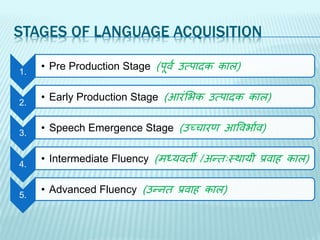
The present slides deal with language acquisition theory and its different stages. Language acquisition takes place when one consciously acquires a language. It undergoes various stages- Pre-production stage, Early production stage, Speech emergence stage, Intermediate fluency and Advanced fluency. It begins from developing BICS (Basic Interpersonal Communicative Skills) to CALP (Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency). The whole process involves quality and quantity of the language that one hears and consistency of the reinforcement offered by others which helps in shaping the child's language behaviour.