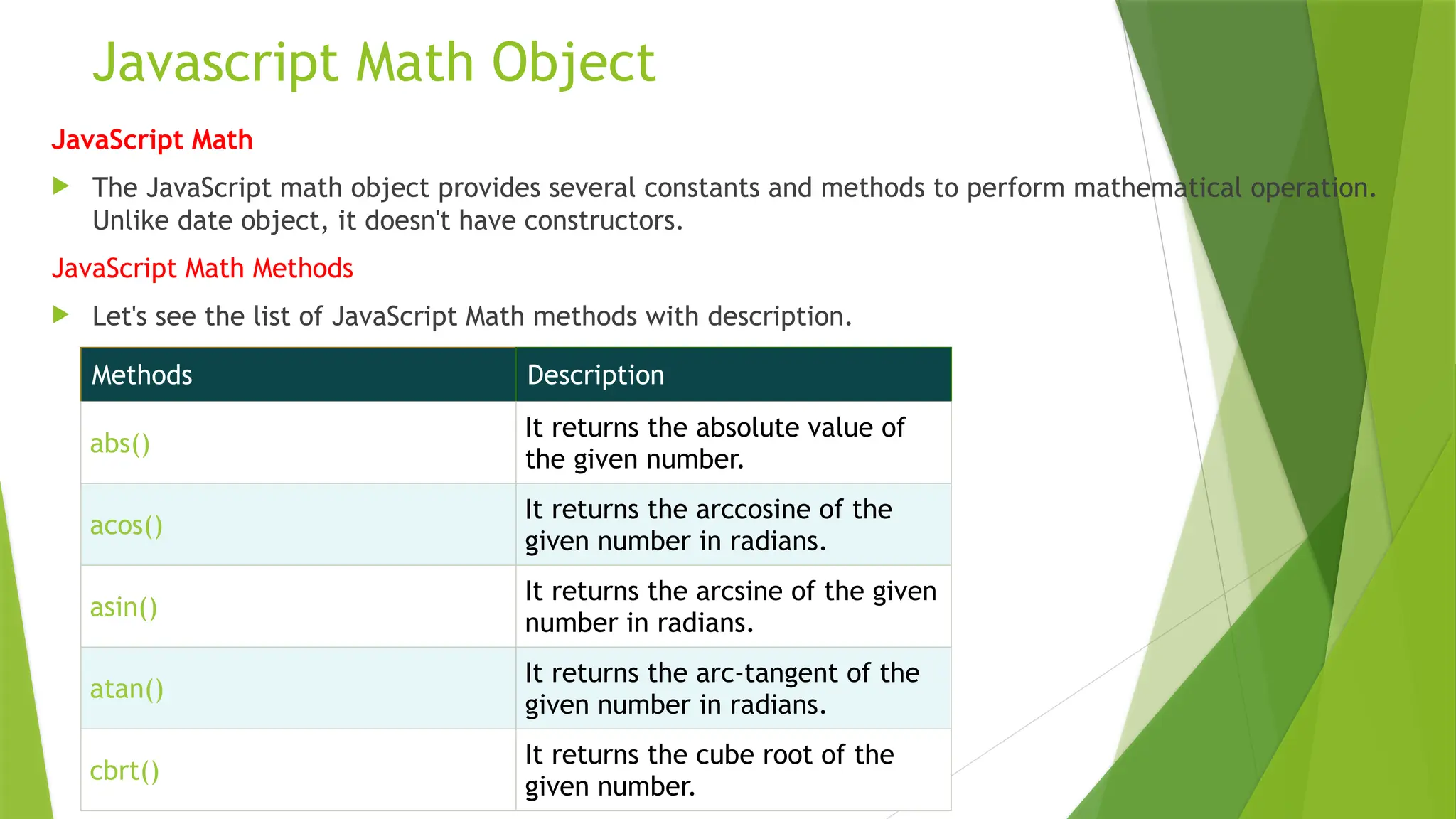
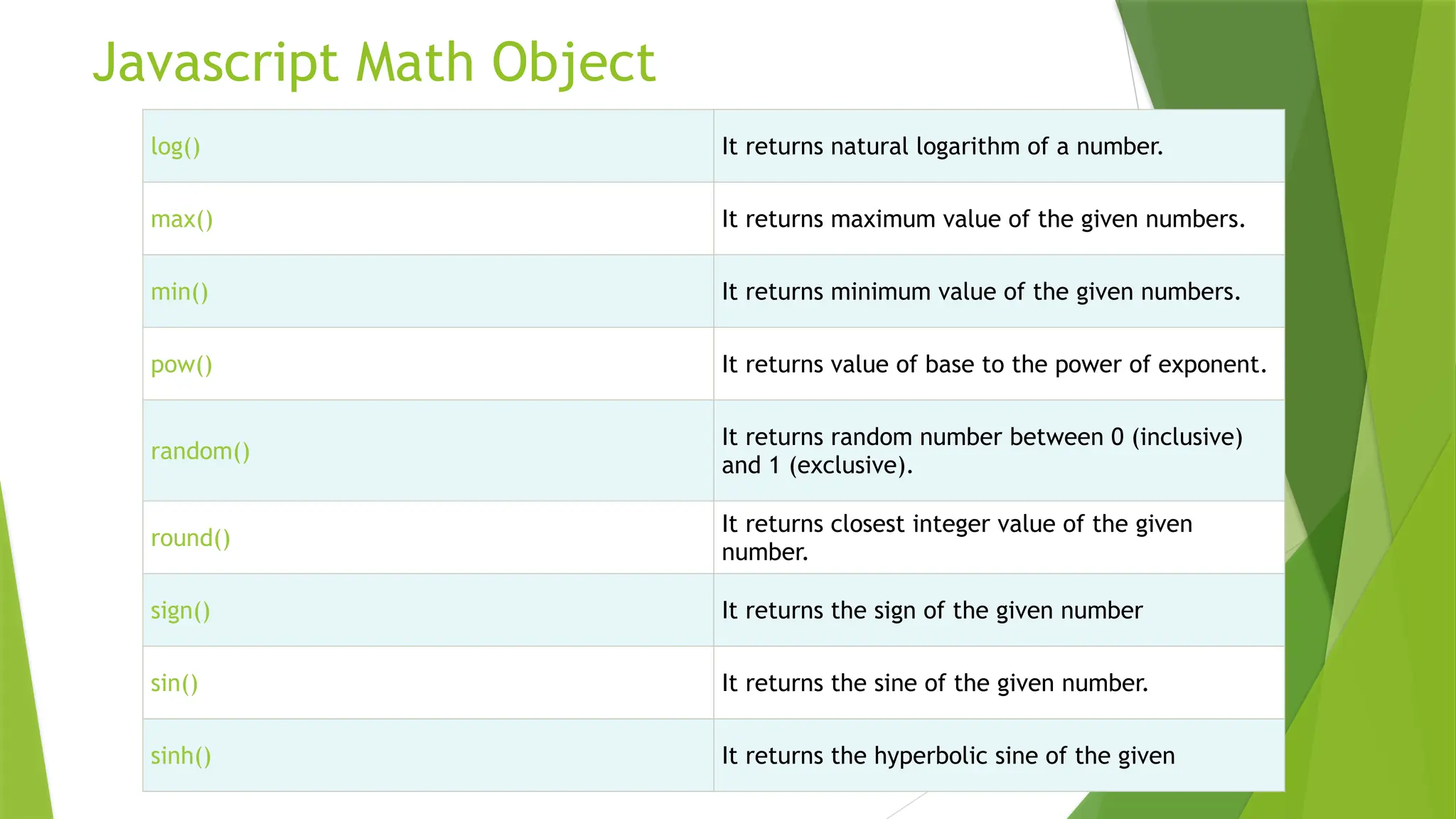
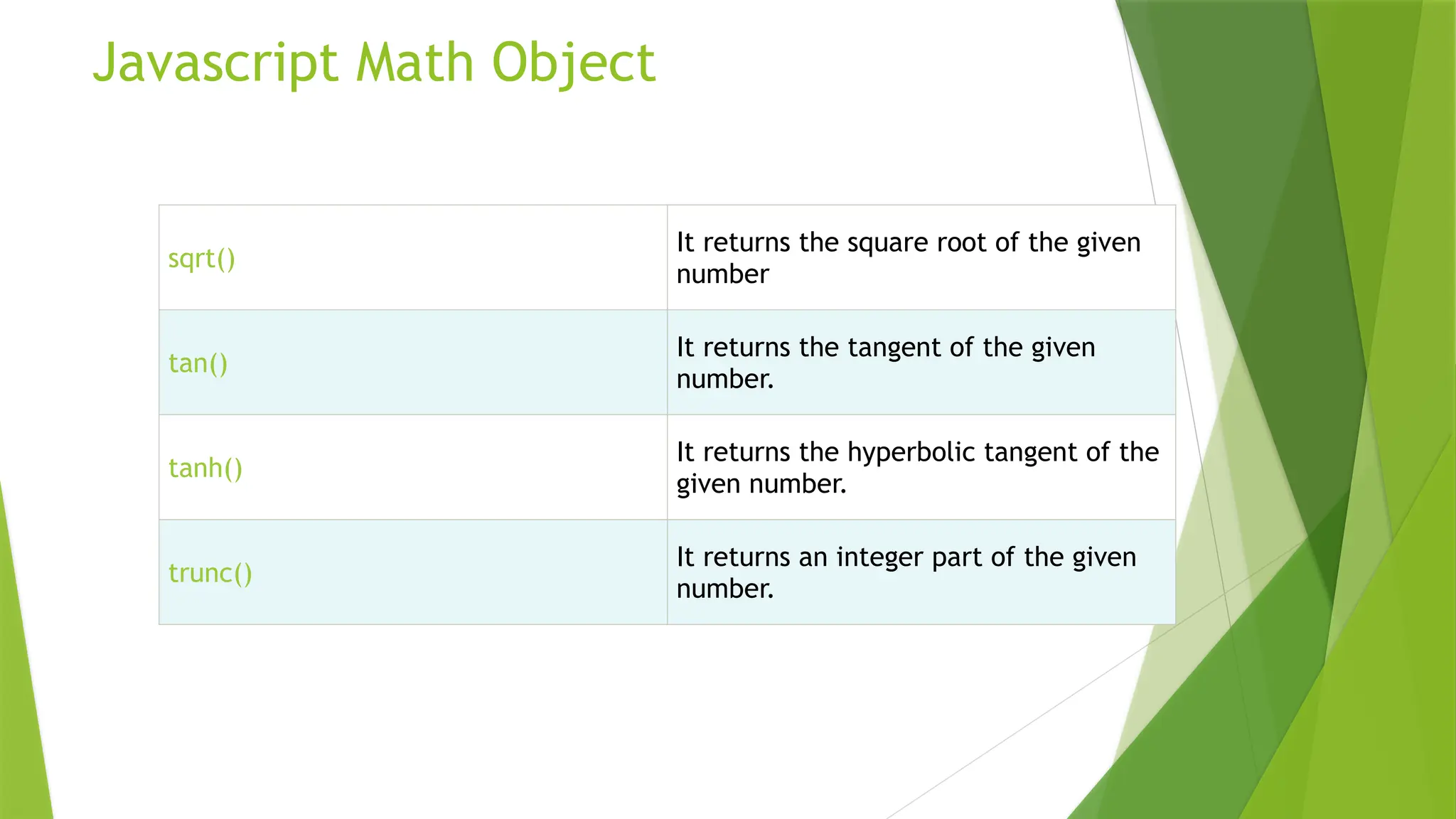
This document explains the concepts of pass by value and pass by reference in JavaScript, detailing how variables are passed to functions. It illustrates the differences with examples, emphasizing that primitive types are passed by value while objects and arrays are passed by reference. The document also covers multidimensional arrays, array manipulation methods, and various mathematical operations provided by the JavaScript Math object.








![Passing Array to Function as Pass by Reference
we will pass an initialized array to a function. Then, we will multiply each array element by 5 and display it.
<script>
let nums = new Array(20, 10, 25, 15, 35, 40);
let arrayLength = nums.length;
document.write("Original array elements are: ", "<br/>");
for(i = 0; i < arrayLength; i++) {
document.write(nums[i]+ " ");
}
document.write("<hr>");
// Function to pass an array by reference.
function modifyArray(x) {
document.write("Modified array elements: ", "<br/>");
for(i = 0; i < arrayLength; i++) {
document.write(nums[i] * 5 + " ");
}
}
// Calling function by passing array.
modifyArray(nums); // entire array passed by reference.
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-9-2048.jpg)

![<script>
let nums = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
document.write("Original array: ", "<br/>");
for(i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
document.write(nums[i]+ " ");
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("Modified array: ", "<br/>");
// Create a function that modifies elements of an array.
function modifyArray(newArray) {
for(j = 0; j < nums.length; j++)
document.write((newArray[j] *= 4)+ " ");
}
modifyArray(nums); // passing an array as passed by reference.
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("nums[3] before modifyElement: " +nums[3], "<br/>");
// Create a function that modifies the value passed.
function modifyElement(e) {
e *= 3;
document.write("nums[3] after modifyElement: " +e);
}
modifyElement(nums[3]); // passing array element nums[3] as passed by value.
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-11-2048.jpg)

![One-Dimensional array:
let arr = []; // Empty 1D array
let arr1 = ["A", "B", "C", "D"] // 1D array contains some alphabets
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] // 1D array contains some digits
Multidimensional-Dimensional array(Method – 1):
1st, need to define some 1D array
let arr1 = ["ABC", 24, 18000];
let arr2 = ["EFG", 30, 30000];
let arr3 = ["IJK", 28, 41000];
let arr4 = ["EFG", 31, 28000];
let arr5 = ["EFG", 29, 35000];
// "salary" defines like a 1D array but it already contains some 1D array
let salary = [arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4, arr5];
//Here arr1, arr2, …arr5 are some 1D arrays that are inside the salary array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![Another Method:
let salary = [
["ABC", 24, 18000],
["EFG", 30, 30000],
["IJK", 28, 41000],
["EFG", 31, 28000],
];
Accessing the element of the salary array:
To access the array element we need a simple index-based notation
salary[0][2];
// Similarly,
salary[3][2]; // Selects 28000
**This notation is used for both Method 1 and Method 2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-14-2048.jpg)
![For many iteration, we need to use loop to access the elements,
// This loop is for outer array
for (let i = 0, l1 = salary.length; i < l1; i++) {
// This loop is for inner-arrays
for (let j = 0, l2 = salary[i].length; j < l2; j++) {
// Accessing each elements of inner-array
documents.write( salary[i][j] );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![Adding elements in Multidimensional Array:
Adding elements in multi-dimensional arrays can be achieved in two ways in inner array or outer
array.
The inner array can be done in two different ways.
Adding elements to inner array:
We can use simple square bracket notation to add elements in multidimensional array.
salary[3][3] = "India";
// It adds "India" at the 4th index of 4th sub-array,
// If we print the entire 4th sub-array, document.write(salary[3]);
// the output will be : ["EFG", 31, 28000, "India"]
// indexing starts from 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![We can use push() method to add elements in the array.
salary[3].push("India", "Mumbai");
// It add "India" at the 4th index and "Mumbai" at
// 5th index of 4th sub-array
// If we print the entire 4th sub-array,
// document.write(salary[3]);
// The output will be : ["EFG", 31, 28000, "India", "Mumbai"]
// Indexing starts from 0
Adding elements to outer array: It is much similar to previous methods.
salary.push(["MNO", 29, 33300]);
// This row added after the last row in the "salary" array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
![Removing elements in Multidimensional Array: We can use pop() methods to remove
elements from inner-arrays, and also use pop() method for removing a entire inner array.
// Remove last element from 4th sub-array
// That is 28000 indexing starts from 0
salary[3].pop();
// Removes last sub-array
// That is "["EFG", 31, 28000]"
salary.pop();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-18-2048.jpg)
![Example
// Prints a simple multidimensional array in JavaScript
let arr1 = ["ABC", 24, 18000];
let arr2 = ["EFG", 30, 30000];
let arr3 = ["IJK", 28, 41000];
let arr4 = ["EFG", 31, 28000];
let arr5 = ["EFG", 29, 35000];
let salary = [arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4, arr5];
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-19-2048.jpg)
![// Prints a simple multidimensional array in
// JavaScript with different declaration
let salary = [
["ABC", 24, 18000],
["EFG", 30, 30000],
["IJK", 28, 41000],
["EFG", 31, 28000],
];
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-20-2048.jpg)
![// Prints a simple multidimensional array in JavaScript
// where we just print the salary of a specific person
let salary = [
["ABC", 24, 18000],
["EFG", 30, 30000],
["IJK", 28, 41000],
["EFG", 31, 28000],
];
console.log("salary of 2nd person : " + salary[1][2]);
console.log("salary of 4th person : " + salary[3][2]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-21-2048.jpg)
![// Prints a simple multidimensional array in
// JavaScript where we add elements in the array
// using simple square bracket and push() method
let salary = [
["ABC", 24, 18000],
["EFG", 30, 30000],
["IJK", 28, 41000],
["EFG", 31, 28000],
];
// Prints first array
console.log("Original array :<br>");
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}
// Adding "India" at the 4th index of 4th sub array
salary[3][3] = "India";
console.log("<br>after adding "India" at the 4th array :<br>");
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}
console.log("<br>after adding "USA" and "Canada" " + "at the 3rd array using "push()" method :");
salary[2].push("USA", "Canada");
// Adding "USA" and "Canada" in the 2nd sub-array
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-22-2048.jpg)
![// Prints a simple multidimensional array in
// JavaScript where we add a new inner array
let salary = [
["ABC", 24, 18000],
["EFG", 30, 30000],
["IJK", 28, 41000],
["EFG", 31, 28000],
];
// Prints first array
console.log("Original array :");
for(let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}
console.log("After adding a new inner array :");
// Pushing a new sub-array
salary.push(["MNO", 29, 33300]);
for(let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![// Prints a simple multidimensional array in
// JavaScript where we remove a single element
// and a entire sub-array
let salary = [
["ABC", 24, 18000],
["EFG", 30, 30000],
["IJK", 28, 41000],
["EFG", 31, 28000],
];
// Prints first array
console.log("Original array :");
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}
console.log("After removing last element " + "of last inner array :");
// Removes the last element of 3rd sub-array
salary[3].pop();
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i] + "");
}
console.log("After removing last inner array :");
// Removes last sub-array
salary.pop();
for (let i = 0; i < salary.length; i++) {
console.log(salary[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsarrays-241217131313-303c5031/75/JavaScript-Arrays-and-its-types-pptx-24-2048.jpg)