Embed presentation
Download to read offline

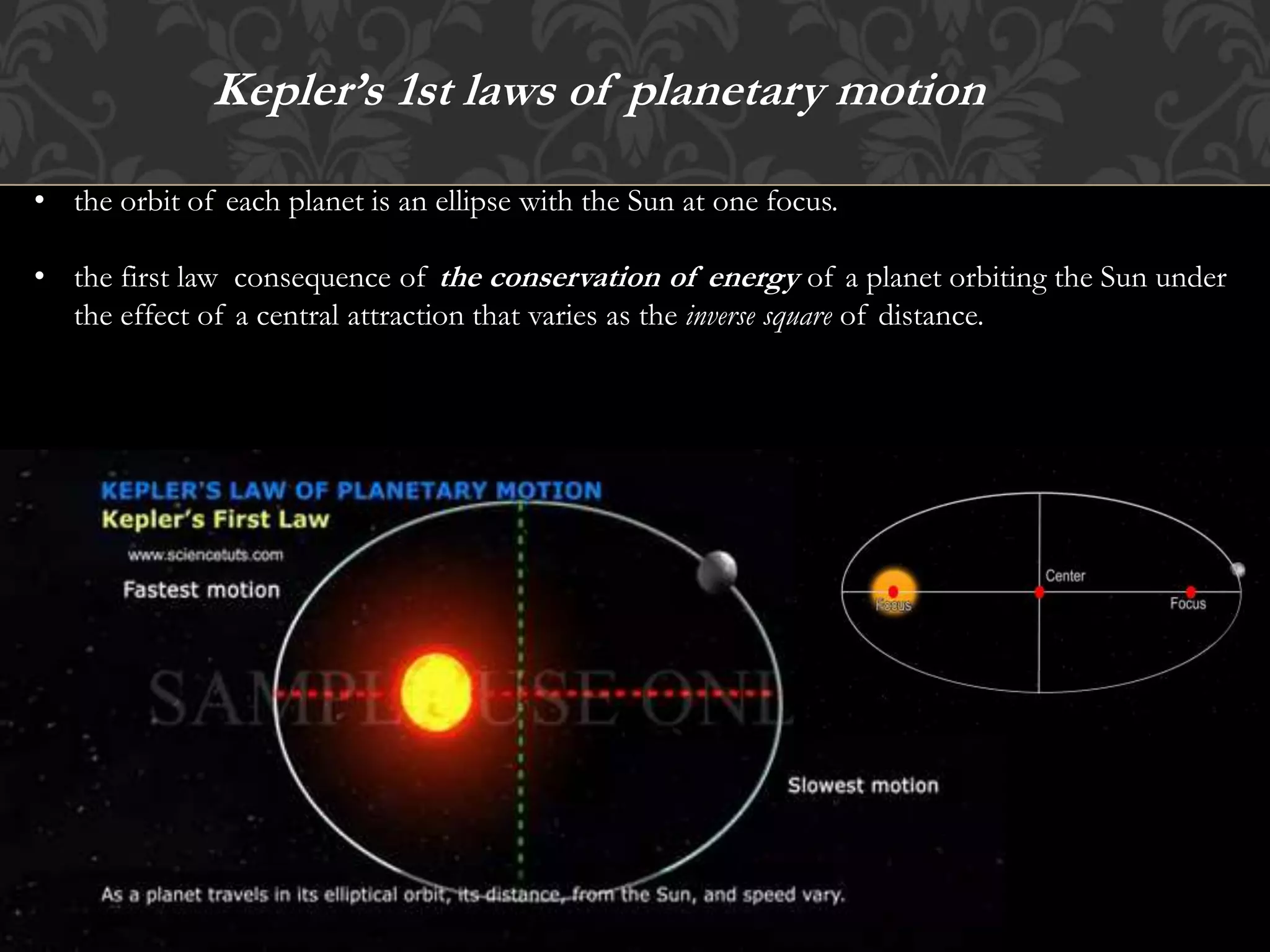
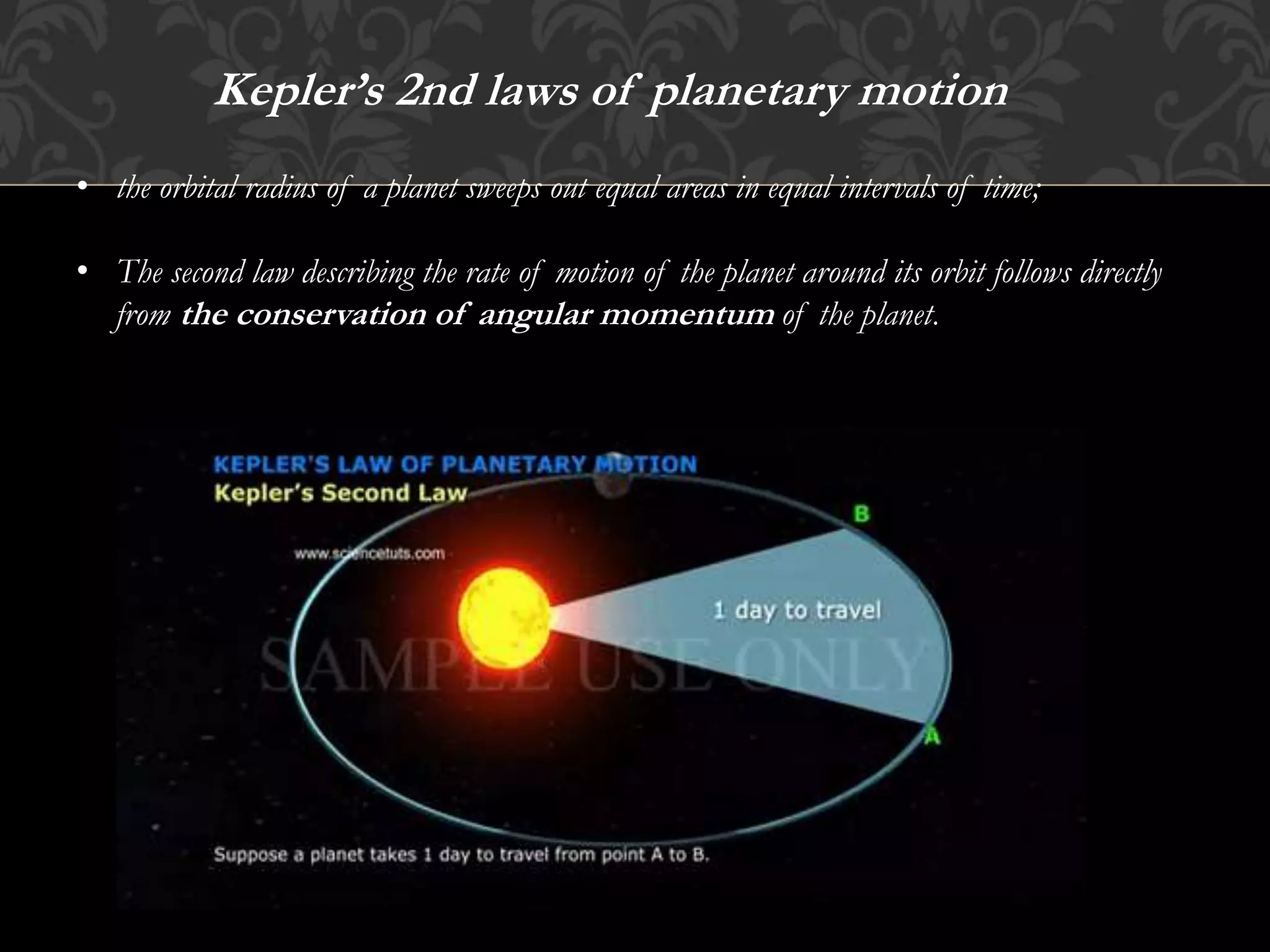
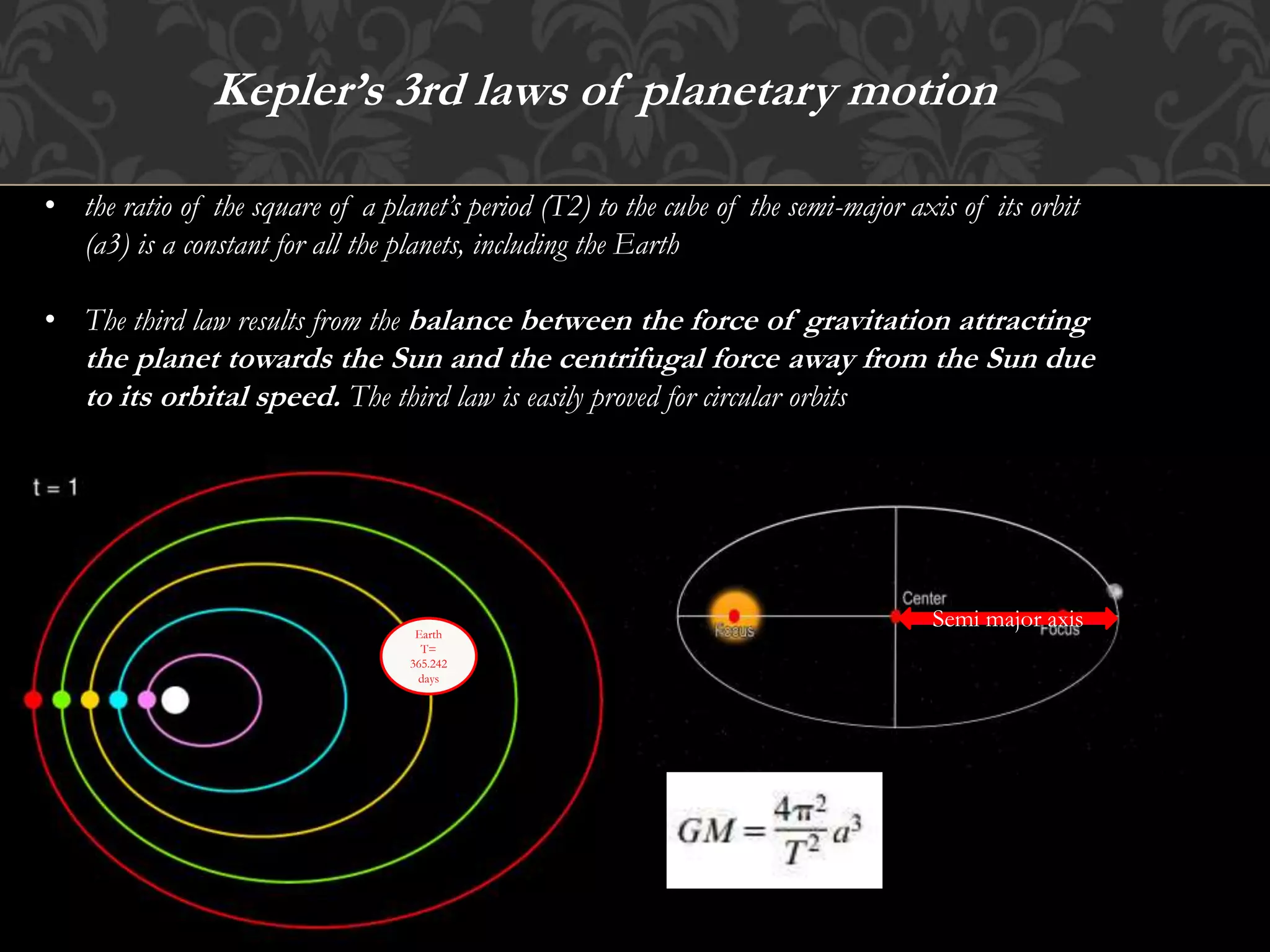
Kepler's laws of planetary motion describe the elliptical orbits of planets with the sun at one focus, the equal area sweep of planetary orbits, and the relationship between a planet's orbital period and the size of its orbit. The first law relates to energy conservation in gravitational fields, the second law is derived from angular momentum conservation, and the third law links gravitational force and centrifugal force. These principles apply to all planets, including Earth, which has an orbital period of approximately 365.242 days.




