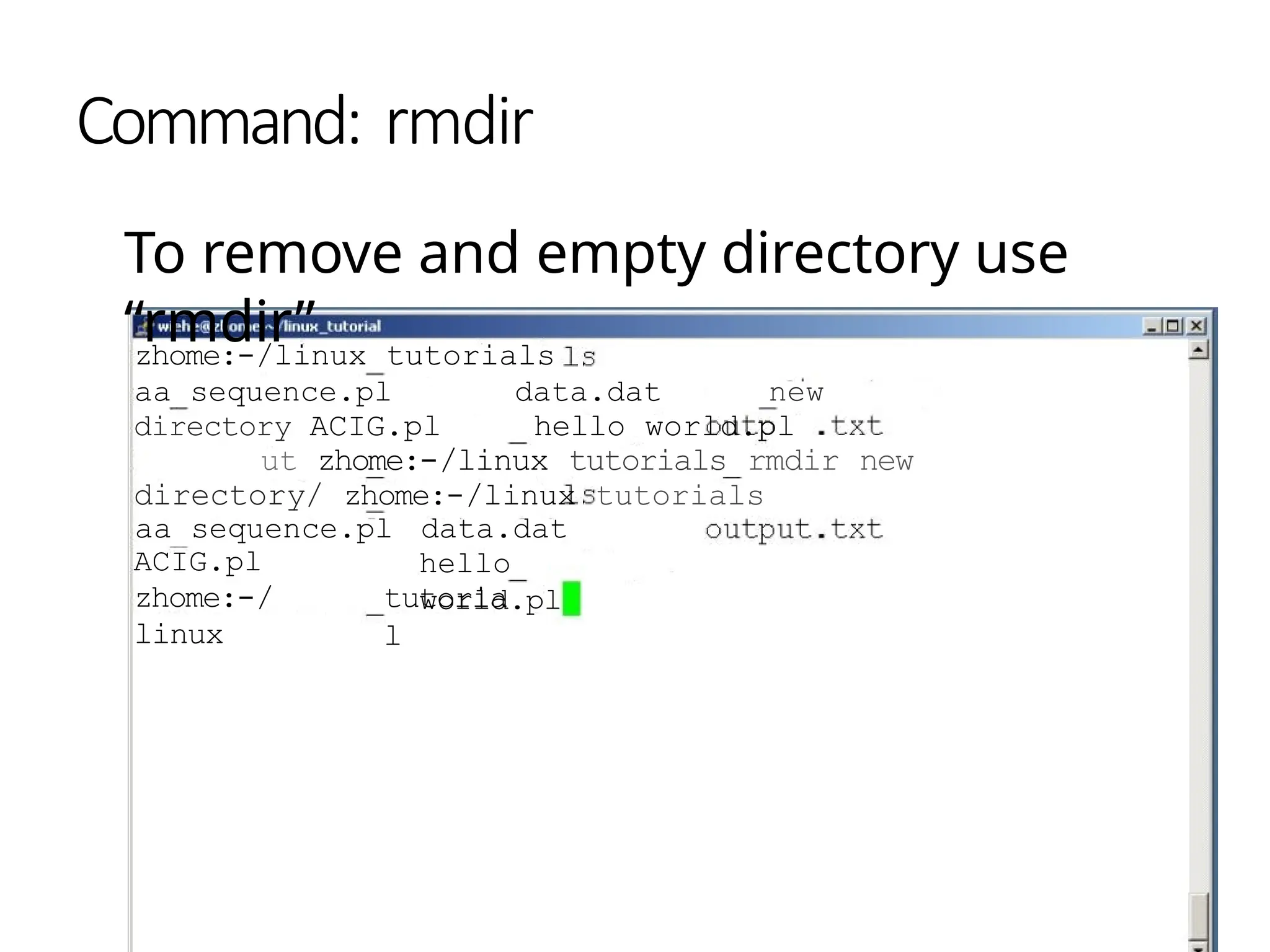
![Command: [tail (option..)(filename)]
Same as head, but shows the last
lines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxcommandsppt-240909110404-df80bd67/75/LINUX_COMMANDS_FOR_BEGINNERS_POWERPOINTPRESENTATION-pptx-26-2048.jpg)



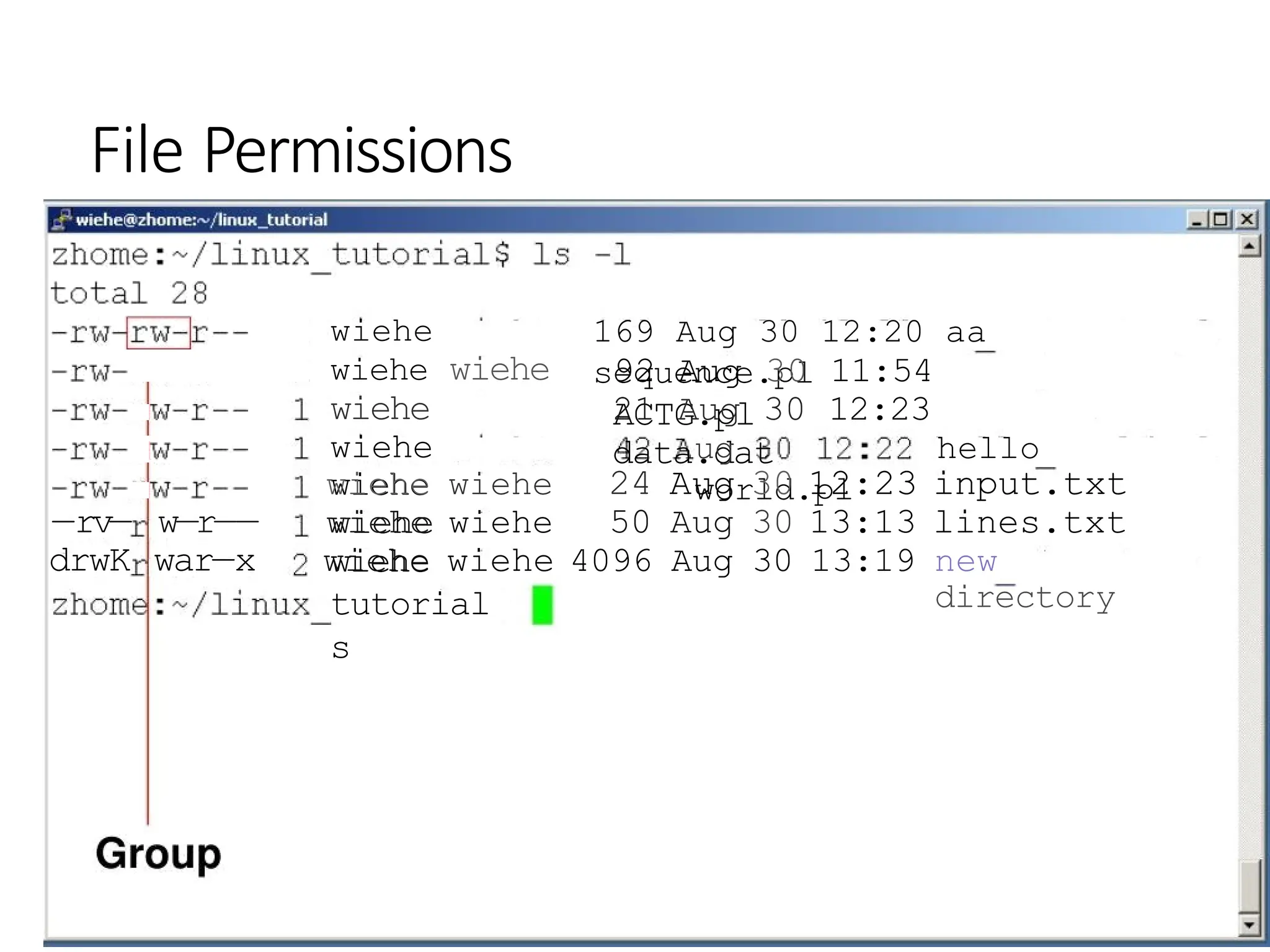
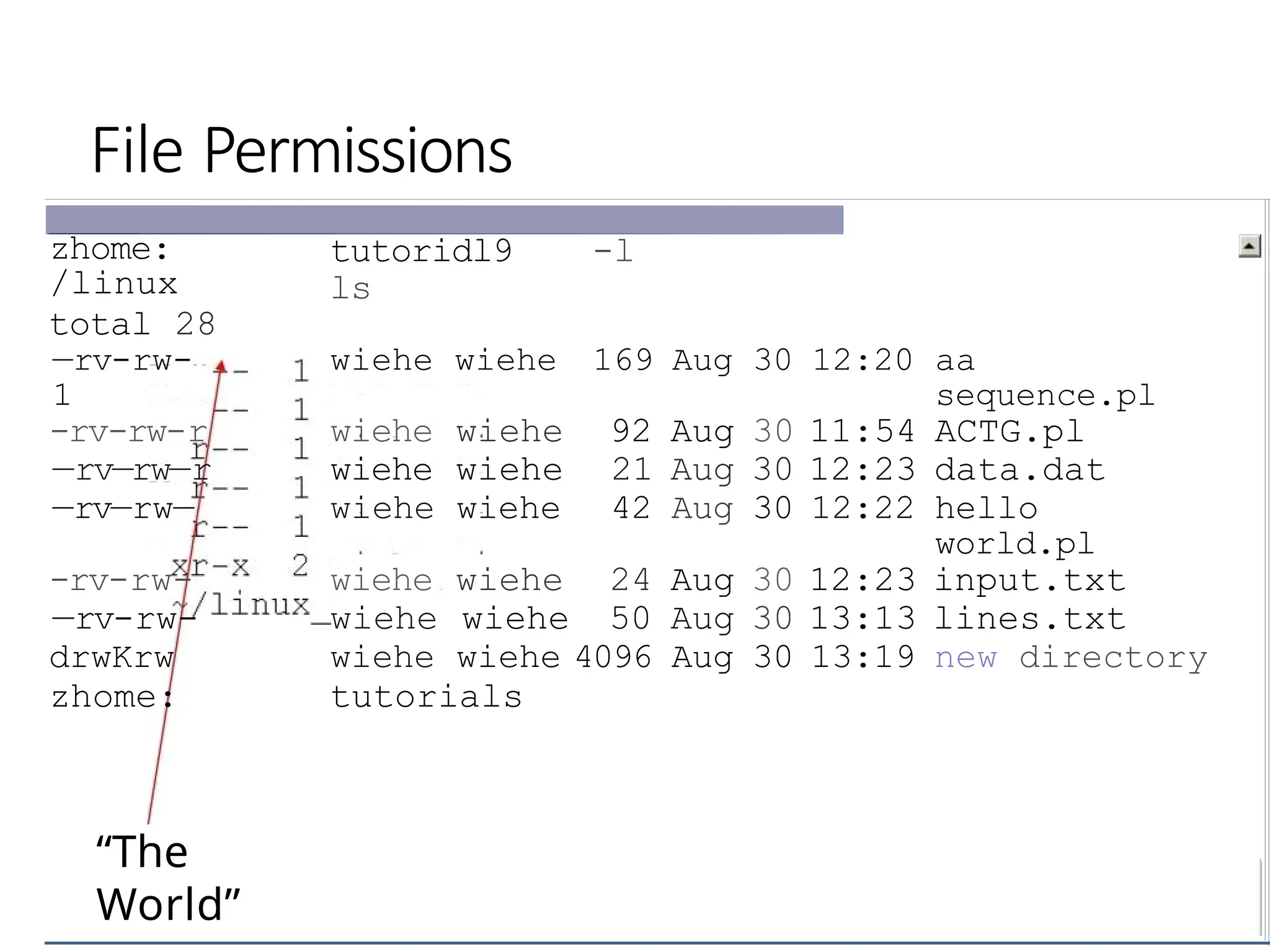
![Command: chmod
•If you own the file, you can change it's permissions with
“chmod”
•Syntax: chmod [user/group/others/alI]+[permission] [file(s)]
Below we grant execute permission to all:
—rw—rw—r—— 1 wiehe
wiehe chmo
d
world.pl
12 22 hello
world.pl hello
world.pl
zhome:-/linux tutorials
—rwxrwxr—x wiehe wiehe 42 Aug 30
12:
zhome:-/linux tutorial$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxcommandsppt-240909110404-df80bd67/75/LINUX_COMMANDS_FOR_BEGINNERS_POWERPOINTPRESENTATION-pptx-38-2048.jpg)