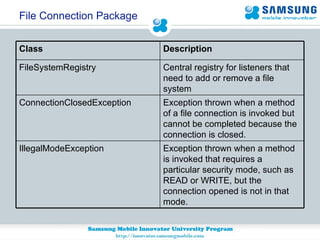
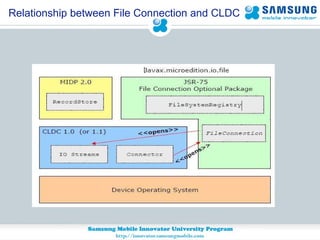
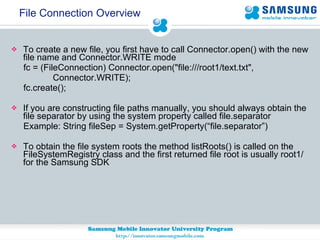
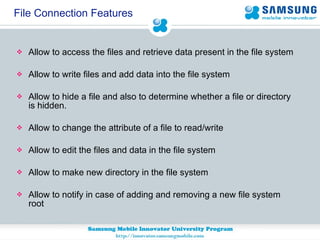
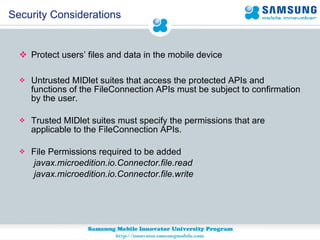
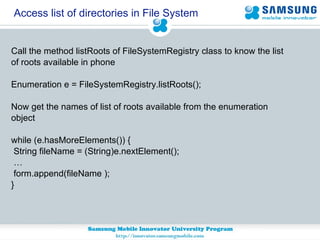
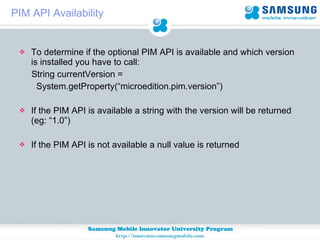
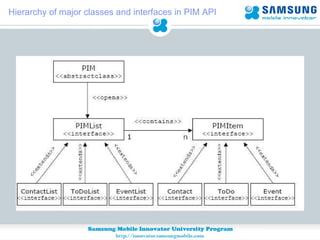
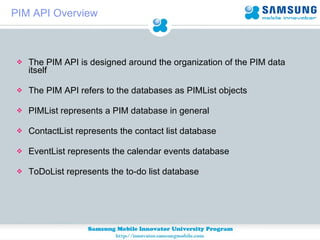
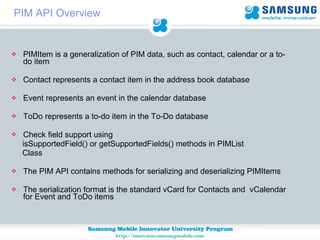
JSR 75 defines optional APIs for accessing files and personal information on mobile devices. The FileConnection API allows accessing and modifying files, while the PIM API provides access to contact, calendar, and to-do list data. Security permissions are required for untrusted apps to access these APIs. The document provides examples of using these APIs to read, write, and modify files and PIM data.








![Read Text File from File System Read the byte data of the text file byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int length = fis.read(b, 0, 1024); convert the byte data to string String str=new String(b,0,length); append the data in form … form.append(str);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsr75sup-100831062453-phpapp01/85/Jsr75-sup-19-320.jpg)
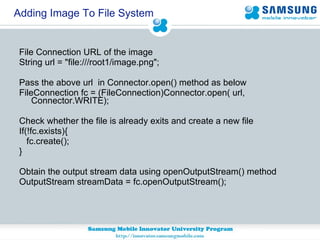
![Adding Image To File System //Add the image byte data in write() method of OutputStream //Get the byte data of the Image --- Byte[] imageBytes=ImageData; streamData.write(imageBytes); And finally close all connections streamData.close(); fc.close(); Image is successfully added in the File System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsr75sup-100831062453-phpapp01/85/Jsr75-sup-21-320.jpg)

![How To Read Telephone Number From openPIMList(int pimListType, int mode) method of PIM class retrieve PIMList object Pass the parameters PIM.CONTACT_LIST as listType and PIM.READ_WRITE as Mode PIMList pimList = PIM.getInstance().openPIMList(PIM.CONTACT_LIST, PIM.READ_WRITE); Then retrieve the enumeration of pimItems using items() method of PIMList class for (Enumeration items = pimList.items(); items.hasMoreElements();) PIMItem pimItem = (PIMItem) items.nextElement(); Now get supported field in each PIMItem int[] fields = pimItem.getPIMList().getSupportedFields();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsr75sup-100831062453-phpapp01/85/Jsr75-sup-31-320.jpg)
![How To Read Telephone Number Retrieve the data types present in each field for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) int fieldIndex = fields[i]; int dataType = pimItem.getPIMList().getFieldDataType(fieldIndex); Now in String data type get the Telephone Numbers using Contant.TEL if(dataType==PIMItem.STRING) { for (int j = 0; j < pimItem.countValues(fieldIndex); j++) { String sValue = pimItem.getString(fieldIndex, j); if(fieldIndex==Contact.TEL){ int attr = pimItem.getAttributes(fieldIndex, j); String label = pimItem.getPIMList().getAttributeLabel(attr); form=new Form(“Telephone numbers”); form.append(label+"="+sValue); display.setCurrent(form); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsr75sup-100831062453-phpapp01/85/Jsr75-sup-32-320.jpg)




