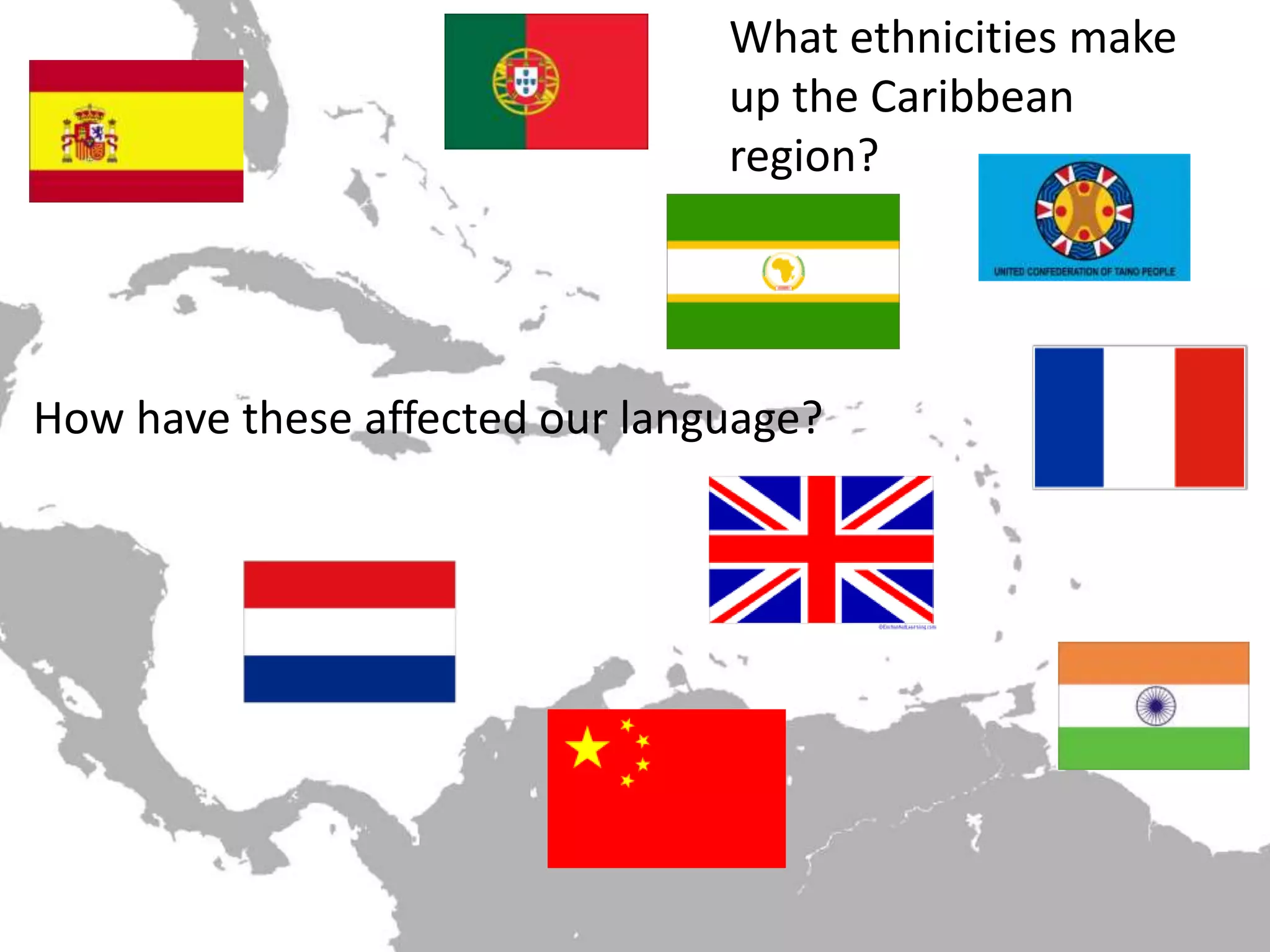
The document discusses language and ethnicity. It defines ethnicity as being identified with a group descended from common ancestors who share cultural traits like language, religion, and dress. Ethnic varieties of English arise from the languages of immigrant groups and can influence mainstream English over time through the spread of lexical and grammatical features. The document asks questions about ethnic identity and the relationship between ethnicity and language, and provides examples of characteristics and influences on ethnic varieties of English in the US and expressions that have spread to mainstream English from ethnic varieties.