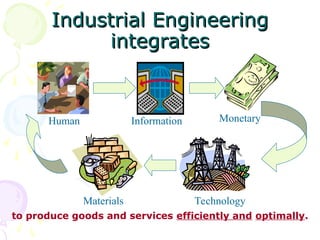
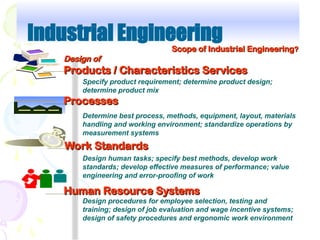
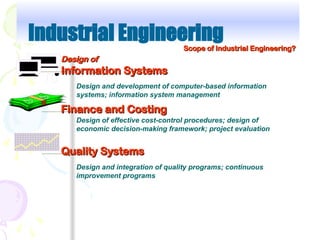
Industrial engineering focuses on designing, improving, and installing integrated systems involving people, materials, equipment, and information, leveraging knowledge from various sciences and engineering principles. It offers diverse career opportunities in both manufacturing and service sectors, with many roles emphasizing efficiency and waste reduction. Certification programs and professional advancement opportunities support industrial engineers' growth in the field, fostering a recognition framework for their expertise and competencies.