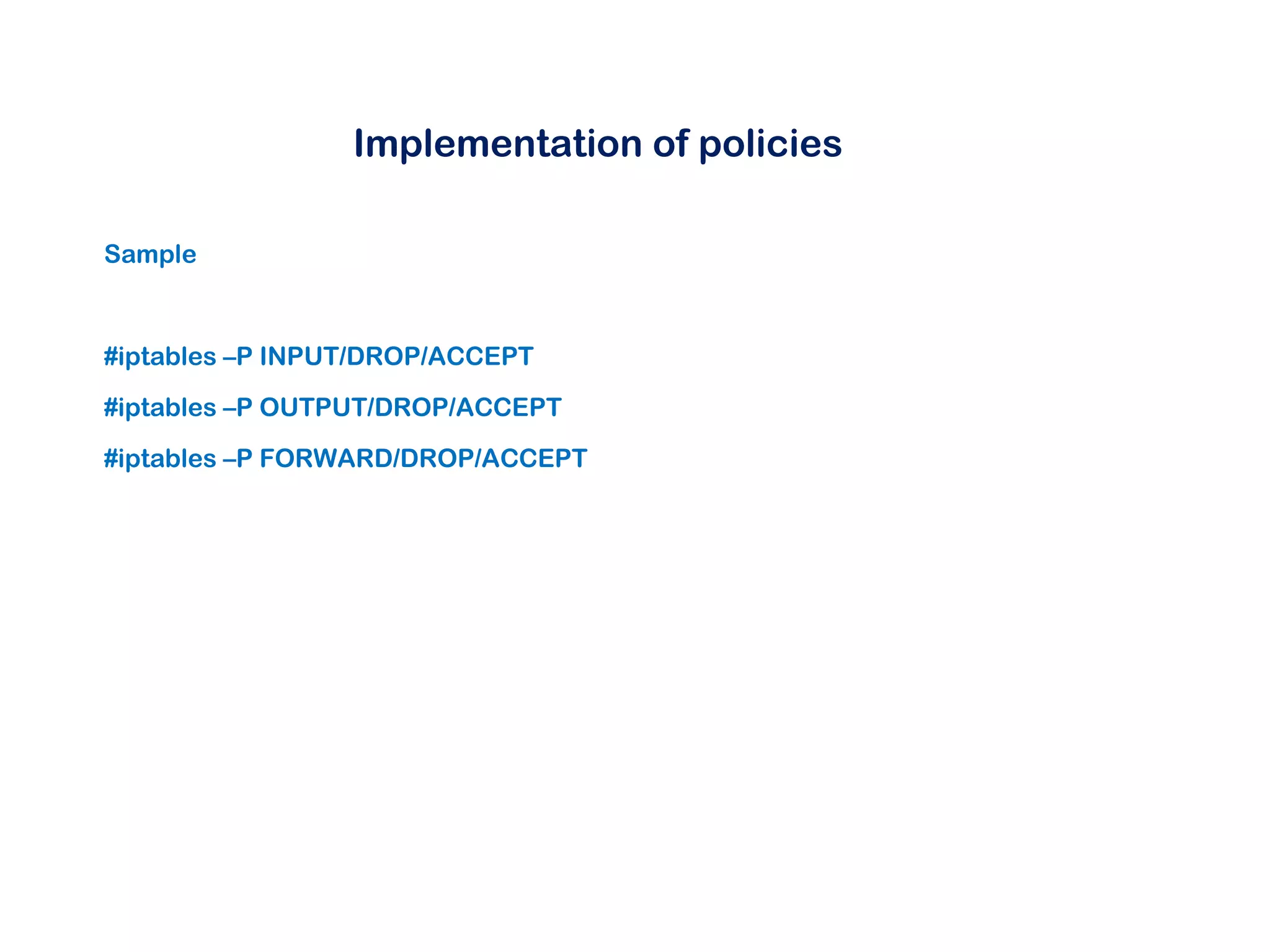
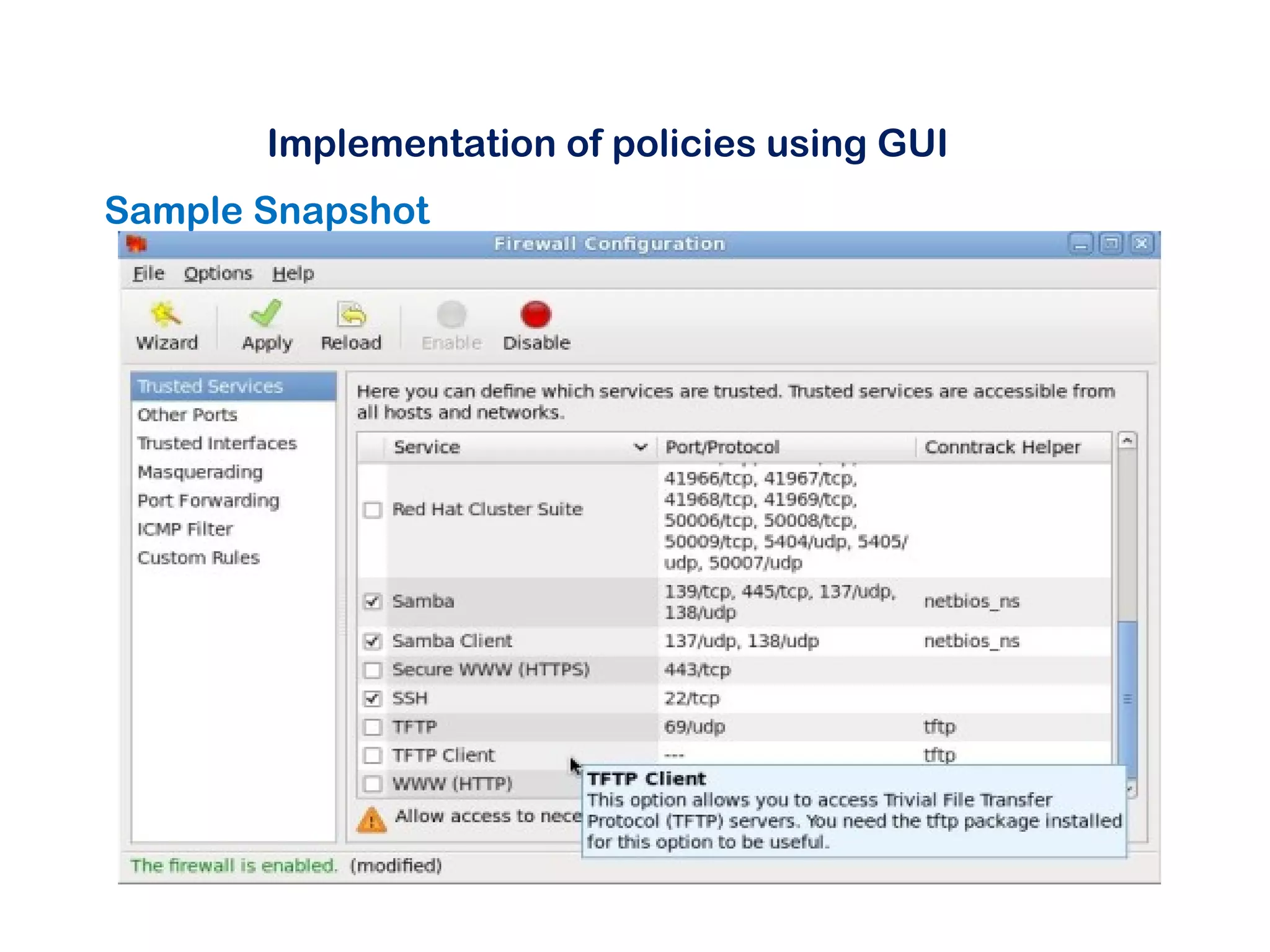
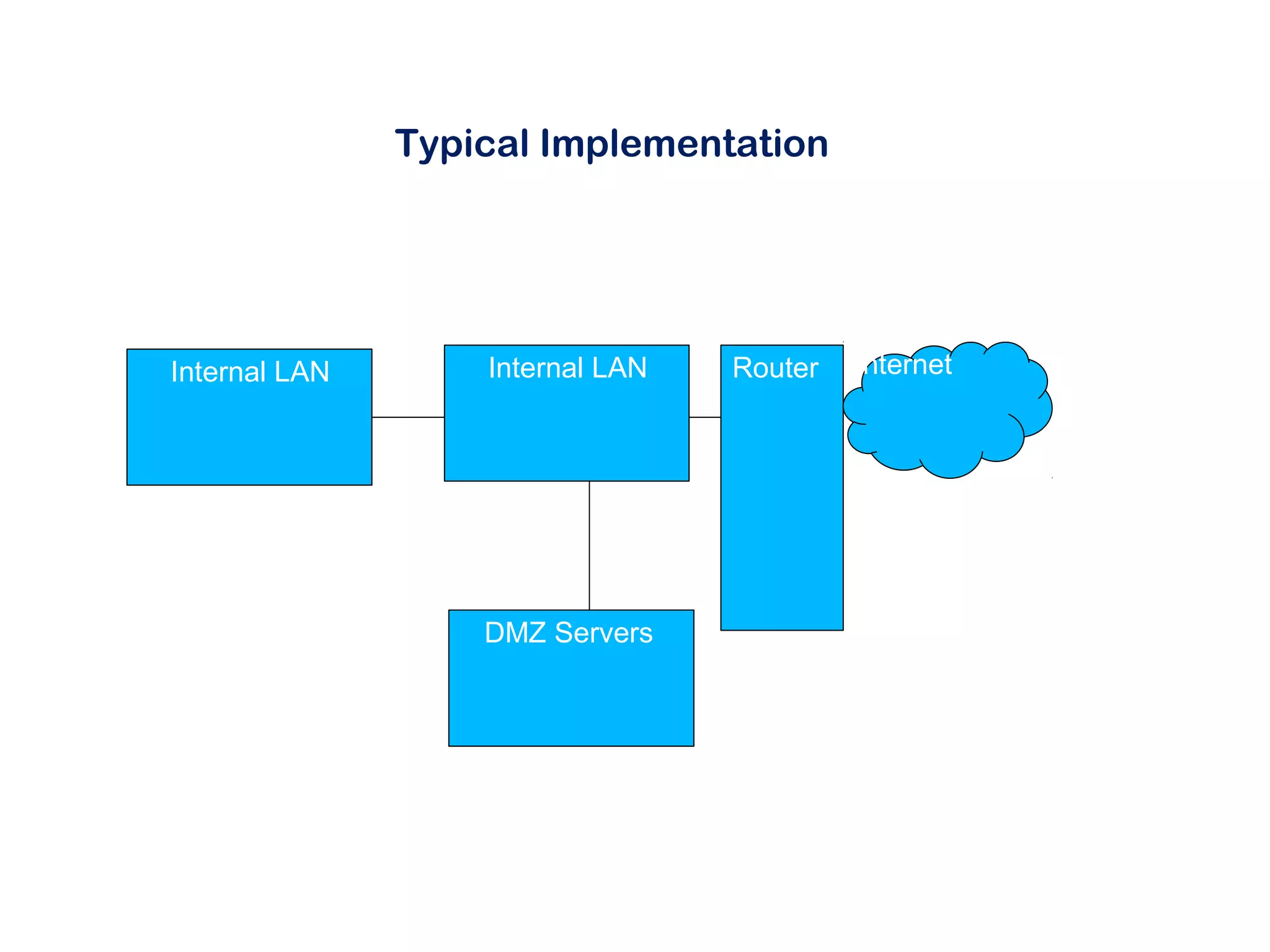
This document discusses Linux firewalls, beginning with an introduction to why firewalls are needed for access control, detection capabilities, and why Linux is a good option. It then covers firewall basics and the different Linux firewall modules - IPChains, which provides basic filtering but no port forwarding, and IPTables, which adds stateful inspection, improved matching, and port forwarding. The document demonstrates how to implement and manage firewall policies using both the command line and GUI tools in Linux. It also discusses typical firewall implementations and tools for compiling IPTables rules.