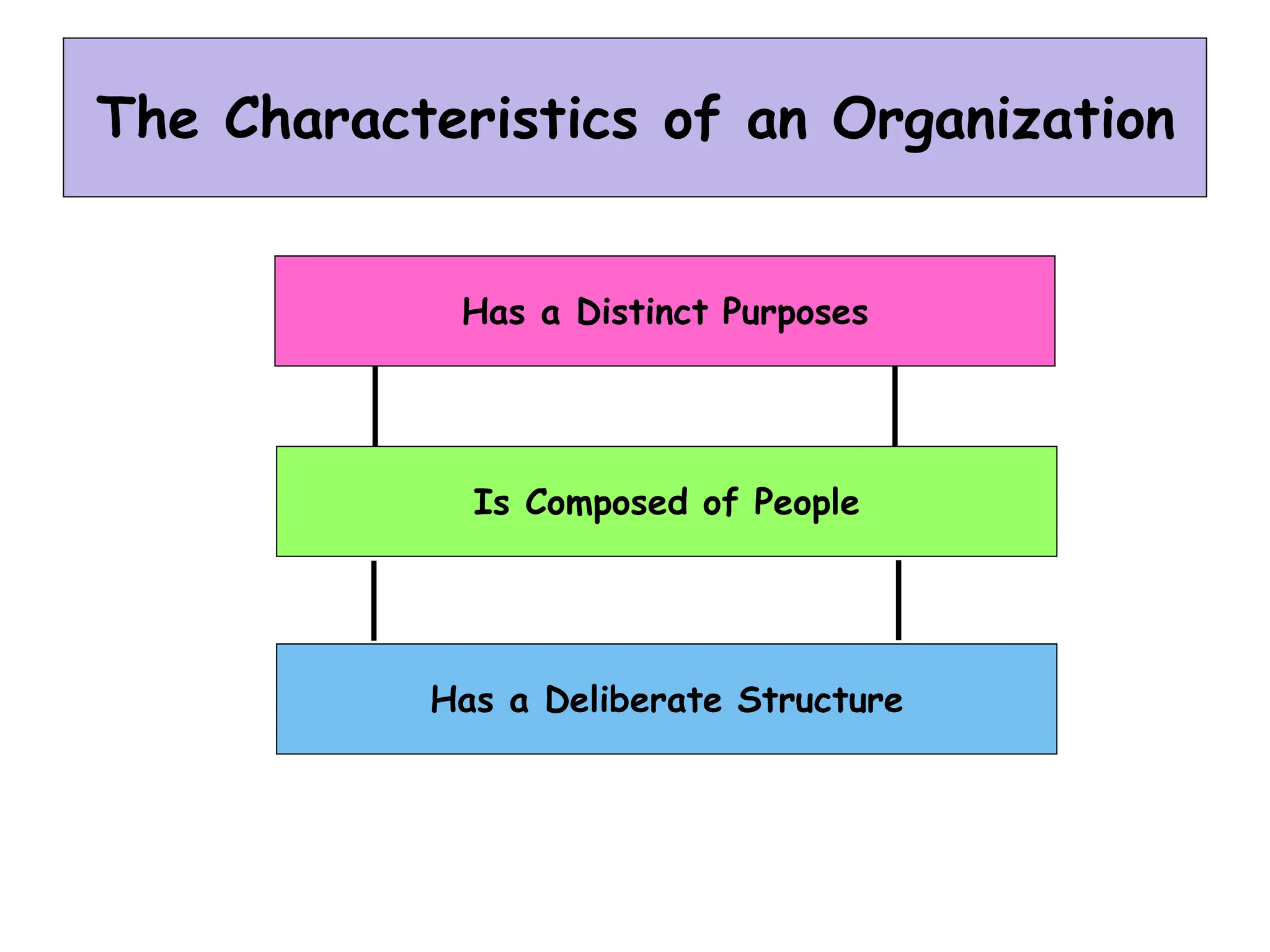
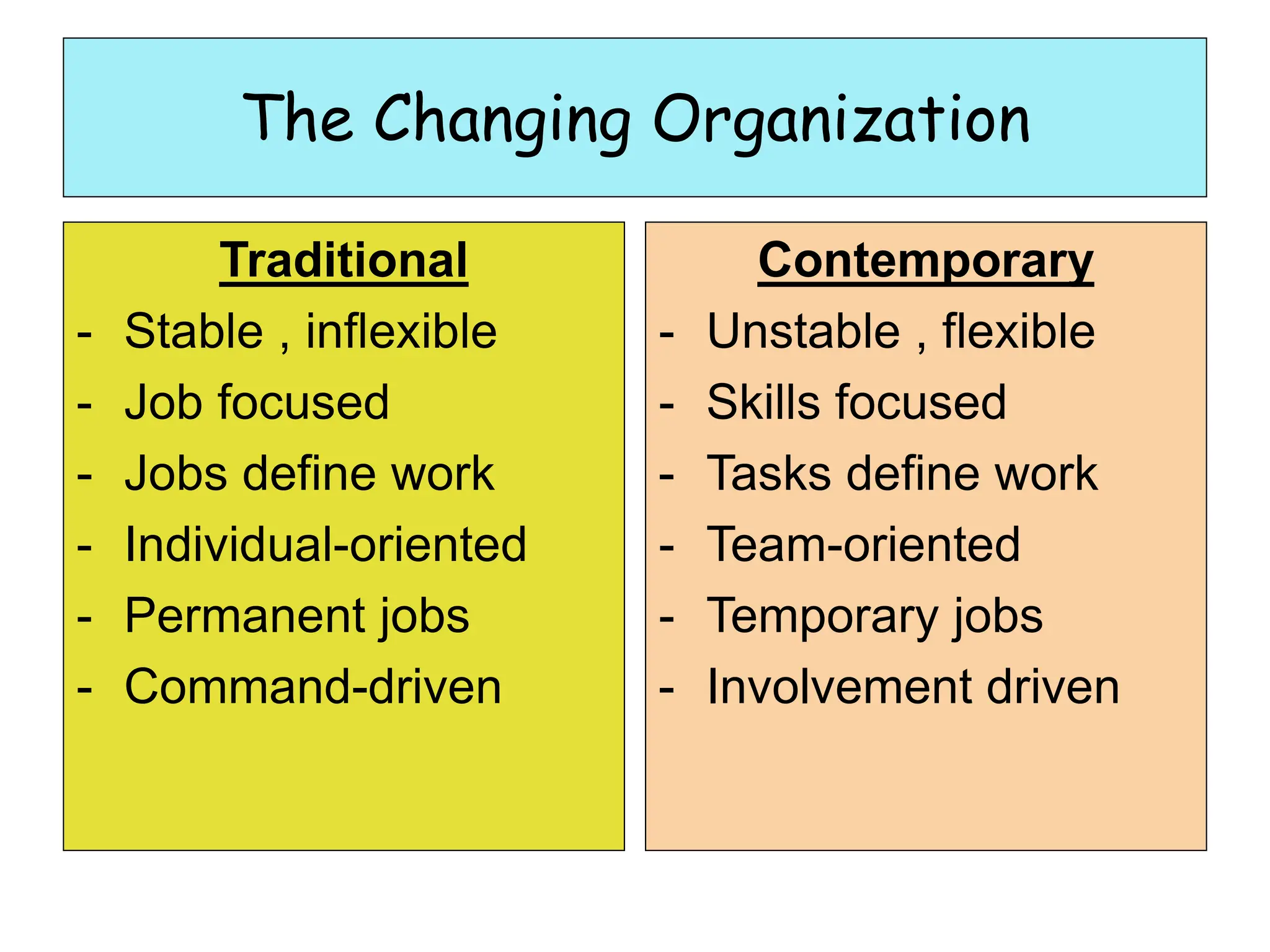
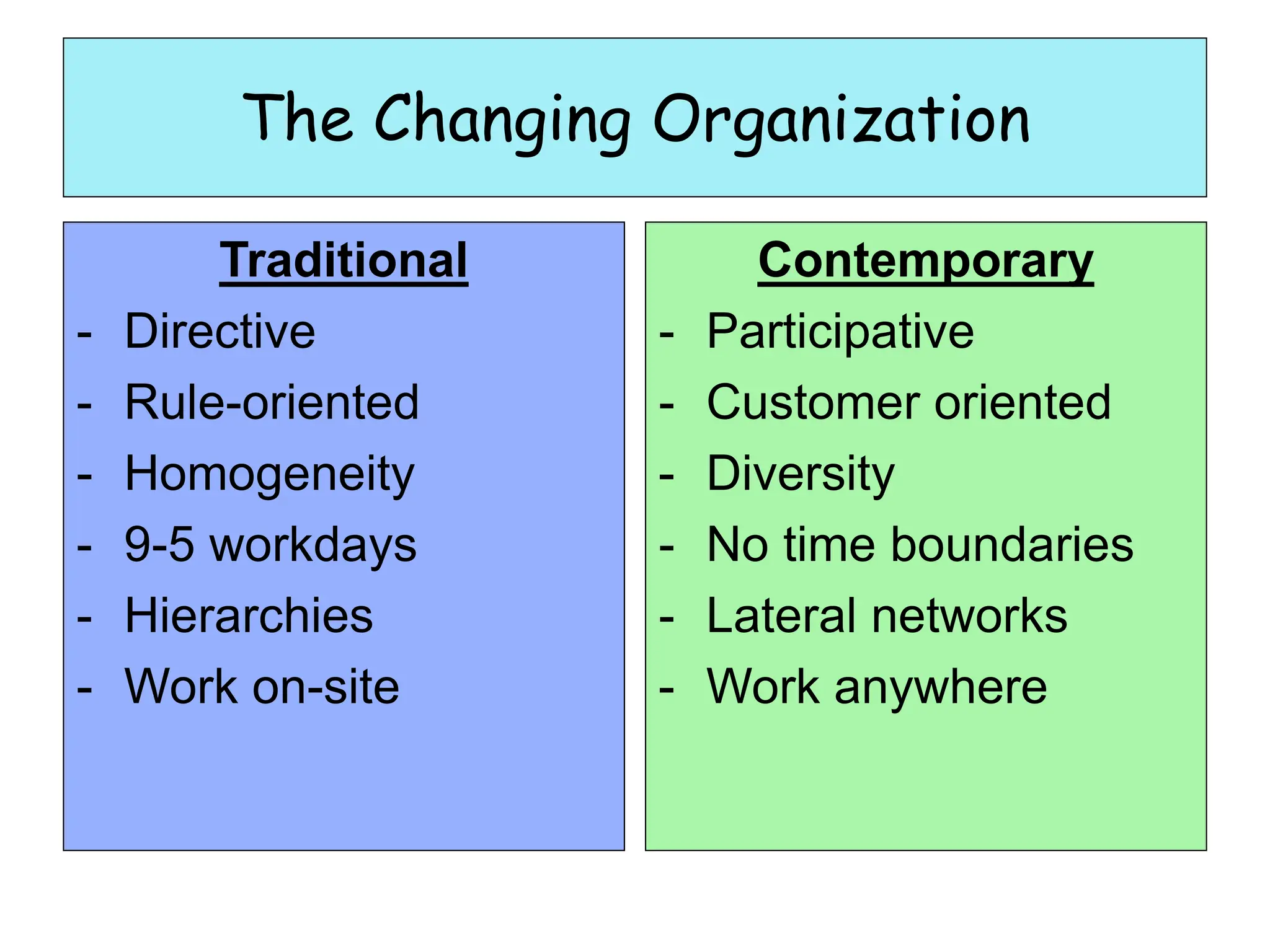
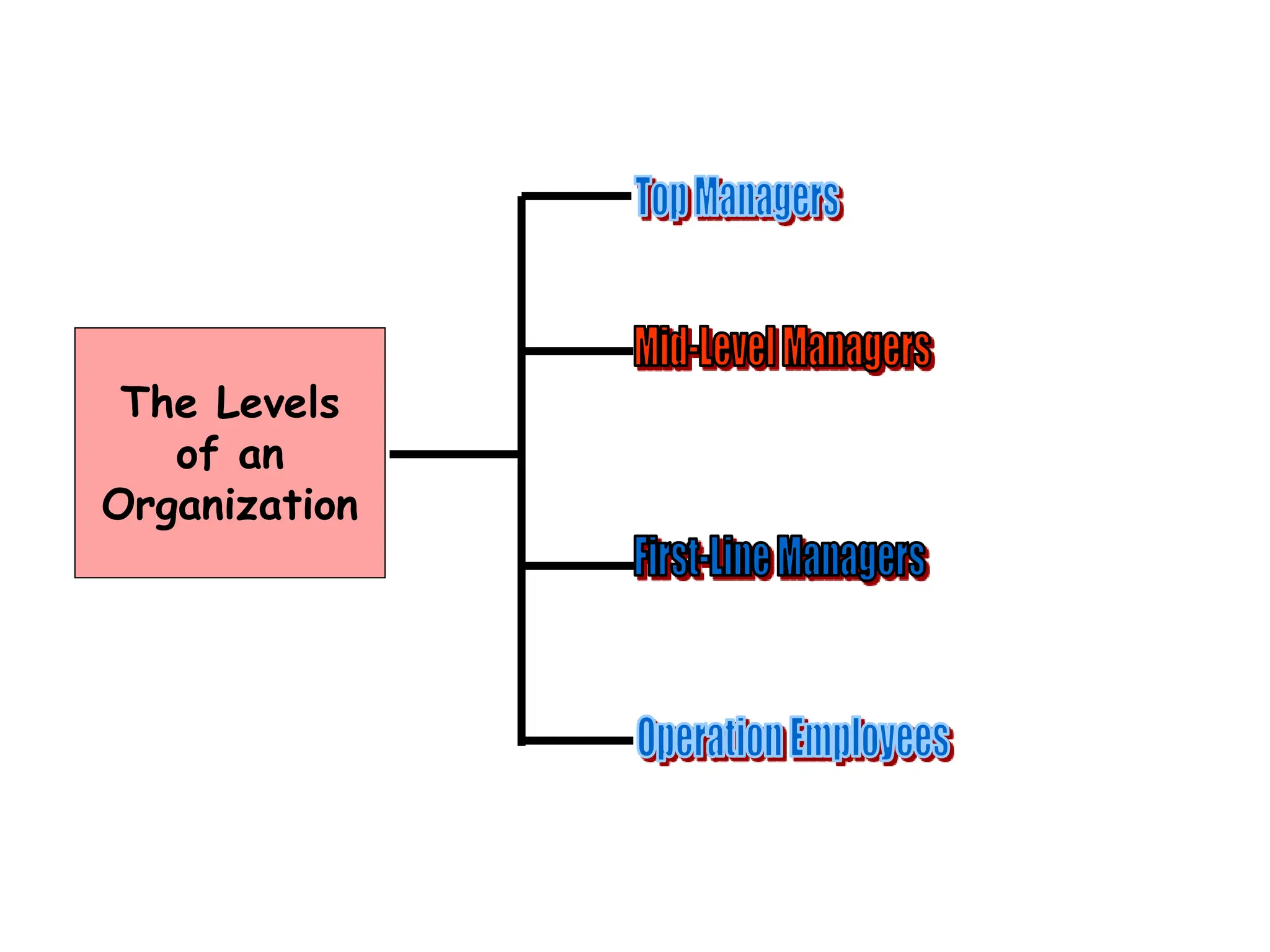
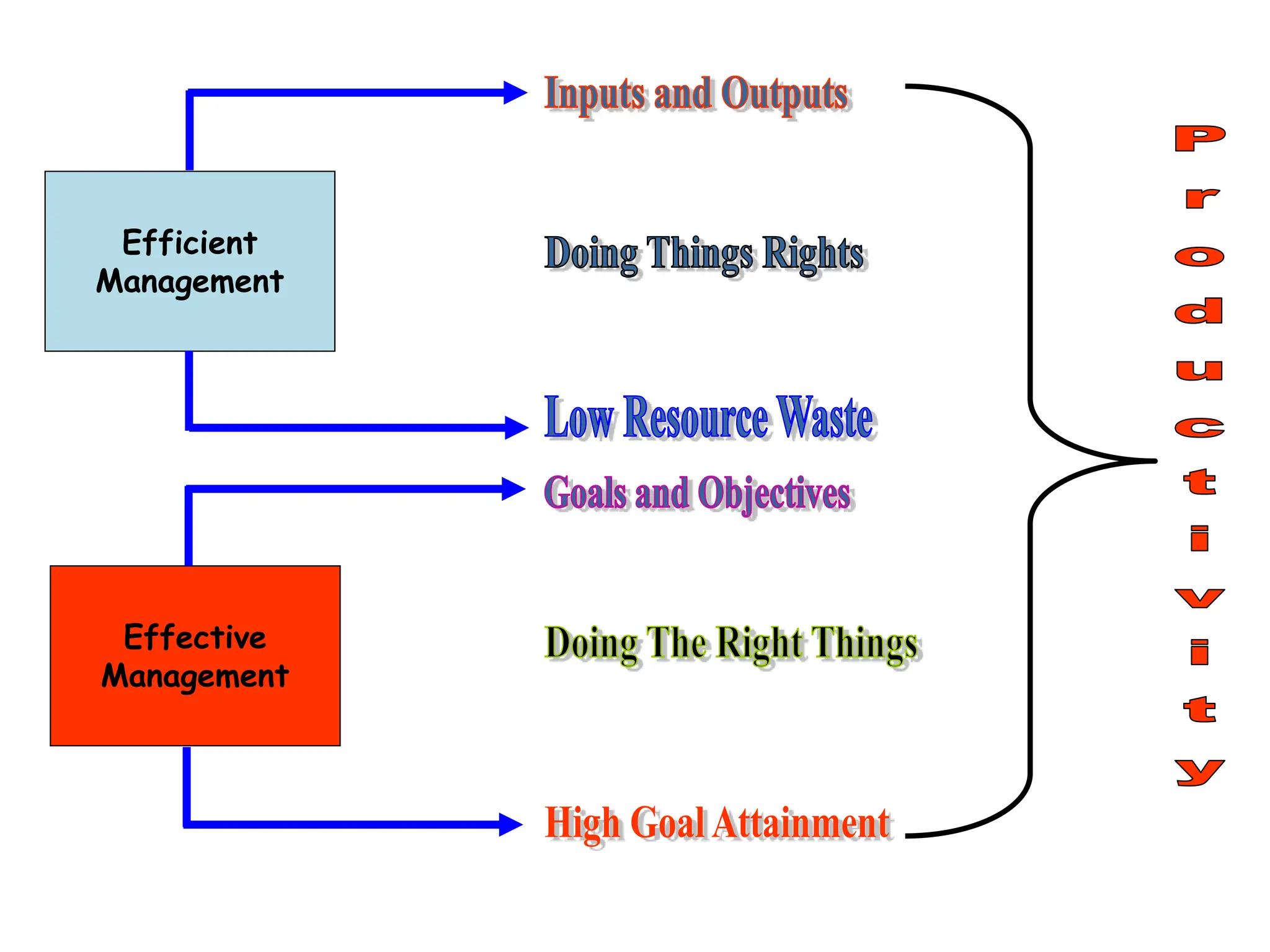
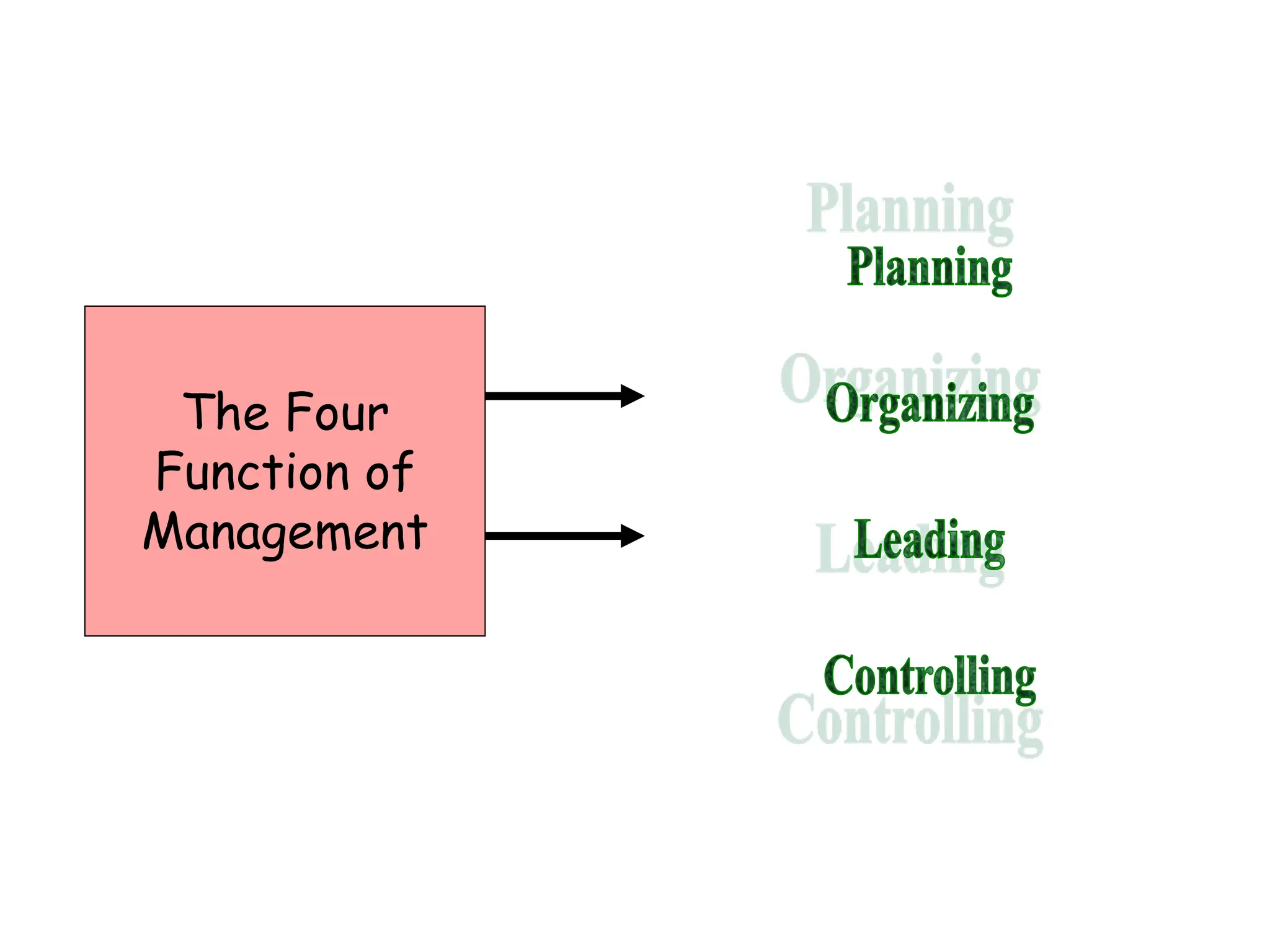
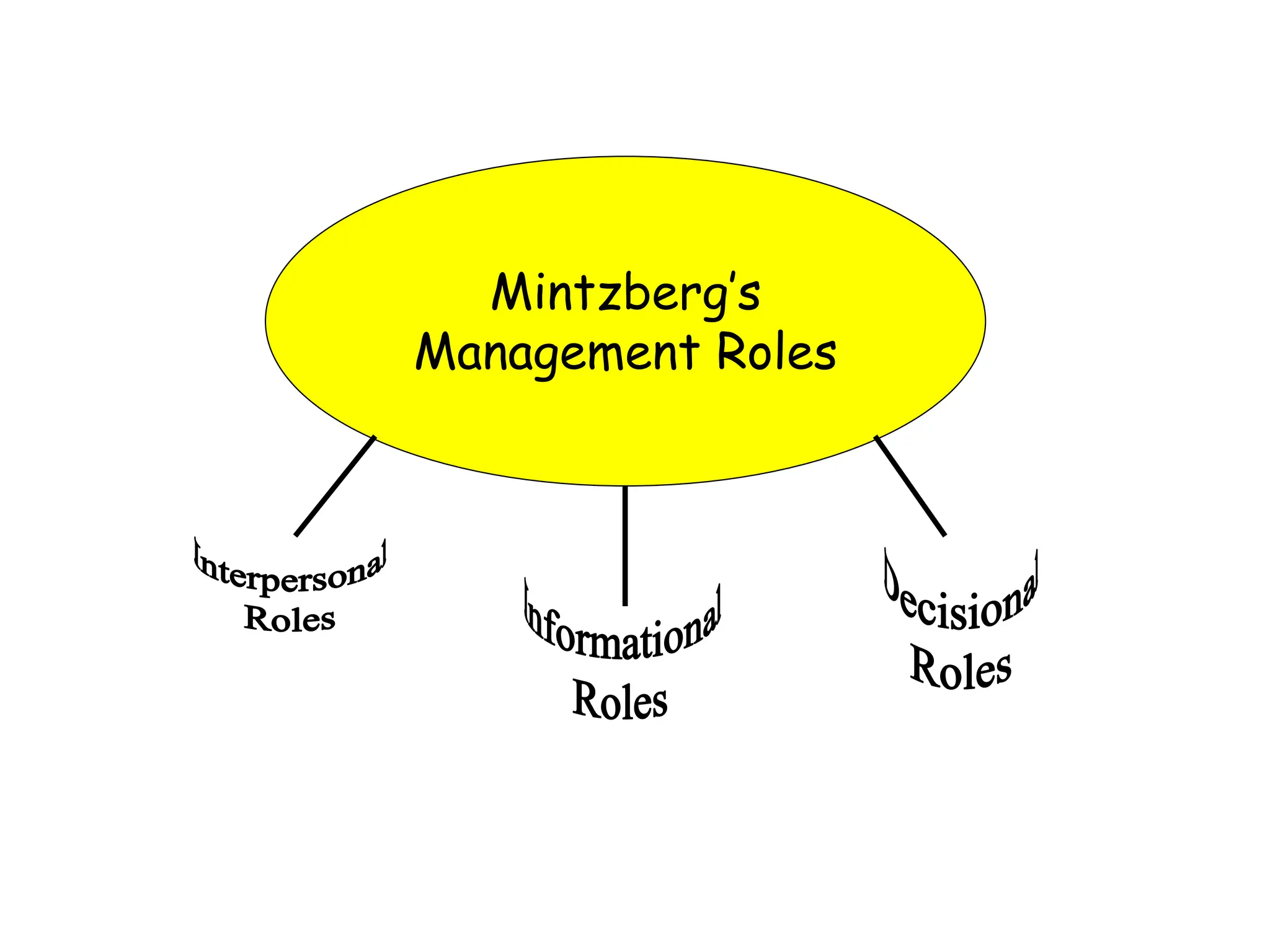
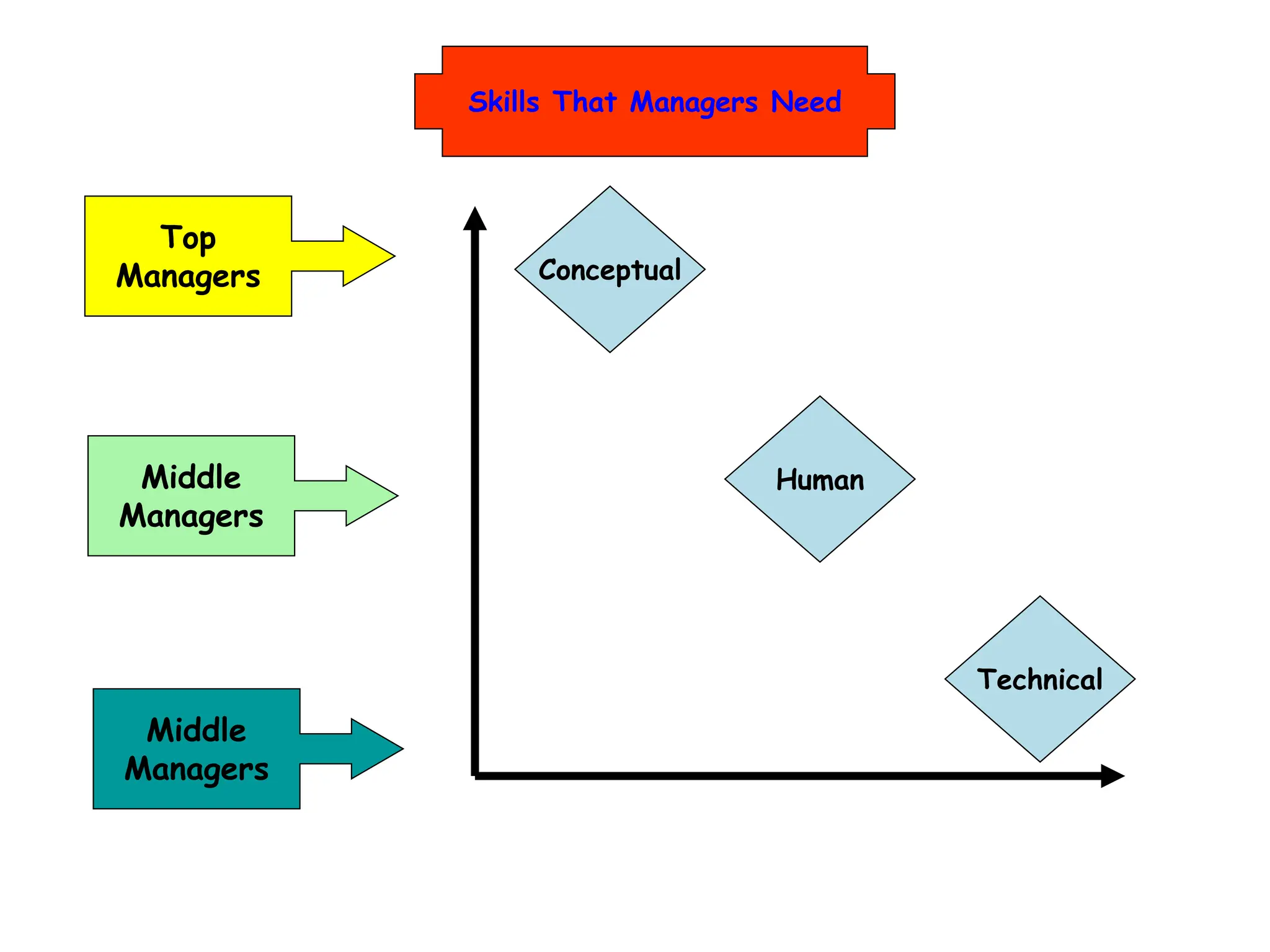
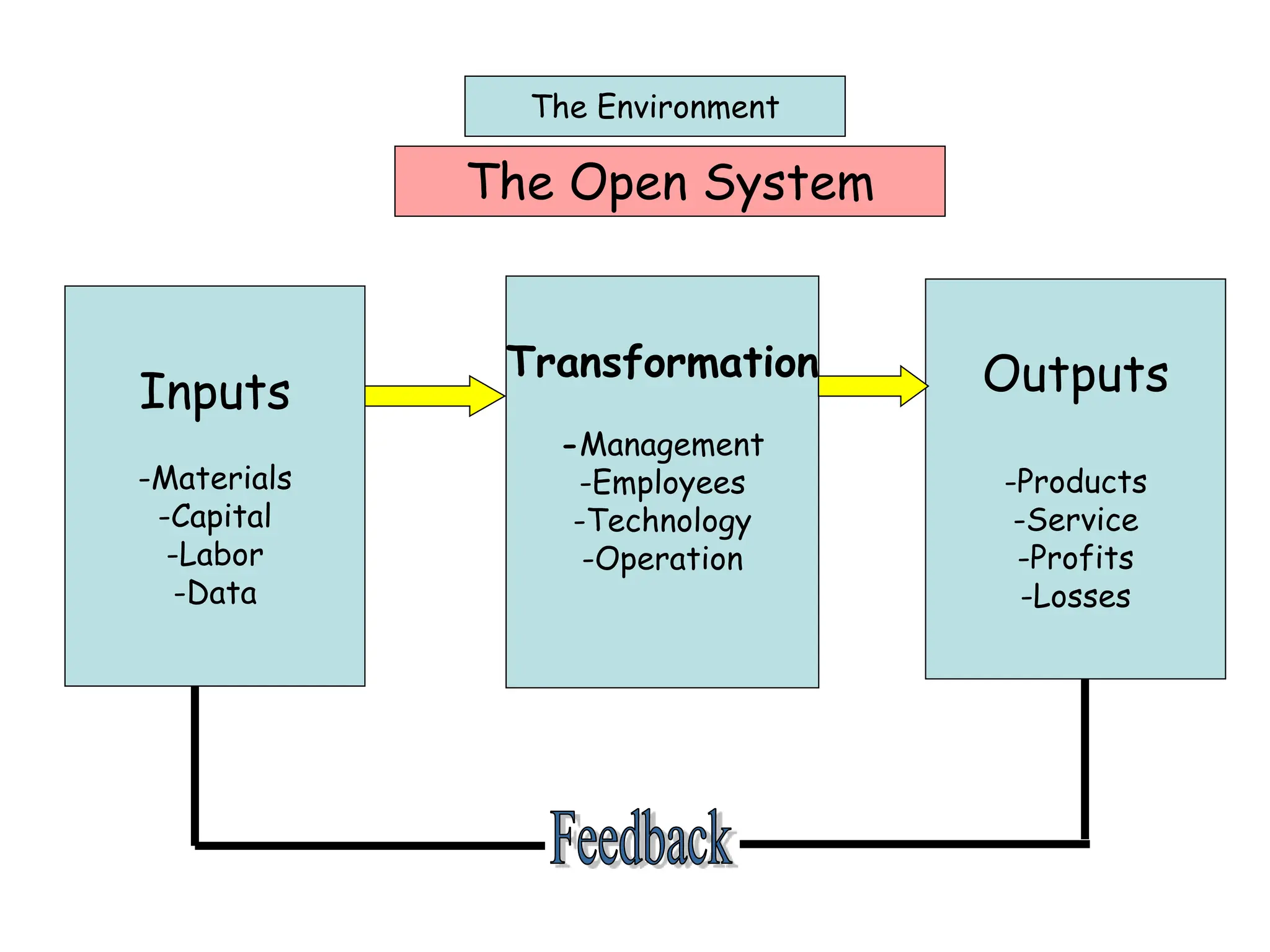
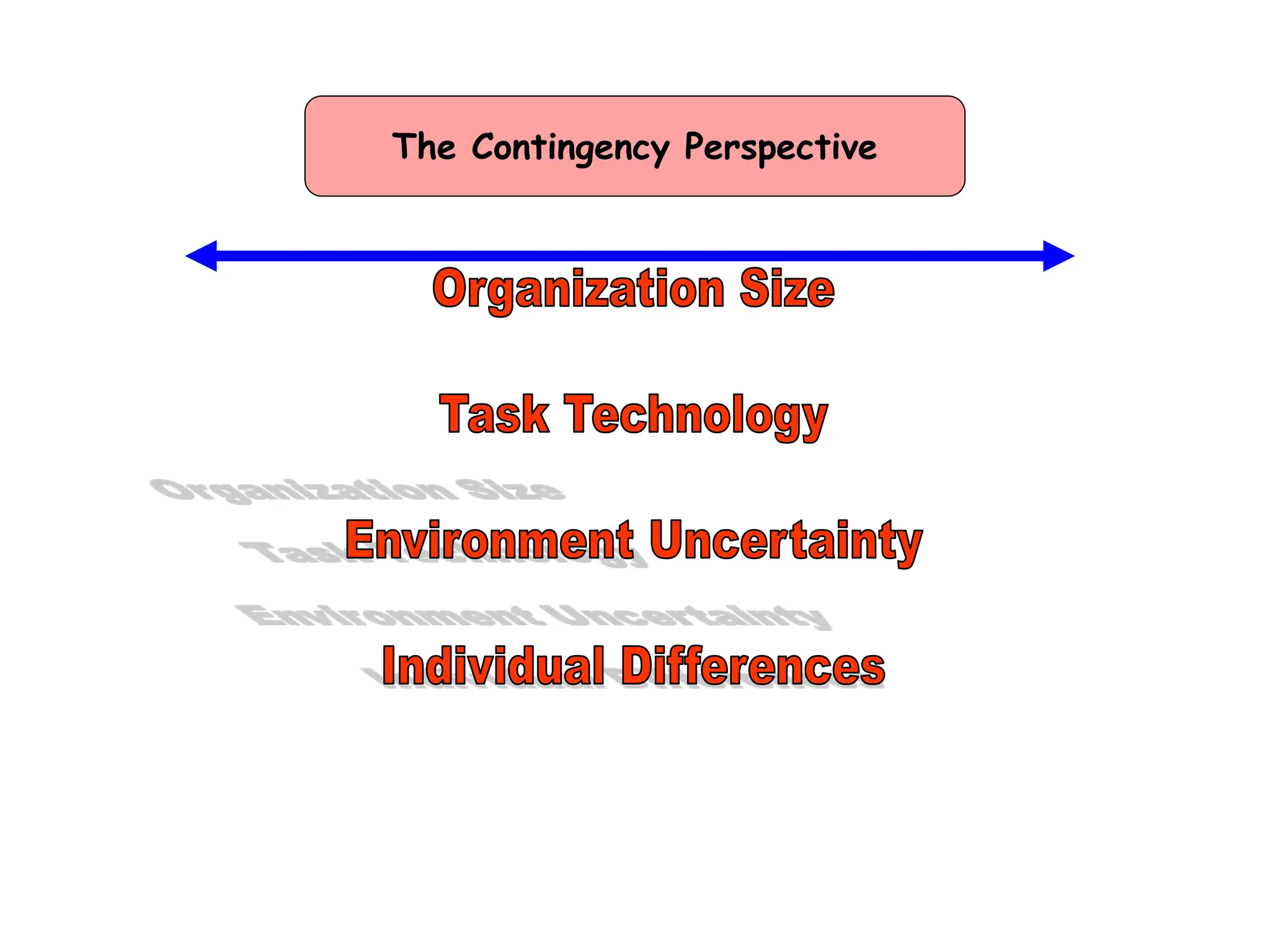
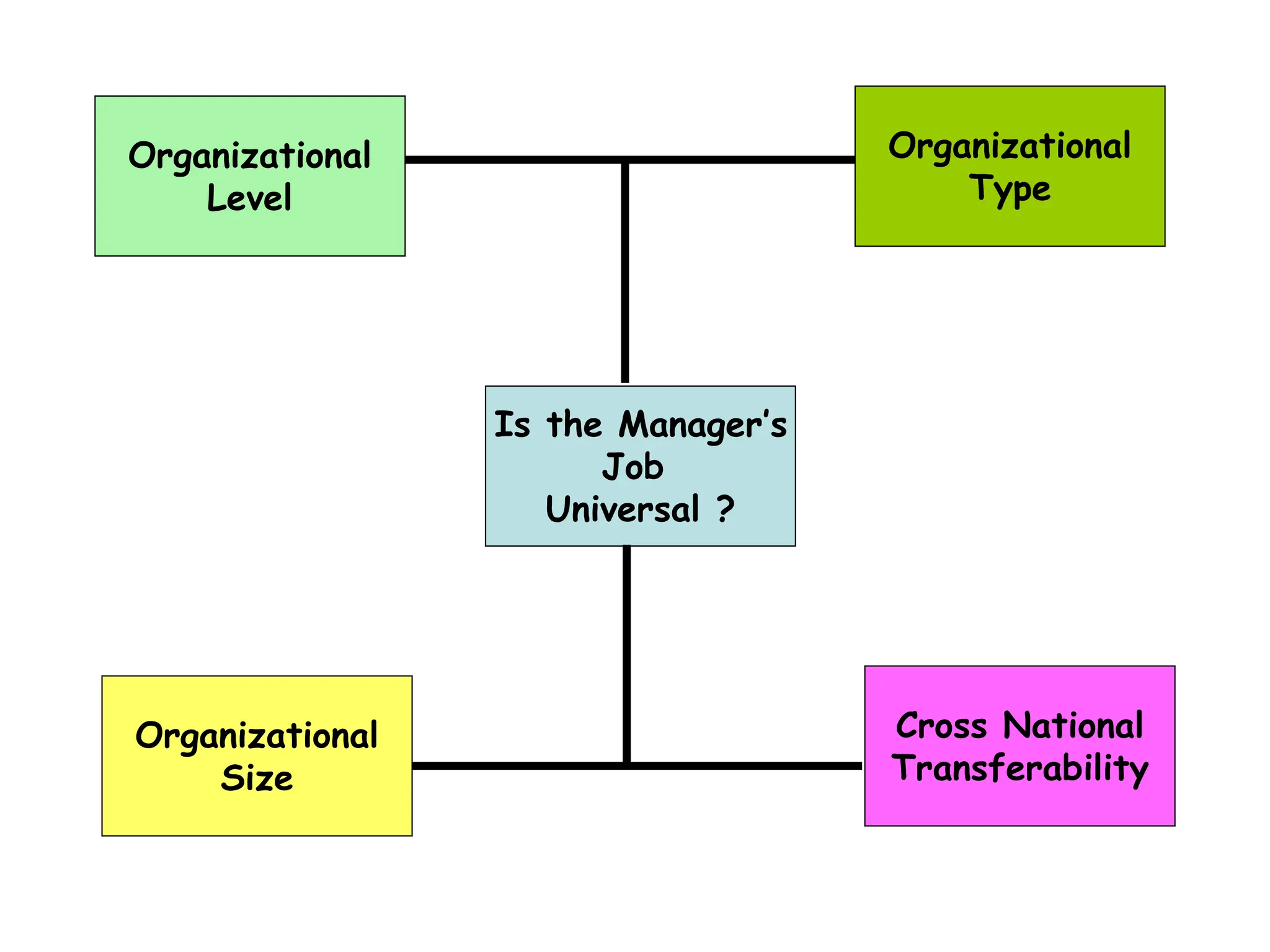
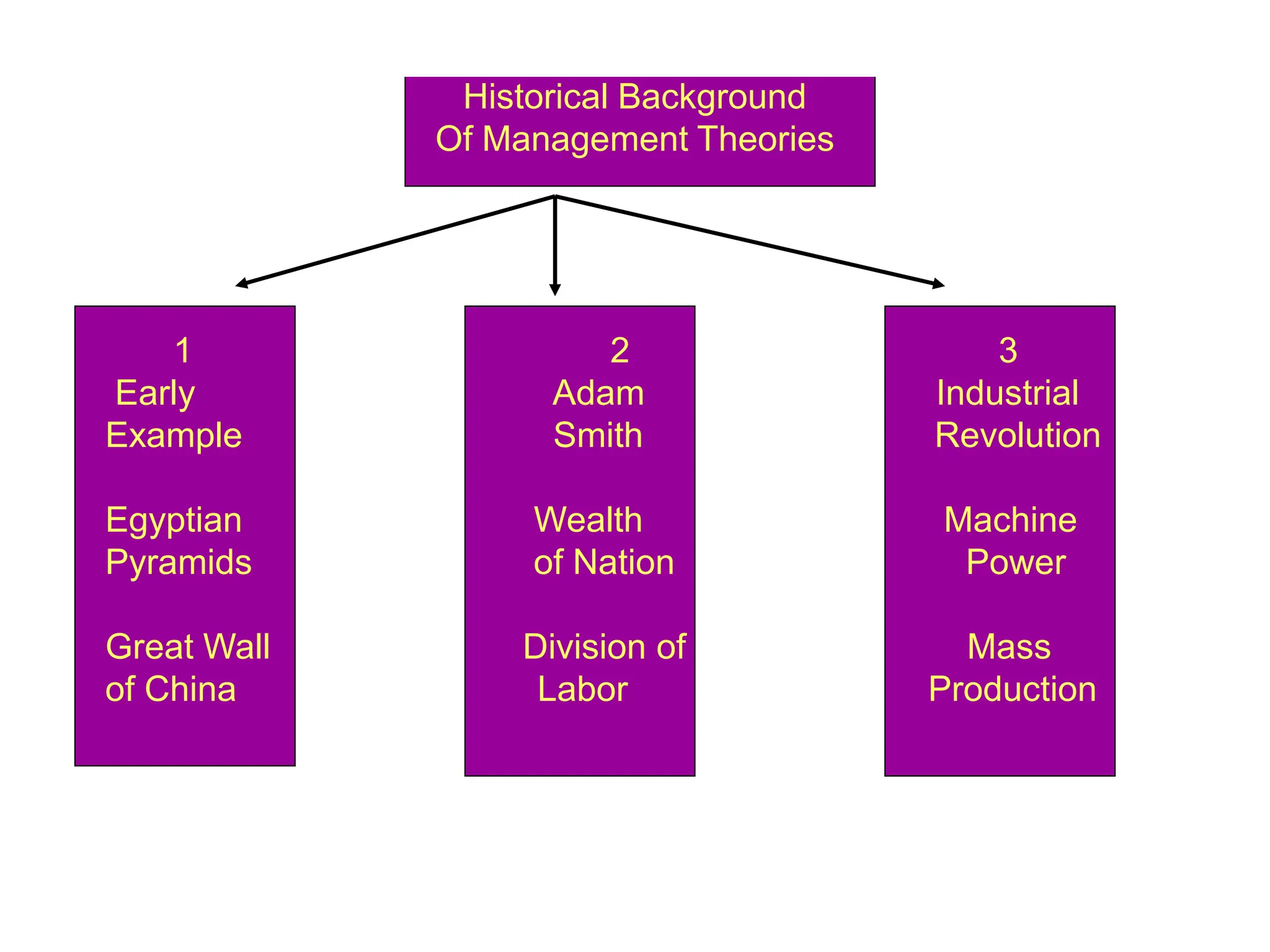
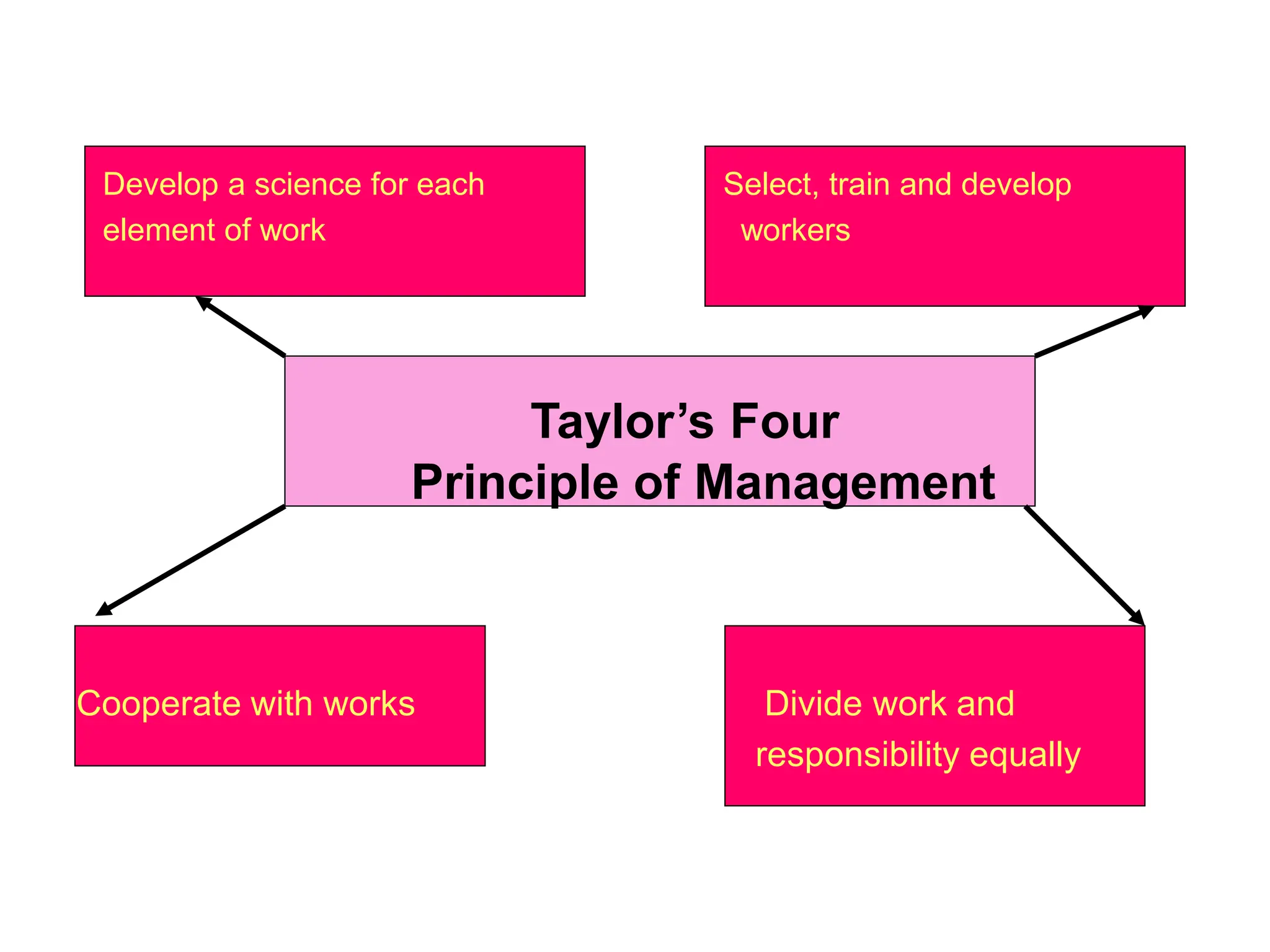
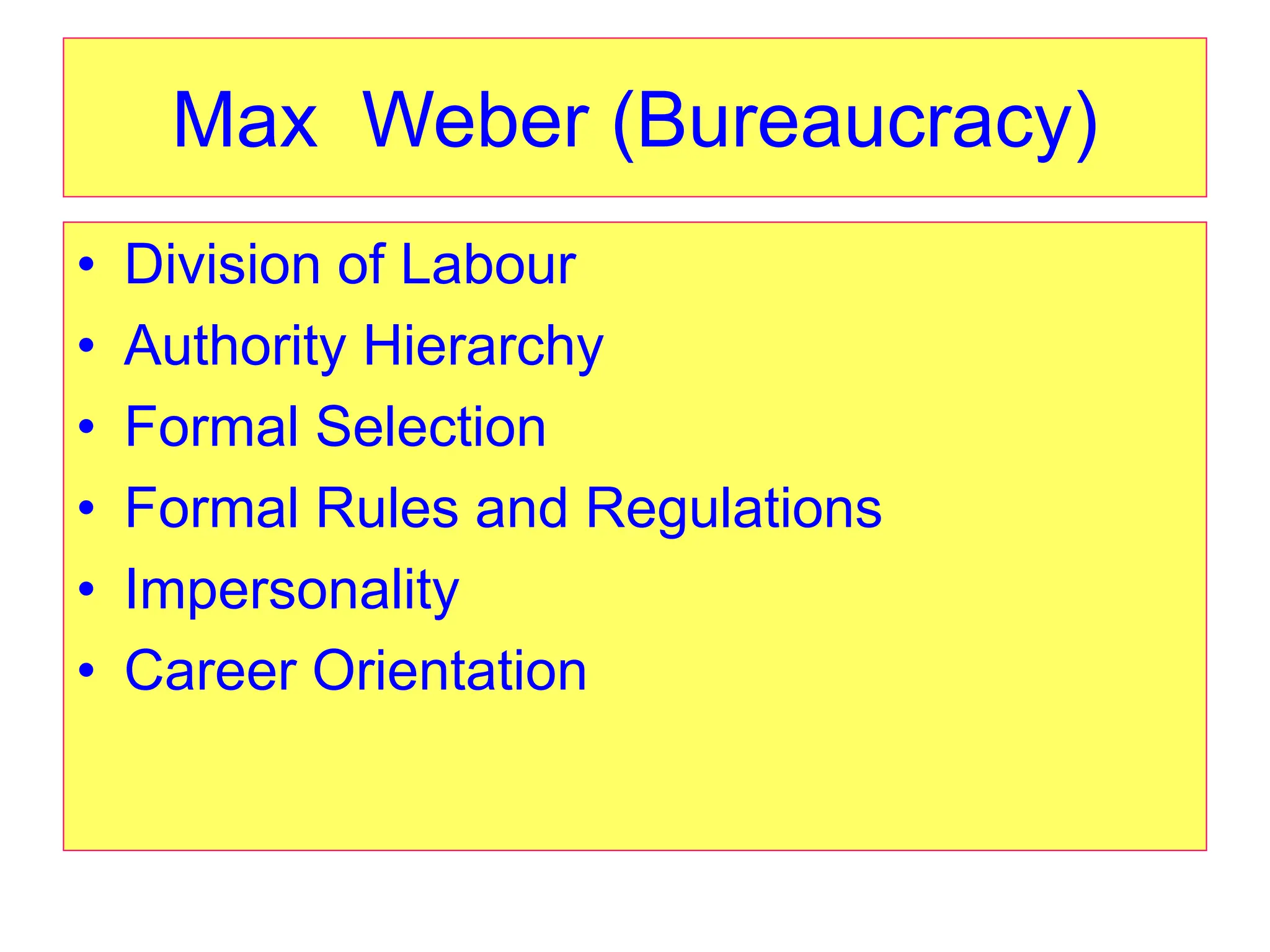
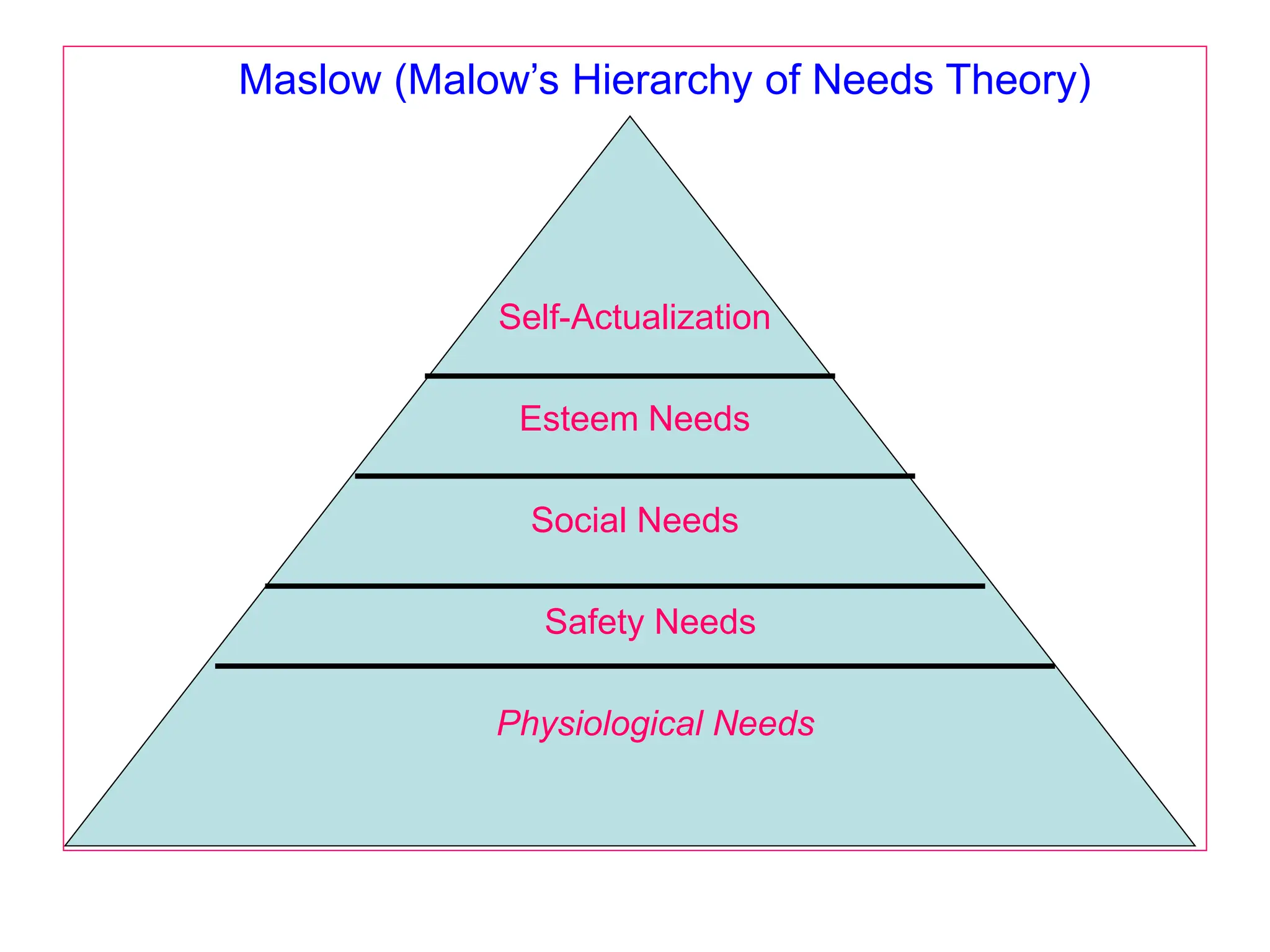
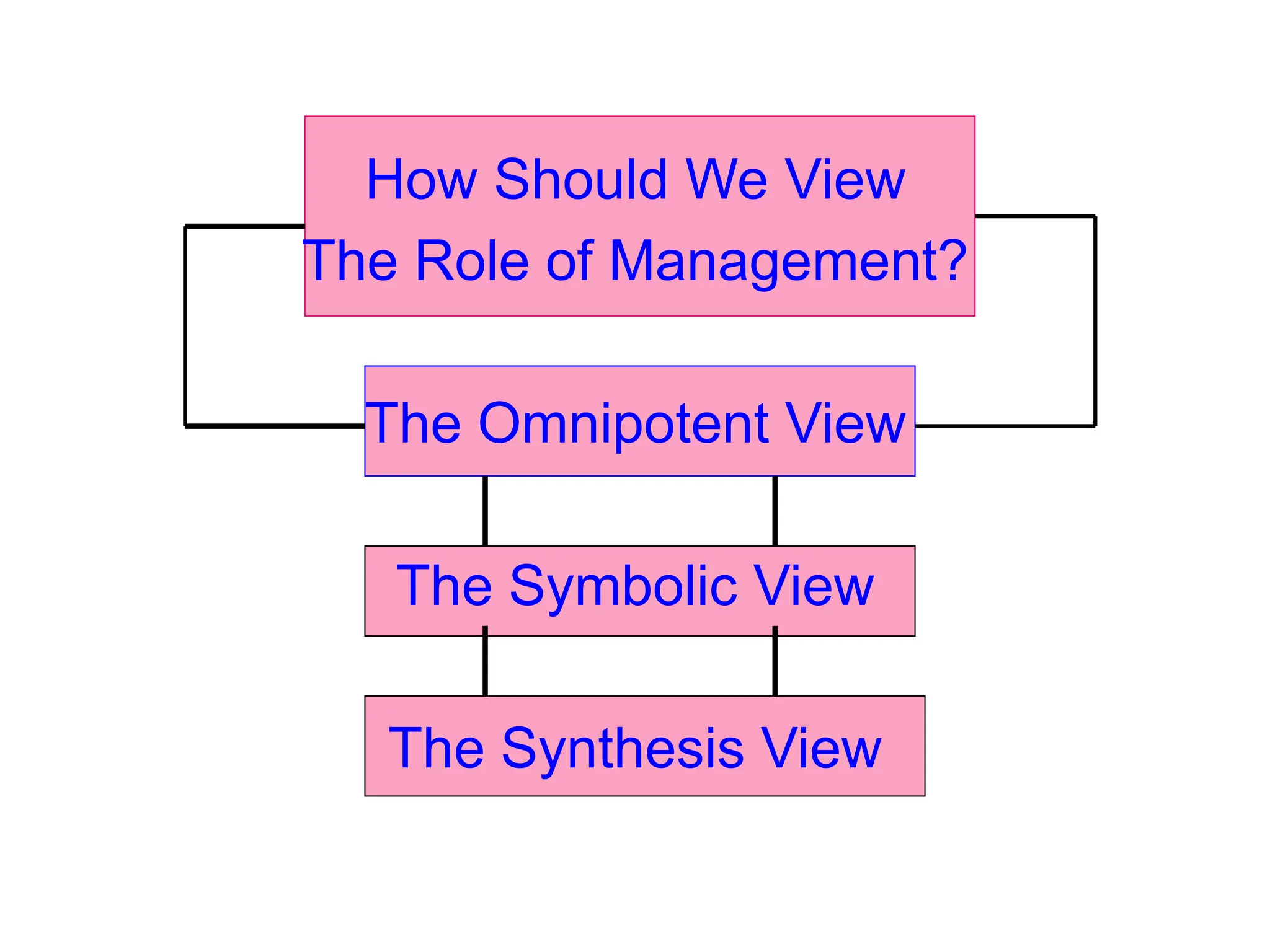
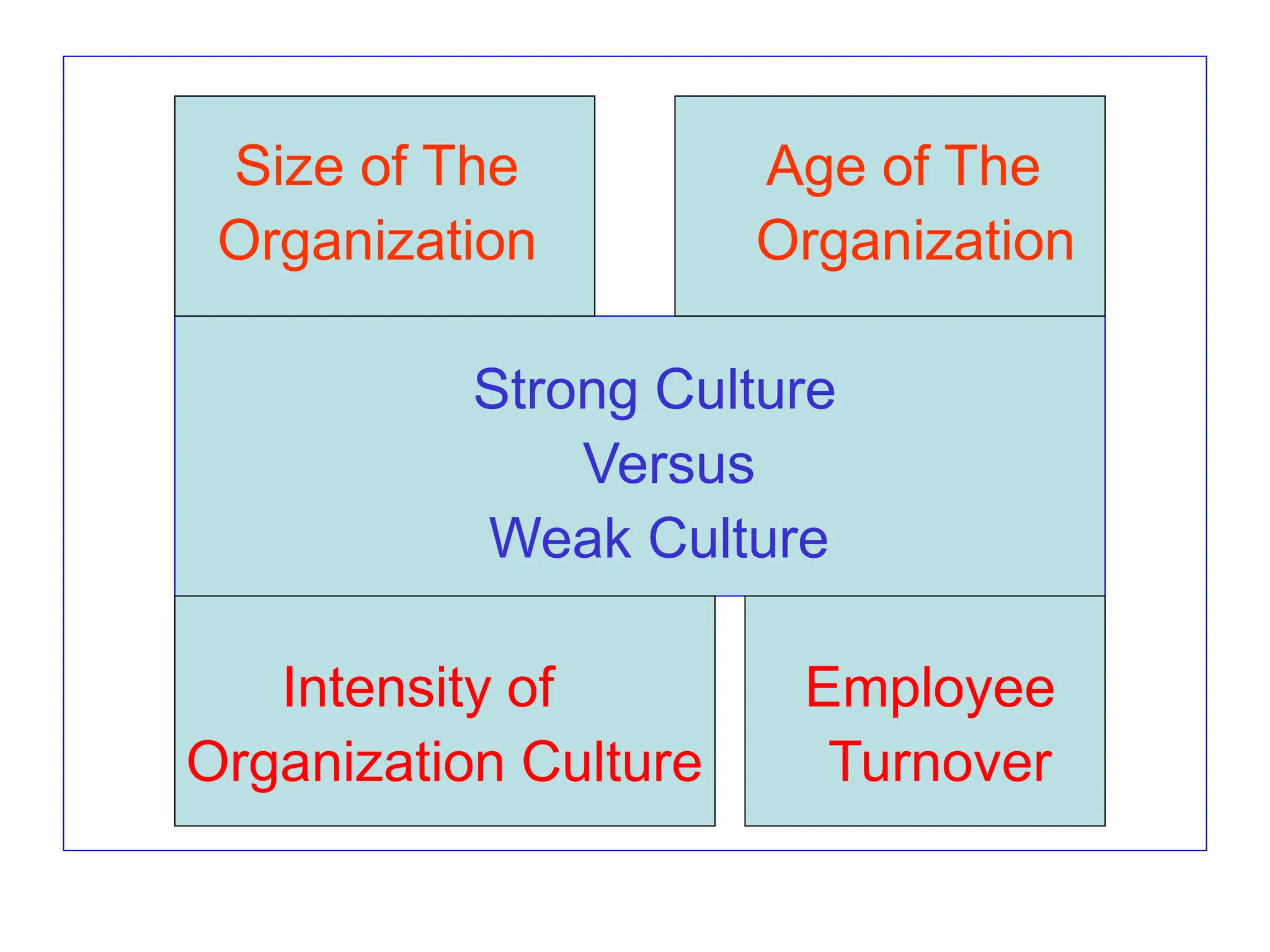
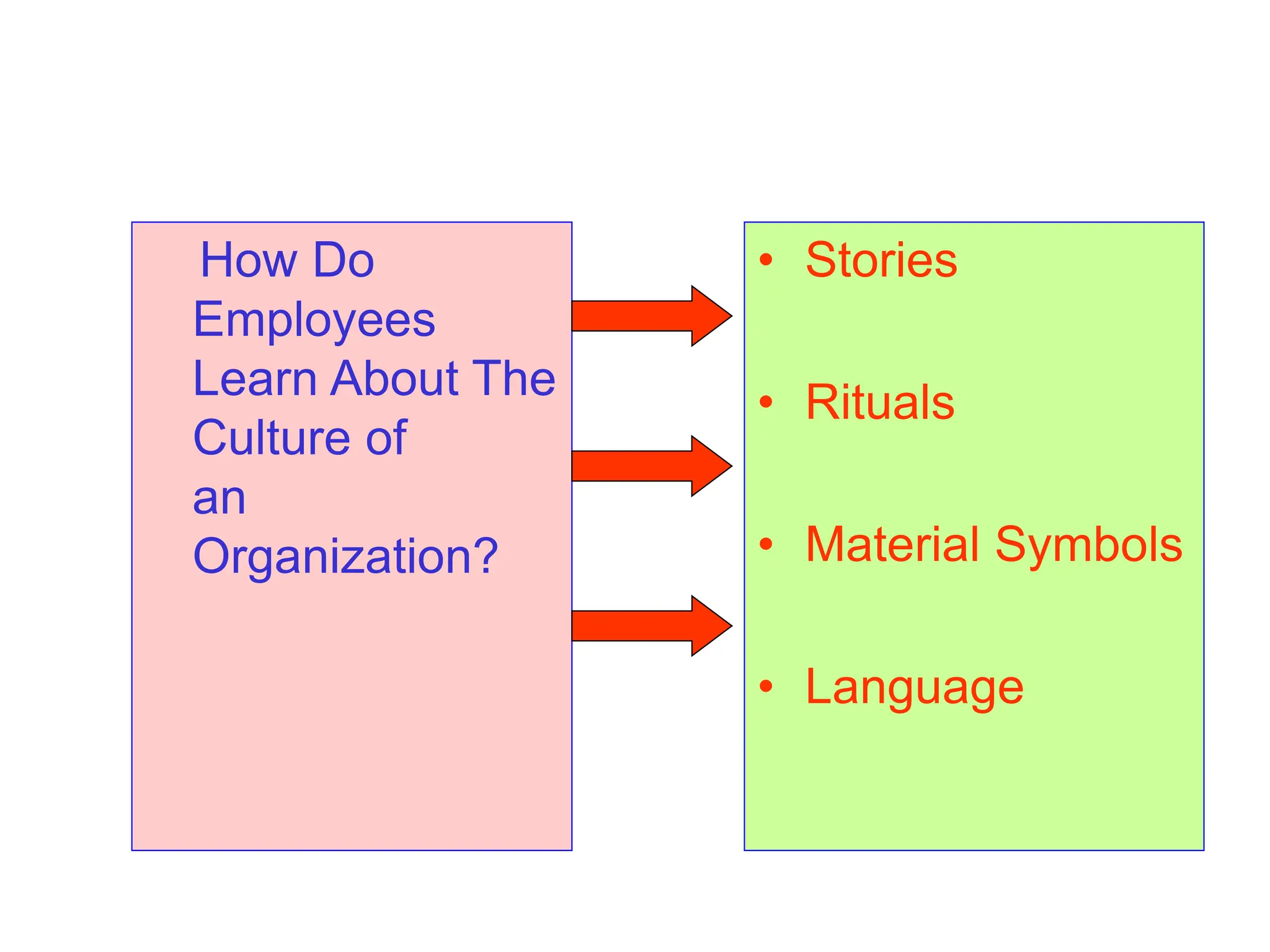
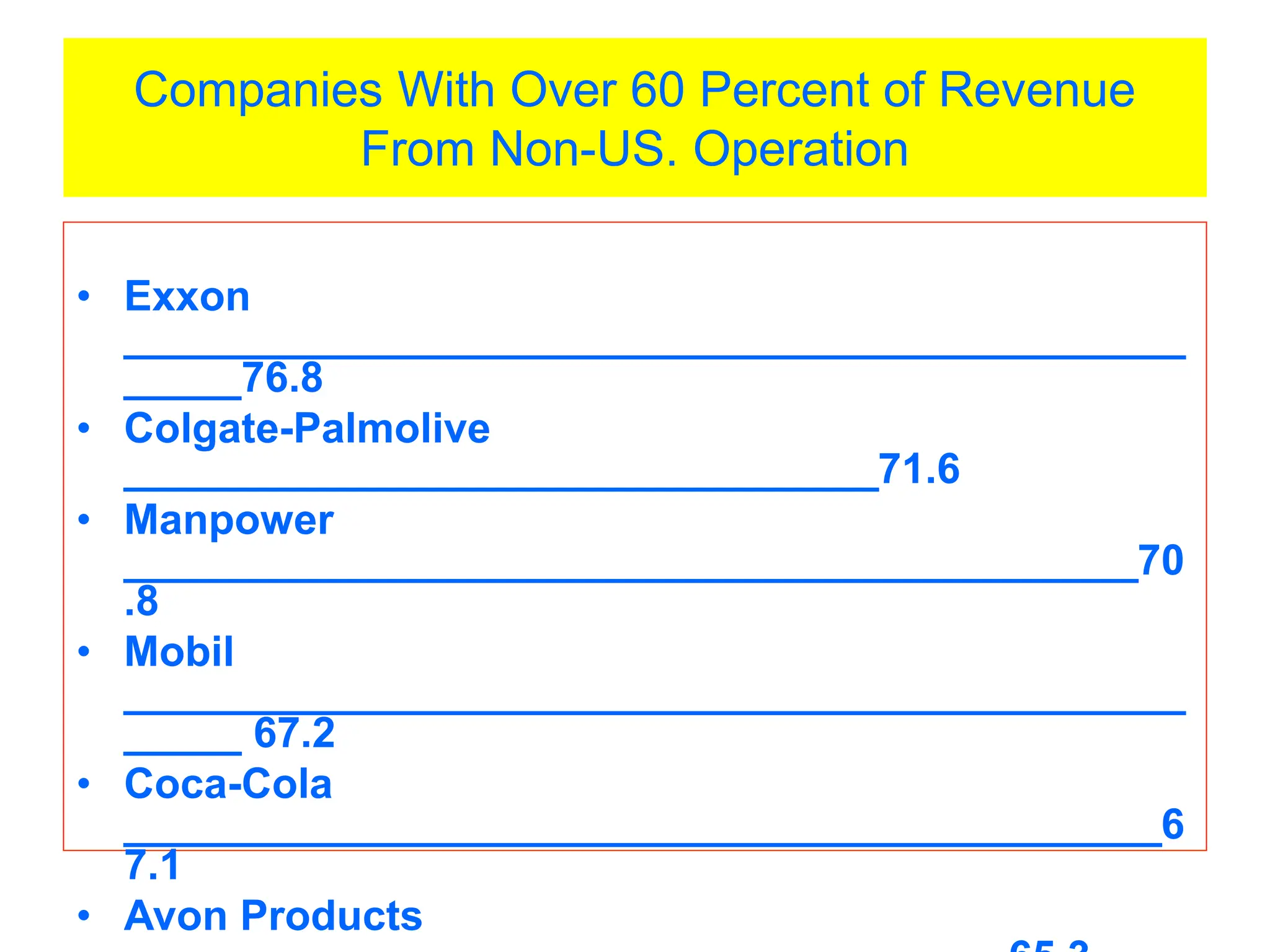
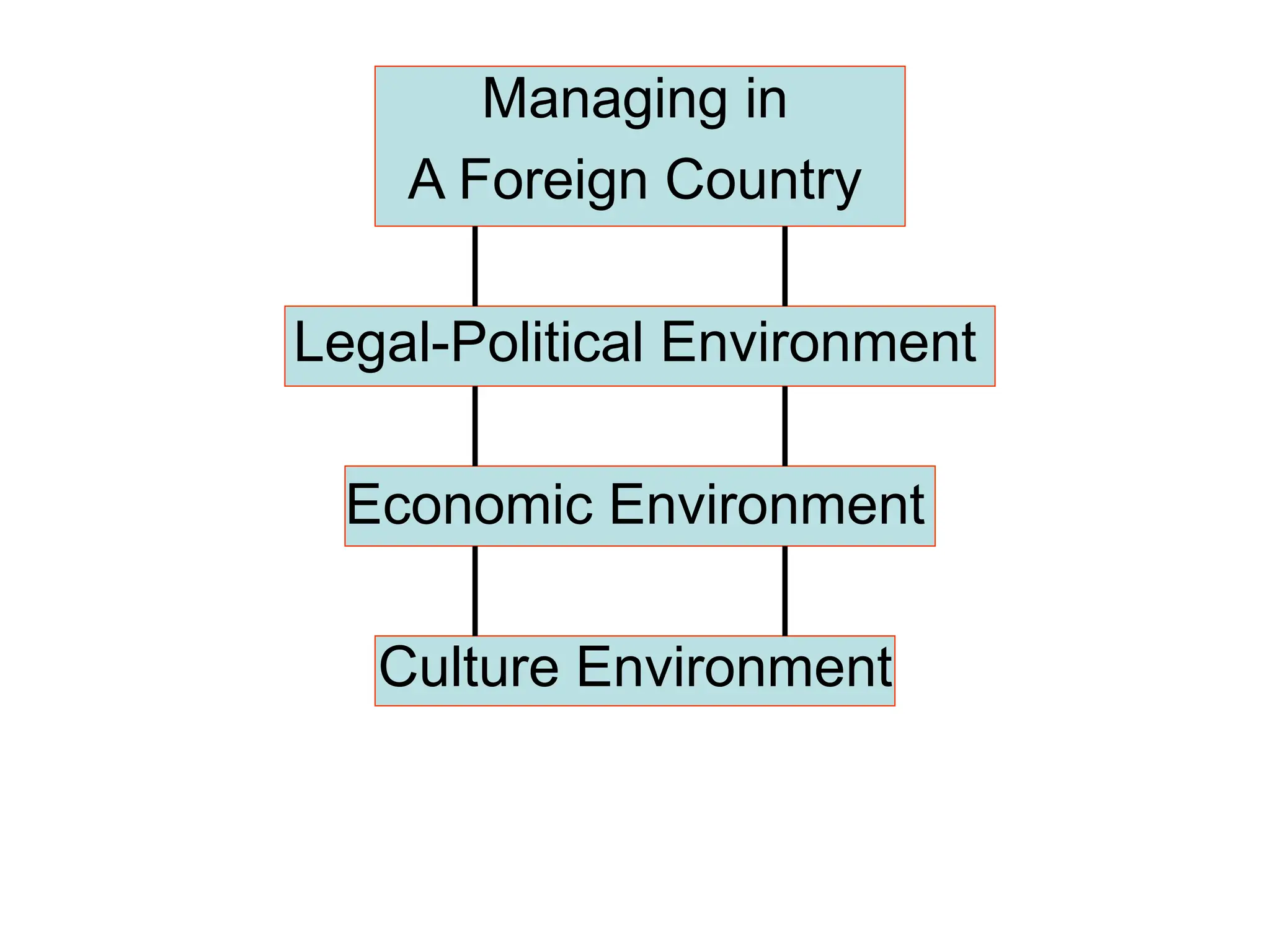
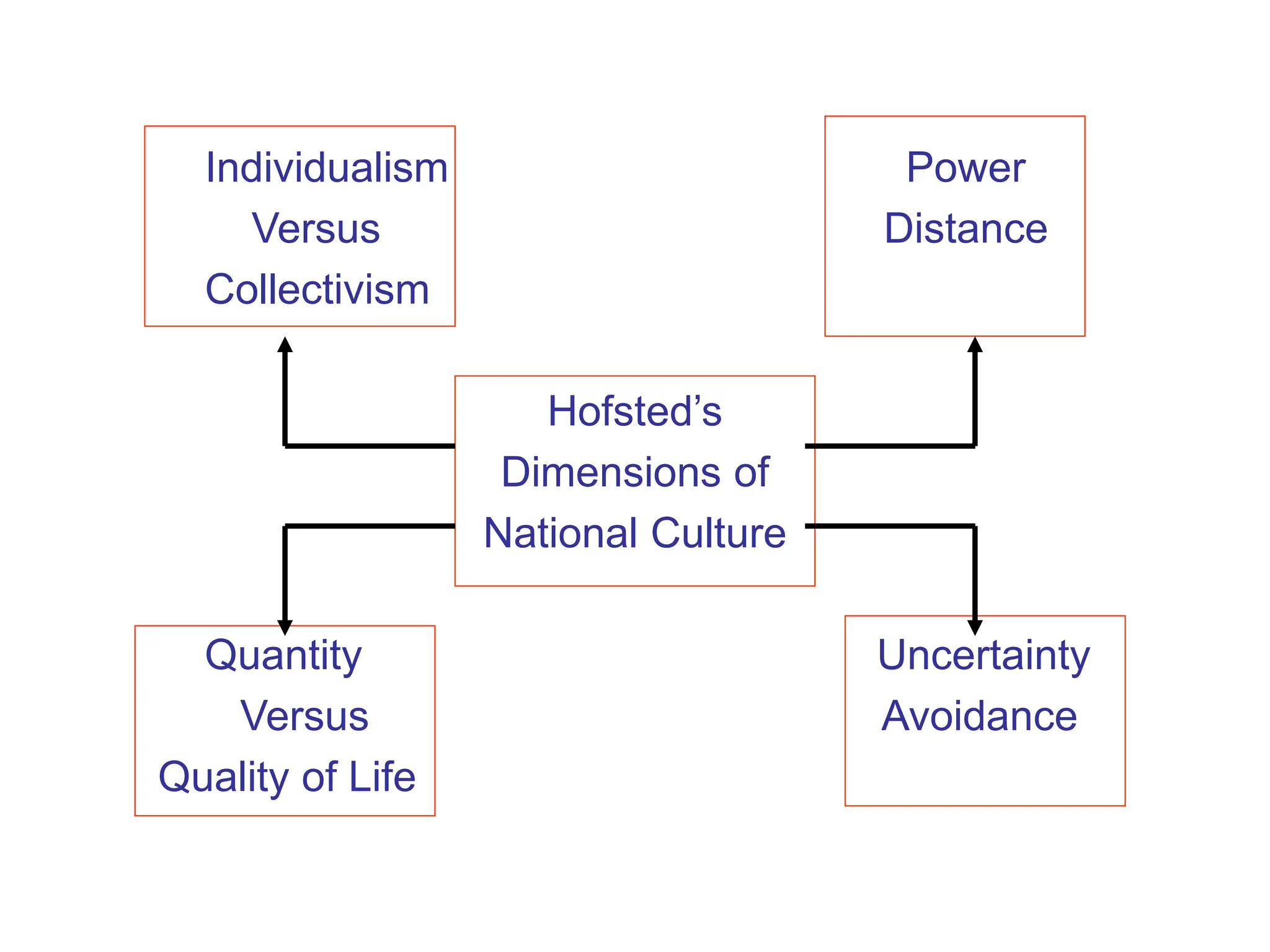
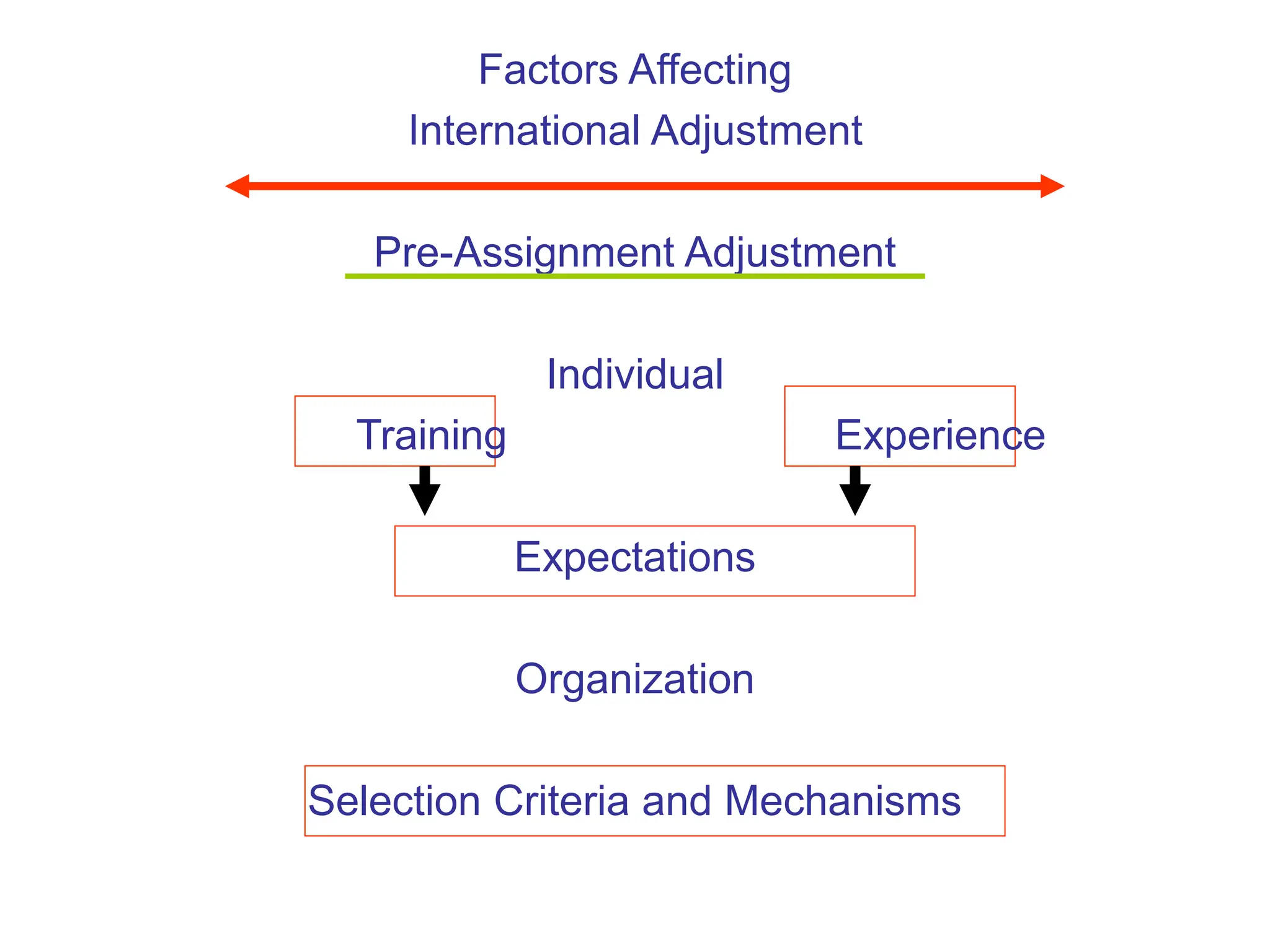
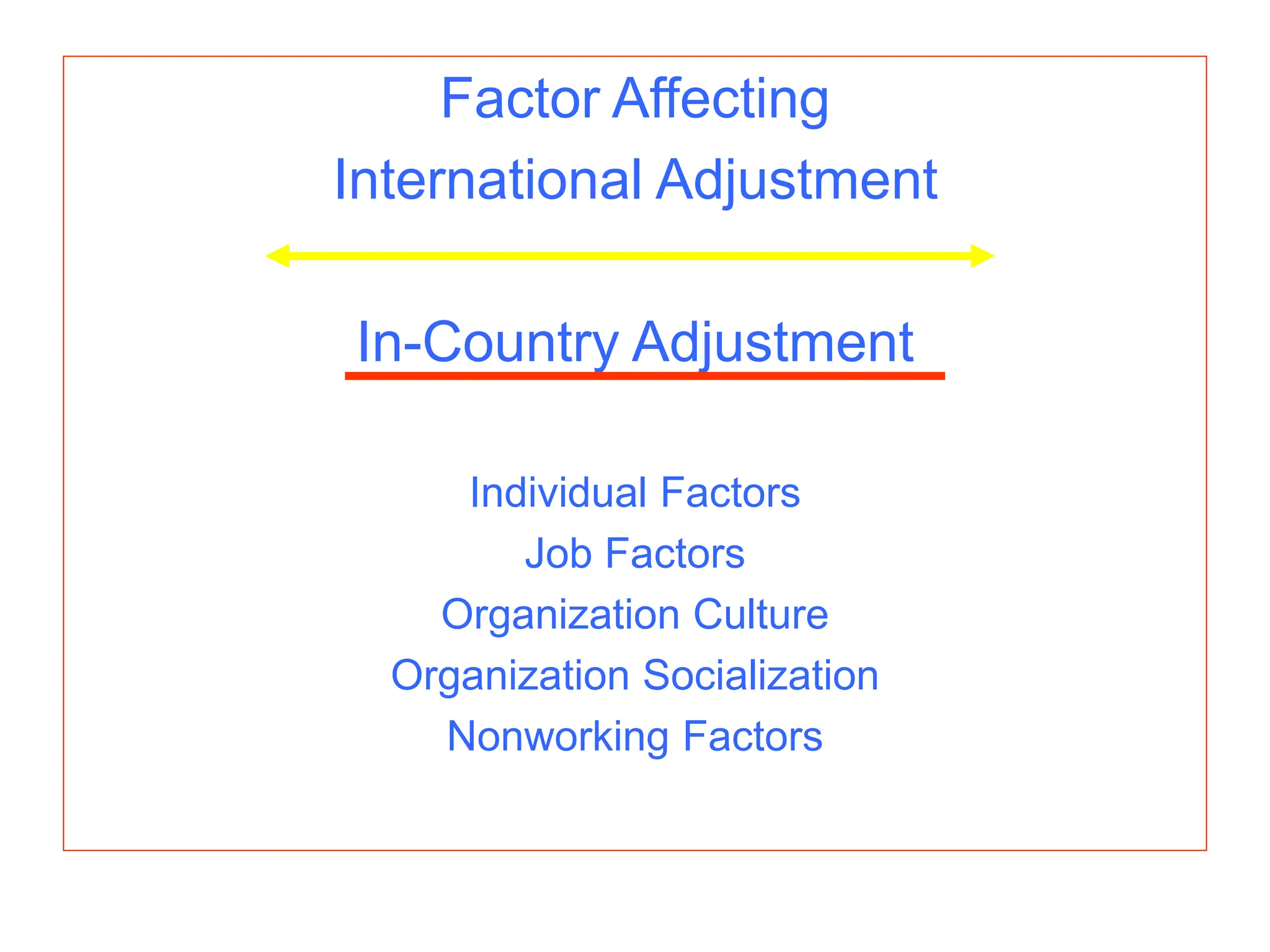
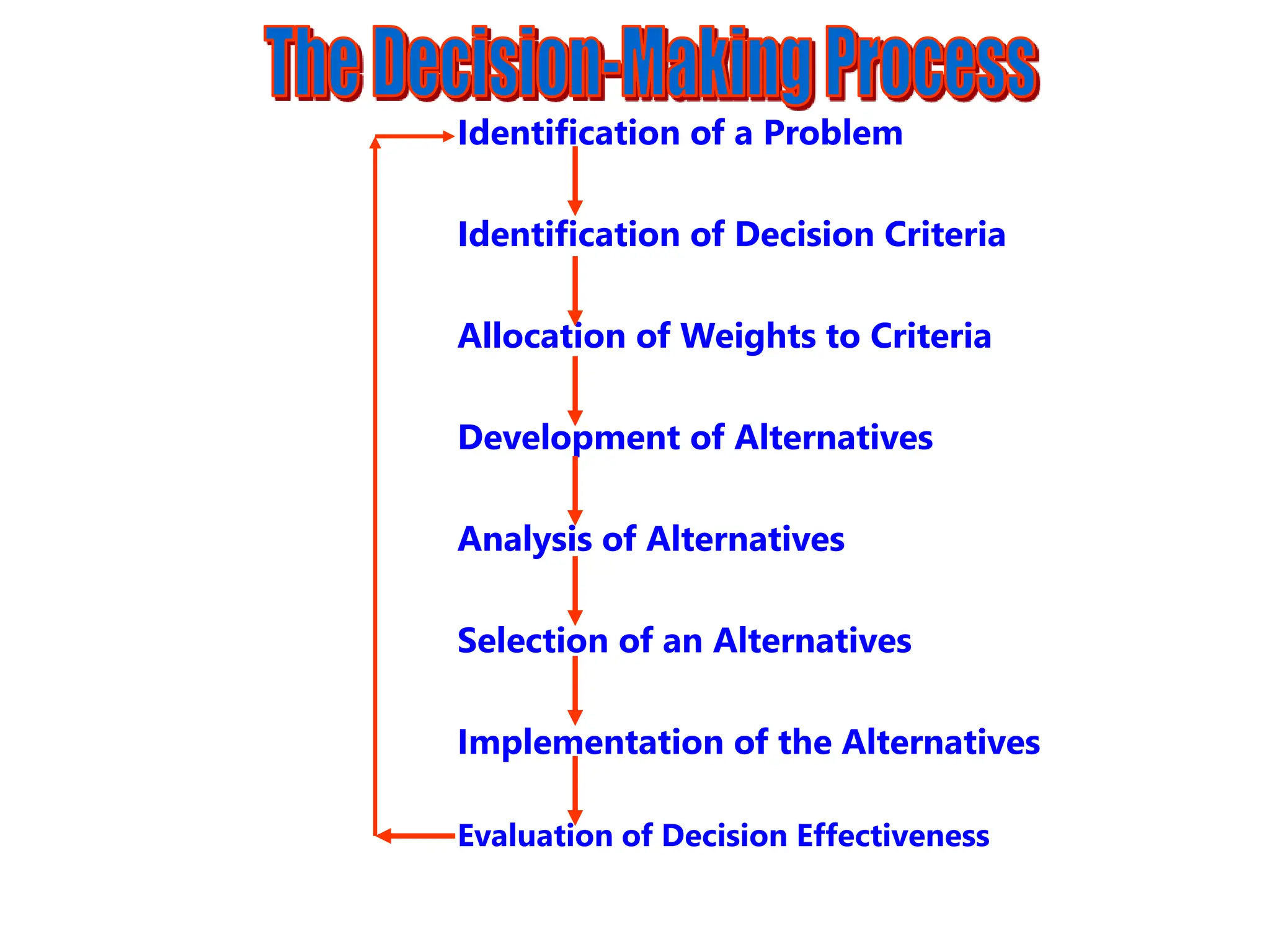
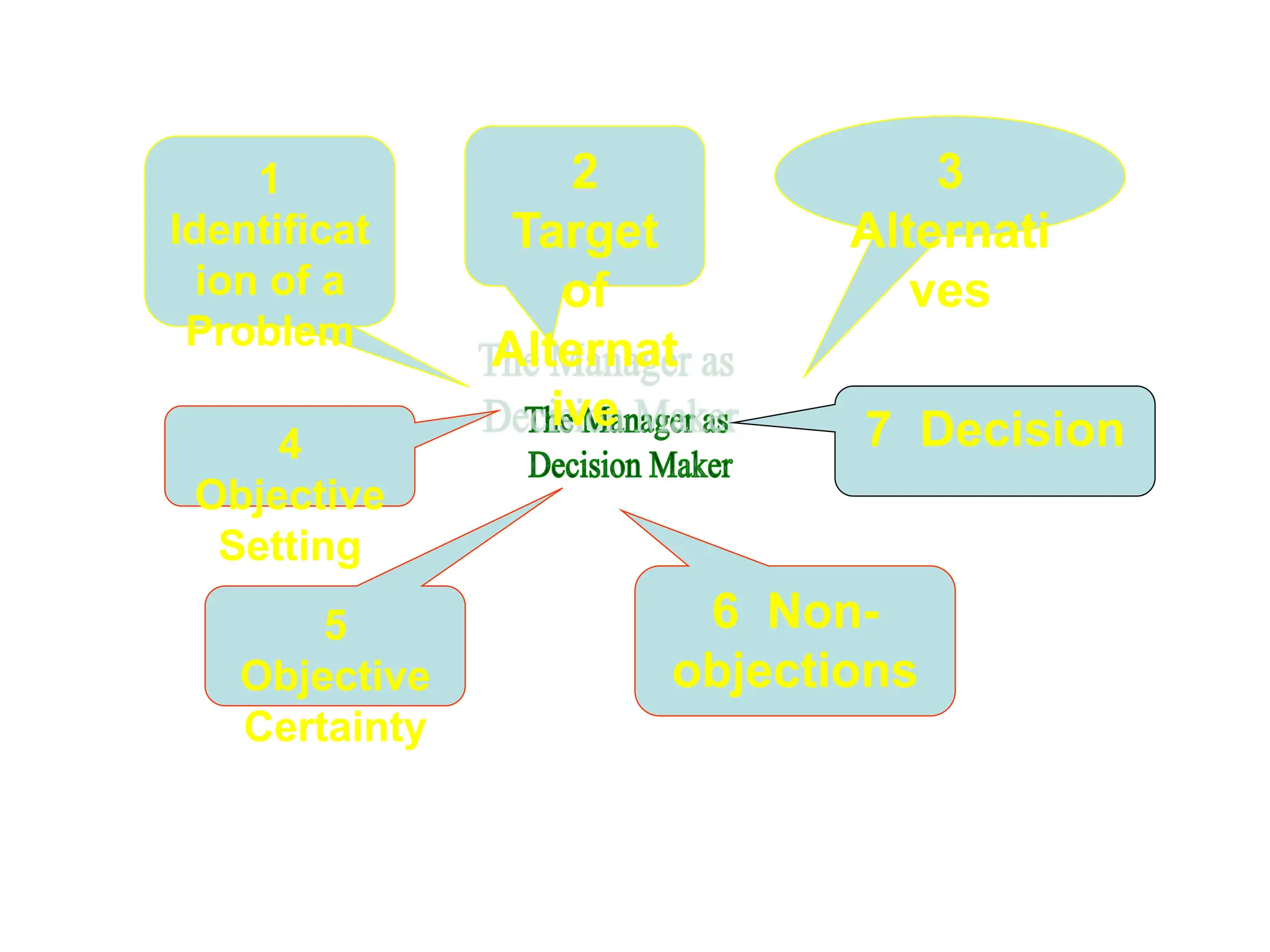
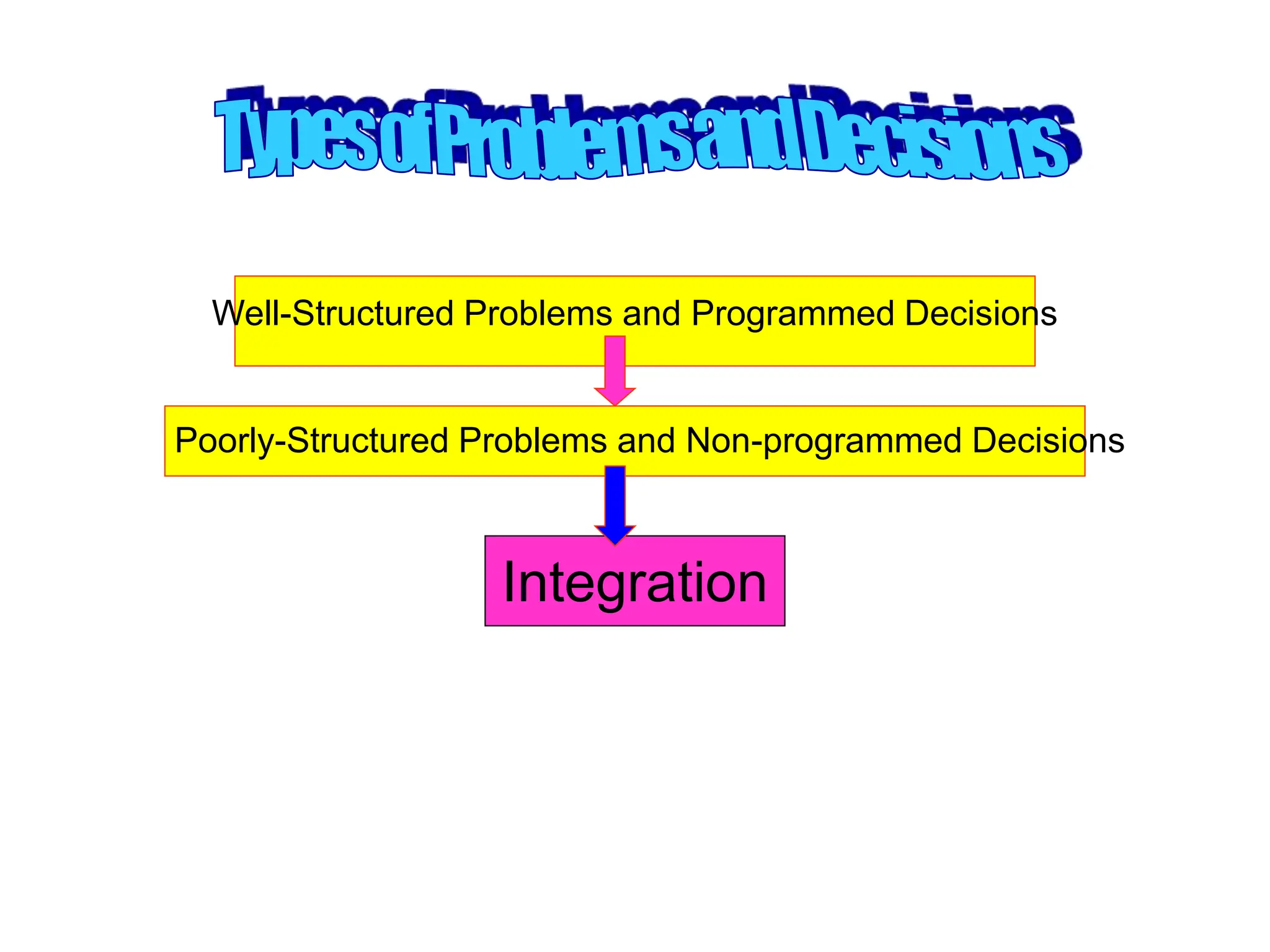
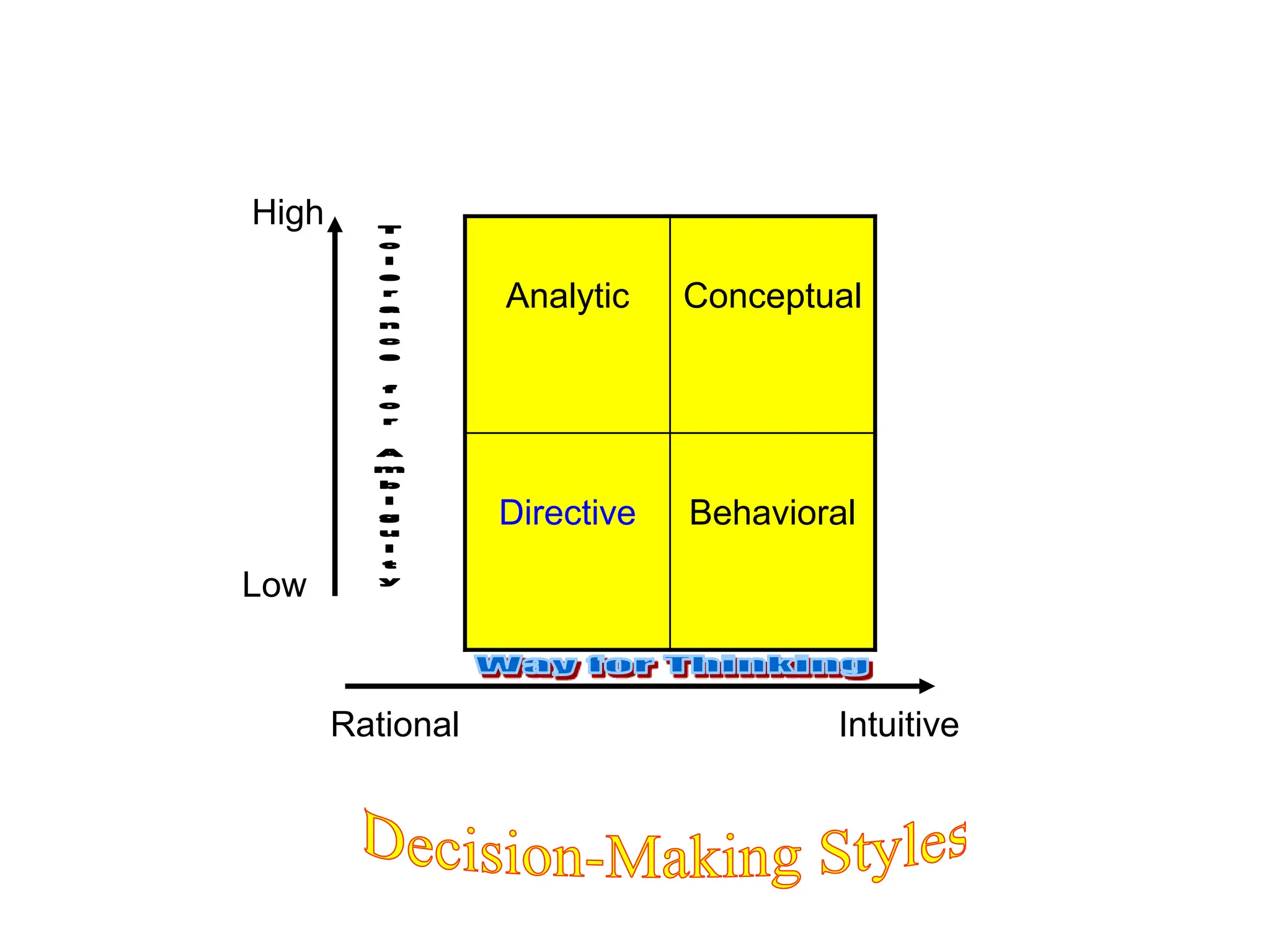
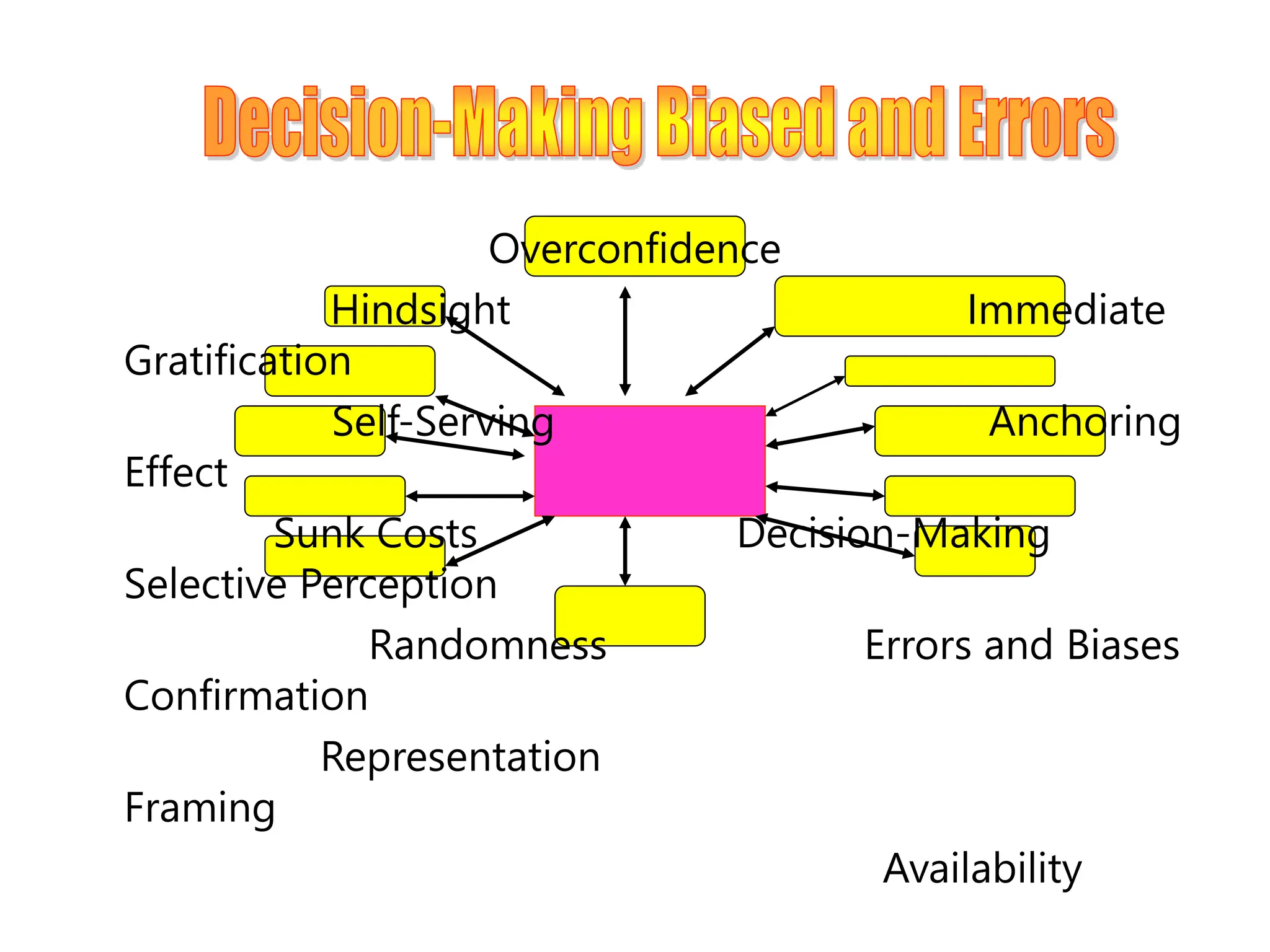
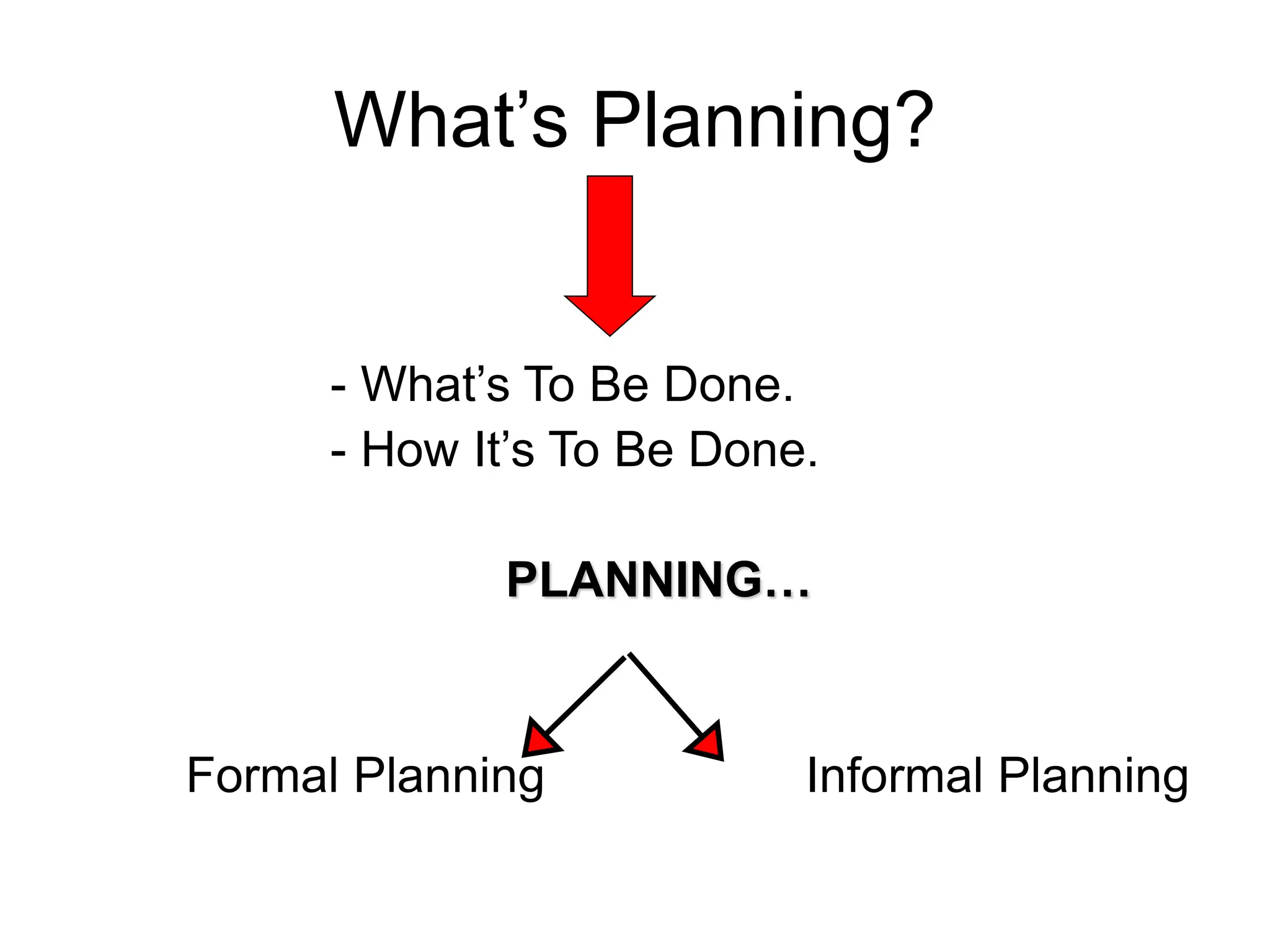
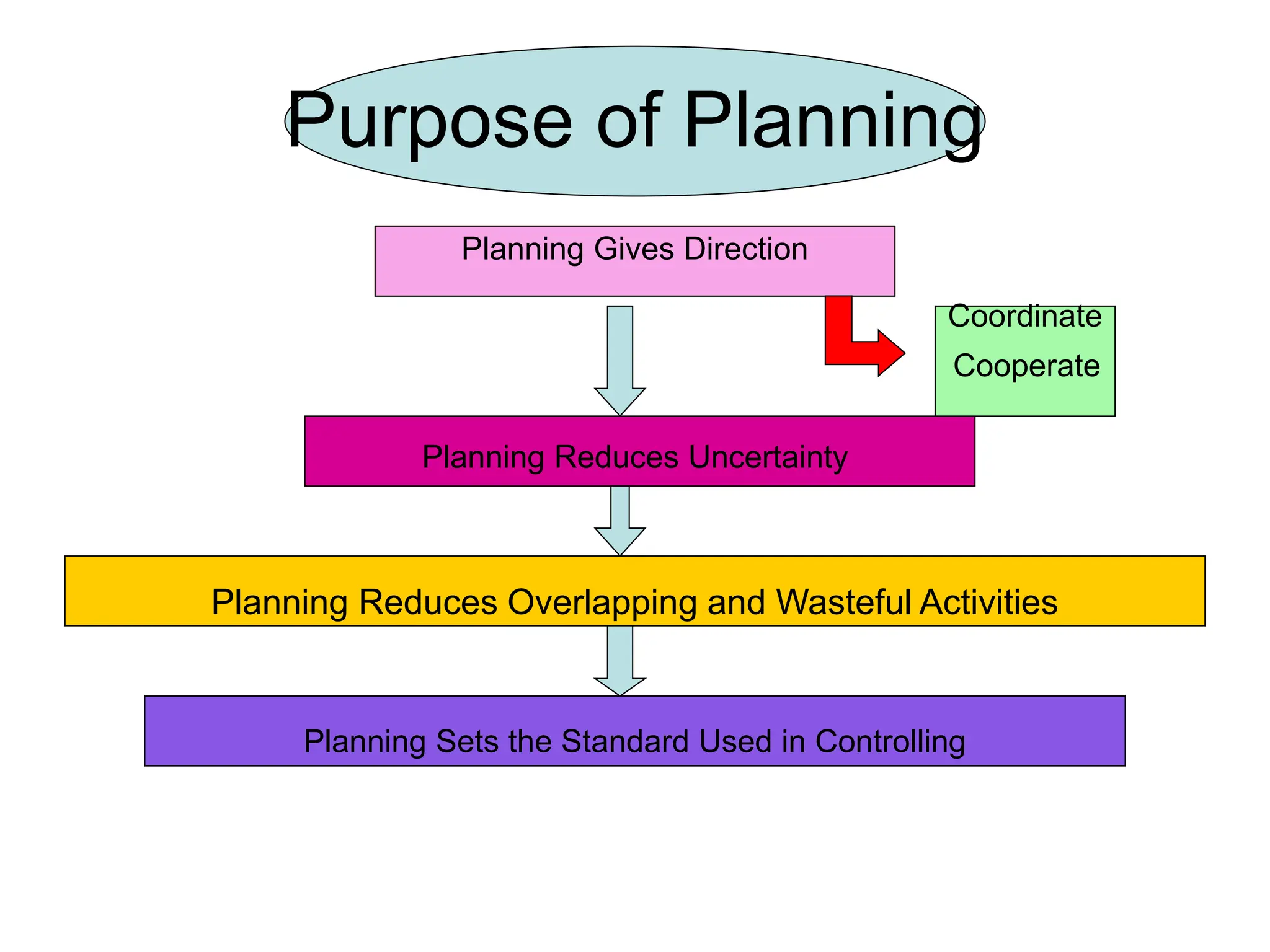
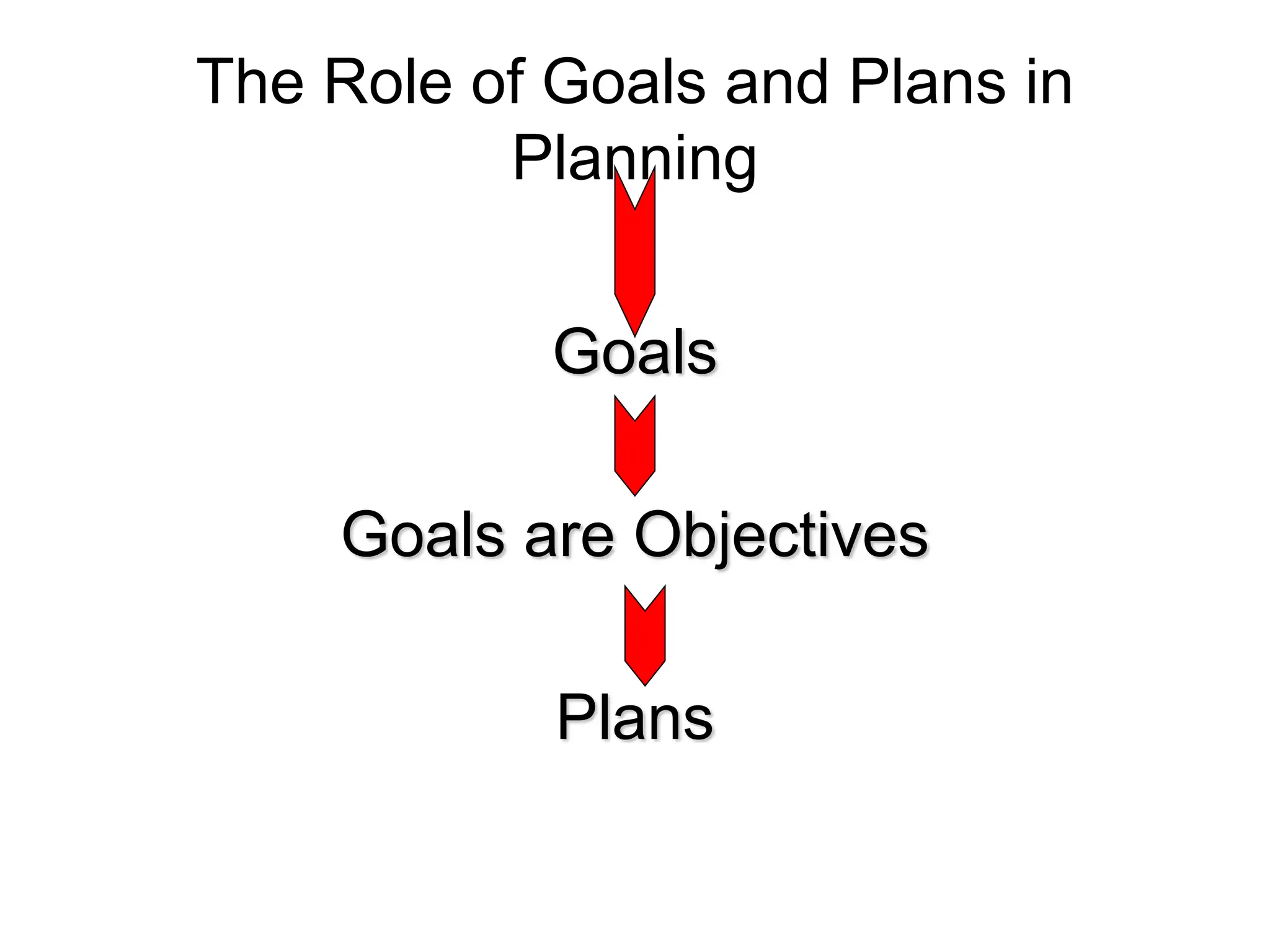
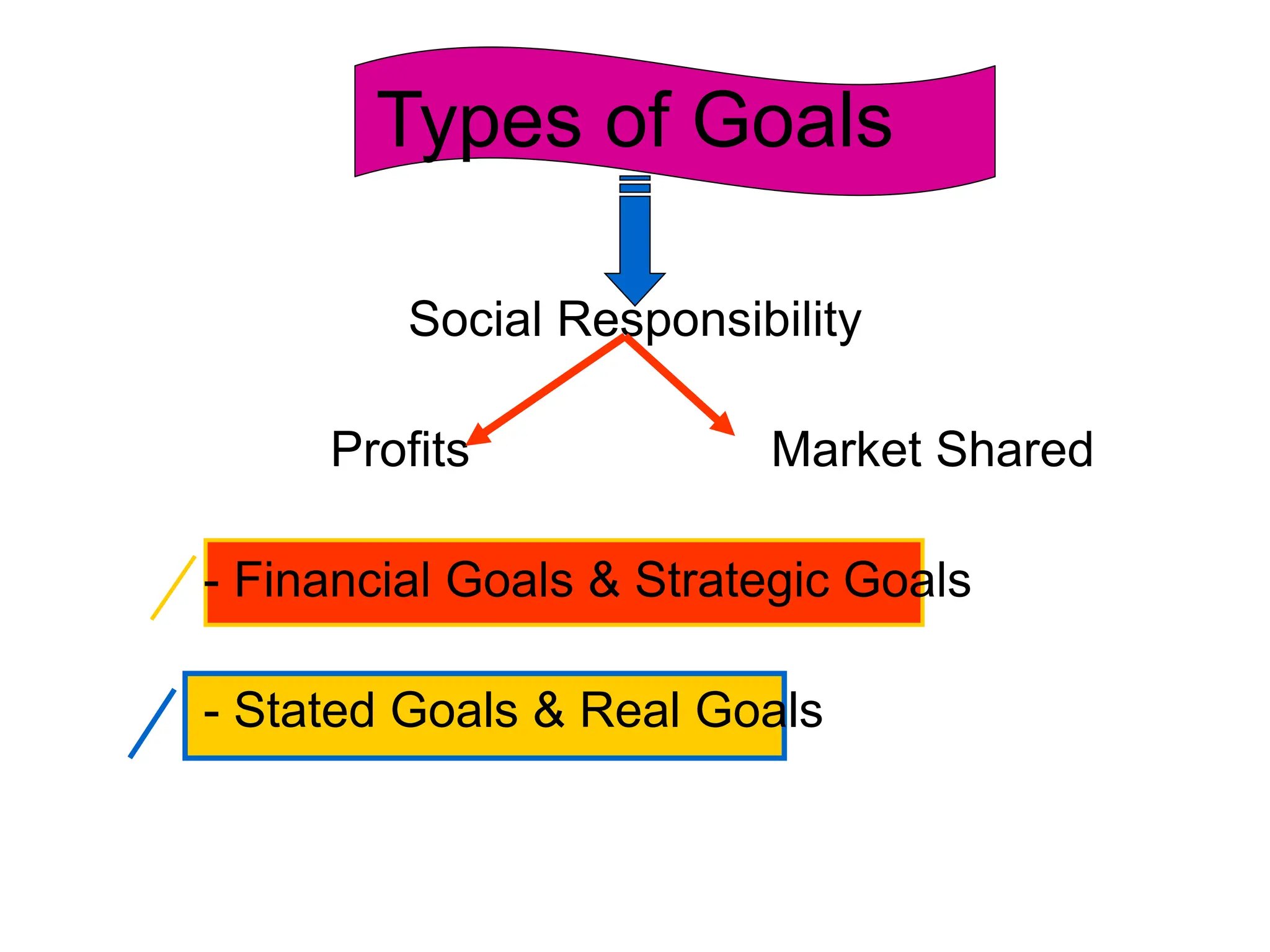
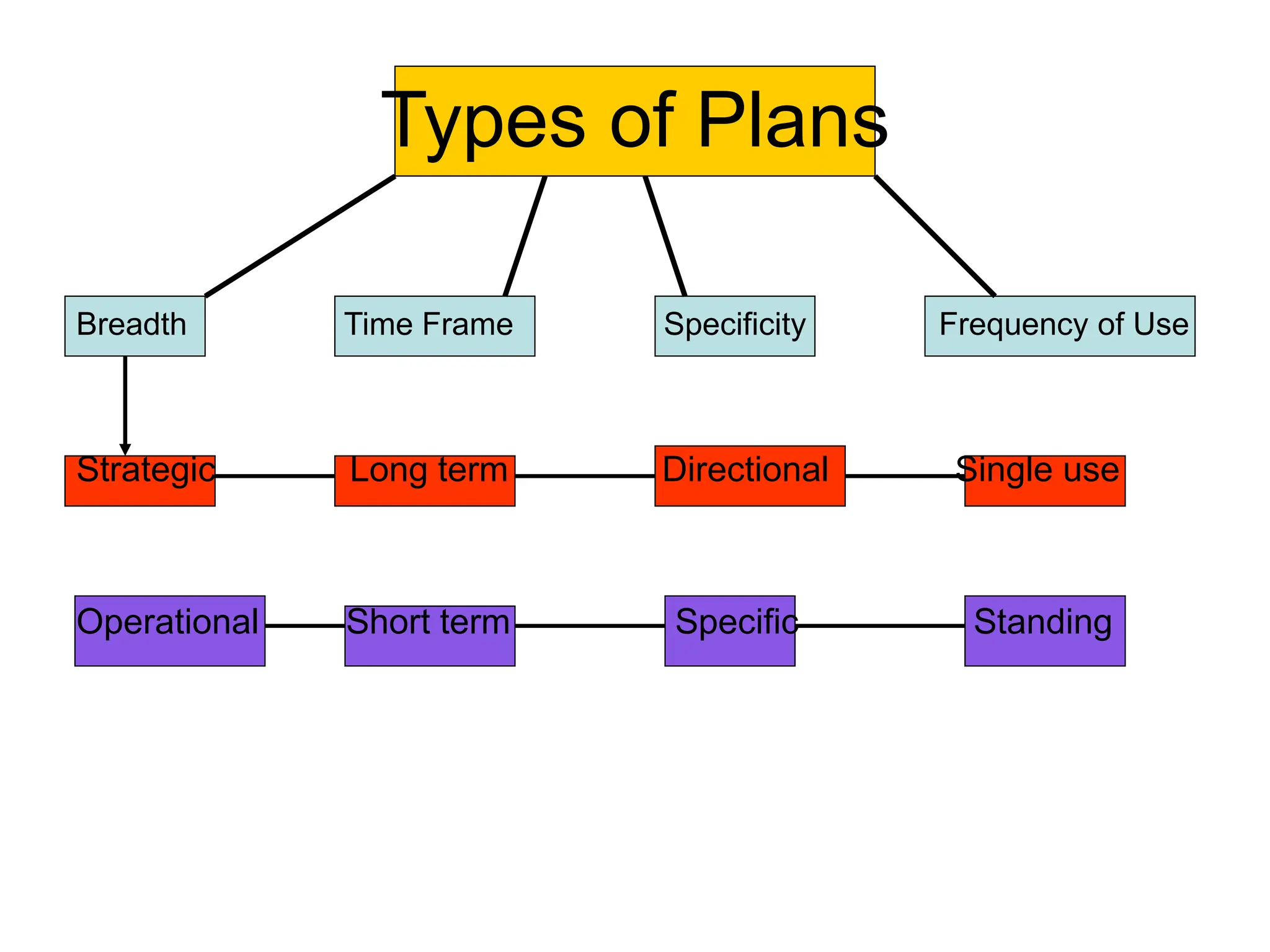
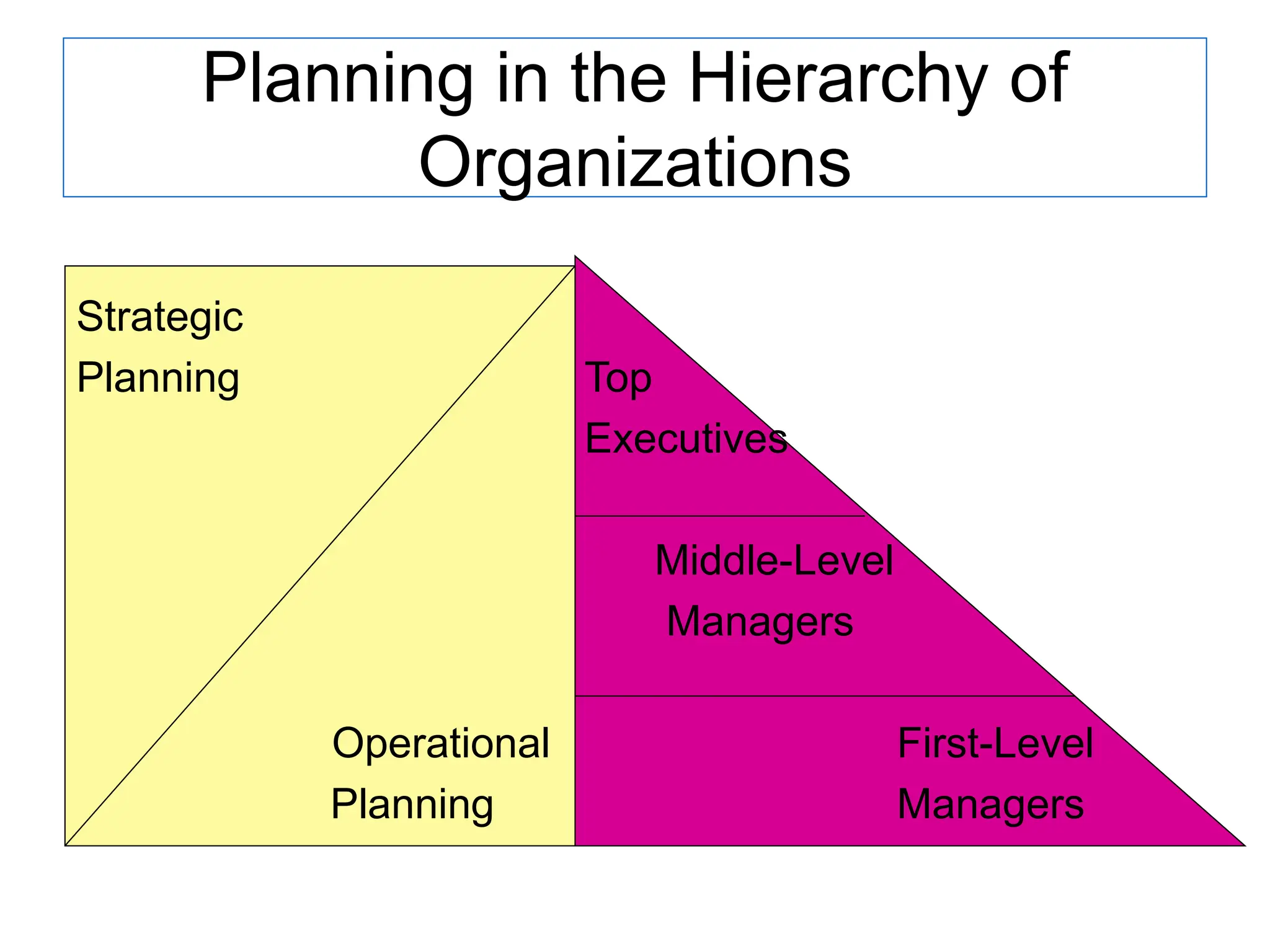
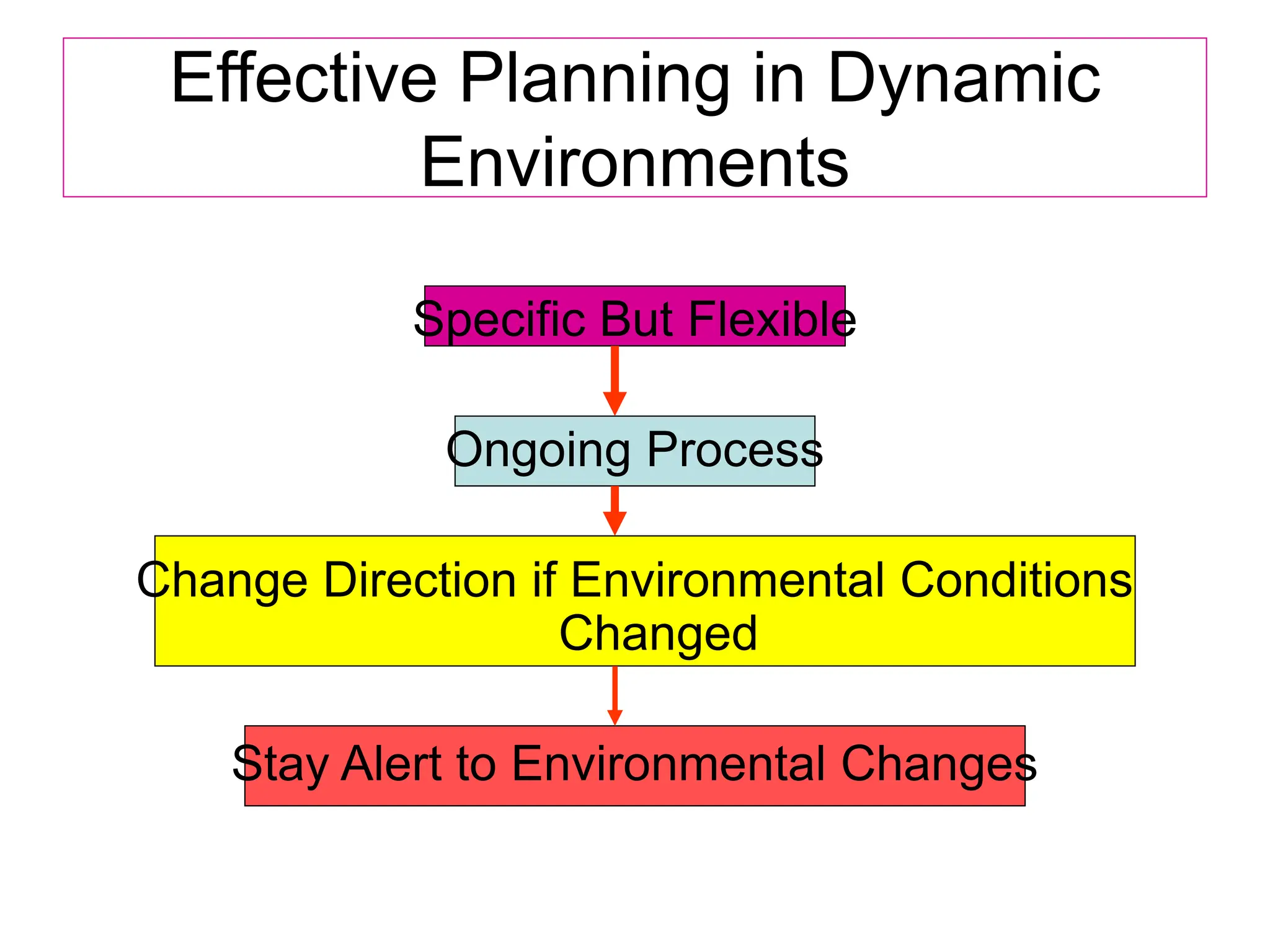
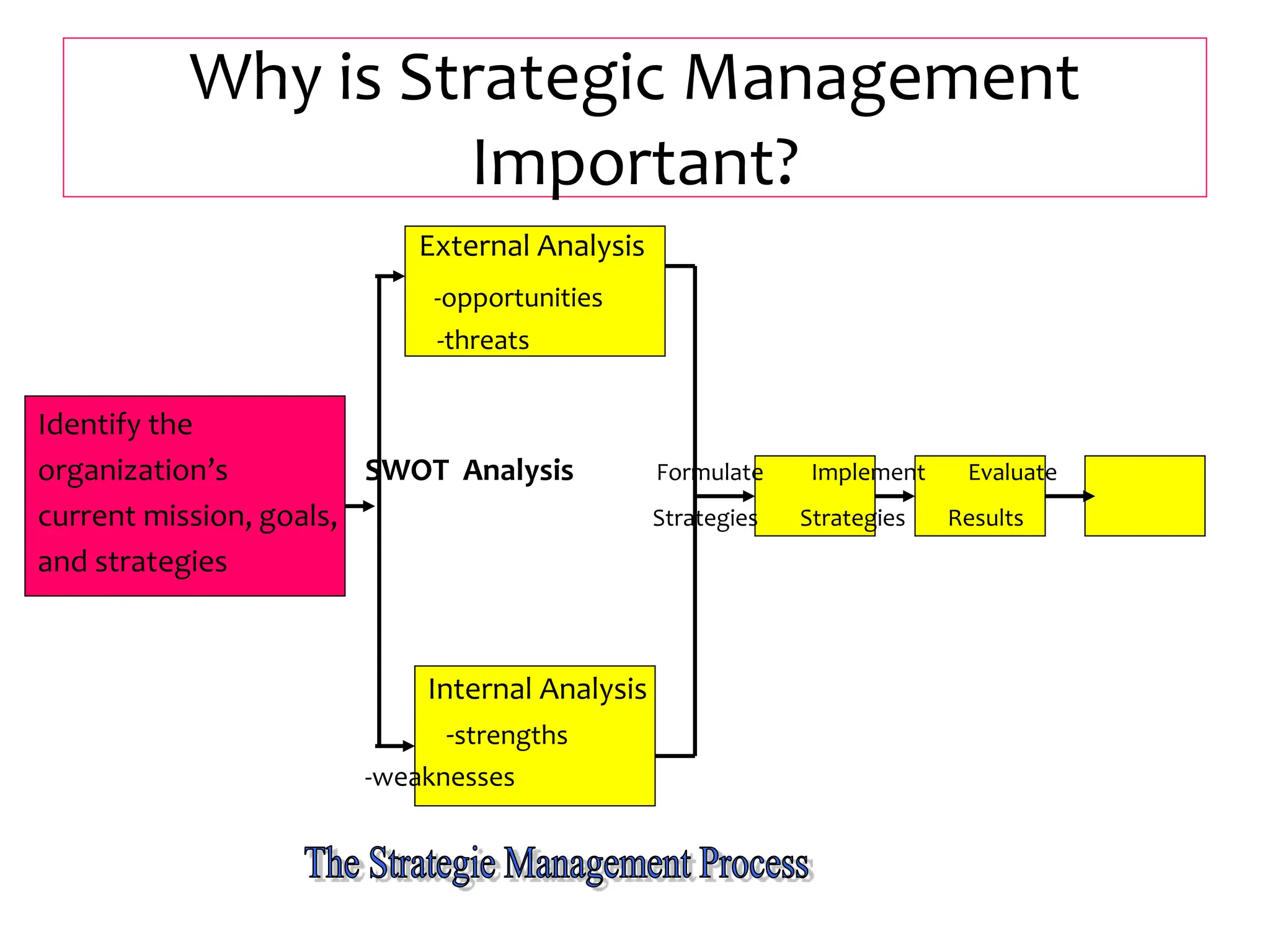
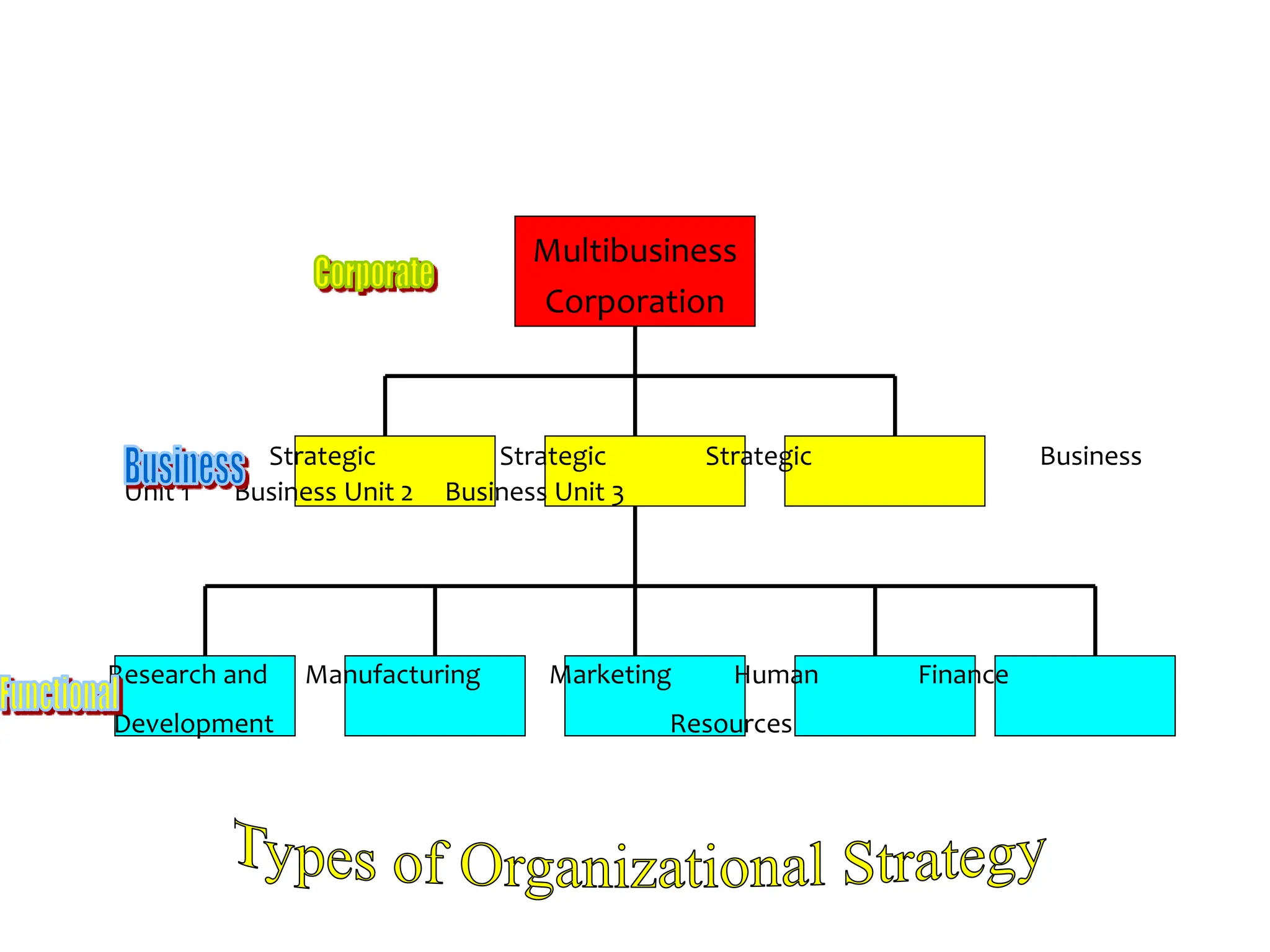
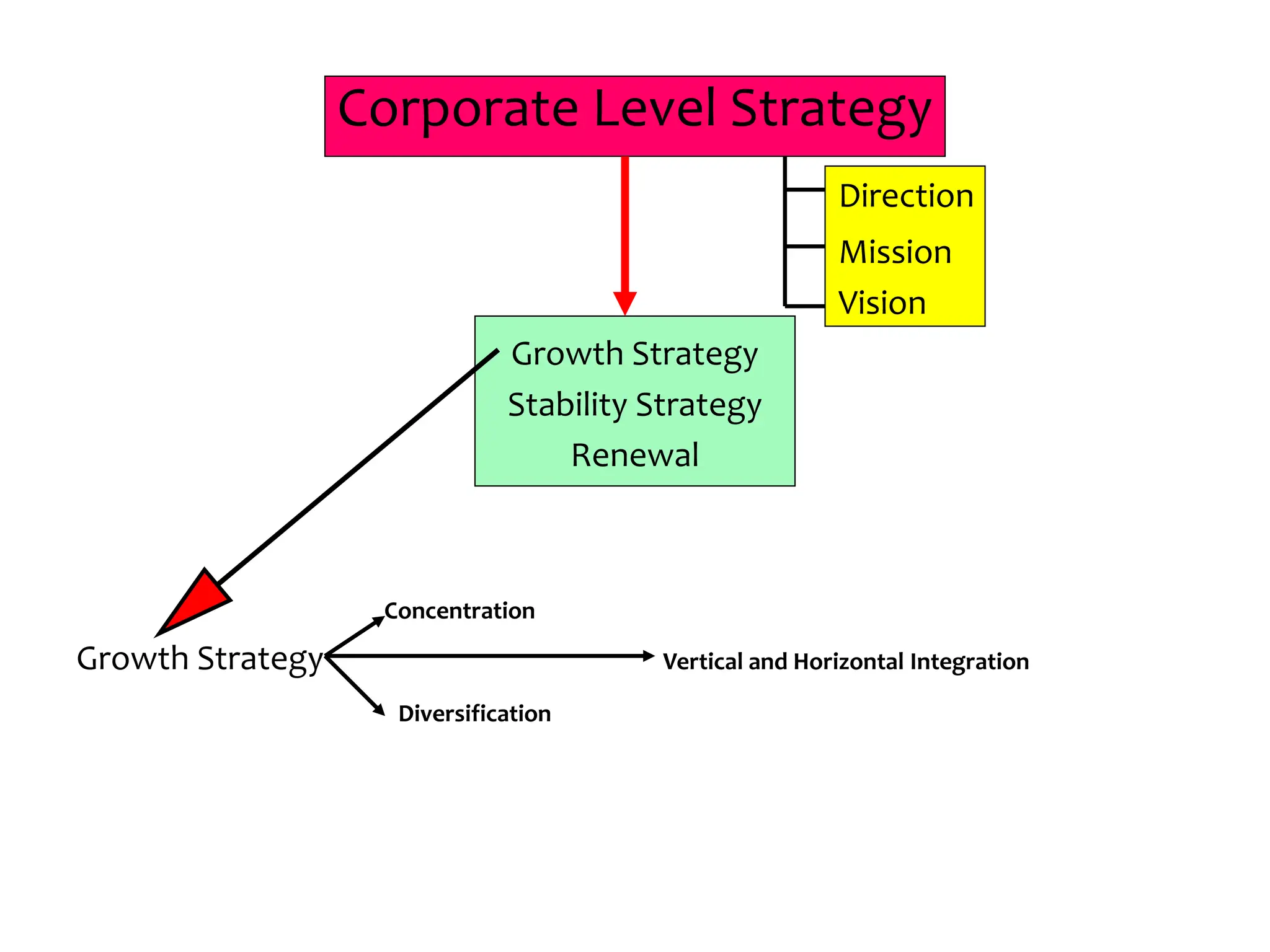
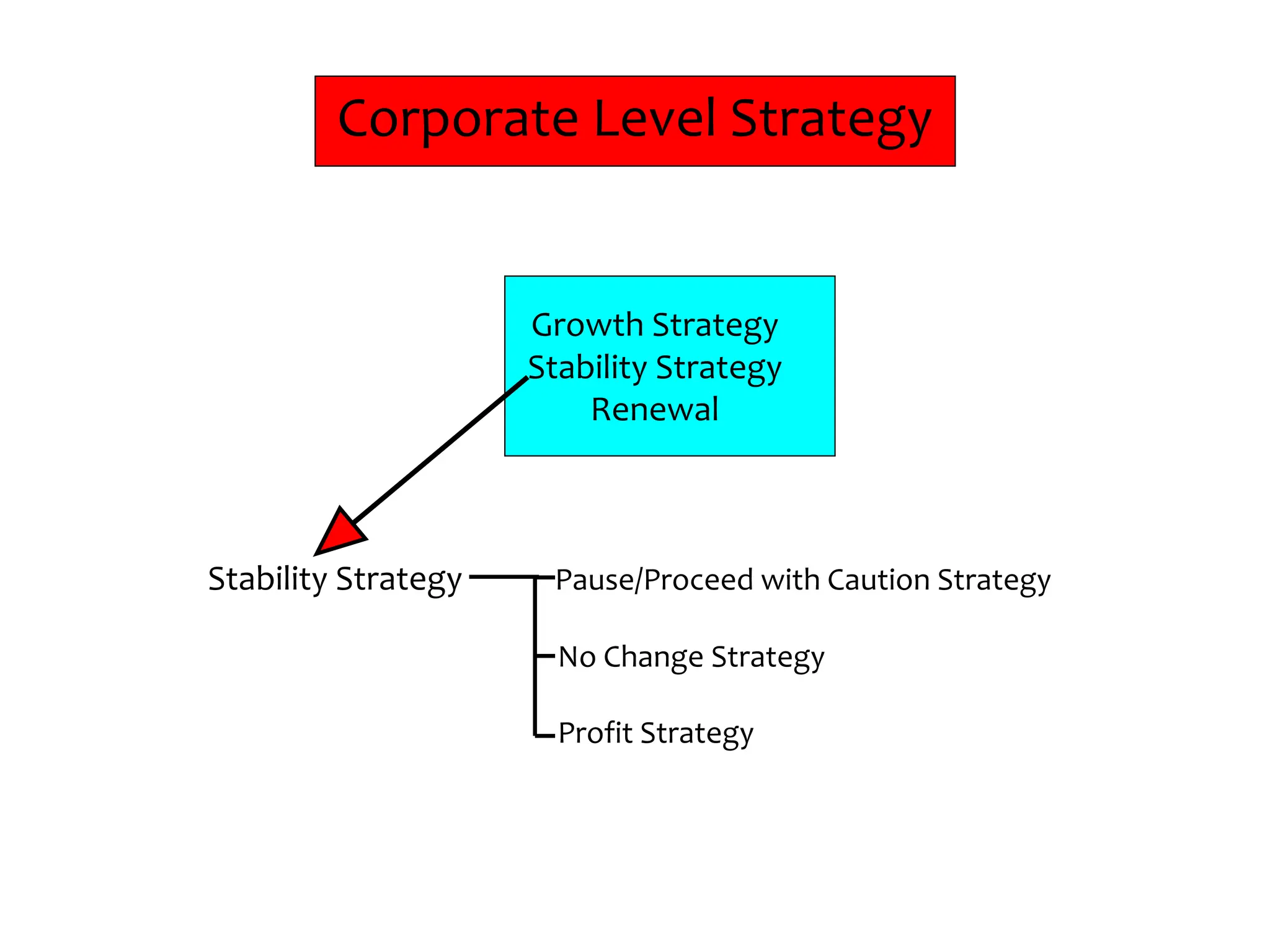
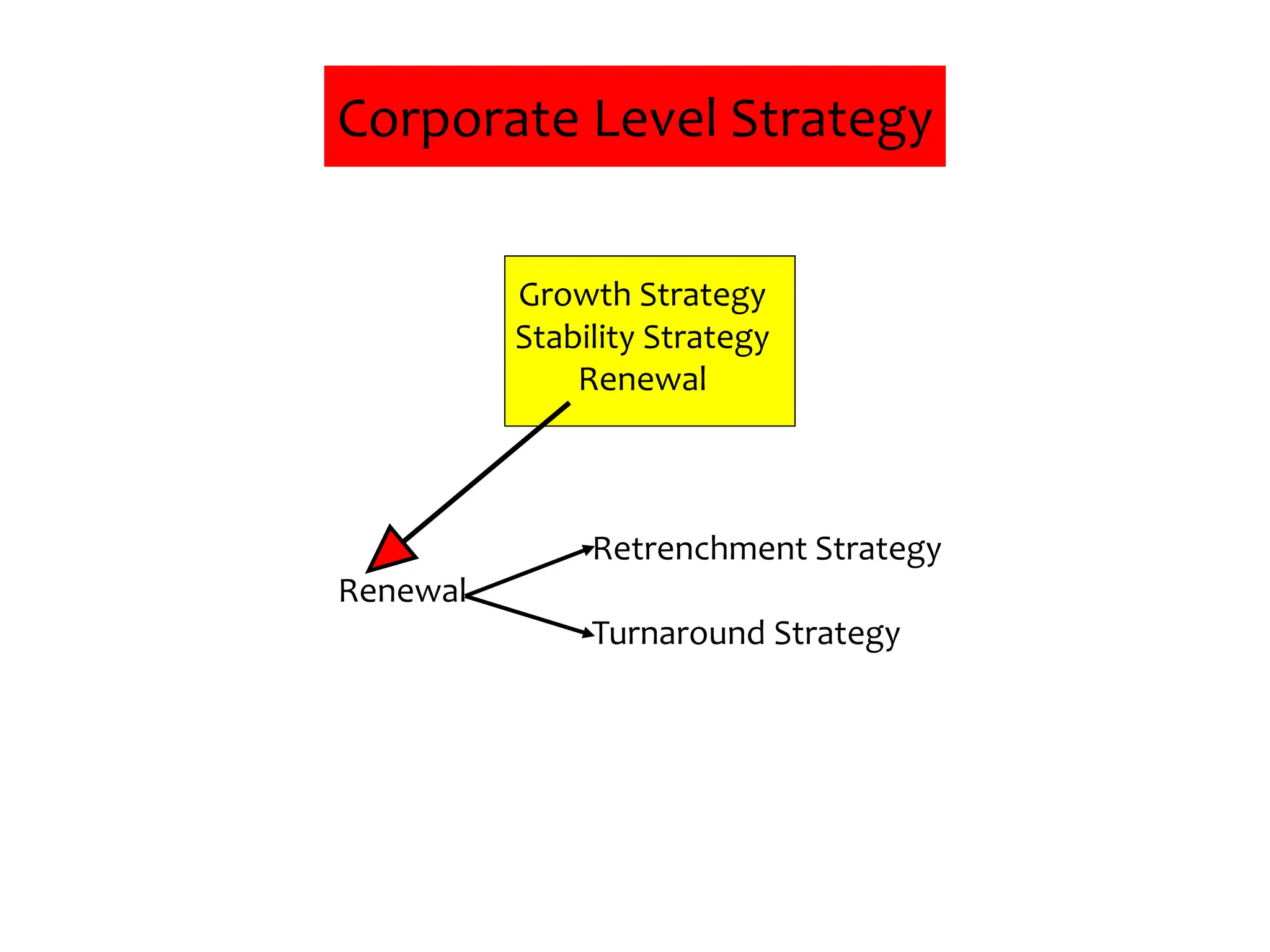
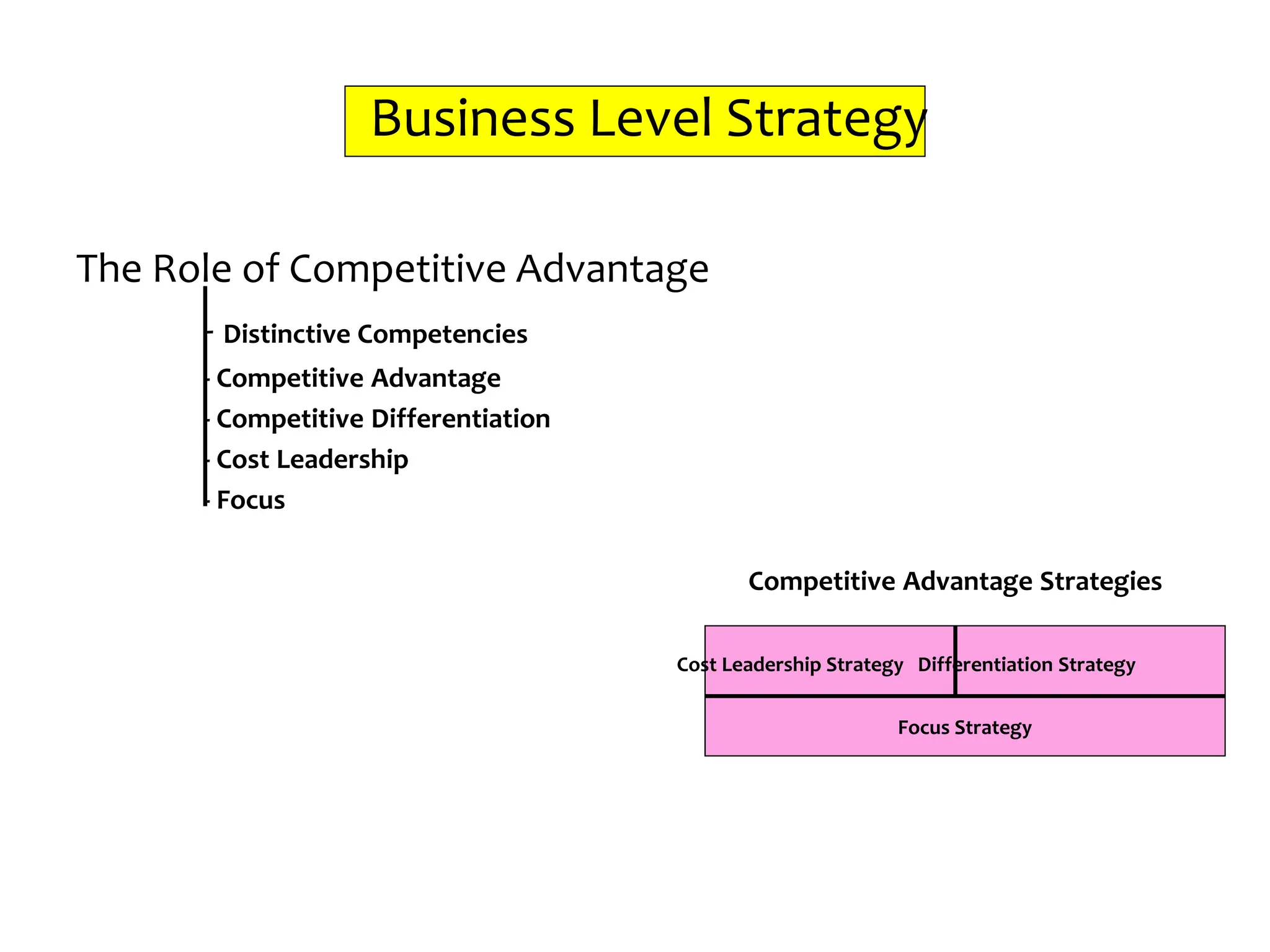
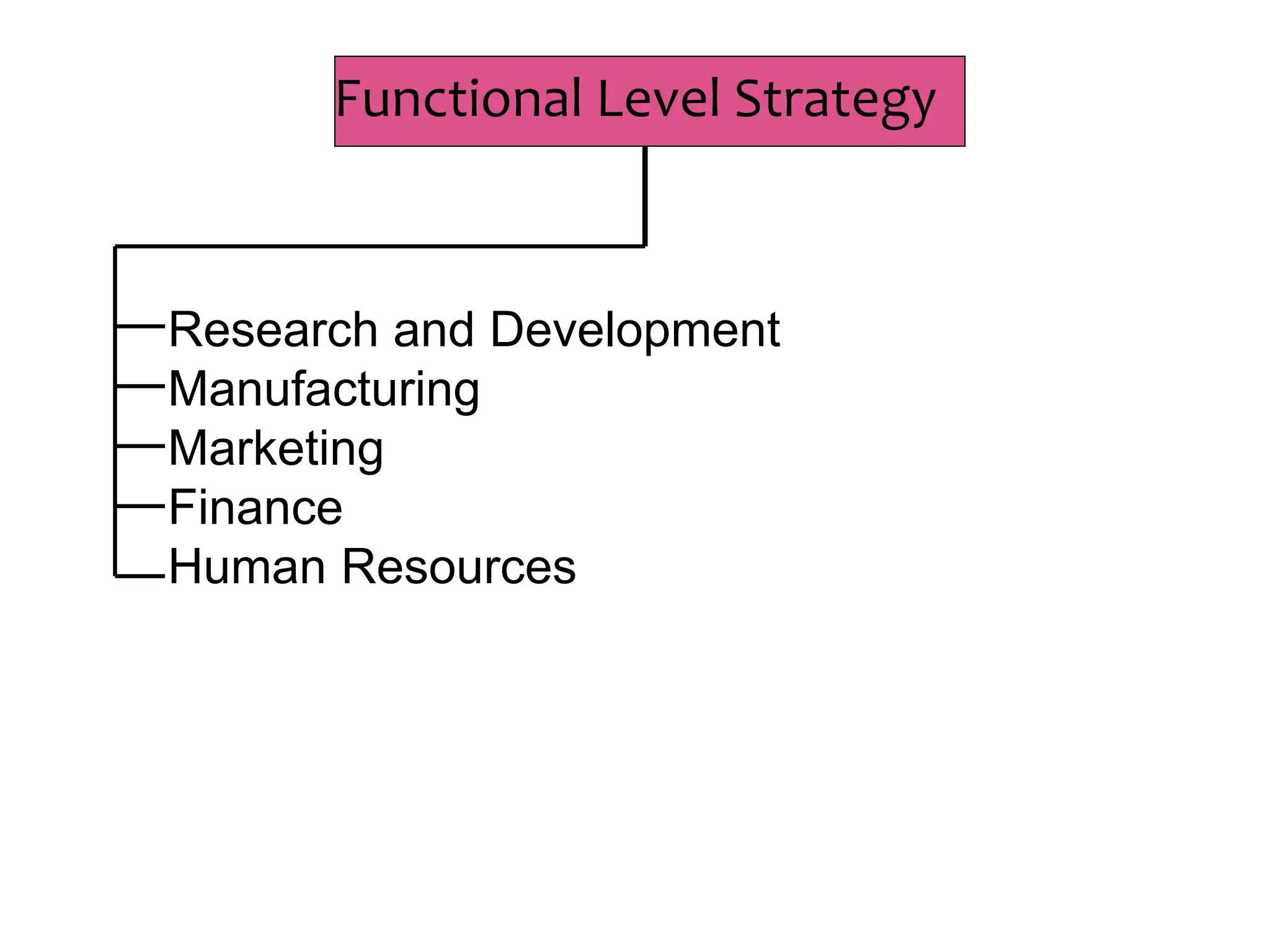
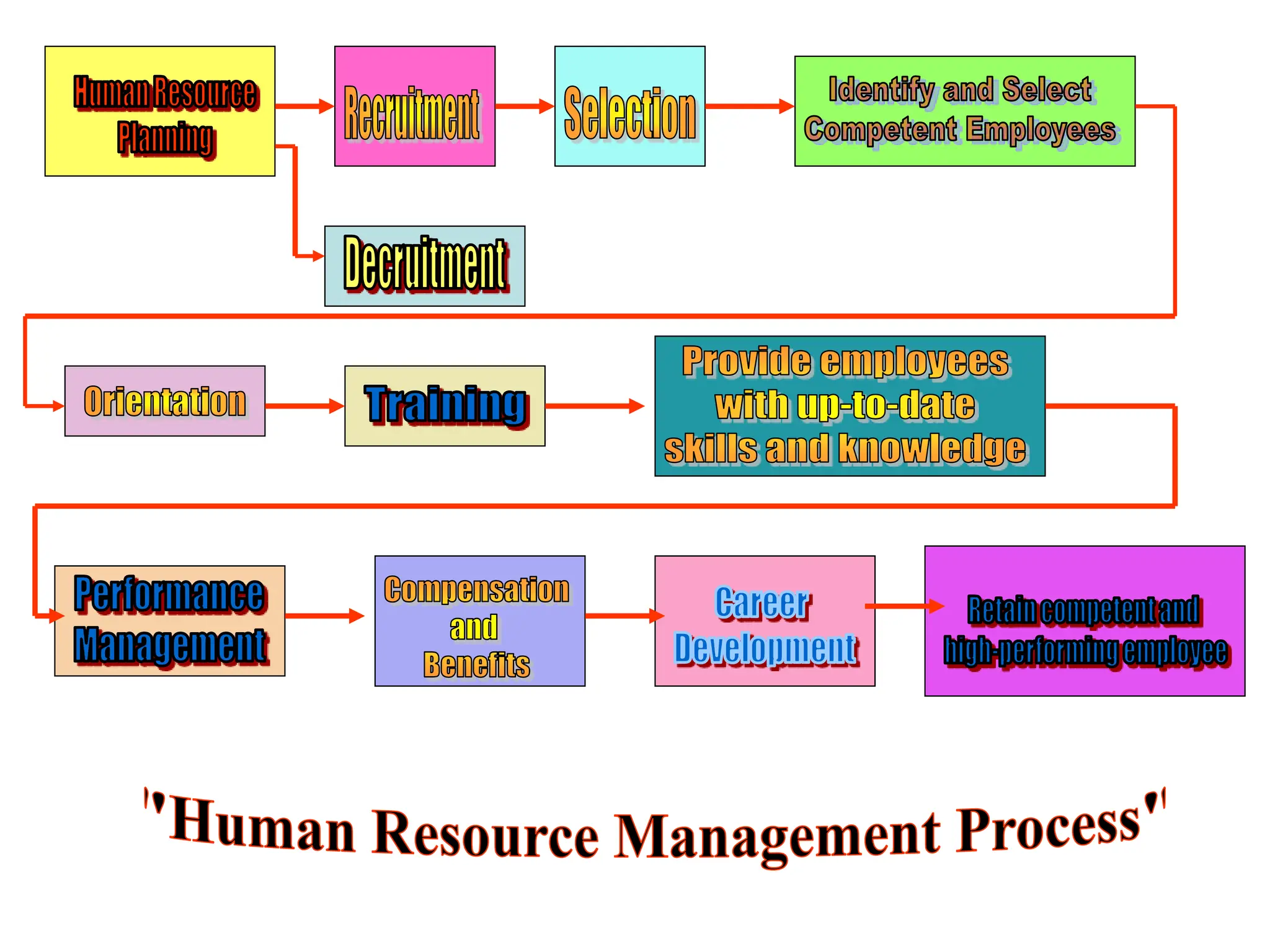
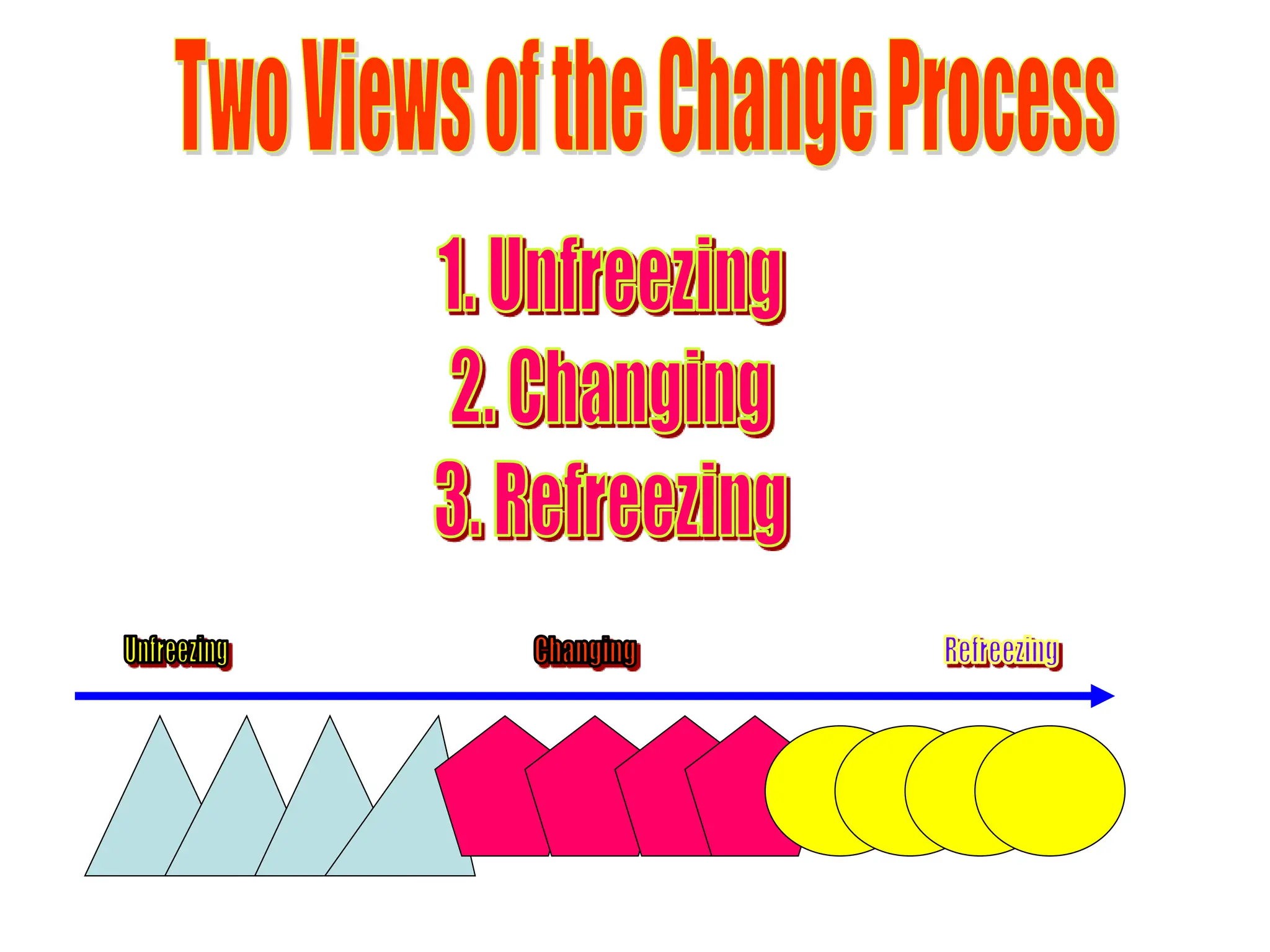
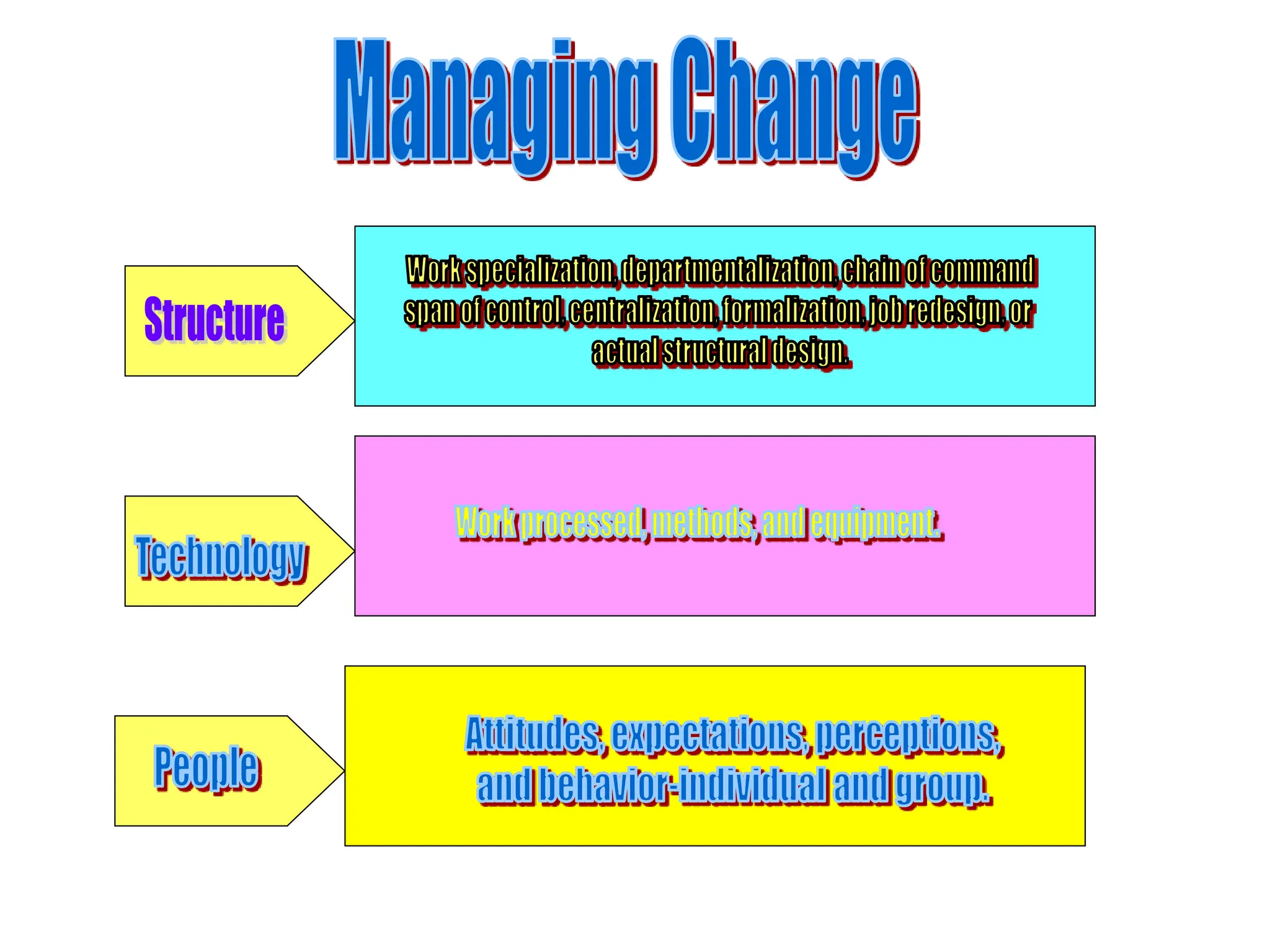
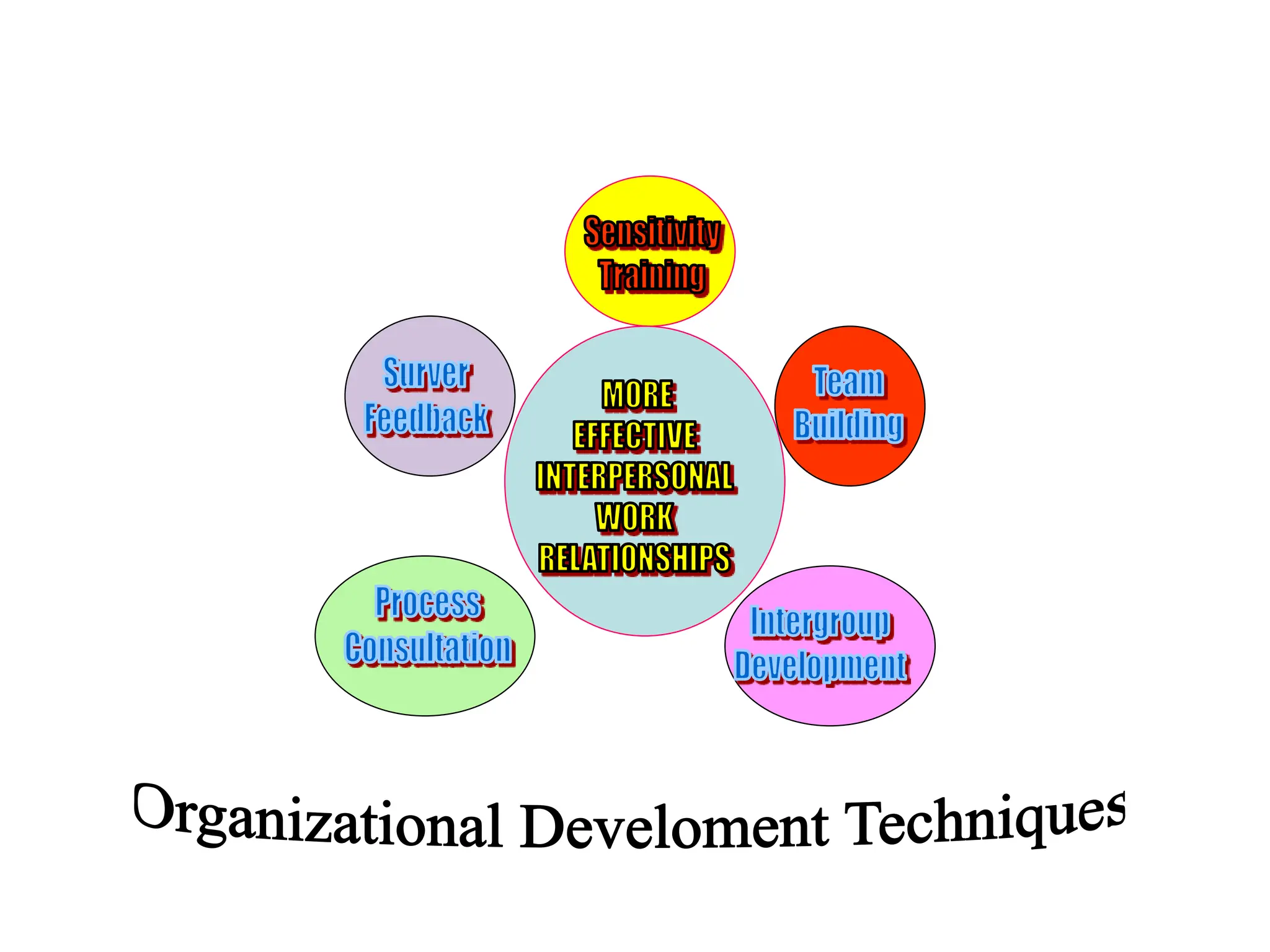
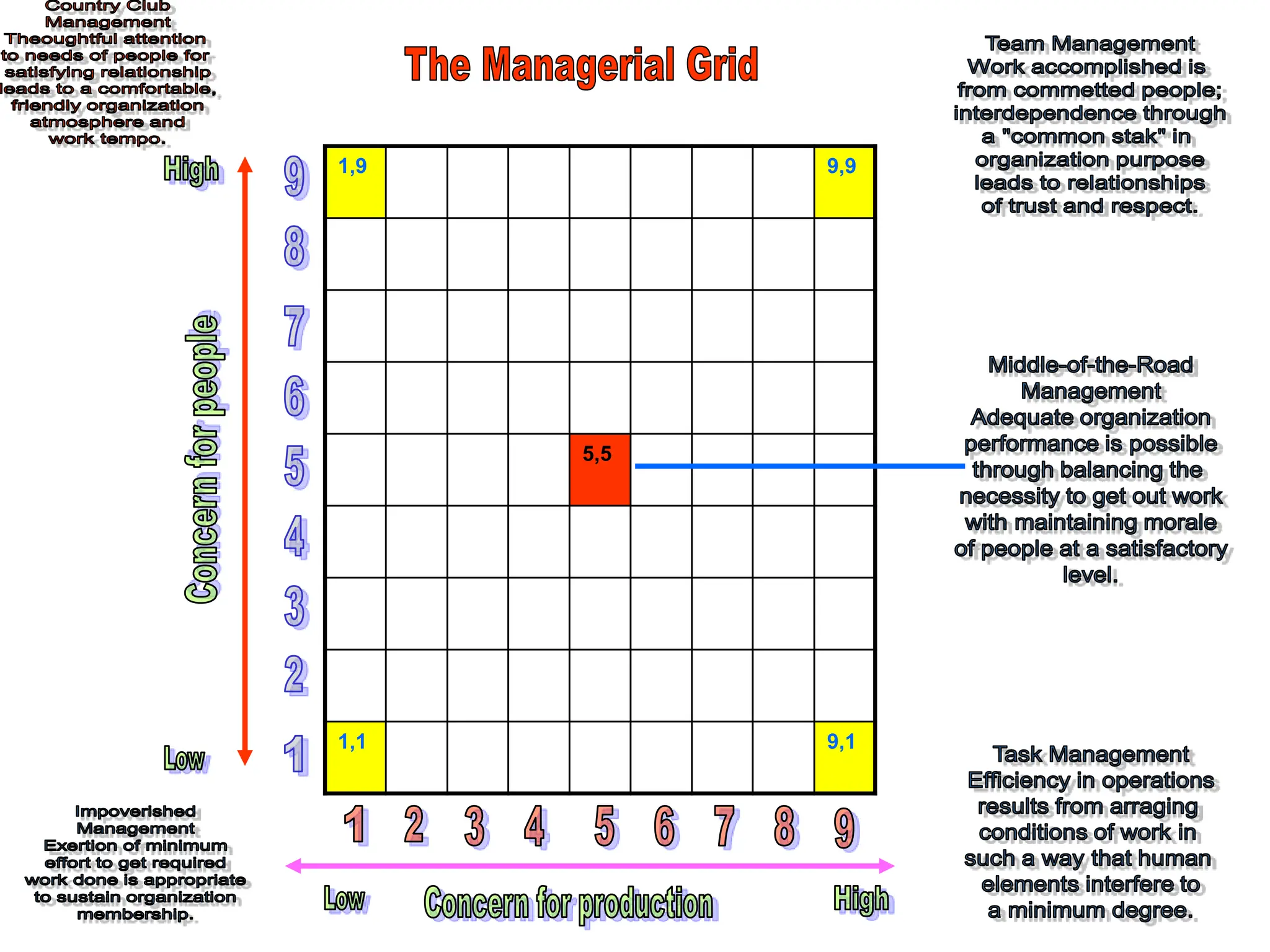
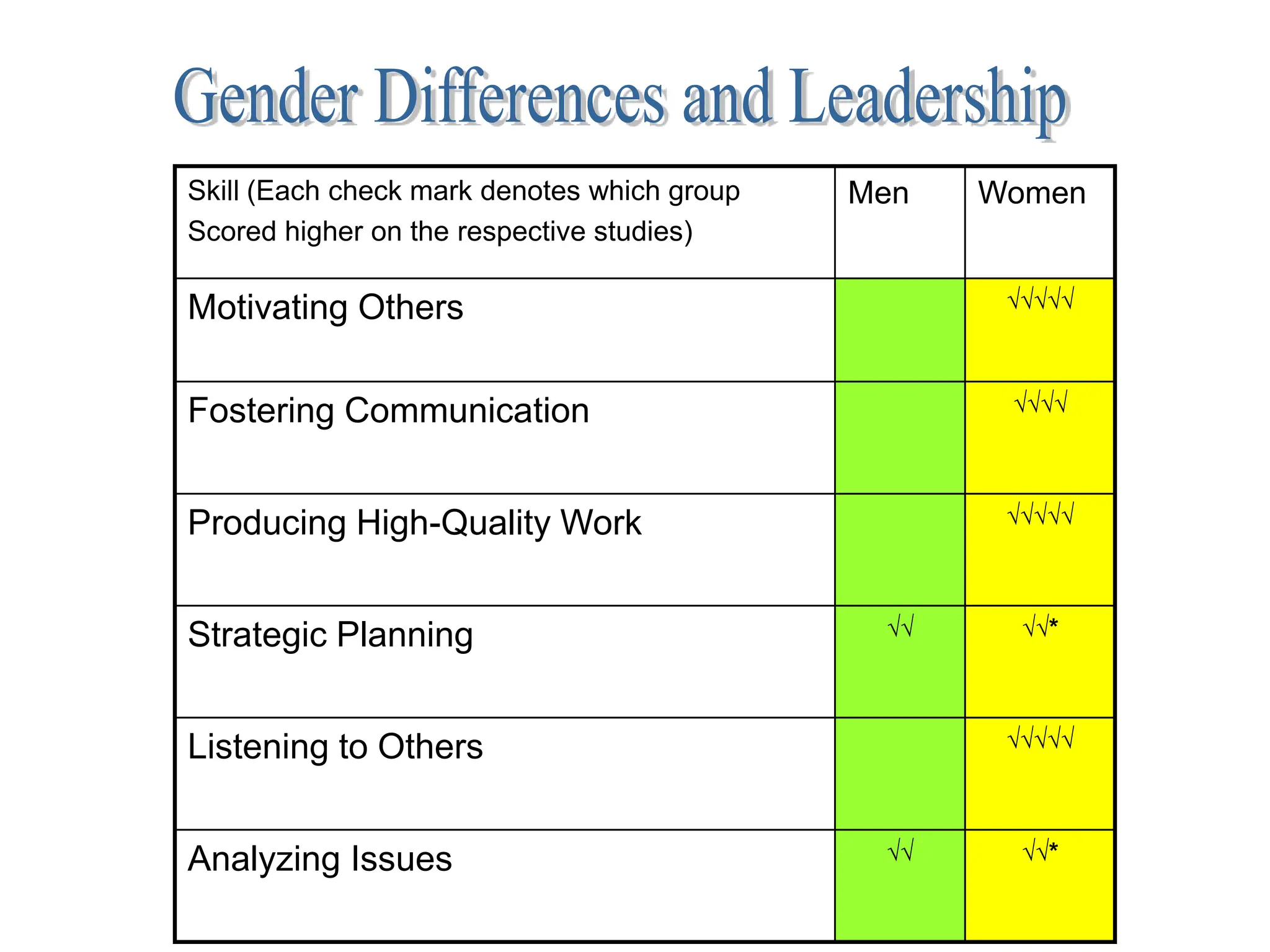
This document provides an introduction to organization and management concepts. It discusses the characteristics of organizations, different types of organizational structures, and how organizations are changing. It also covers management functions, levels within organizations, skills needed by managers, and perspectives on management such as contingency theory. Finally, it discusses the environment organizations operate within and why studying management is important. The document aims to give the reader an overview of foundational organization and management topics.