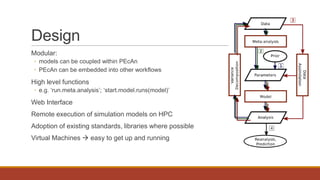
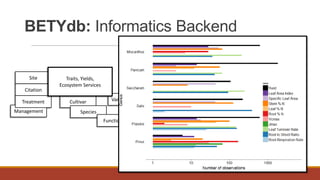
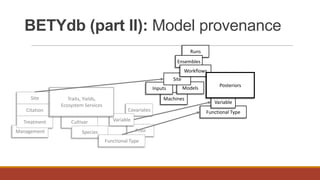
PEcAn is a framework that aims to synthesize heterogeneous data and bridge the gap between conceptual and computational ecosystem models. It allows users to summarize current knowledge based on available data and mechanistic models, and identify sources of uncertainty to prioritize future data collection and model improvement. PEcAn has a modular design that allows models to be coupled within it or embedded in other workflows. It includes high-level functions and a web interface for remote execution and visualization of simulation models on high-performance computers. PEcAn modules support analysis, modeling, utilities, and an informatics backend database.