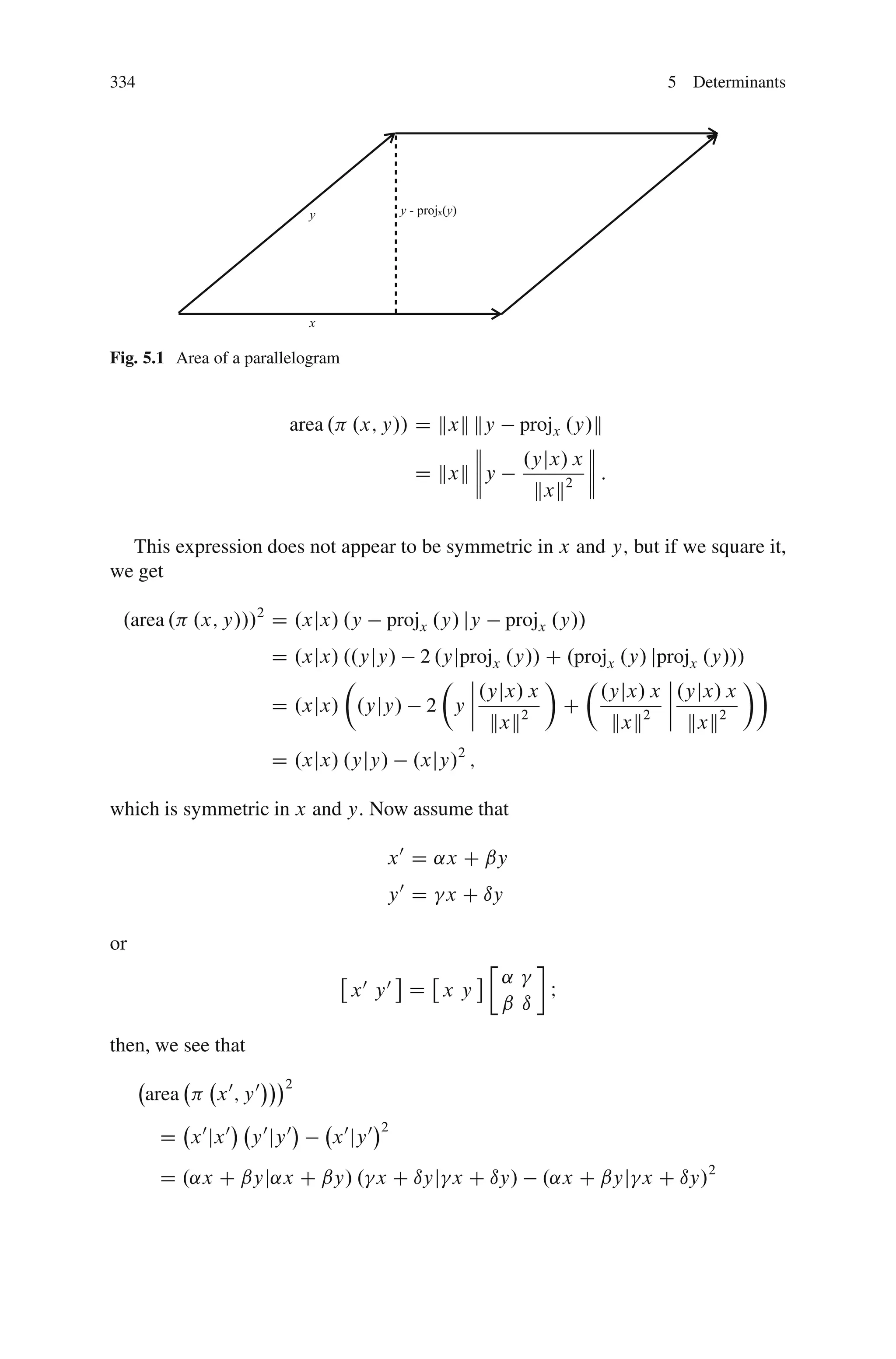
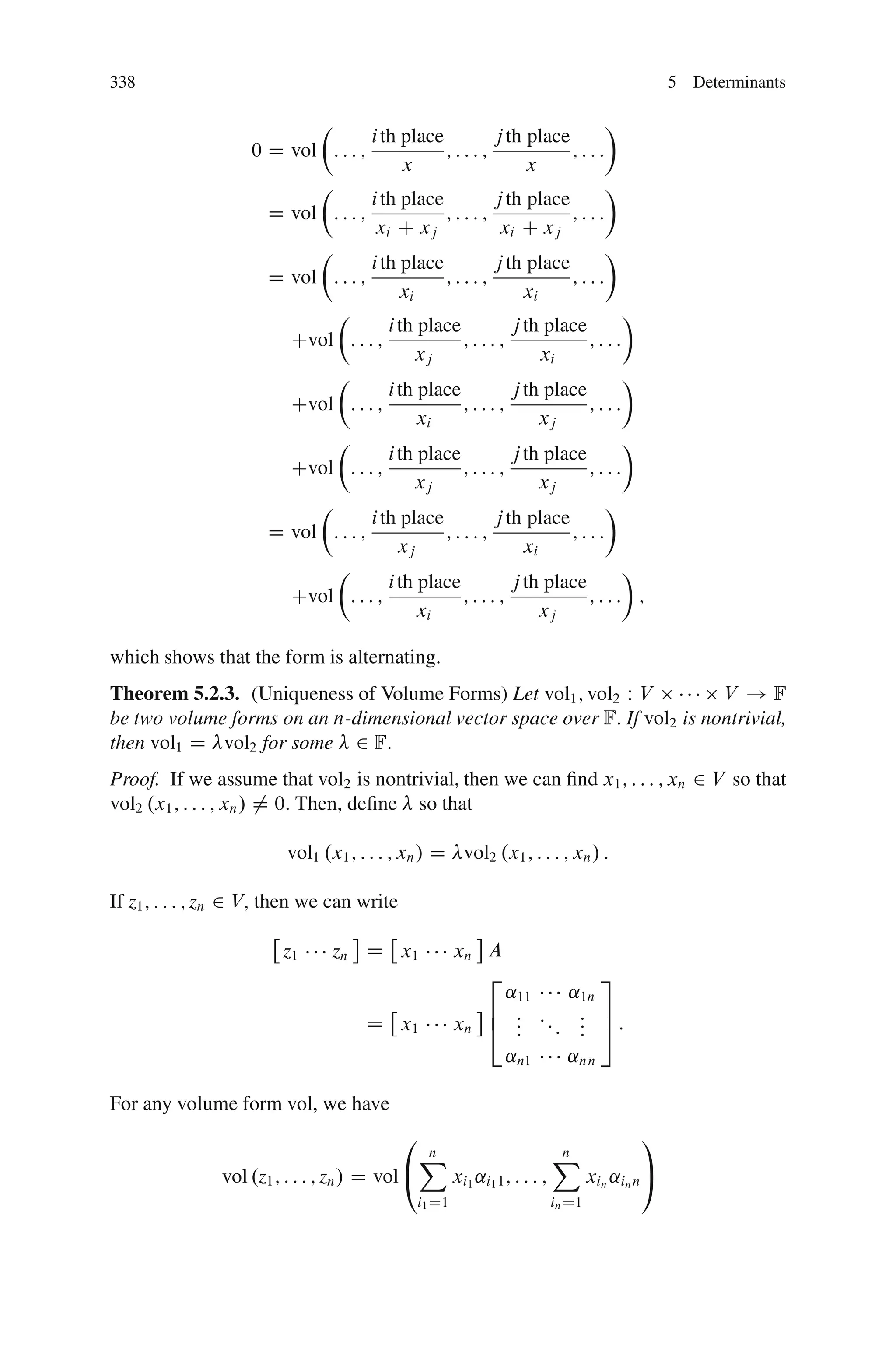
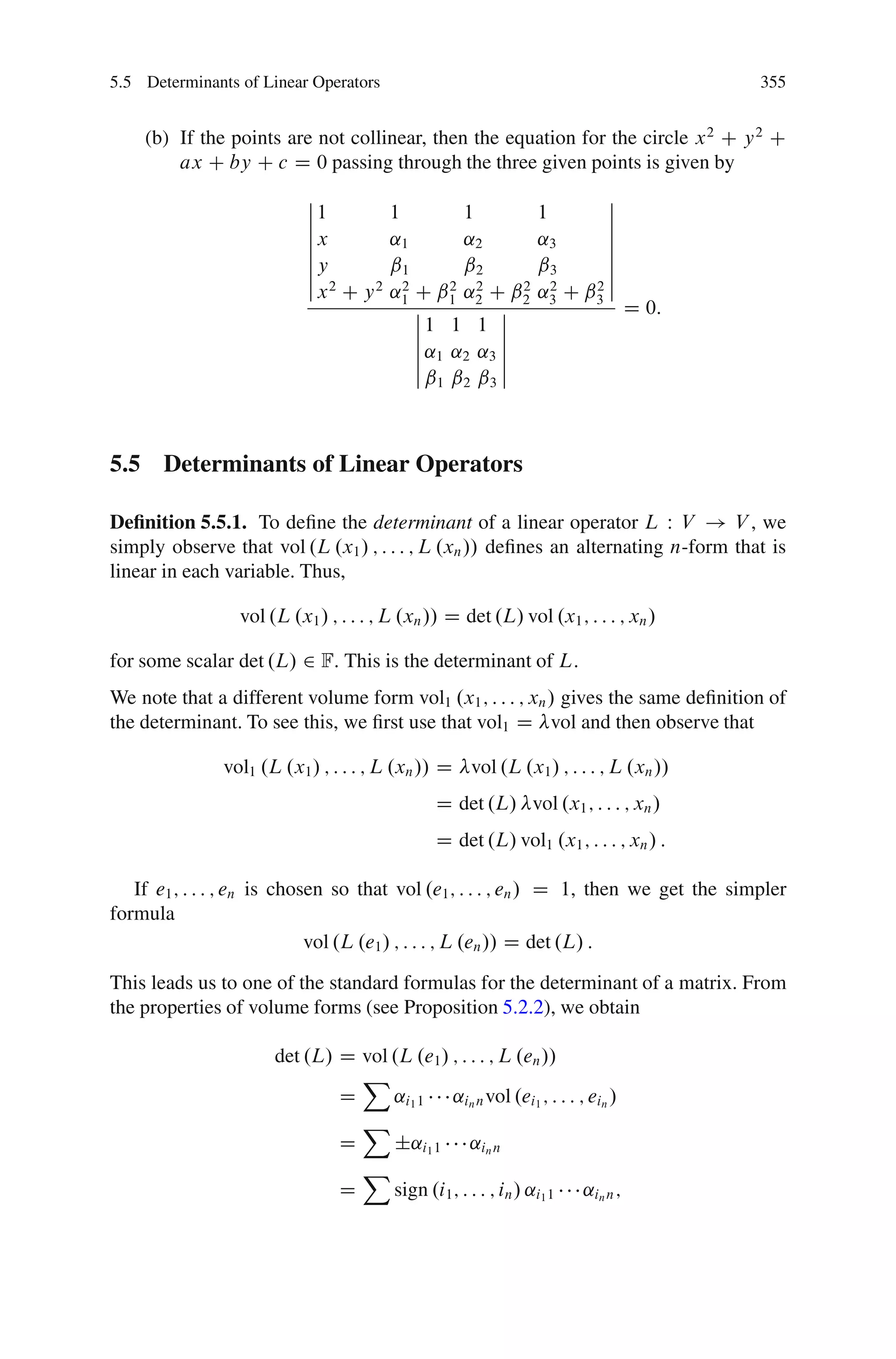
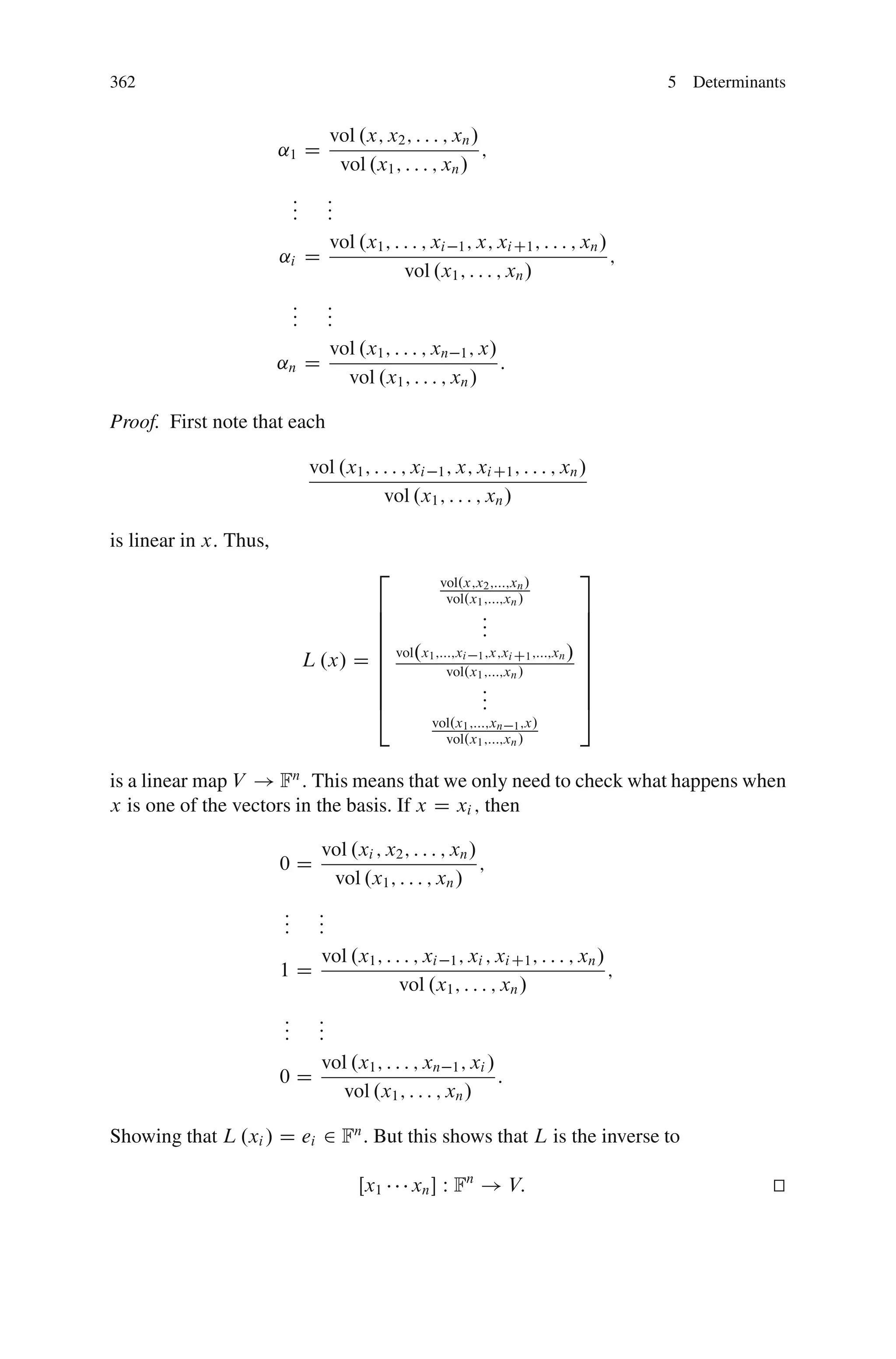
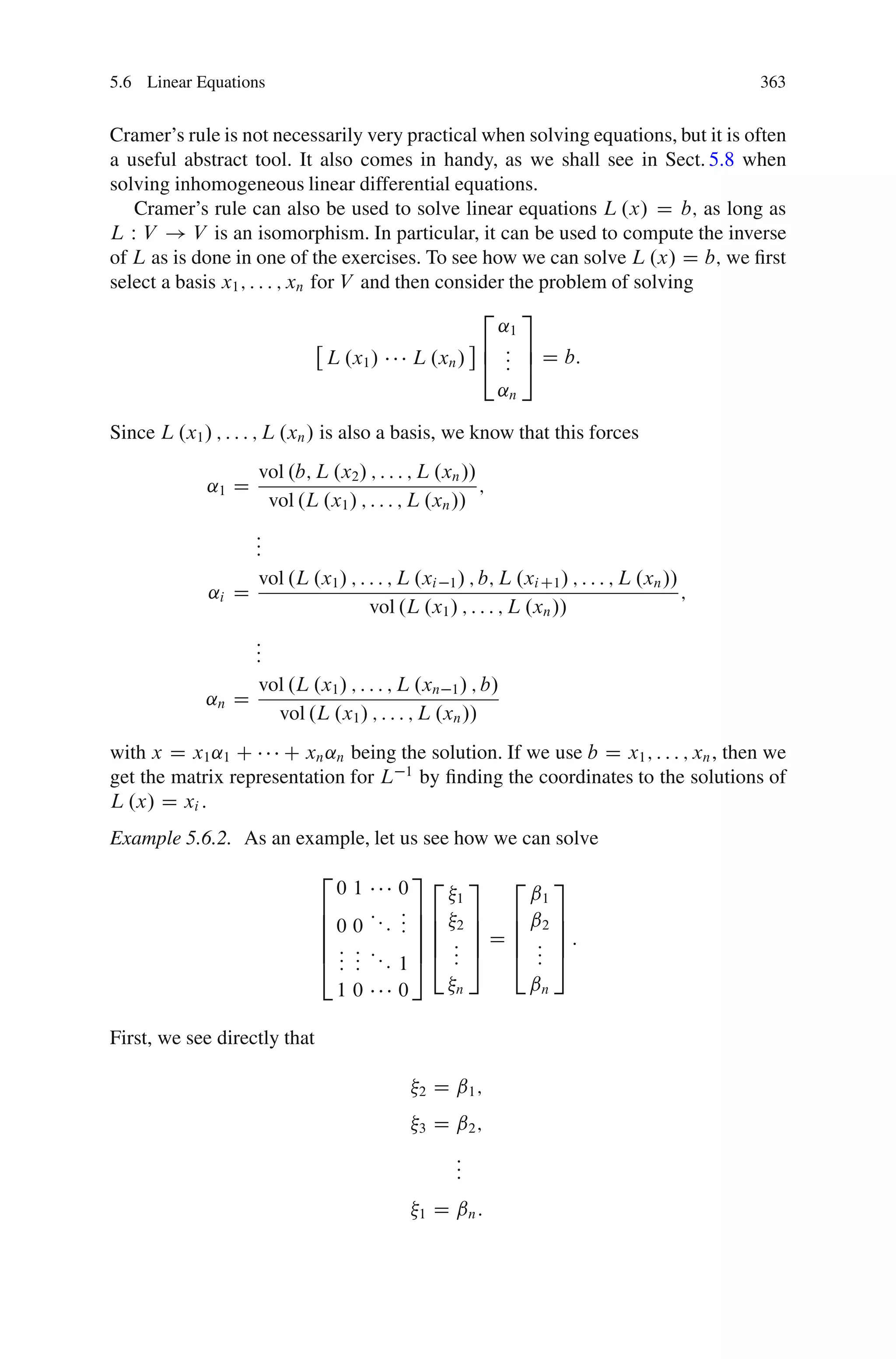
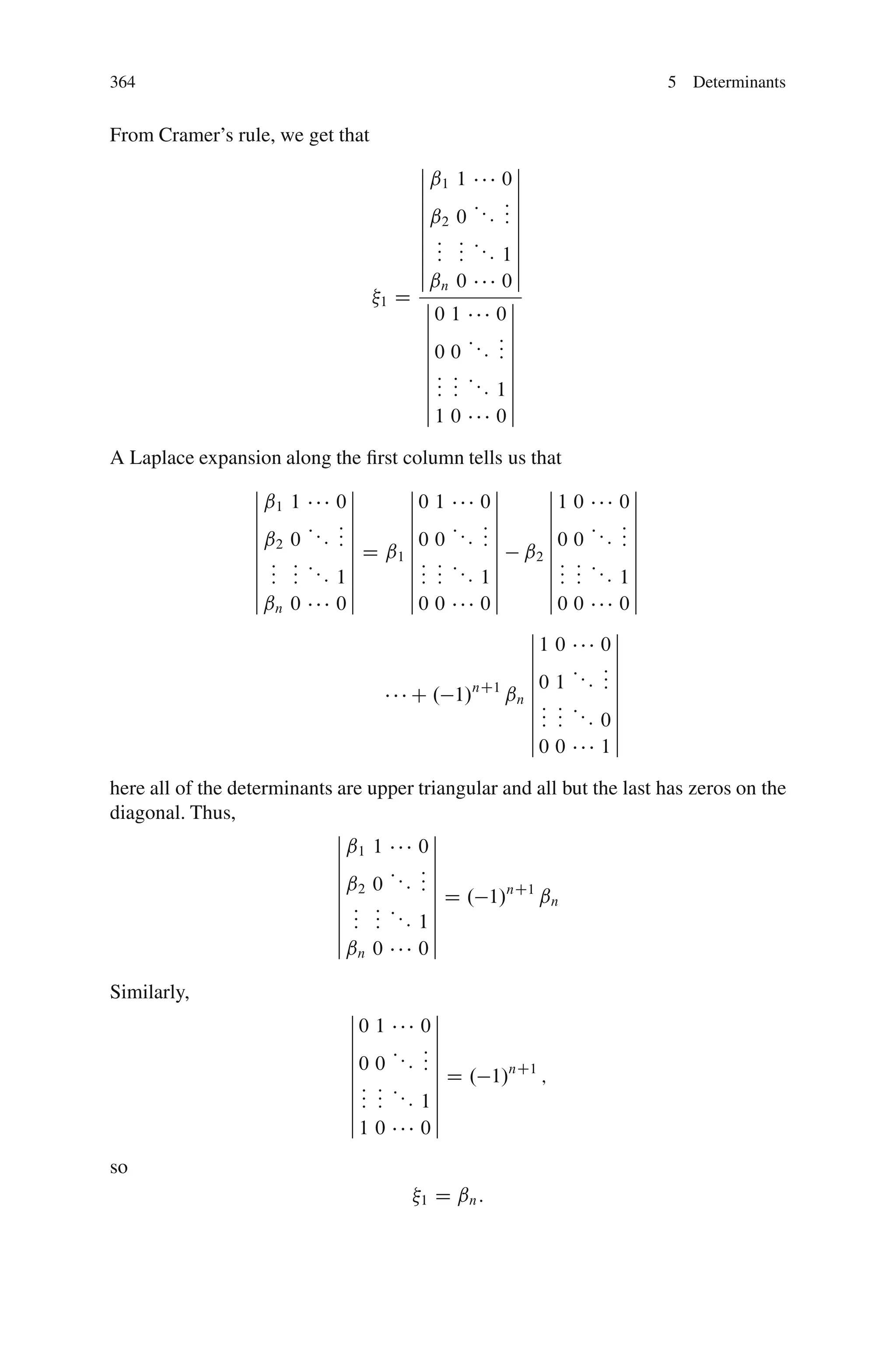
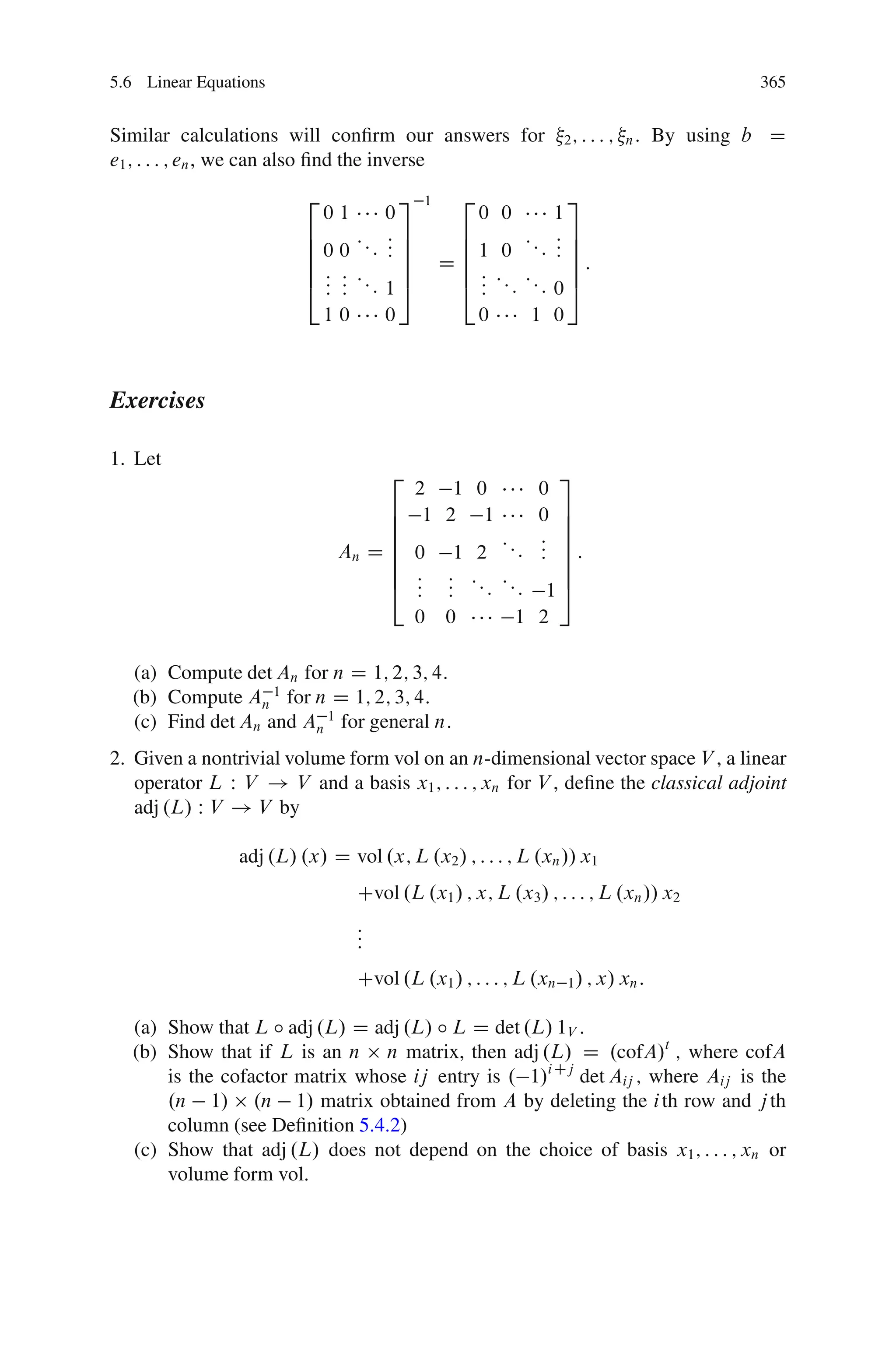
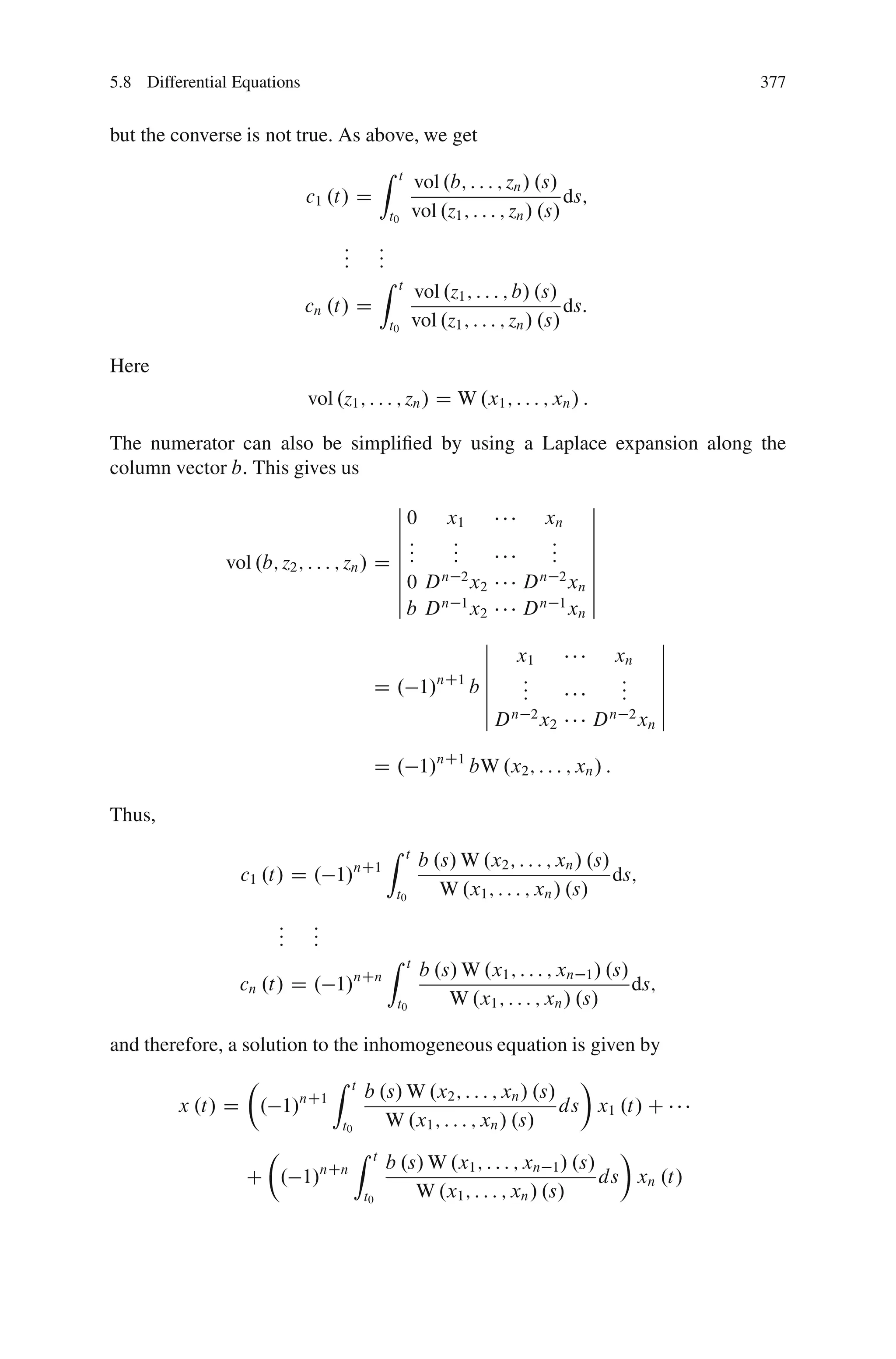
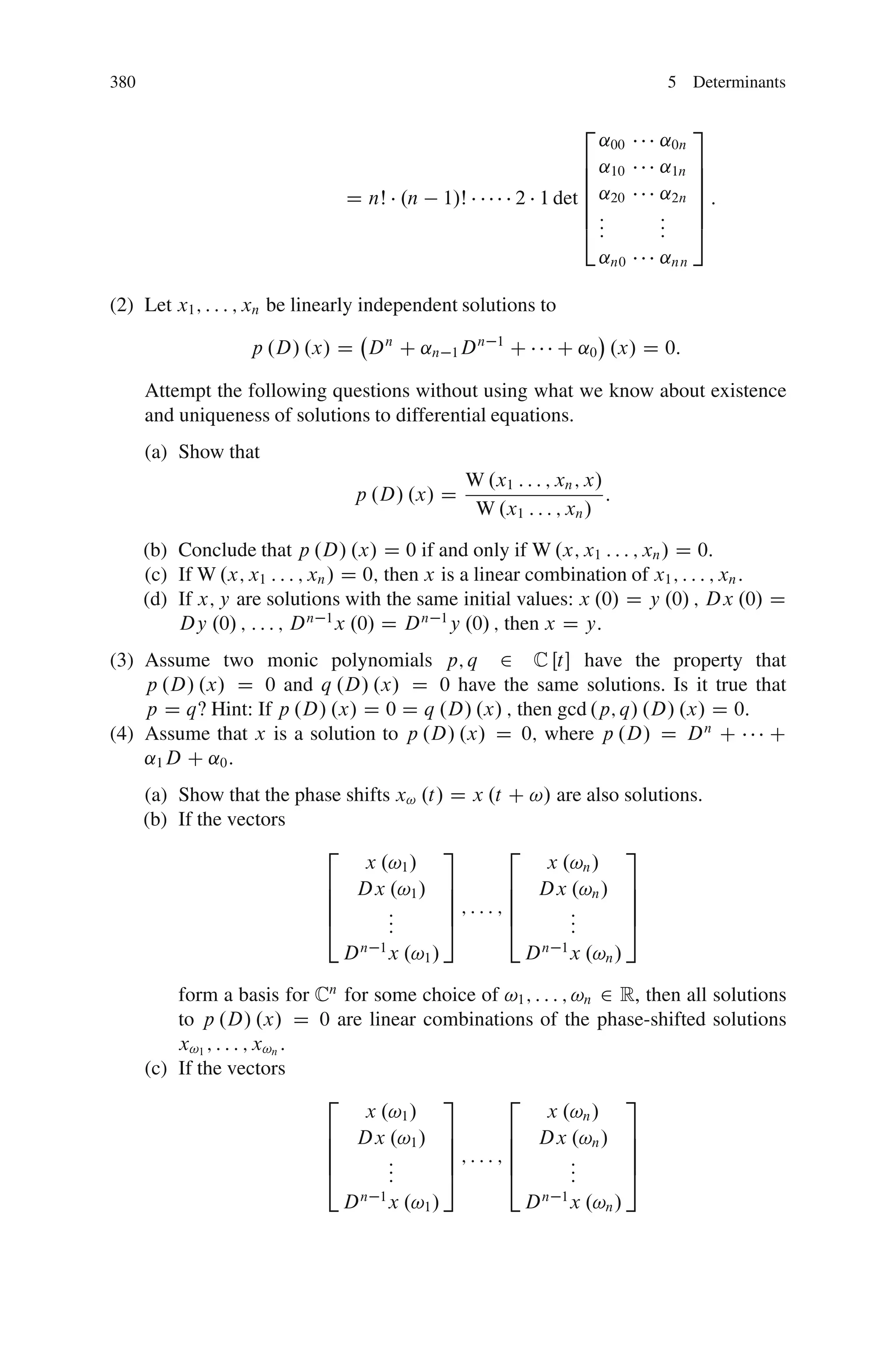
This document discusses determinants from both a geometric and algebraic perspective in three dimensions or less.
Geometrically, determinants can be thought of as measuring how a linear operator L changes the volume of objects in a vector space V. In one dimension, L must be of the form L(x) = λx, and λ describes how L changes the length of vectors. In two dimensions, the determinant of L is defined such that the ratio of the areas of two parallelograms is not dependent on the choice of vectors or inner product used to compute the areas.
Algebraically, a volume form is defined as a multi-linear map from the direct product of V with itself n times