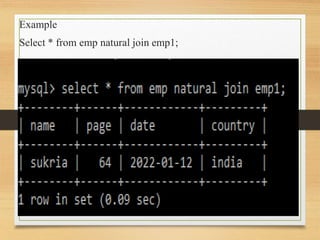
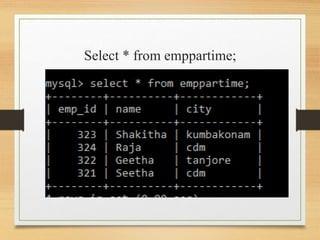
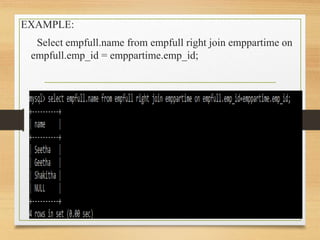
This document discusses different types of joins in SQL including inner joins, natural joins, left outer joins, and right outer joins. It provides the syntax for each type of join and examples of queries using employee data from emp and emp1 tables. Key details covered include how natural joins form a cartesian product and remove duplicate columns, and that left/right outer joins return all records from one table and matched records from the other table.