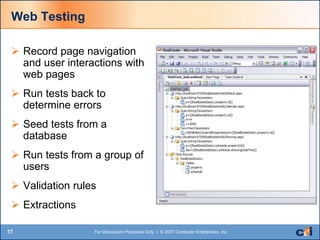
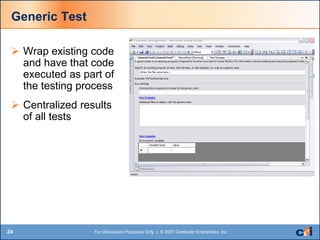
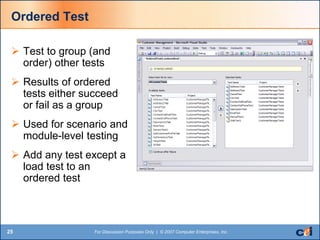
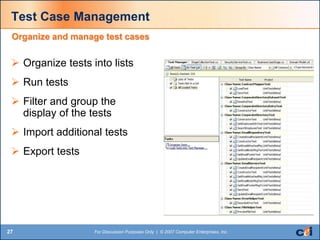
The document discusses automated testing tools in Visual Studio Team Services/Team Foundation Server (VSTS/TFS) including unit, web, load, and manual testing. It summarizes the benefits of these tools such as increased code quality through testing, code analysis, and issue identification. Key aspects covered include unit testing, code coverage, static code analysis, web testing, load/stress/performance testing, and test case management.














![15 For Discussion Purposes Only | © 2007 Computer Enterprises, Inc.
Static Code Analysis
Provides a means to enforce coding standards
Configurable
Reduction in code reviews for small issues
Provides guidance on how to fix
Define a check-in policy to enforce code analysis pass
Coverage includes issues with design, globalization, interoperability,
maintainability, naming, performance, reliability, security, and usage
Warning: developers can supress messages with attirbute
[SuppressMessage("AdventureWorks.Rules", "AW14441")]
MORE INFO see, “Writing Quality Code” in TFS documentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/justin-presentation-ppt-upload262/85/Justin-Presentation-PPT-Upload-15-320.jpg)