The document outlines the course content for an Introduction to Programming 1 python course, including an overview of programming languages, the features and reasons for using python, variable declaration and data types, and how to handle errors, expressions, conditional and iterative statements, and functions in python programs. It also lists recommended textbooks and describes how python code can be run using an interactive interpreter, as a script from the command line, or within an integrated development environment.

















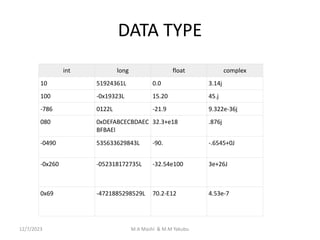

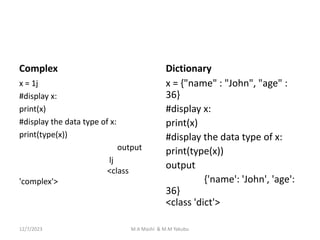
![Getting data types
You can get the data type
of any object by using the
type() function.
integer
Number =5
Print(type(number)) output
<class 'int'>
float
x = 20.5
#display x:
print(x)
#display the data type of x:
print(type(x)) output
x= 20.5
<class
‘flaot’>
String
x = "Hello World"
#display x:
print(x)
#displa
y the data type of x:
print(type(x)) Output
Hello World
<class 'str'>
List
x = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
#display x:
print(x)
#display the data type of x:
print(type(x))
Output
['apple',
'banana', 'cherry']
<class
'list'>
12/7/2023 M.A Mashi & M.M Yakubu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-231207153133-15dec88d/85/Lecture1-pptx-20-320.jpg)