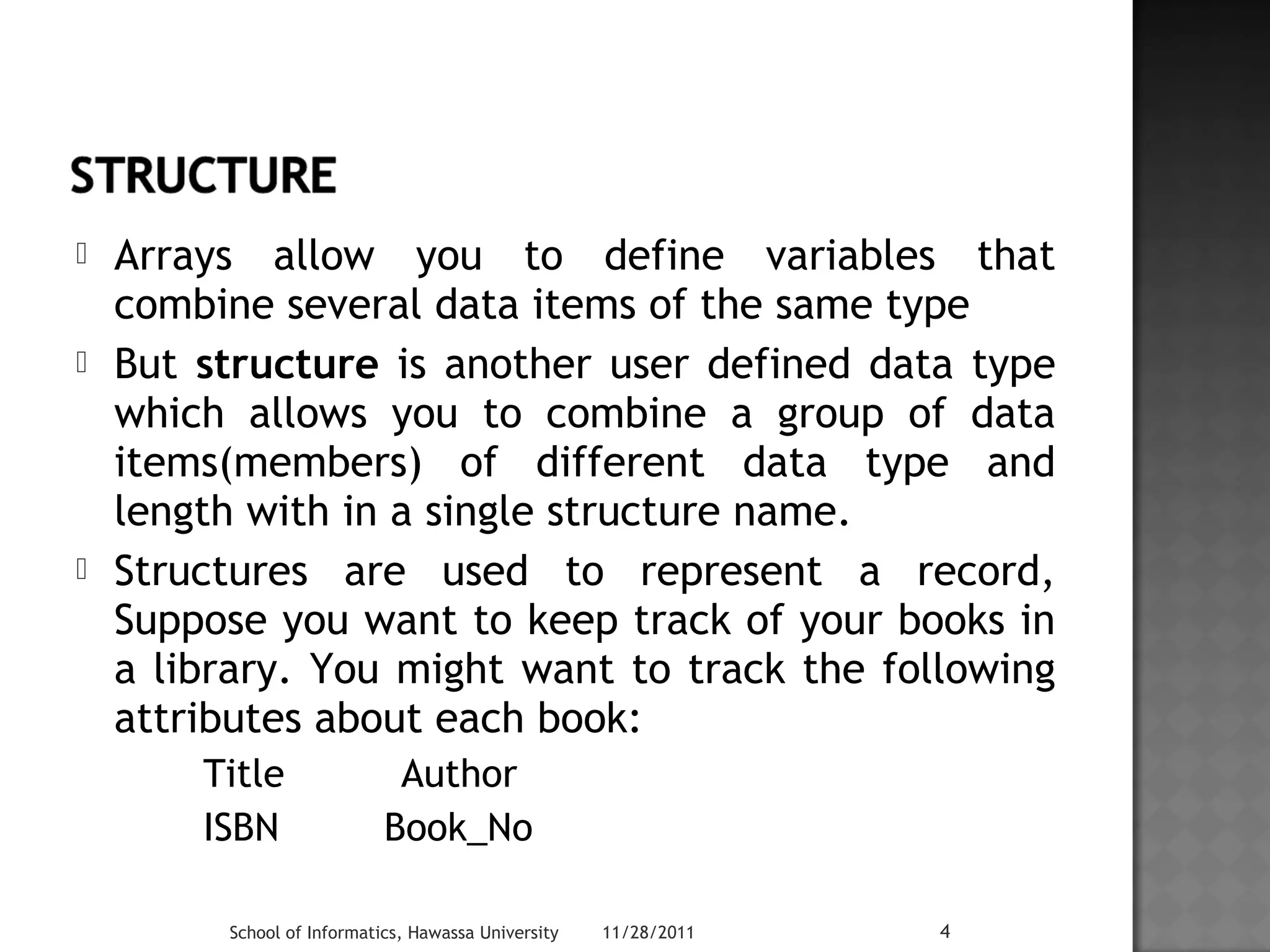
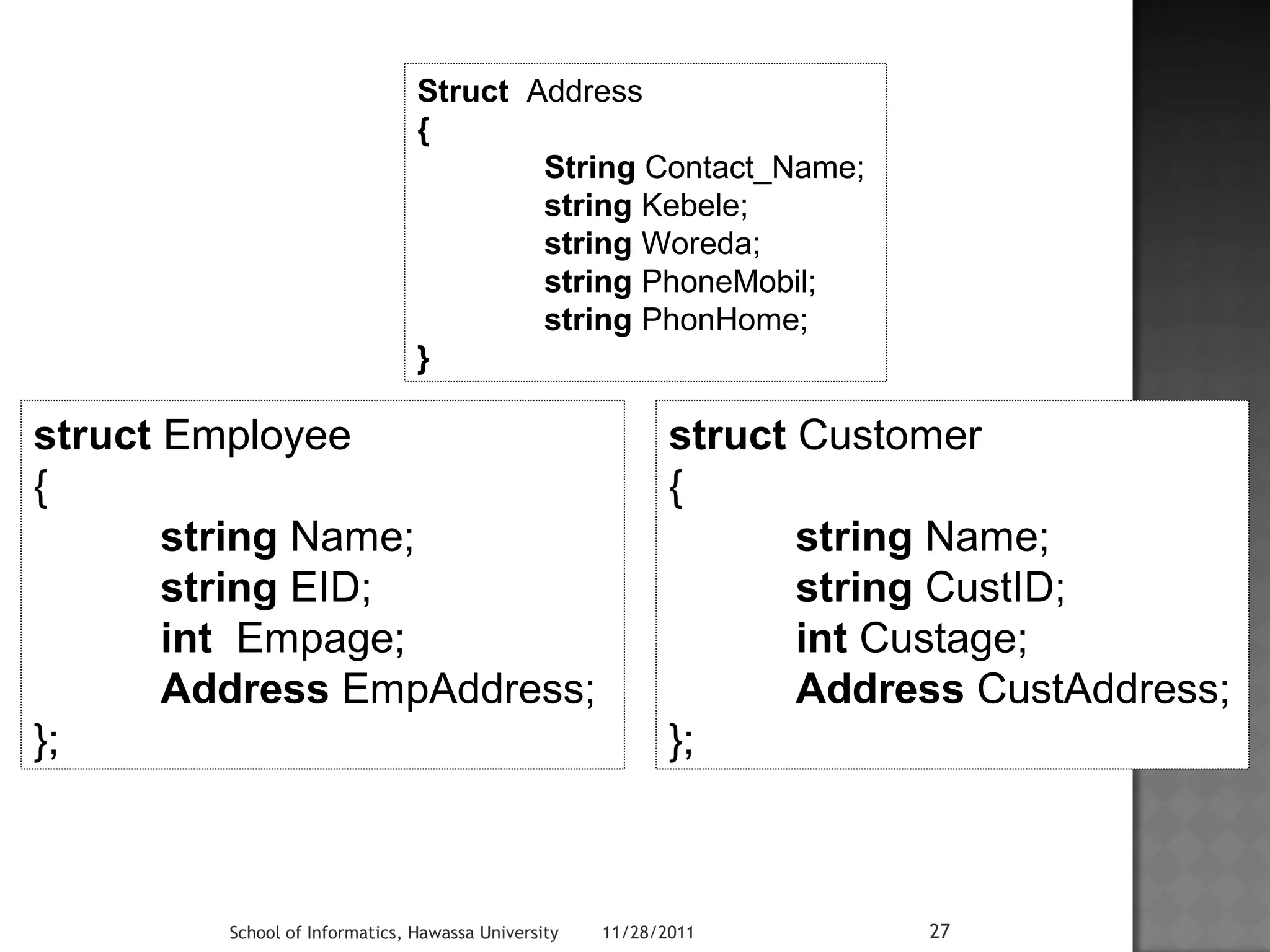
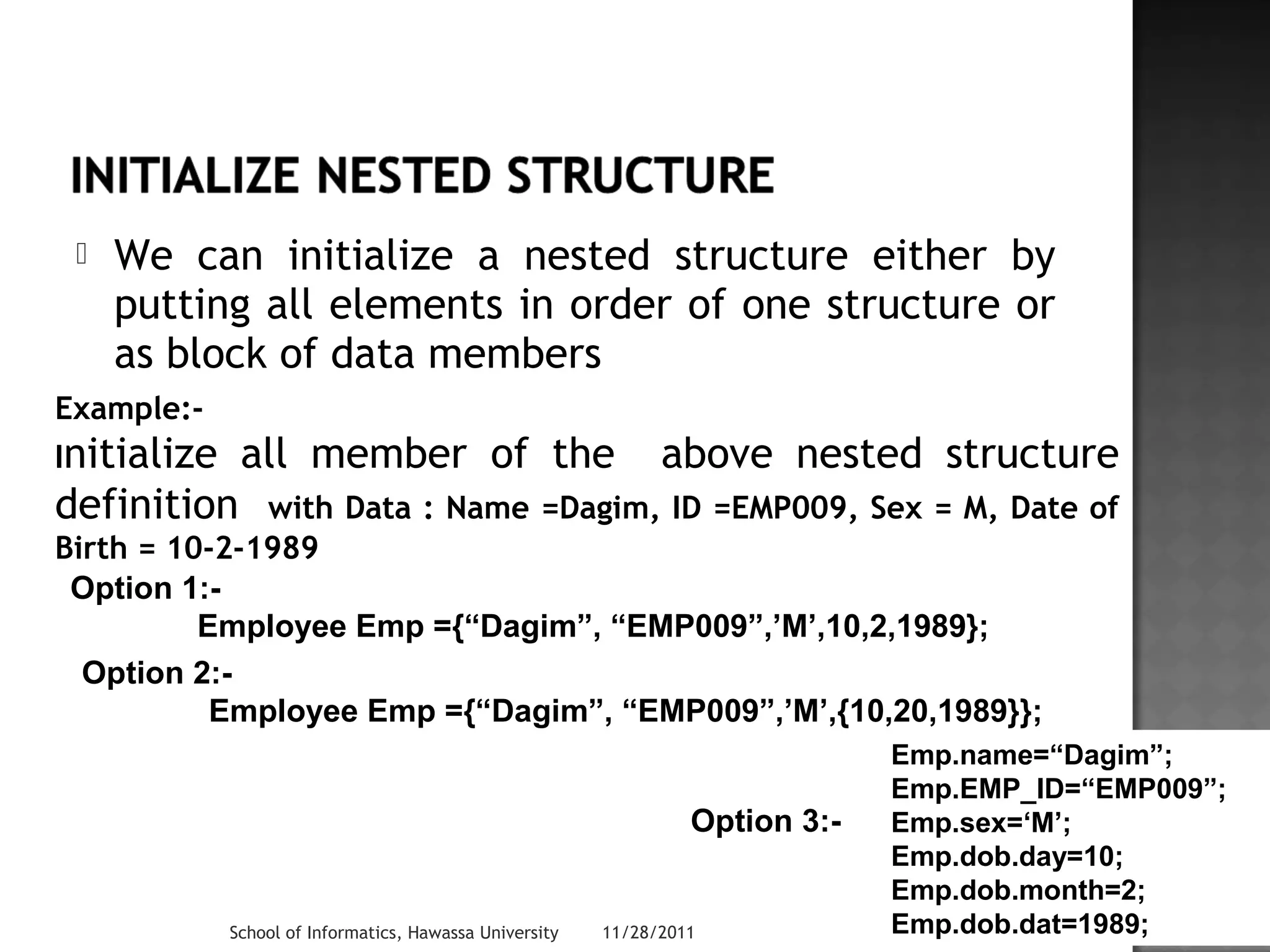
The document discusses structures in C++. It defines a structure called Employee that contains data members for an employee's first name, last name, and date of birth. It shows how to declare a structure variable Emp initialized with values, and print out the employee's details using dot operators to access individual data members like Emp.dob.month. Structures allow storing different data types together and can be nested, like including a date structure within the Employee structure.


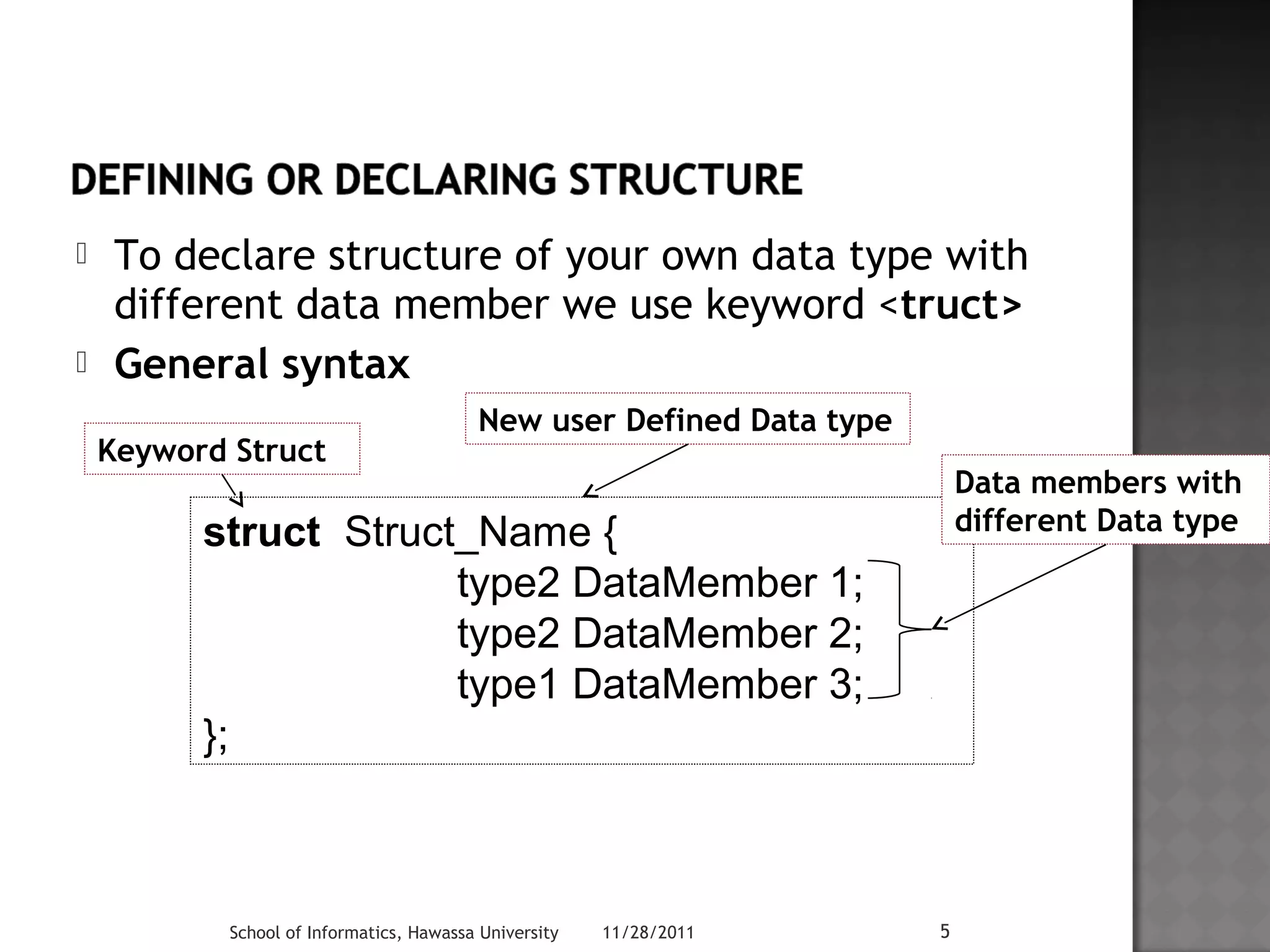
![ Create structure called Book which has
attributes Title, Author, ISBN, Book_No
Struct Book {
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 7
};
Struct Book {
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
} bookObj;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-7-2048.jpg)
![ As with arrays and variables, structure members
can also be initialized. This is performed by
enclosing the values to be initialized inside the
braces { and } after the structure variable name
while it is defined.
Struct Book {
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
} Book1 = {“C++”, ” John”, “12-34-034-234”,12};
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-8-2048.jpg)
![ The Second way to initialize structure
Struct Book {
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
} ;
int main()
{
Book Book1 = {“C++”, ” John”, “12-34-034-234”,12};
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 9
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-9-2048.jpg)

![ Syntax
struct_var.Member1=//some operation;
Example
Struct Book
{
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 11
}Book1;
Assign Individual Member
Book1 .Title= “C++”;
Book1.Author= ”John”;
Book1.ISBN= “12-34-034-234”
Book1.Book_No=12;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-11-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Books {
char Title[50];
char Author[25];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No; };
int main() {
Books Book1 = {"Java","Johe","123-3243-2312",1};
Books Book2 = {"C++","Johe","123-3243-2313",3};
Books Book3 = {"C#","Johe","123-3243-2314",2};
cout<<"tTitle tAuthor tISBN ttBook Number"<<endl;
cout<<"t................................................................"<<endl;
cout<<"t"<<Book1.Title<<"t"<<Book1.Author<<"t“
Initializing 3 Books
With 4 data members
for each book
<<Book1.ISBN<<"t"<<Book1.Book_No<<endl;
cout<<"t"<<Book2.Title<<"t"<<Book2.Author<<"t“
<<Book2.ISBN<<"t"<<Book2.Book_No<<endl;
cout<<"t"<<Book3.Title<<"t"<<Book3.Author<<"t“
<<Book3.ISBN<<"t"<<Book3.Book_No<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 13
•Printing 3 books
data by using dot
operator access
operator
Structure declaration and
member definition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-13-2048.jpg)
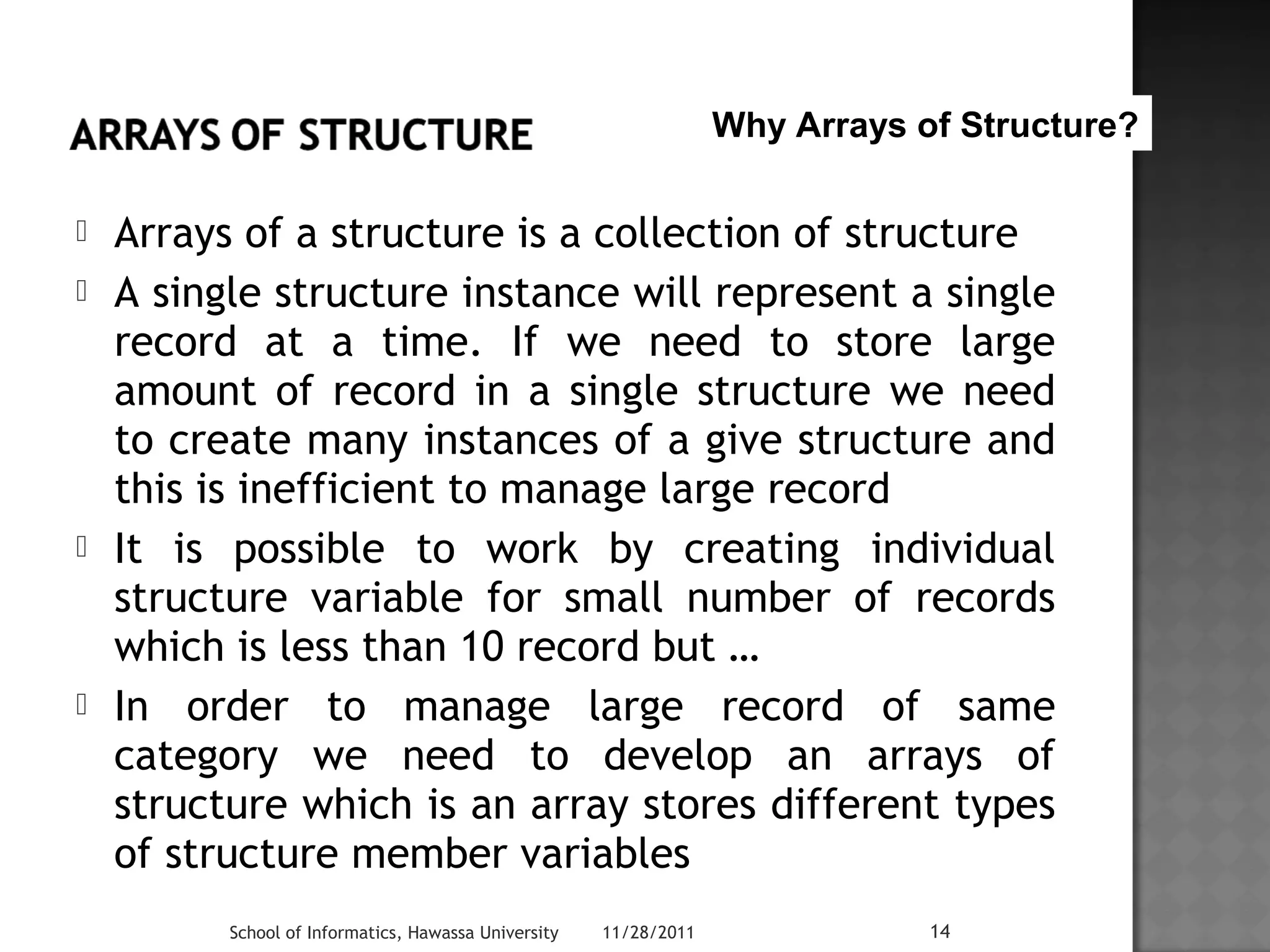

![Struct Books
{
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
}Book1, Book2, Book3, Book4 …Book1000;
Individual
structure variable
Using arrays of structure
Struct Books
{
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
} BookObj[1000];
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-16-2048.jpg)
![ To access individual elements of arrays of
structure we need to specify the index number
with in a square bracket of the structure
instance like simple array operation
Assume that you have structure as follow
Struct Books
{
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
} BookObj[10];
How to access the first
three books from your book
storage structure?
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-17-2048.jpg)
![Book one information Book Two information Book Three information
BookObj[0].Title
BookObj[0].Author
BookObj[0].ISBN
BookObj[0].Book_No
BookObj[1].Title
BookObj[1].Author
BookObj[1].ISBN
BookObj[1].Book_No
BookObj[2].Title
BookObj[2].Author
BookObj[2].ISBN
BookObj[2].Book_No
Title
Author
ISBN
Book_No
BookObj[0]
Title
Author
ISBN
Book_No
BookObj[1]
Title
Author
ISBN
Book_No
BookObj[2]
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-18-2048.jpg)

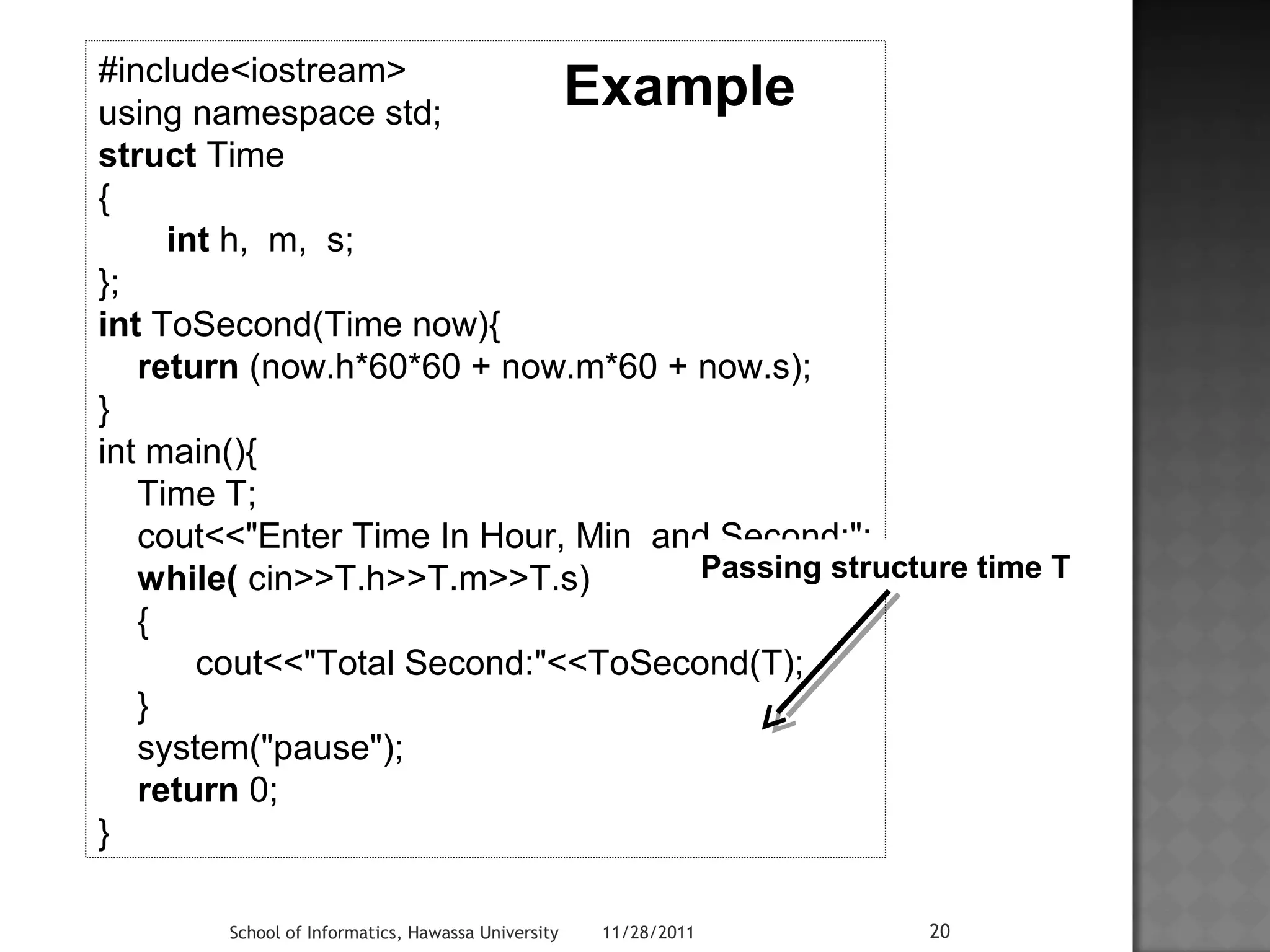

![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Books
{
char Title[50];
char Author[20];
char ISBN[15];
int Book_No;
};
const int size = 100;
void display(Books Book[size], int n)
{
cout<<"Title"<<"t"<<"Author"<<"t“
<<"ISBN"<<"t"<<"Book No"<<endl;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++) {
cout<<Book[i].Title<<"t"<<Book[i].Author<<"t"
<<Book[i].ISBN<<"t"<<Book[i].Book_No<<"t"
<<endl;
}
}
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 22
void input()
{
Books Book[size];
cout<<"nEnter No of Books:";
int n; cin>>n;
for(int i = 0;i < n ; i++) {
cout<<"nEnter Title:“; cin>>Book[i].Title;
cout<<"nEnter Author:“; cin>>Book[i].Author;
cout<<"nEnter ISBN:“; cin>>Book[i].ISBN;
cout<<"nEnter Book No:"; cin>>Book[i].Book_No;
} display(Book,n);
}
int main()
{
input();
system("pause");;
return 0;
}
Input function
(initialize struct)
Output function
Structure declaration
Main function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-22-2048.jpg)
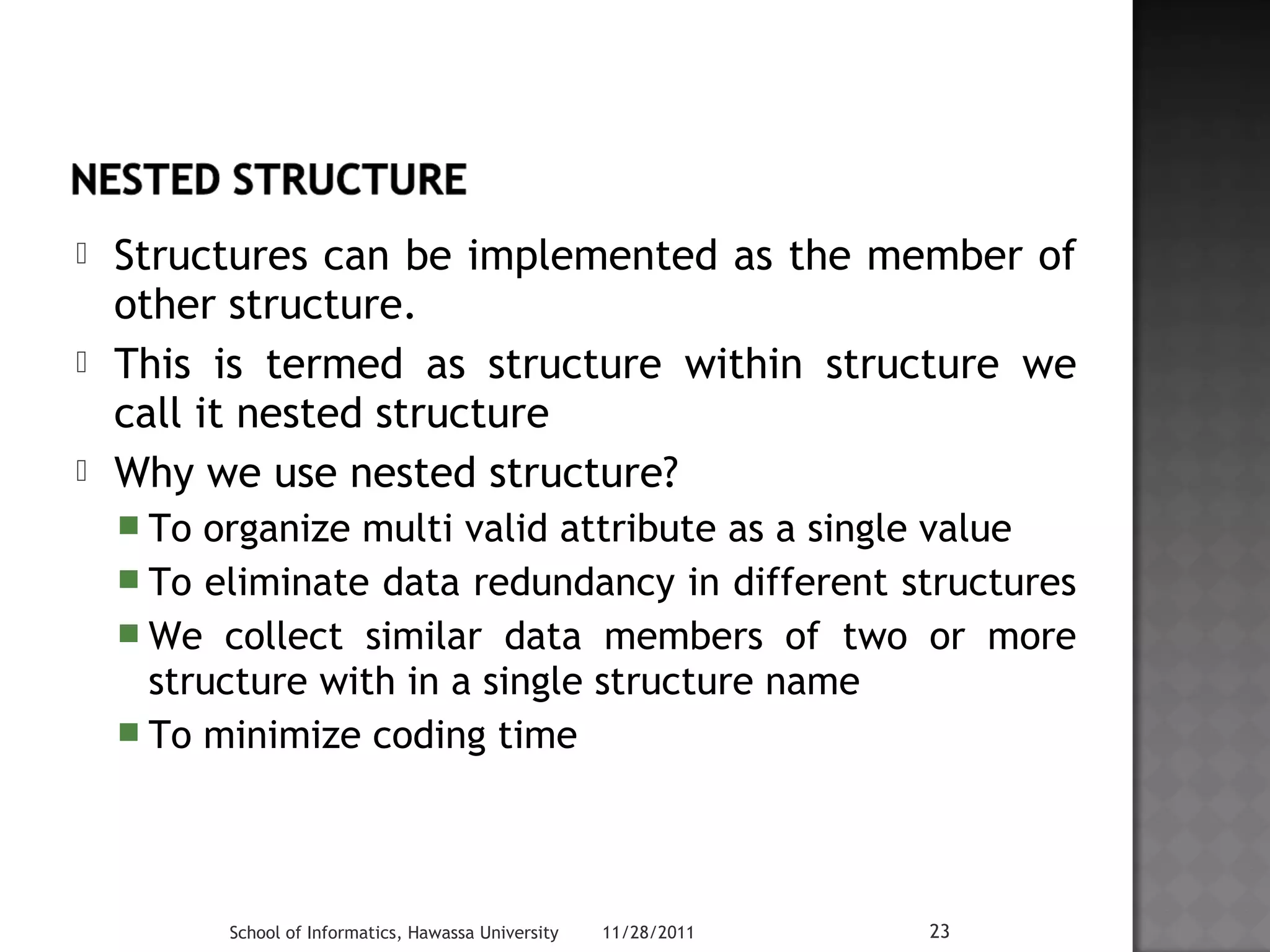
![struct date{
int day;
int month;
int year;
};
struct Employee {
char name[40];
long int Emp_ID;
char sex[5];
date dob;
Example: Using nested structure
to manipulate multi valid attribute
Example: Date of Birth has 3
integer values to manipulate it
we use Date as nested struct in
Employee struct
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 24
};
Using date structure as Member
of Employee structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-24-2048.jpg)
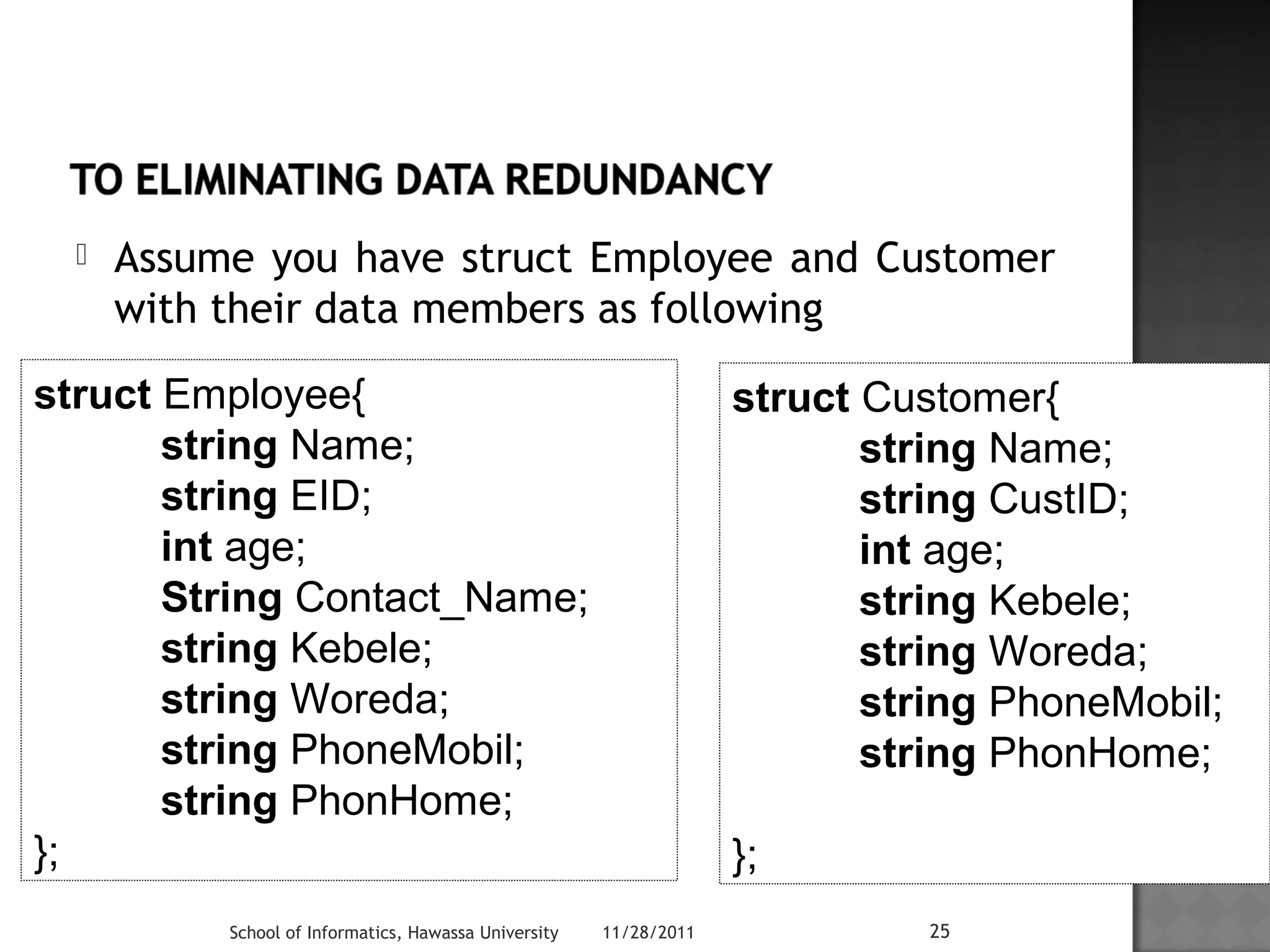


![#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct date {
int day;
int month;
int year;
};
struct Employee {
char First_Name[23];
char Last_Name[24];
date dob;
} Emp= {"DEMEKE","BIRHANU",{16 , 2, 2012}};
int main()
{
cout<<"ntFirst NametLast NametDate of Birth"<<endl;
cout<<"nt"<<Emp.First_Name<<"tt"<<Emp.Last_Name<<"tt"
<<Emp.dob.day<<"-"<<Emp.dob.month<<"-"<<Emp.dob.year<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
School of Informatics, Hawassa University 11/28/2011 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04-141111083315-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-04-30-2048.jpg)
