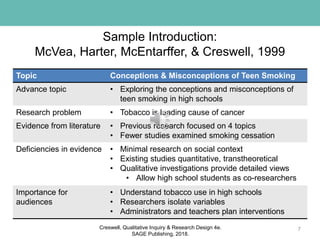
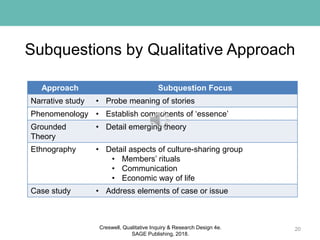
This document discusses key elements of developing a qualitative research study, including the problem statement, purpose statement, and research questions. It provides guidance on writing each element to properly encode and reflect the chosen qualitative approach. The problem statement should create a rationale and need for the study. The purpose statement identifies the qualitative approach, central phenomenon, and participants/site. Research questions include an overarching central question and several open-ended subquestions that further divide and explore the central question. Examples are given for how to write each element through different qualitative lenses.