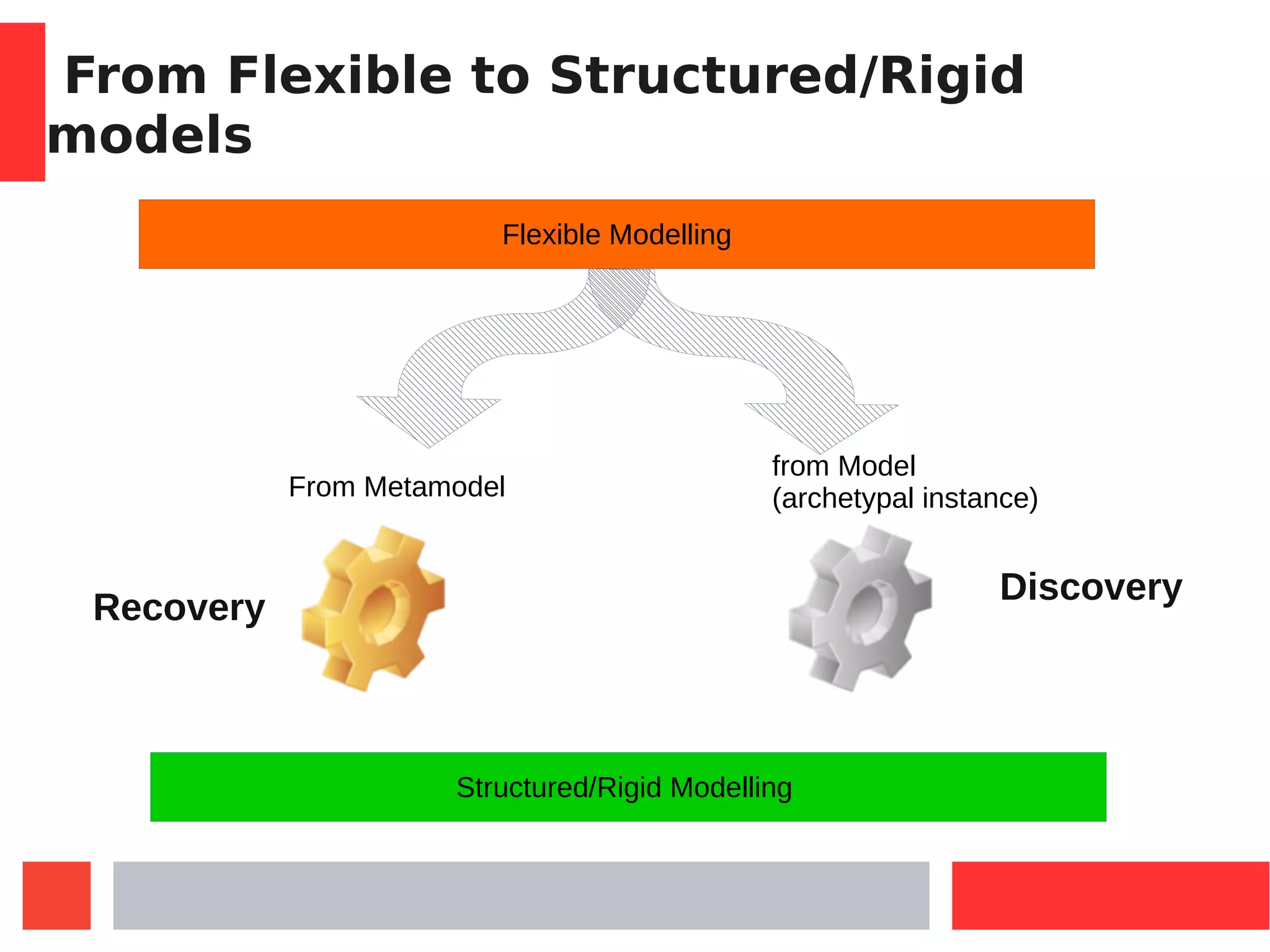
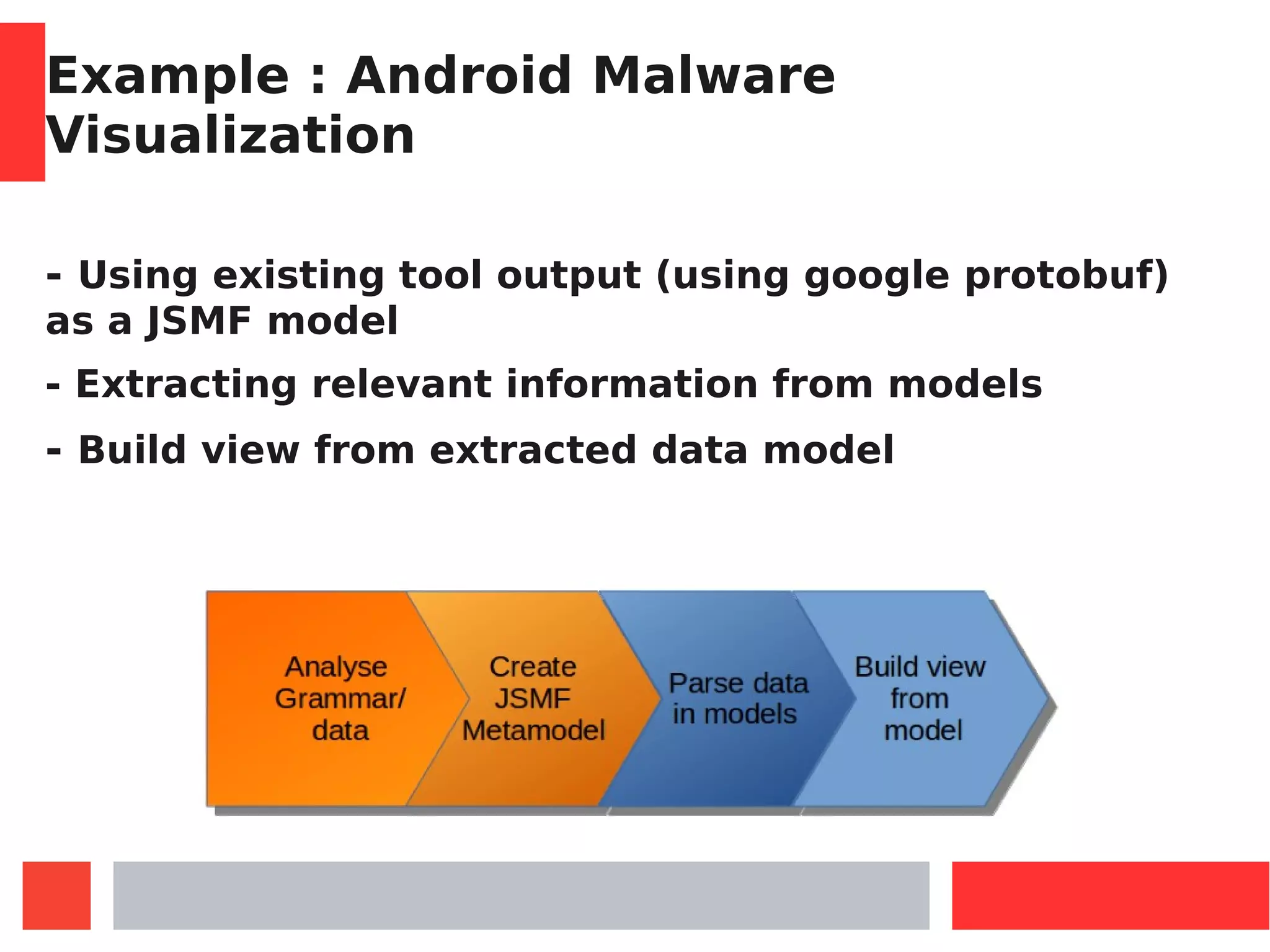
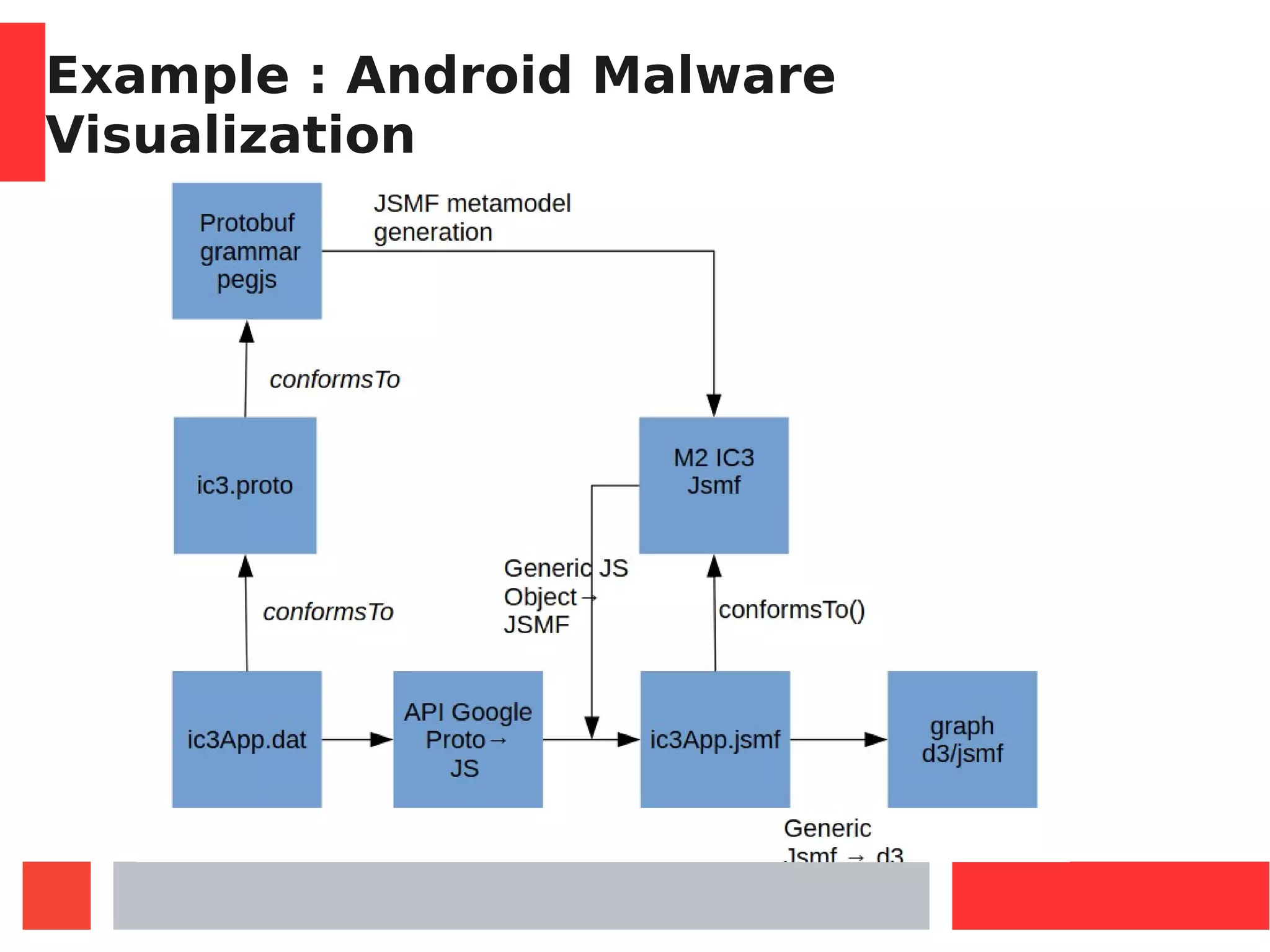
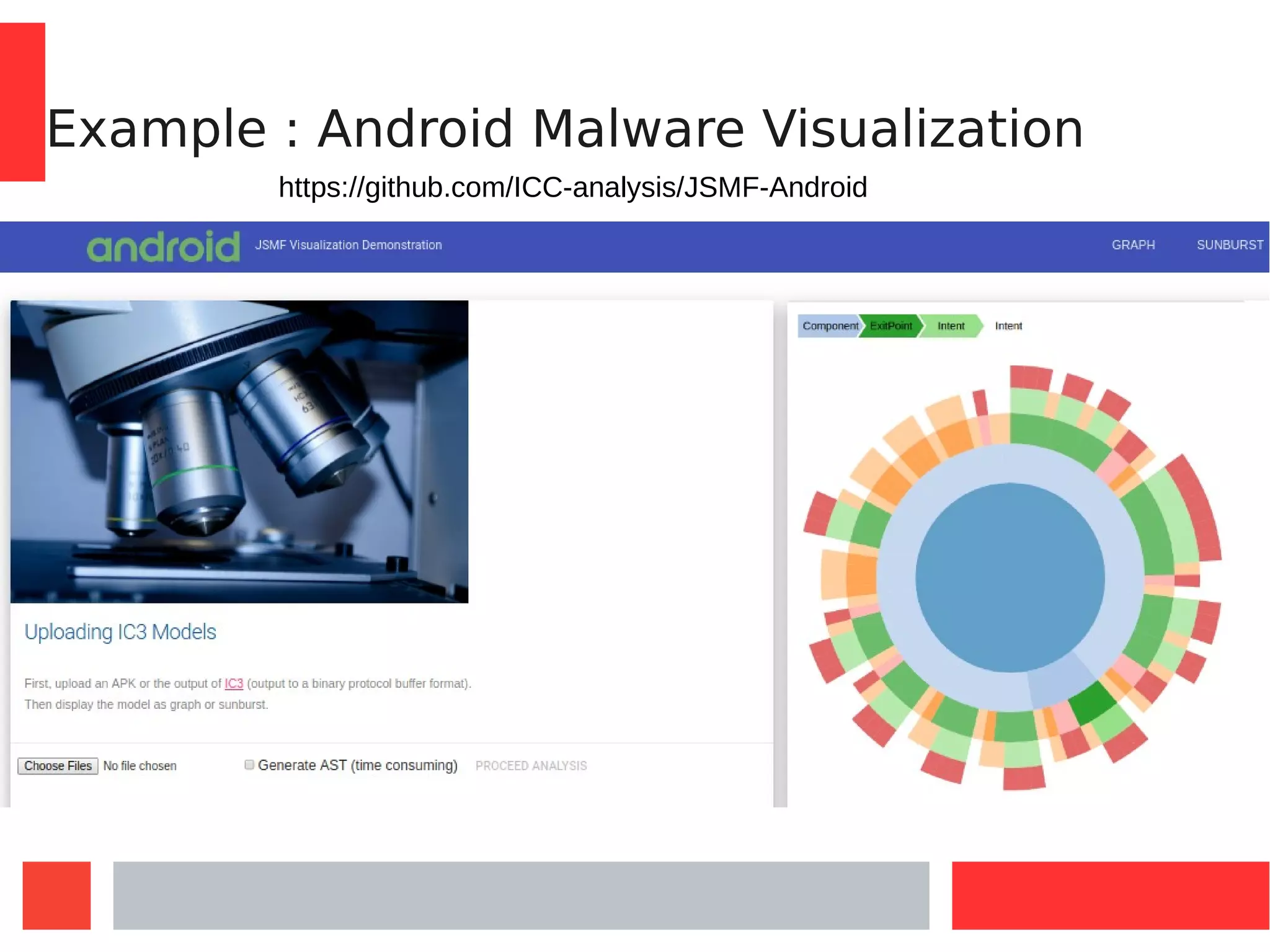
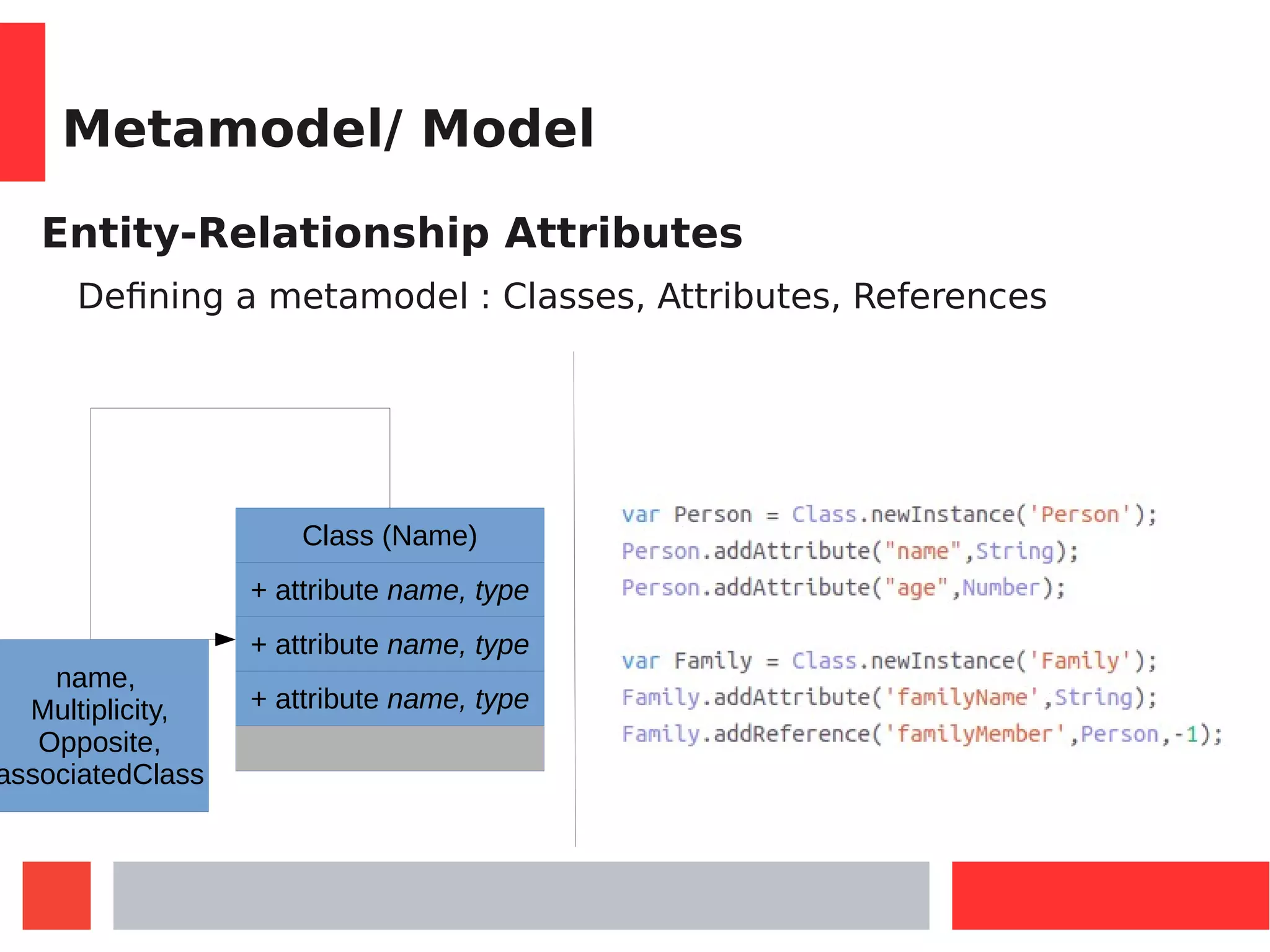
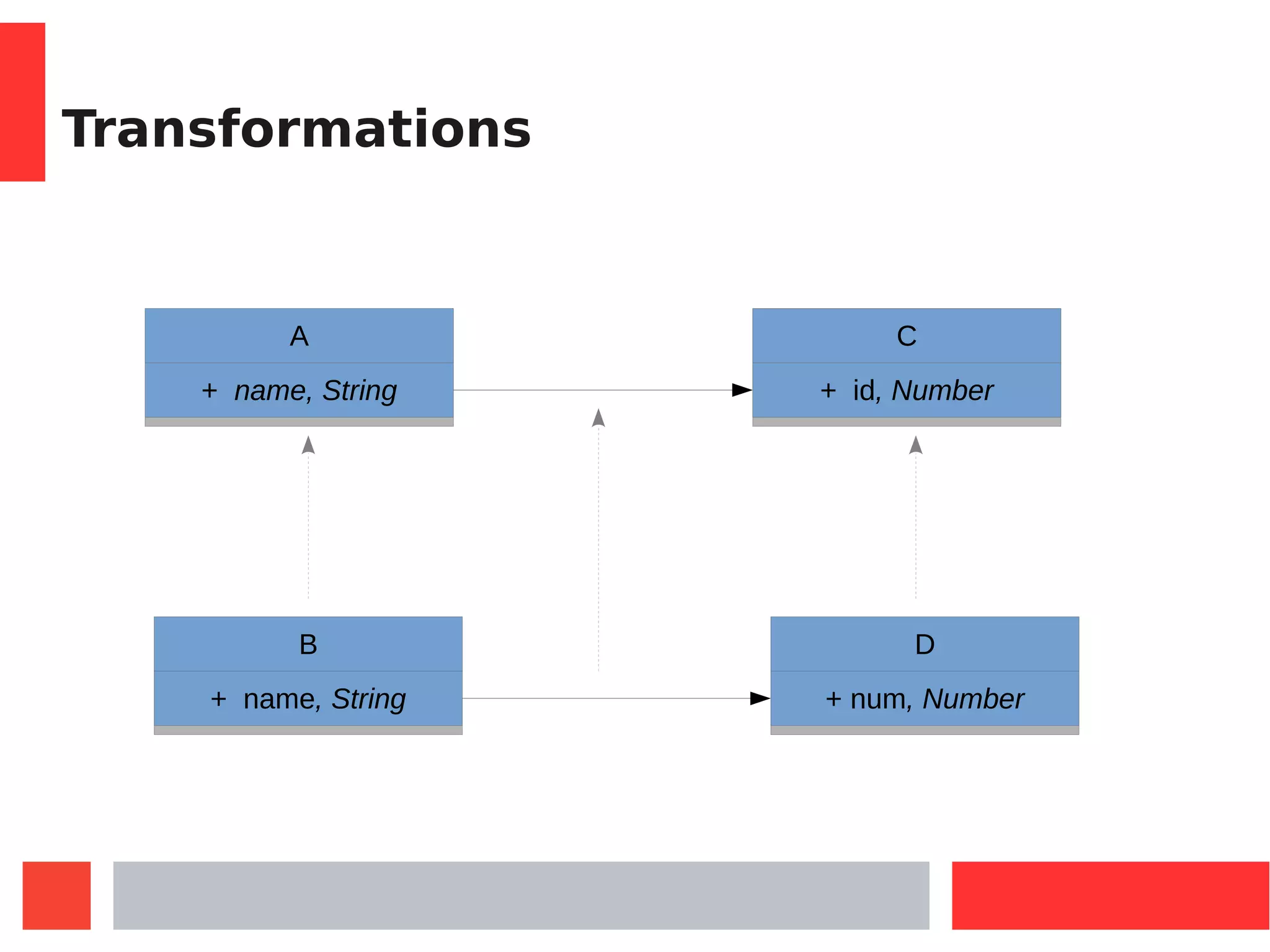
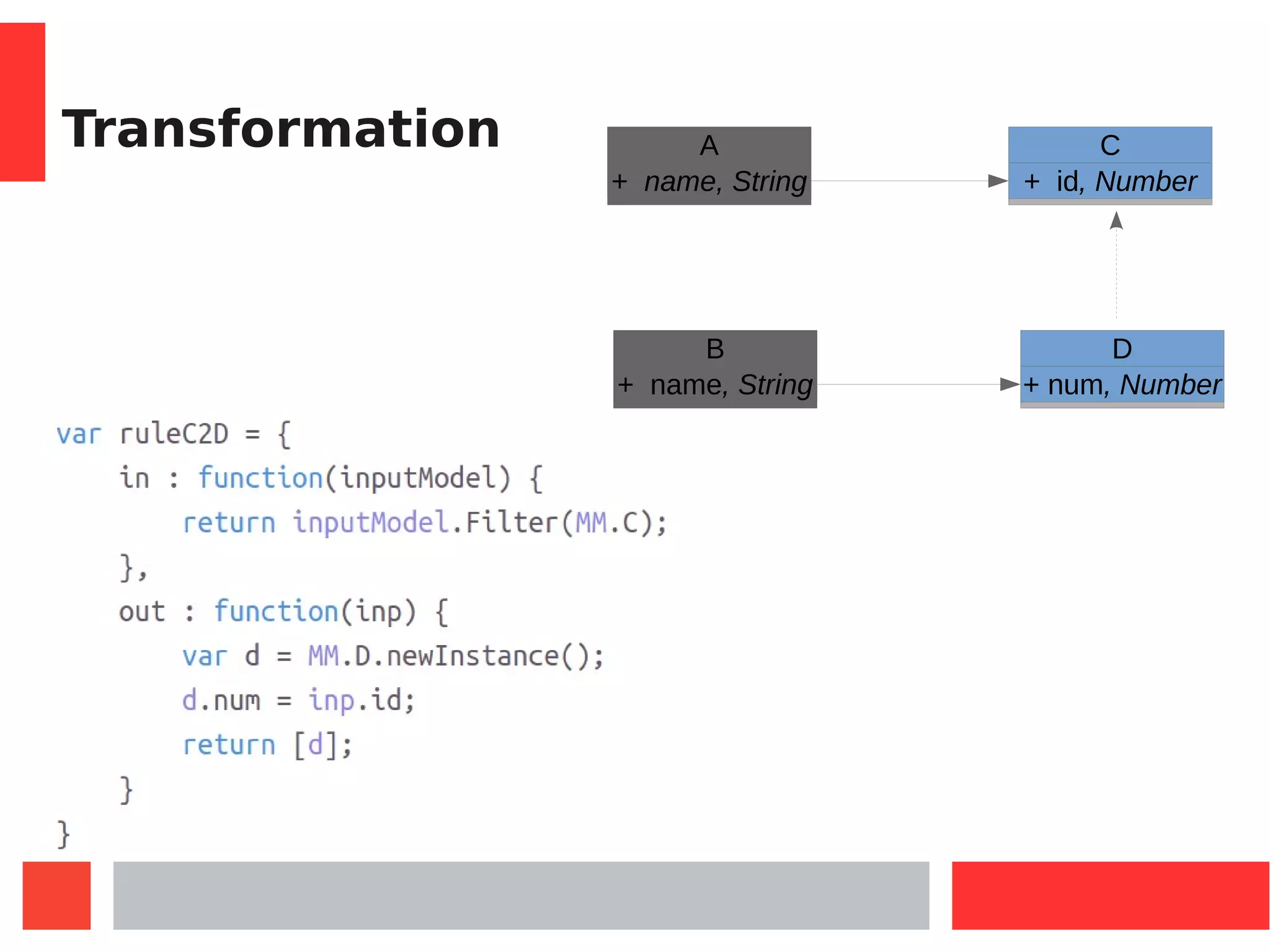
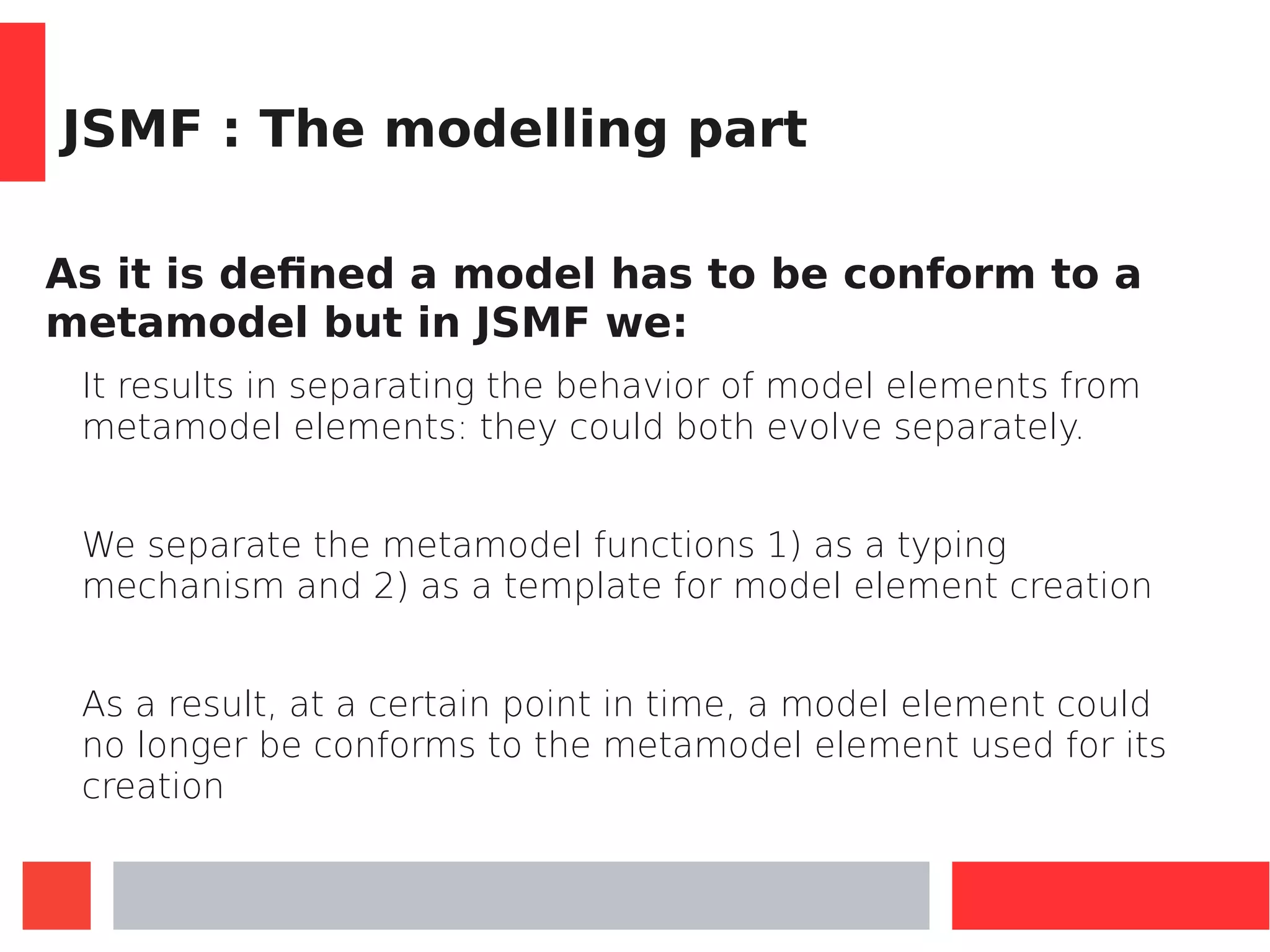
This document introduces Model-Driven Engineering (MDE) and modelling frameworks. It defines key MDE concepts like models, metamodels, and transformations. It then discusses modelling frameworks like Eclipse Modelling Framework (EMF) and their limitations. The document introduces JSMF as a new JavaScript modelling framework that aims to provide more flexibility compared to frameworks like EMF by separating model and metamodel definitions and allowing dynamic changes. It provides examples of using JSMF for tasks like Android malware visualization.


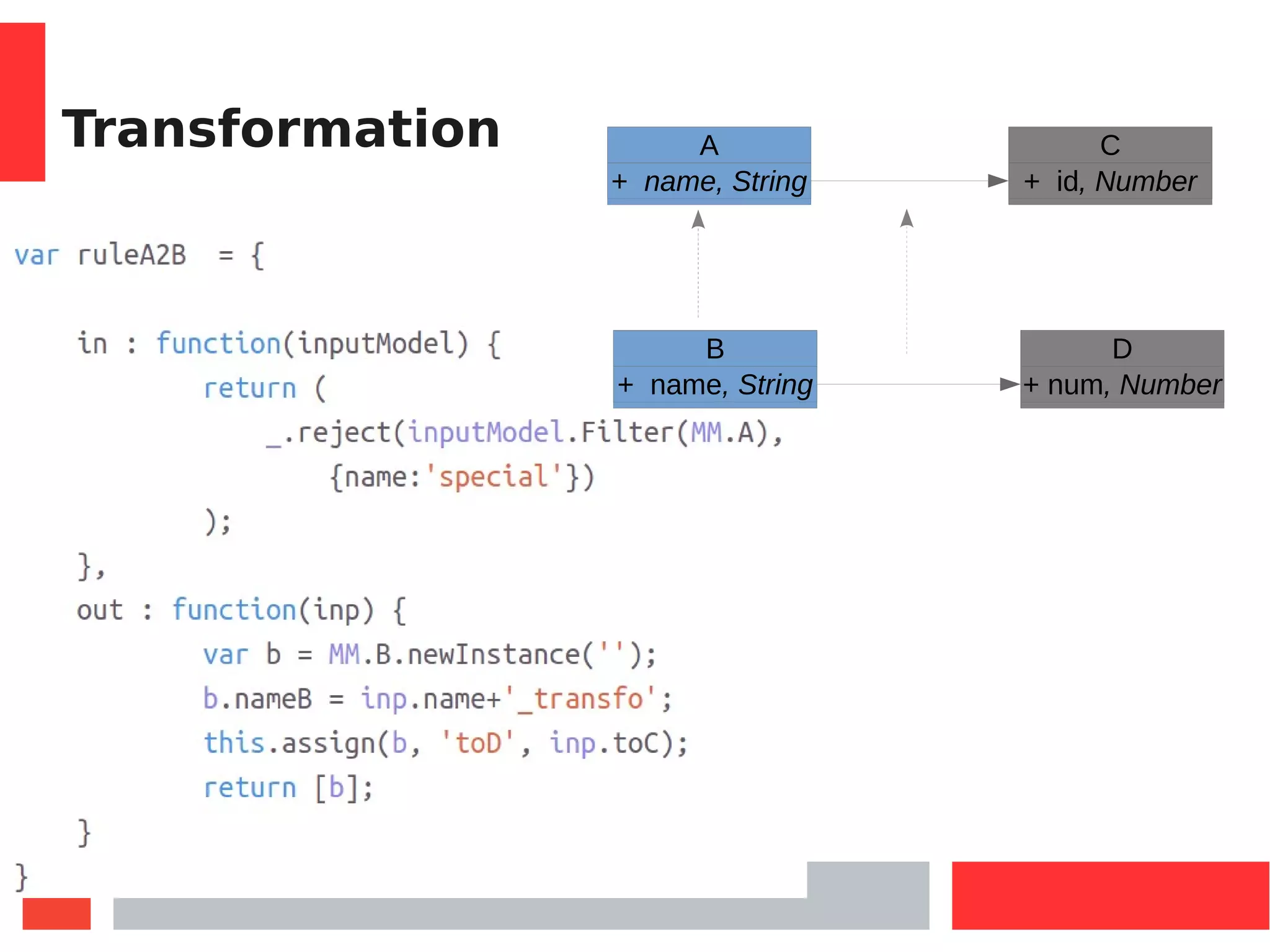
![Some specific functions
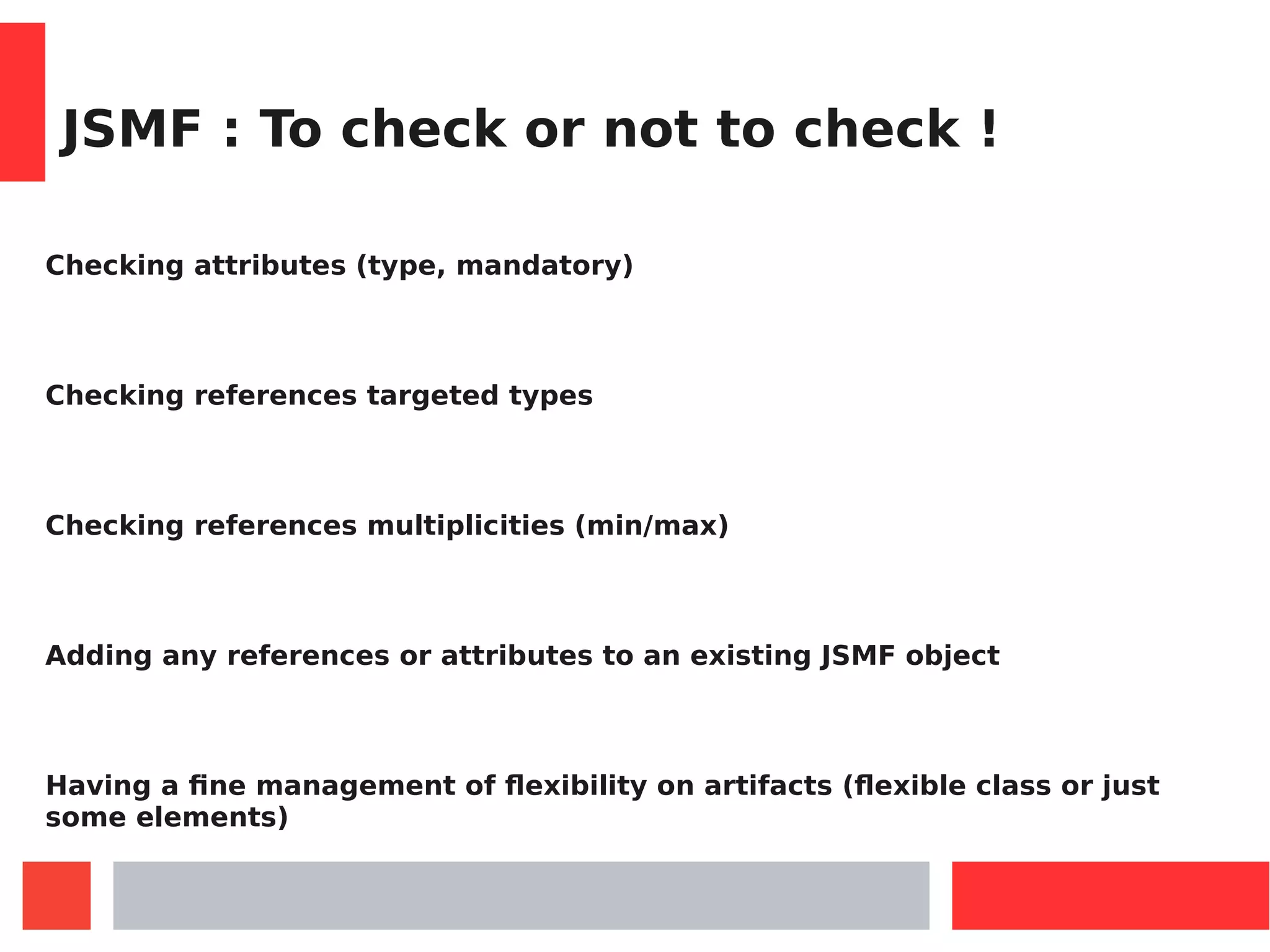
Checking attributes (type, mandatory)
const Family = Class . newInstance ( ’ Family ’ , [] , { lastname : { type : String ,
mandatory : true }}
Level of check for individual references or attributes (using
errorCallback function):
OnError.silent to avoid checking,
OnError.thow to get a JavaScript error with JSMF properties,
Implement your own error callback function!
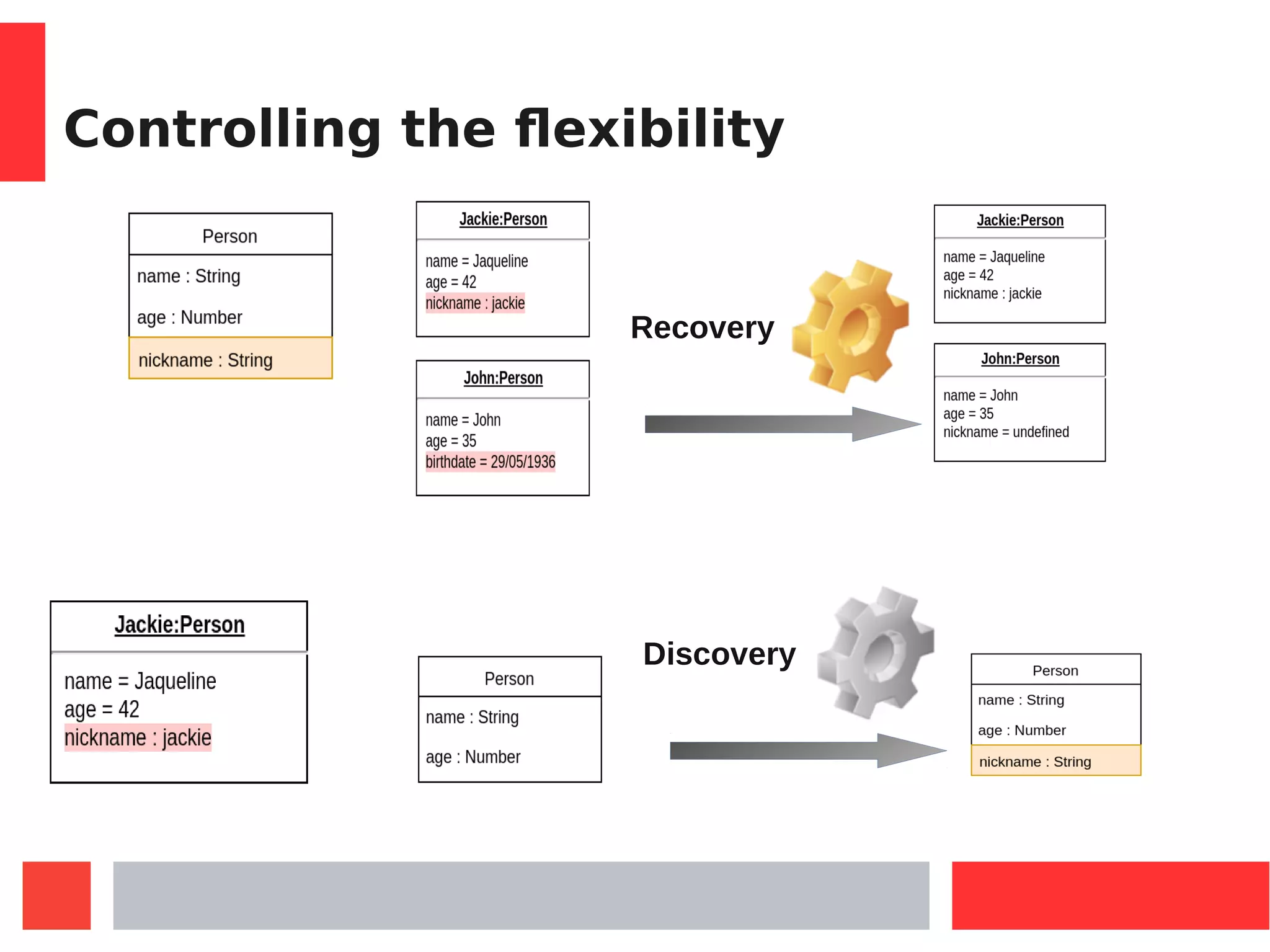
All instances of a Class can be declared flexible :
Person.setFlexible(true)
Simply adding any reference or attributes to an existing JSMF object
As any JavaScript object: one can add any property (attribute or reference)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsmfmdejs-180110154503/75/JavaScript-Modelling-Framwork-MDE-23-2048.jpg)