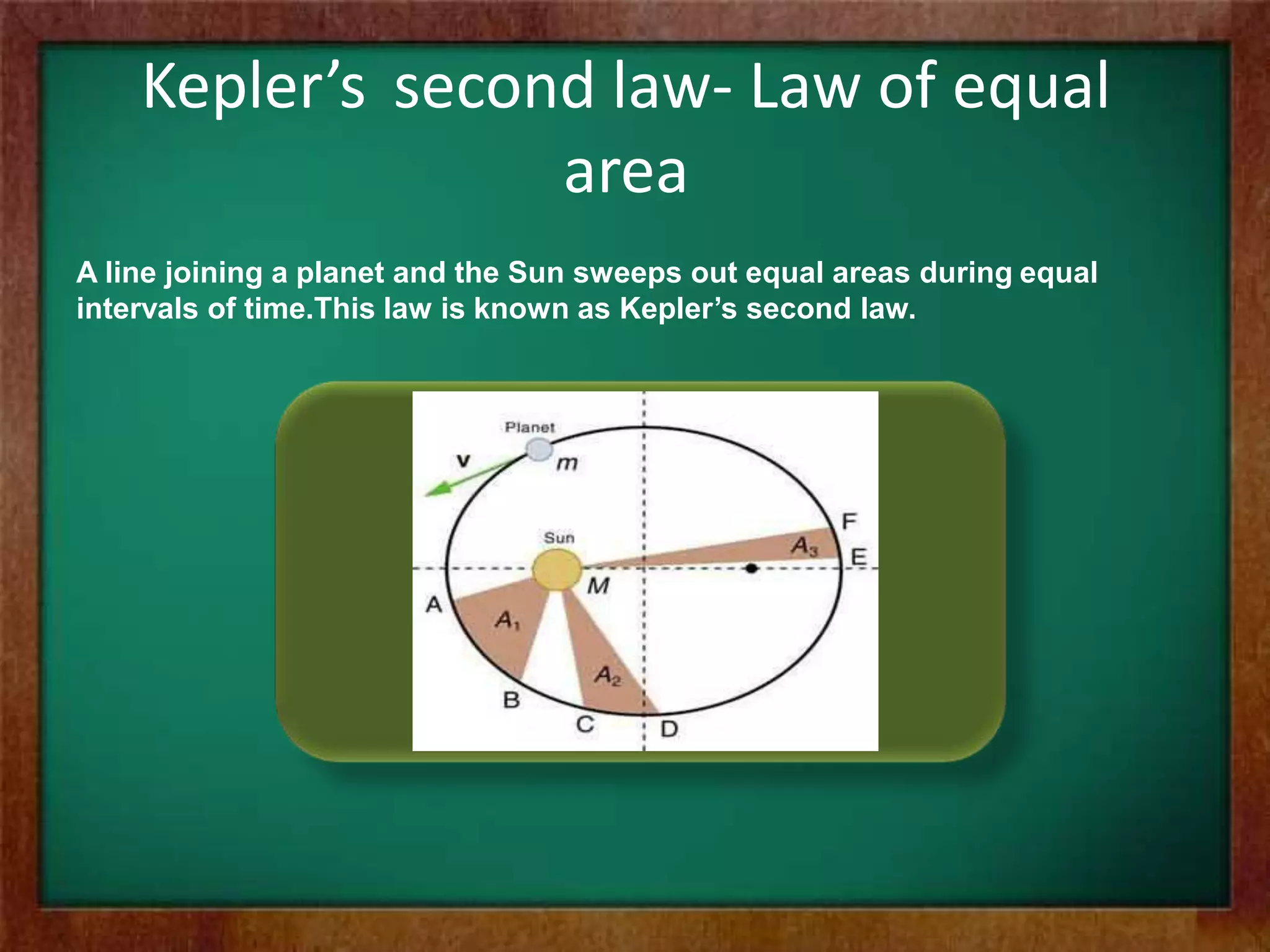
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer best known for his laws of planetary motion. Kepler's three laws describe the motion of planets around the sun: 1) planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus, 2) a line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times, and 3) the square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis. Kepler's laws formed a basis for Isaac Newton's theory of universal gravitation and are still important for studying planetary orbits and satellite motion.