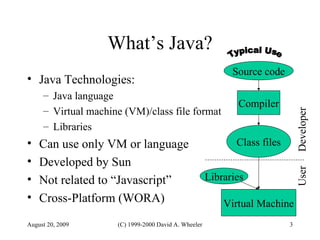
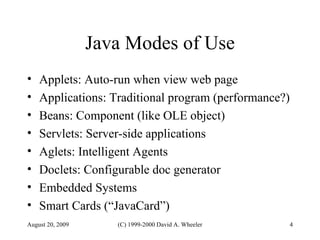
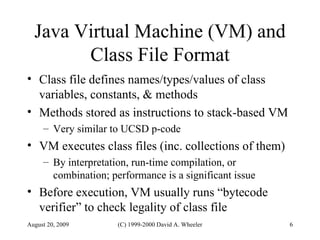
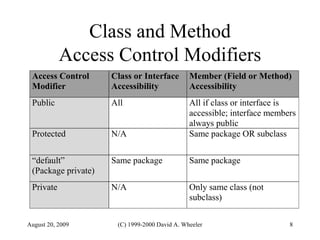
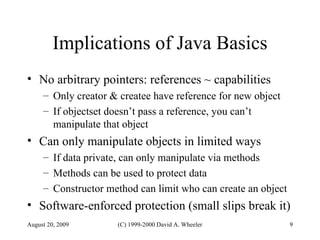
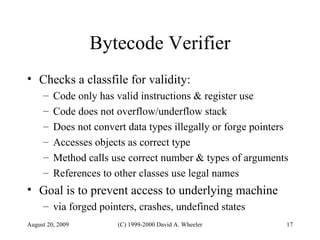
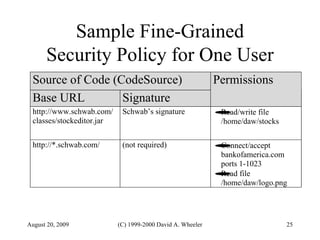
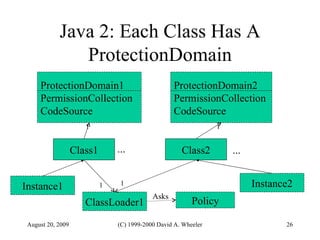
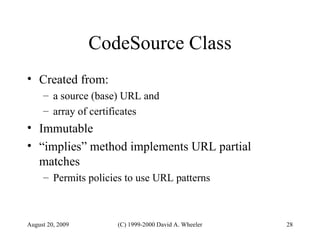
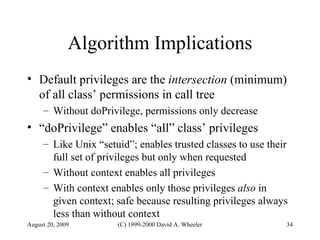
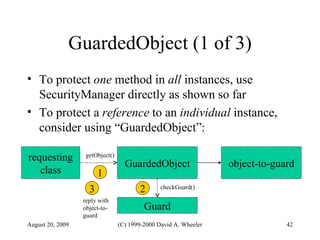
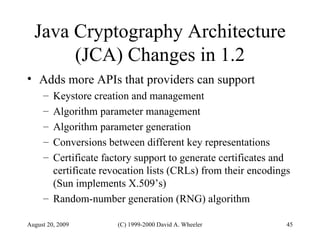
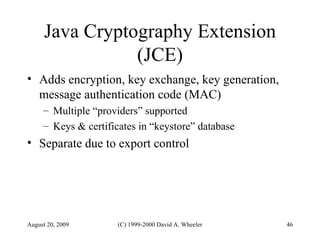
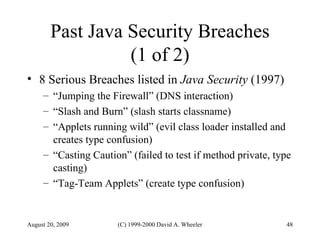
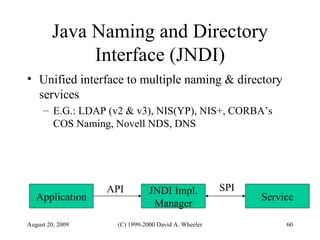
Java provides security capabilities that have evolved over time. Version 1.0 used a sandbox model but allowed unlimited access to local applications. Version 1.1 added digital signatures to optionally grant full trust to signed applets. Version 1.2 introduced fine-grained access control policies that can grant specific privileges based on code source and signatures. Java implements security through mechanisms like class loaders, bytecode verification, security managers, and protection domains.
![Java Security David A. Wheeler [email_address] (703) 845-6662 April 24, 2000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javasec-1227968505752597-9/75/Java-Security-1-2048.jpg)