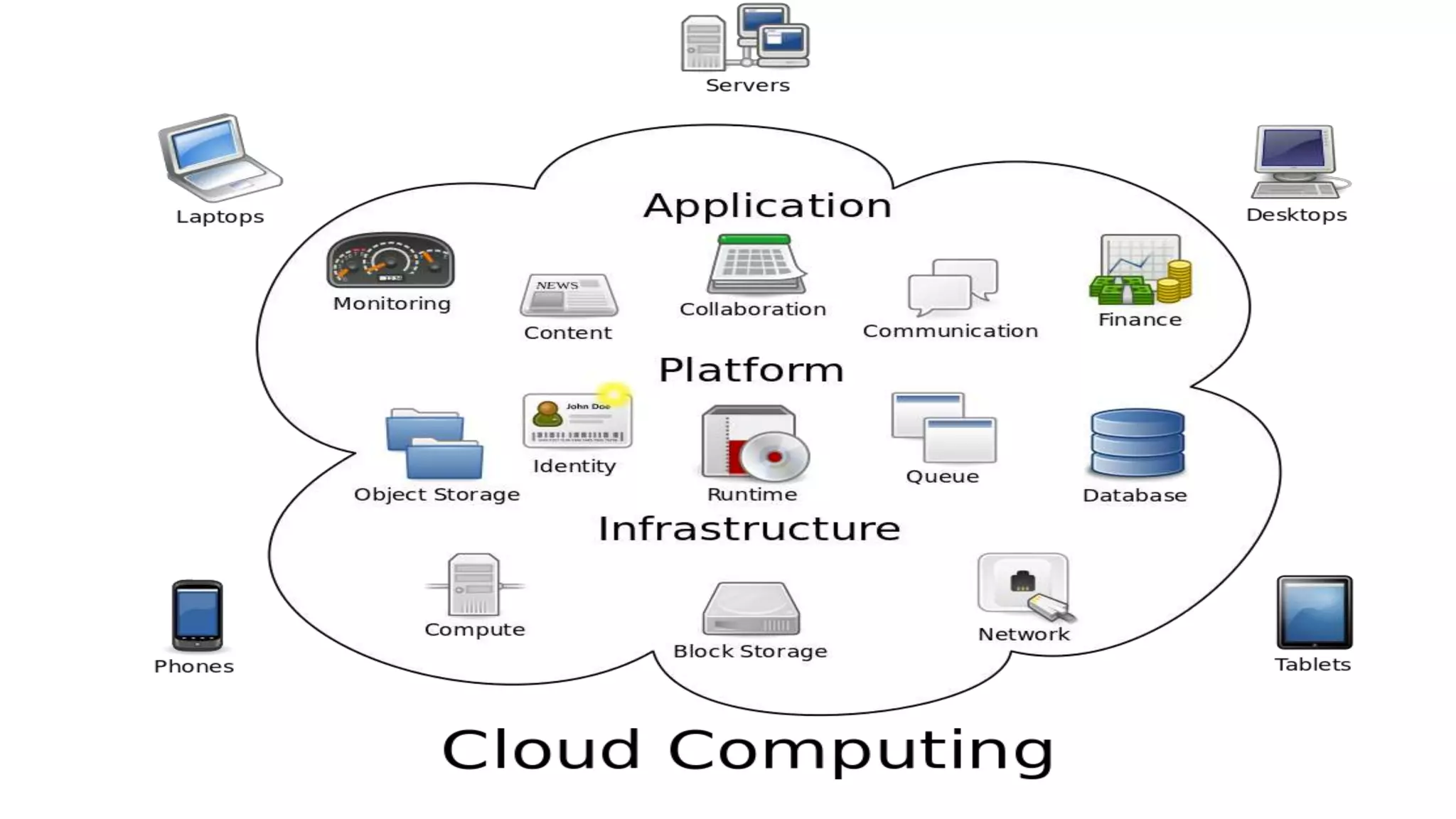
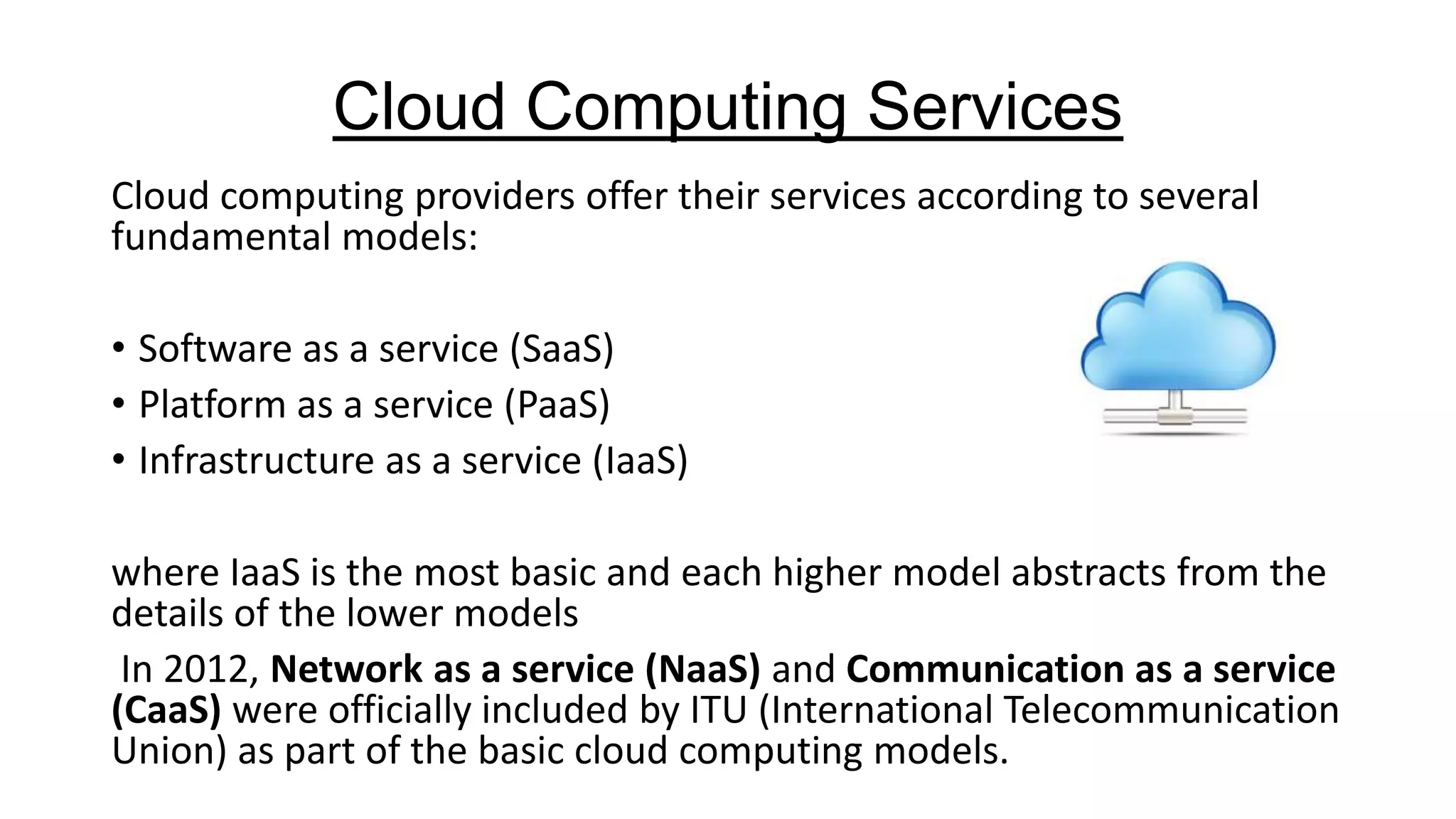
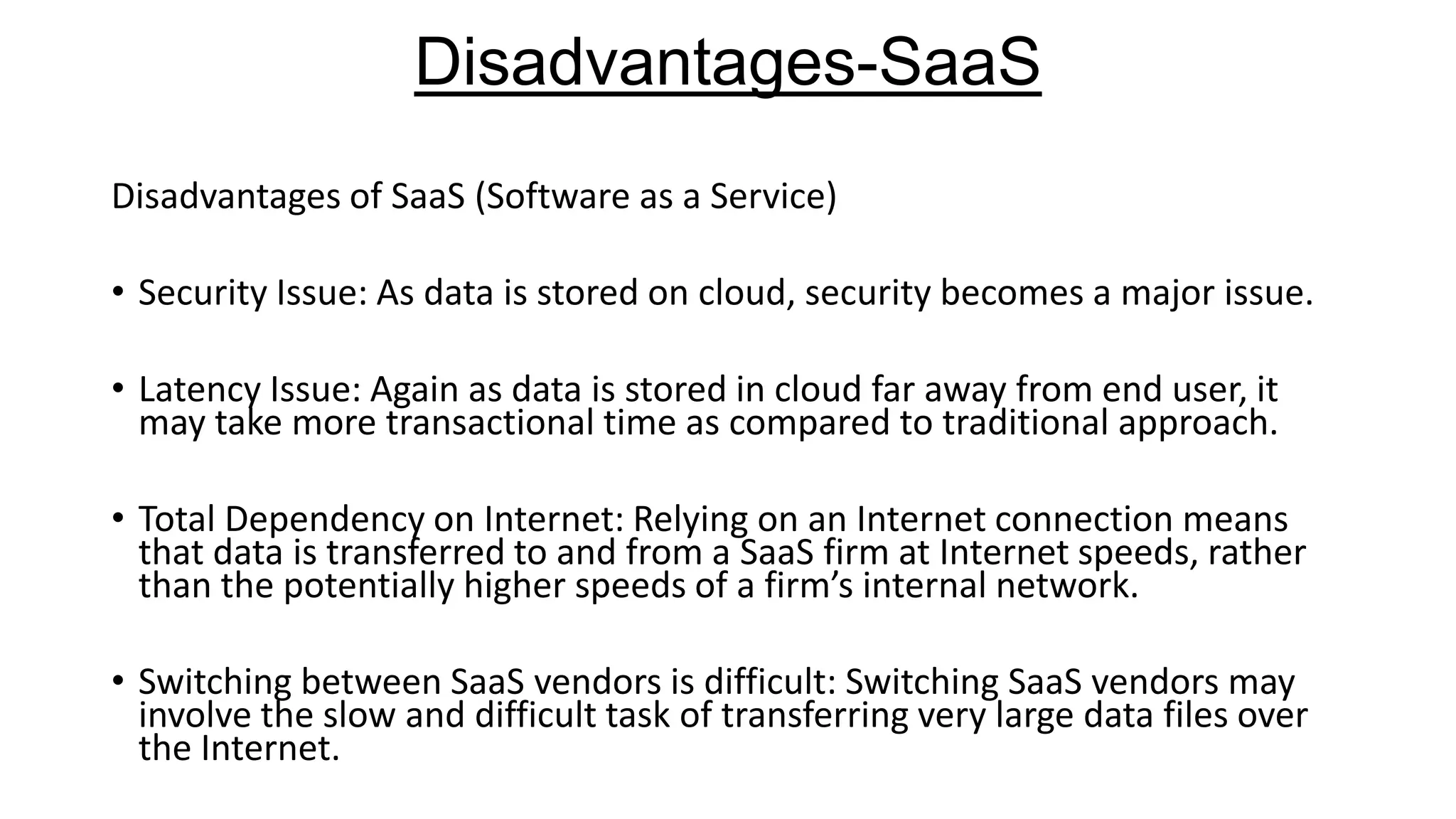
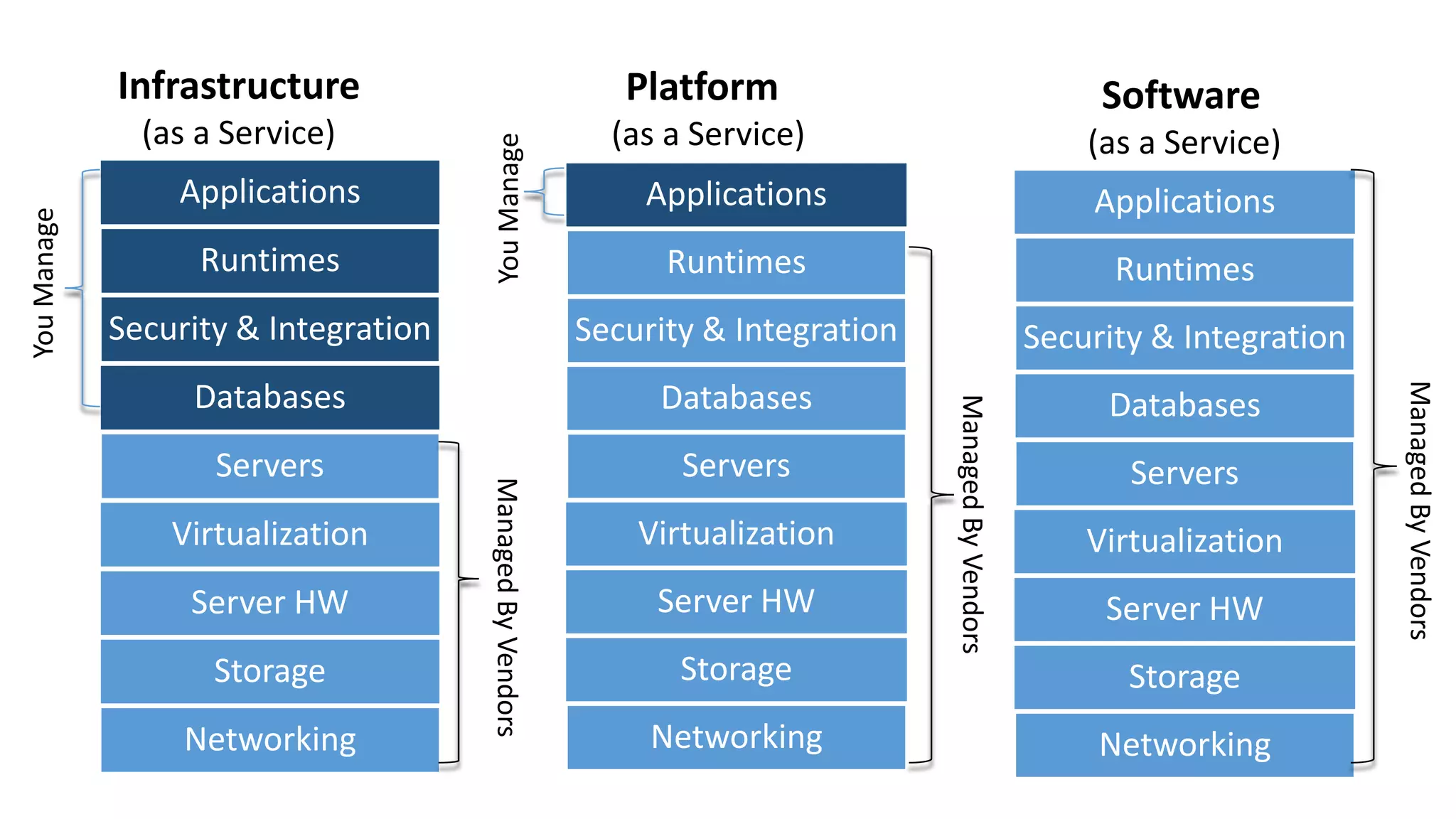
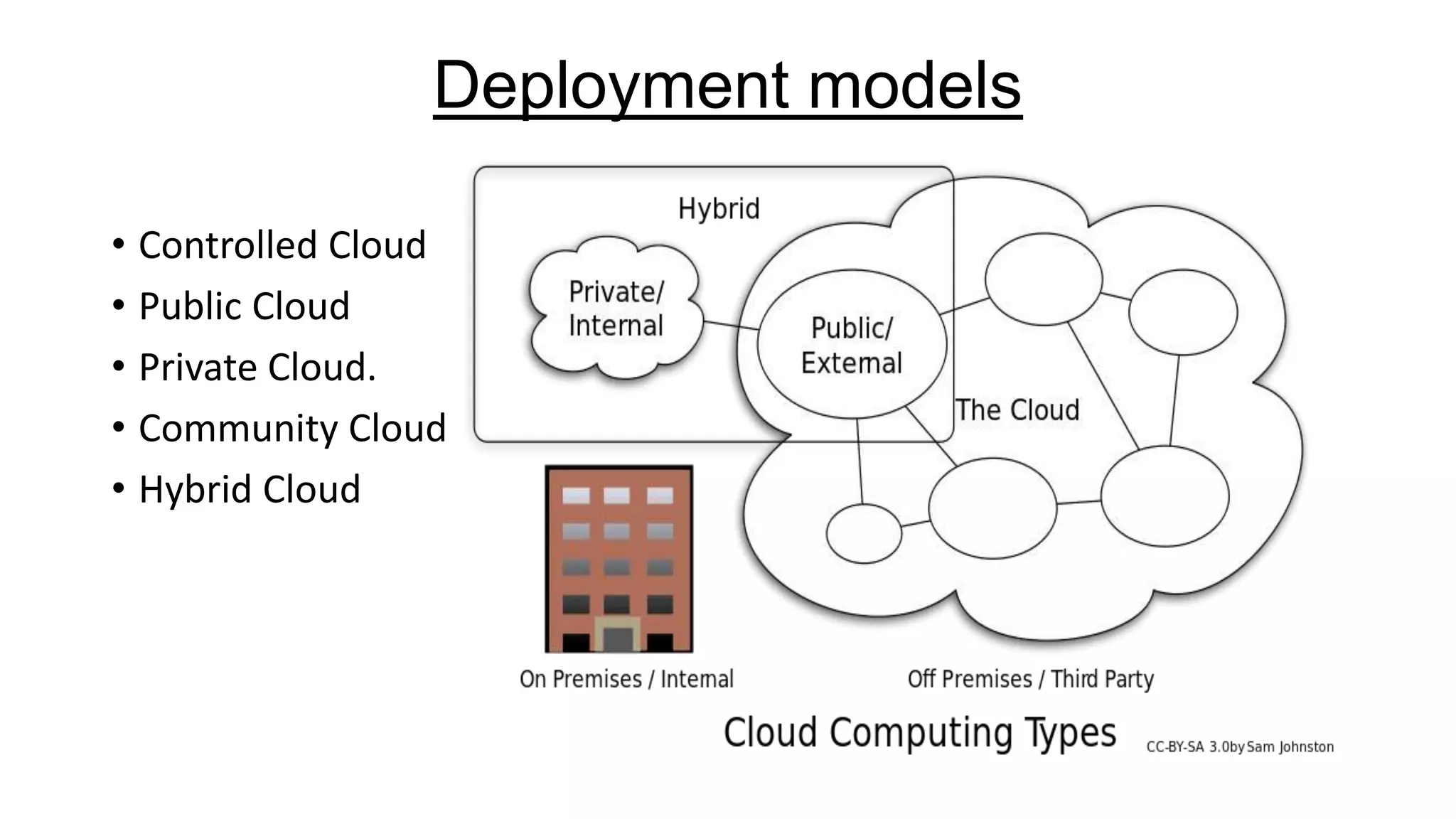
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, defining it as the storage and access of data over the internet rather than on local hard drives. It discusses various cloud service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), each with its advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it outlines different cloud deployment models including public, private, community, and hybrid clouds, alongside the benefits and challenges associated with cloud computing.