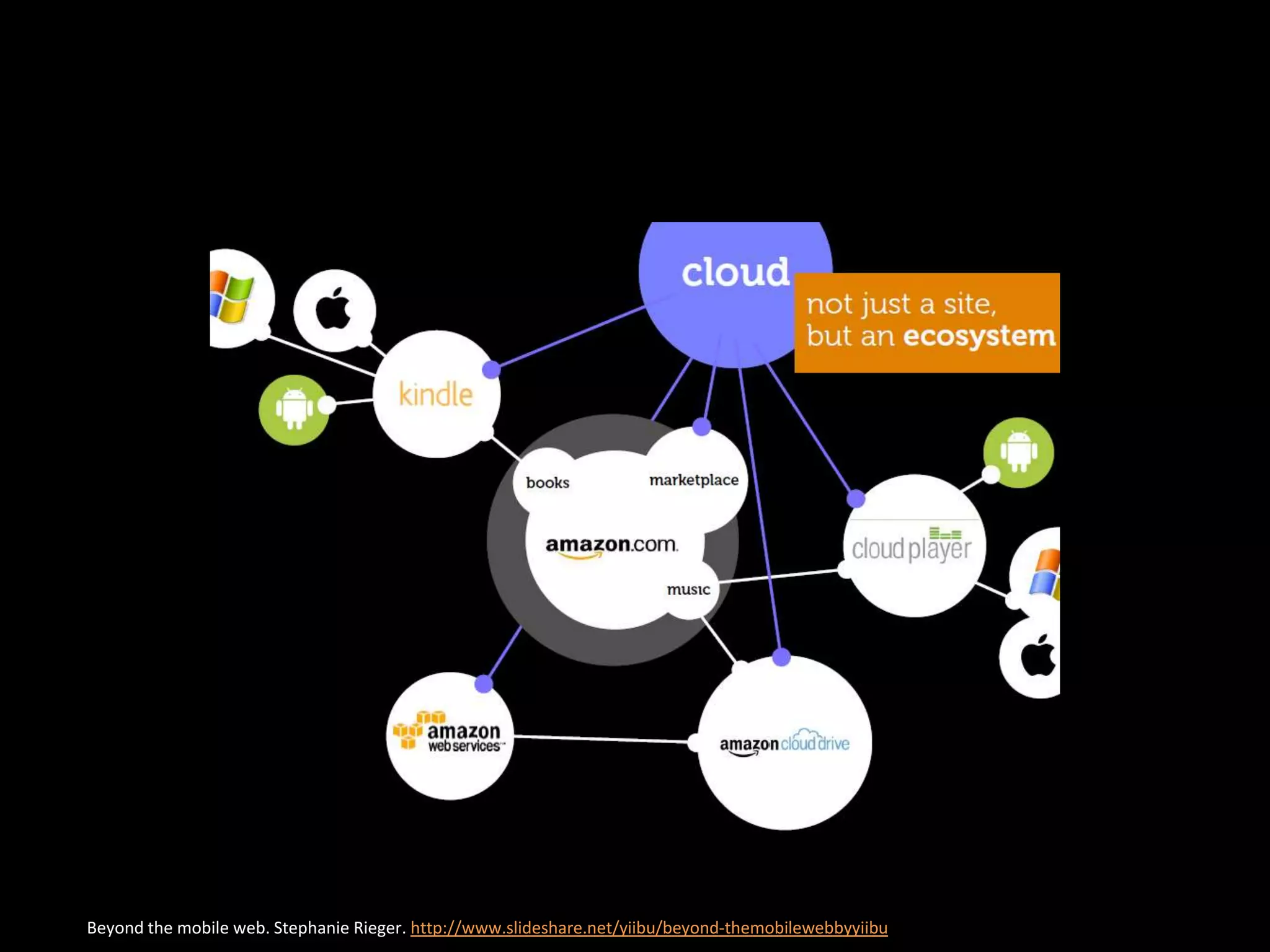
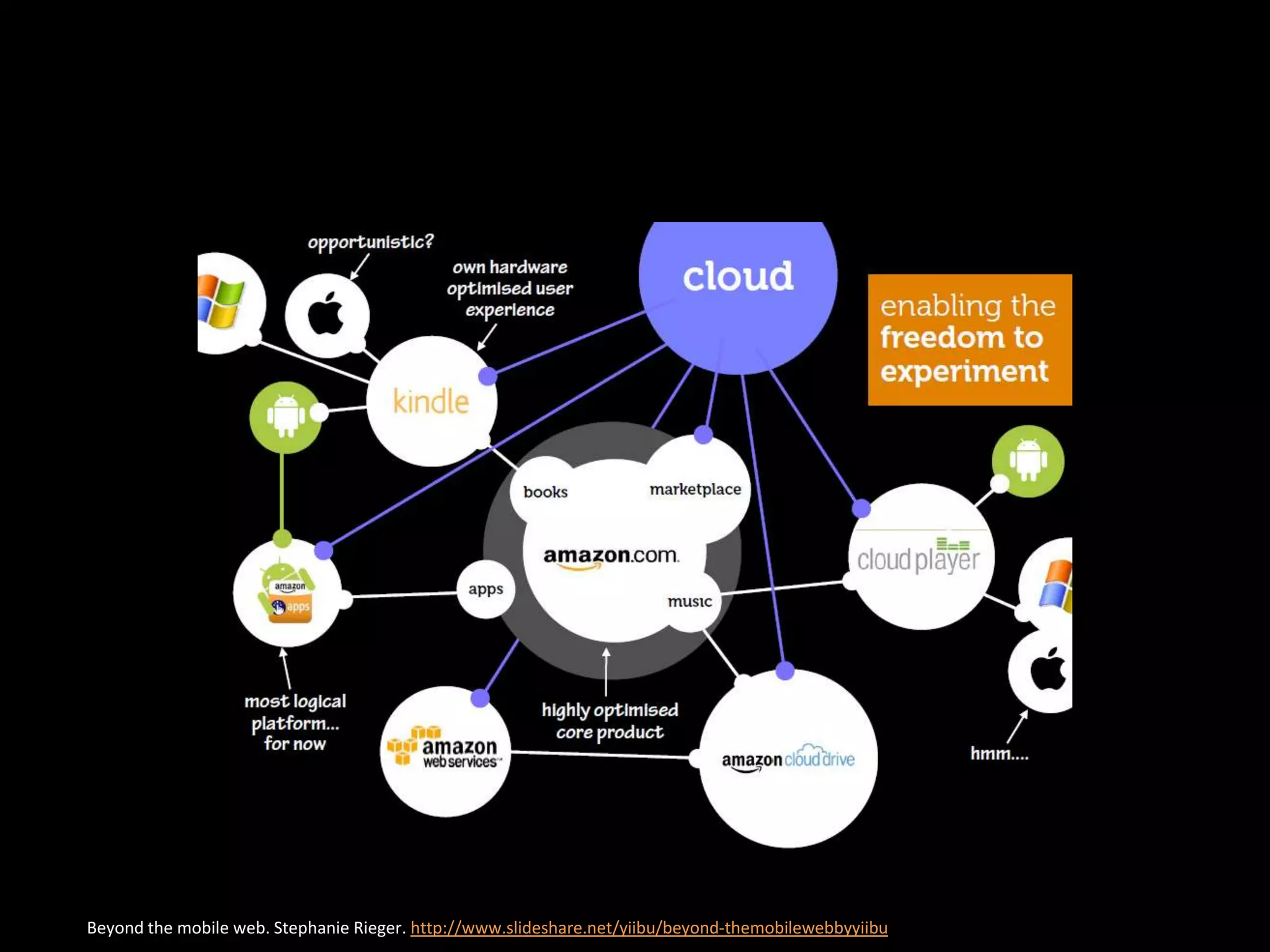
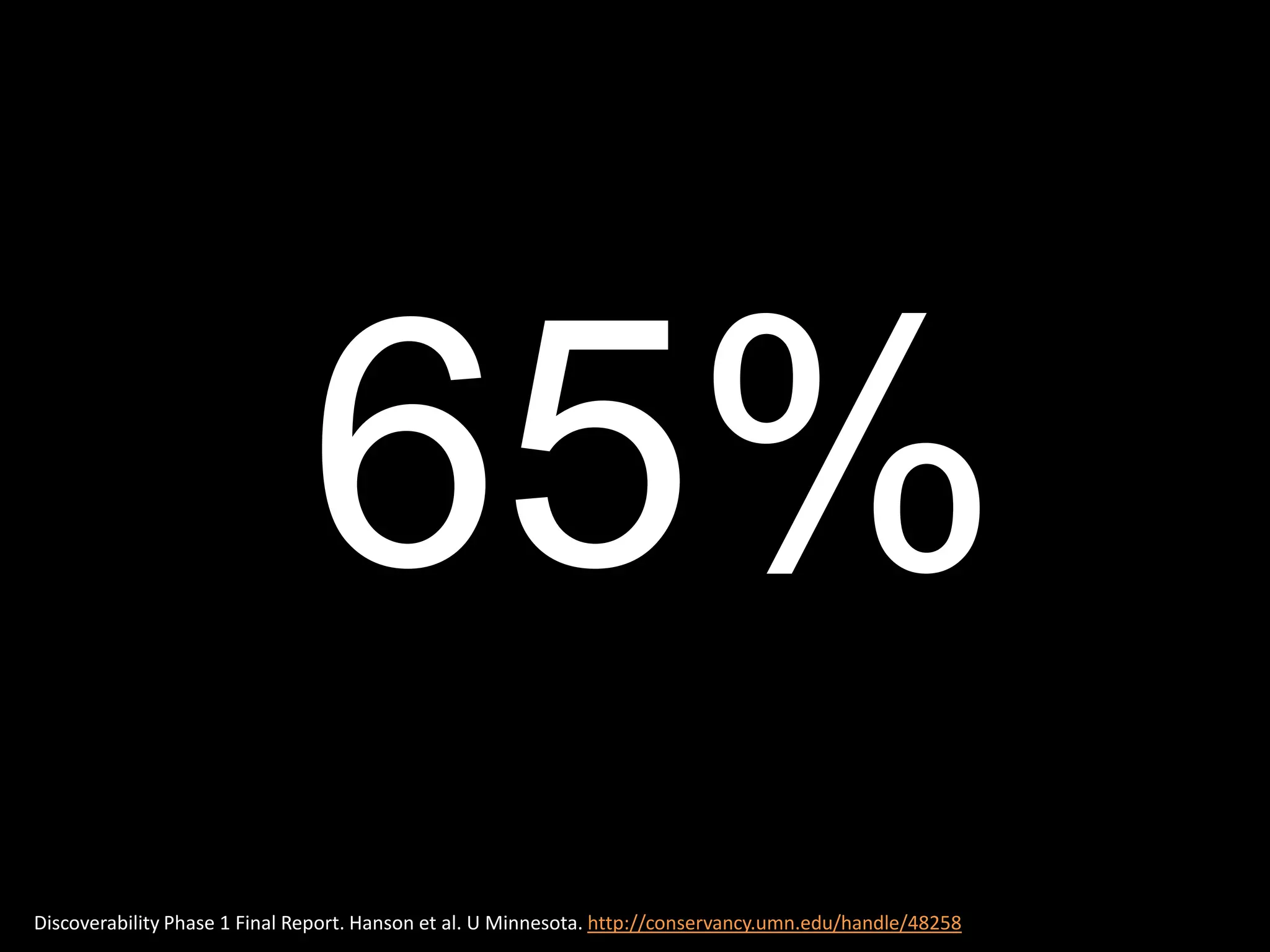
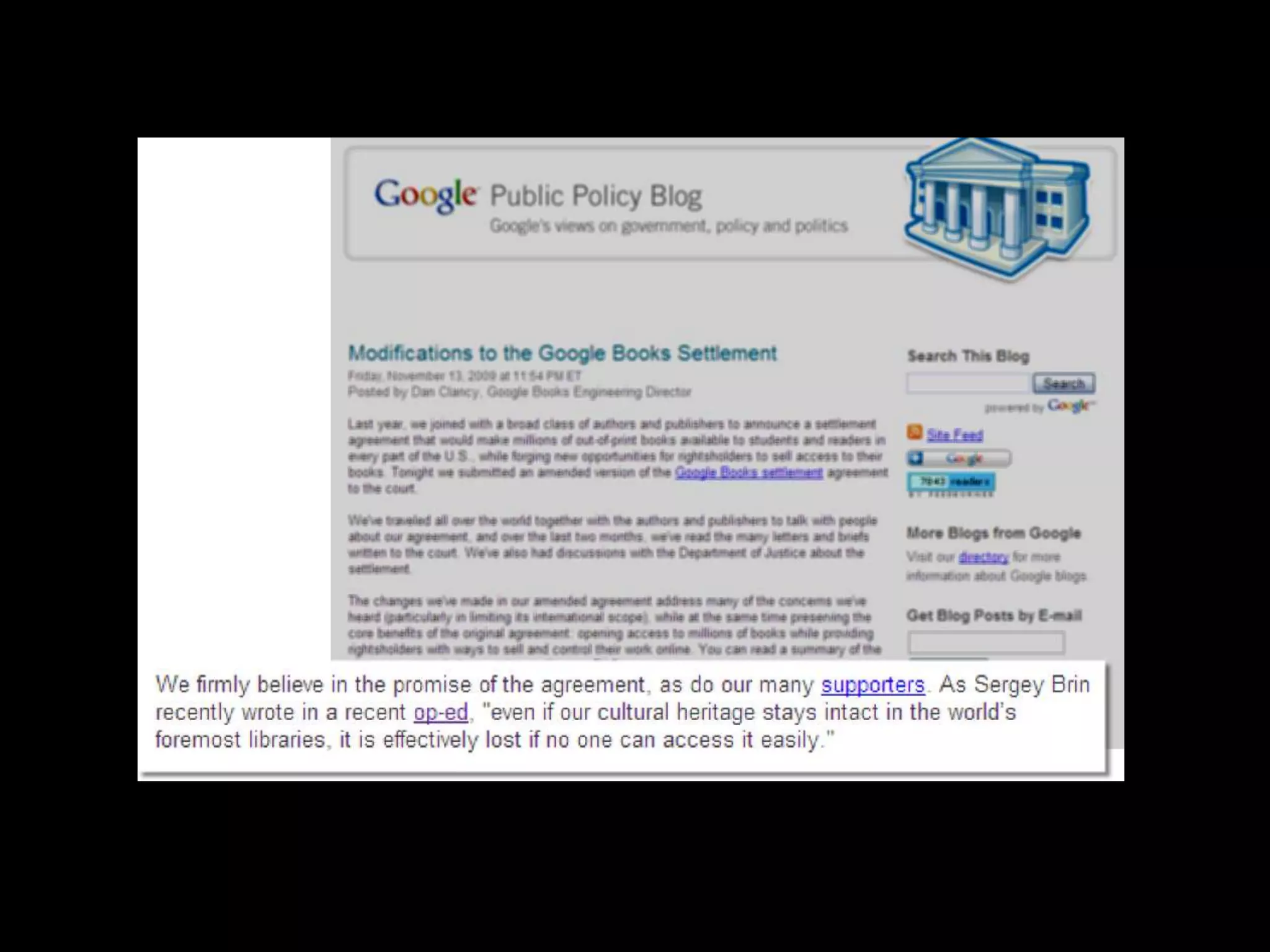
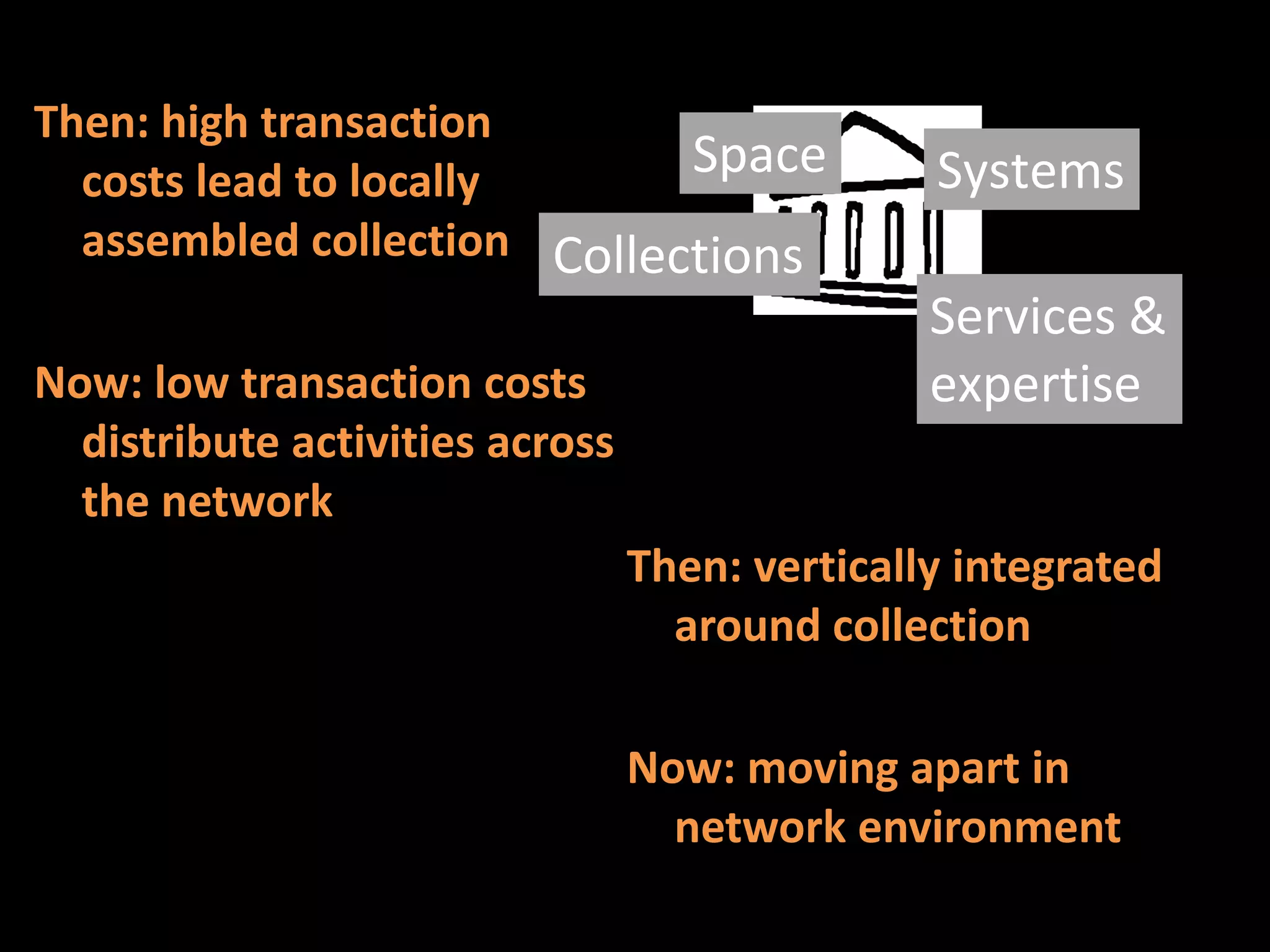
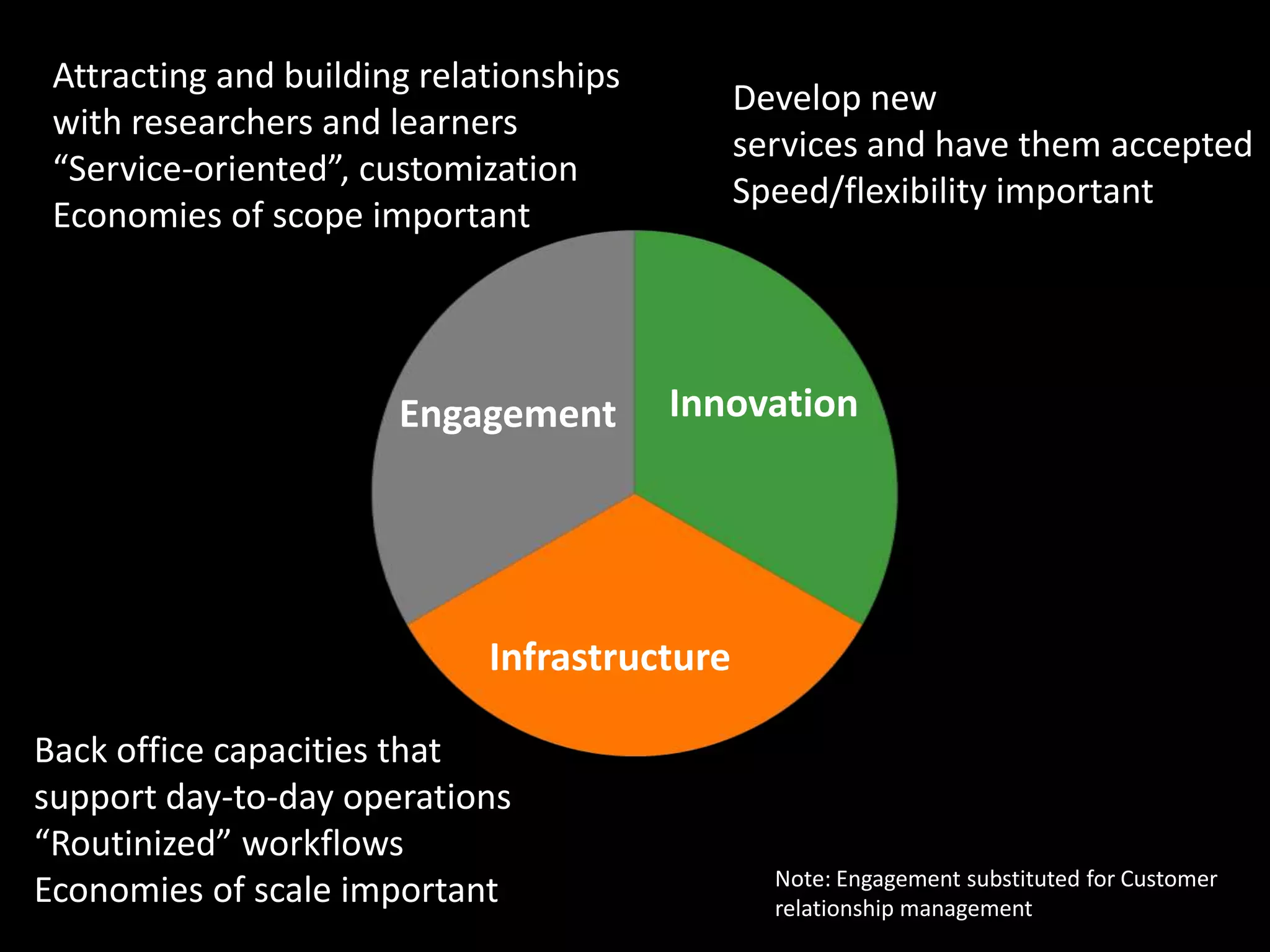
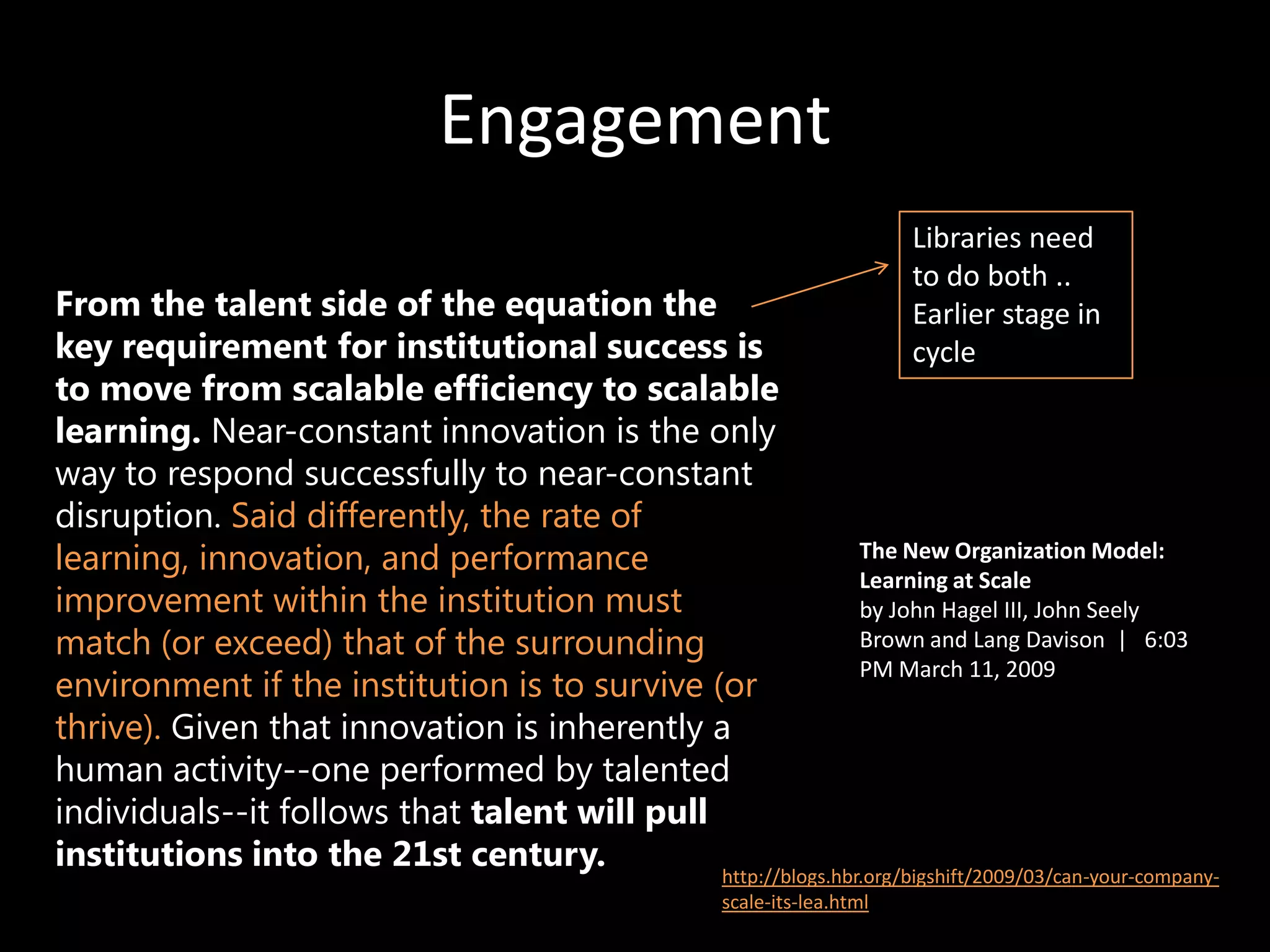
The document discusses the evolving role of research libraries in the context of increasing enrollment, costs, and declining state funding. It emphasizes the need for libraries to shift from collection-centric models to engagement-based strategies that leverage cloud-based infrastructures and promote collaboration with researchers and learners. The future of libraries is envisioned as engagement-centered, focusing on community development and knowledge production to enhance their impact and adaptability in a rapidly changing environment.