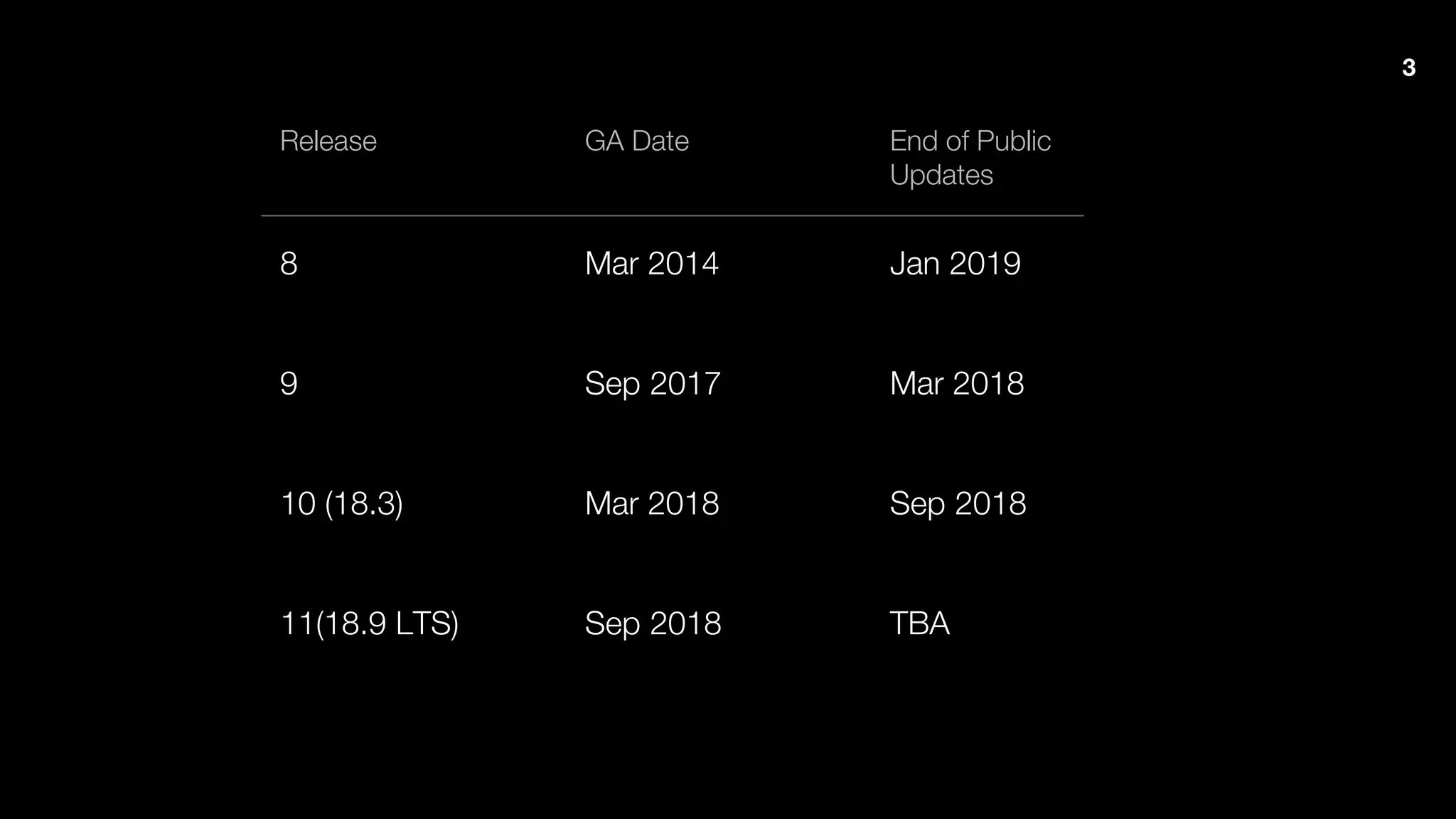
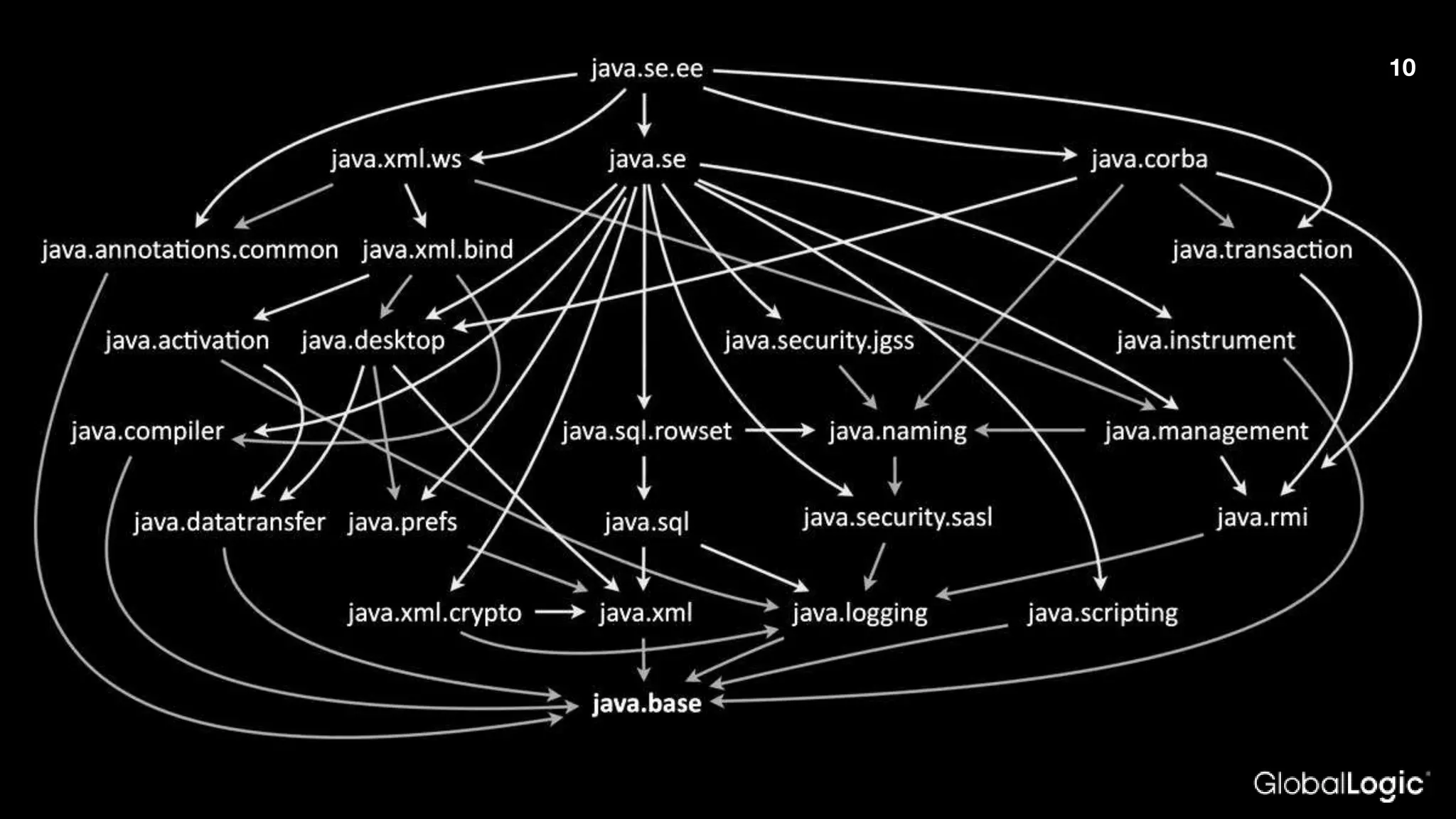
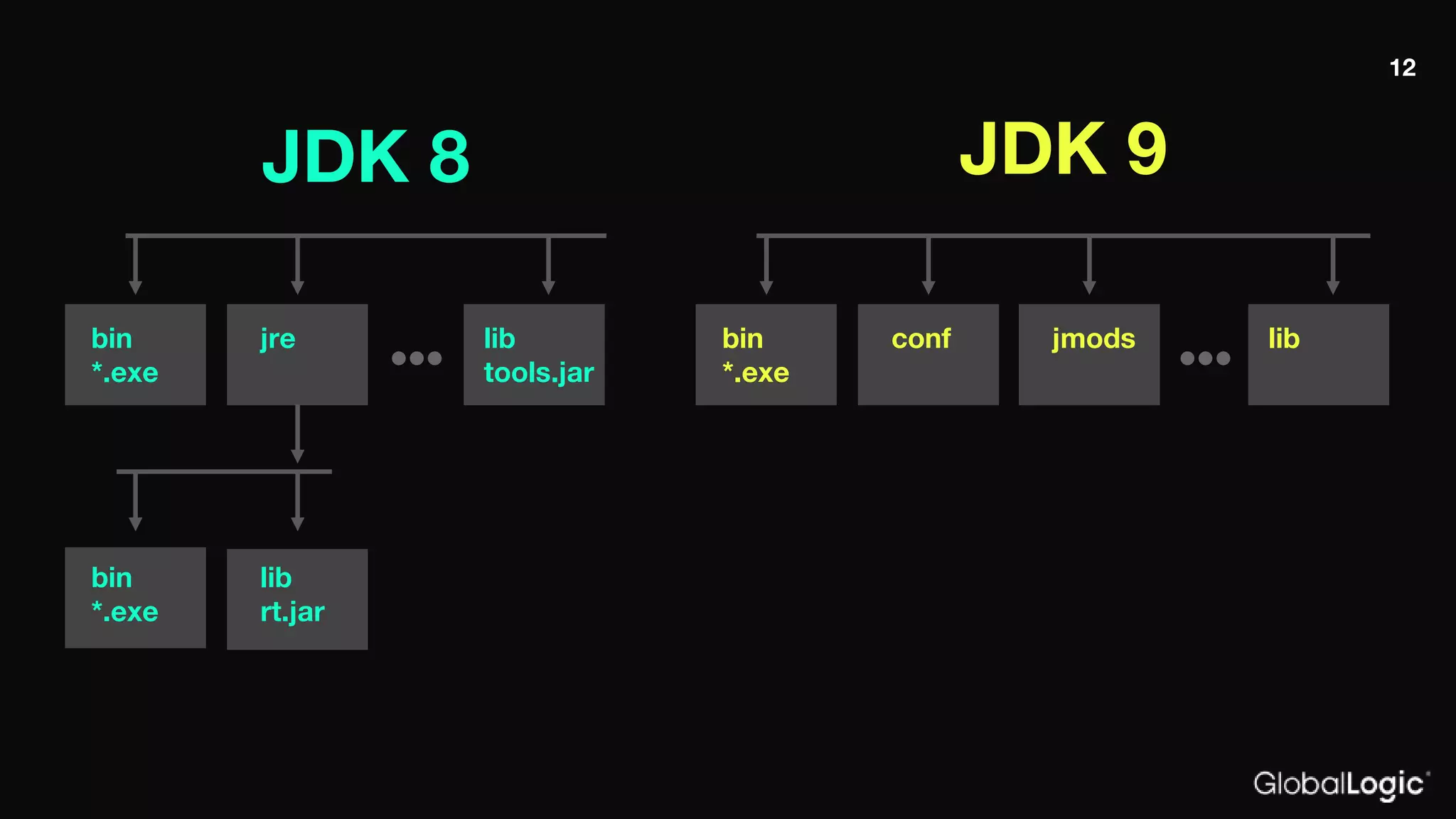
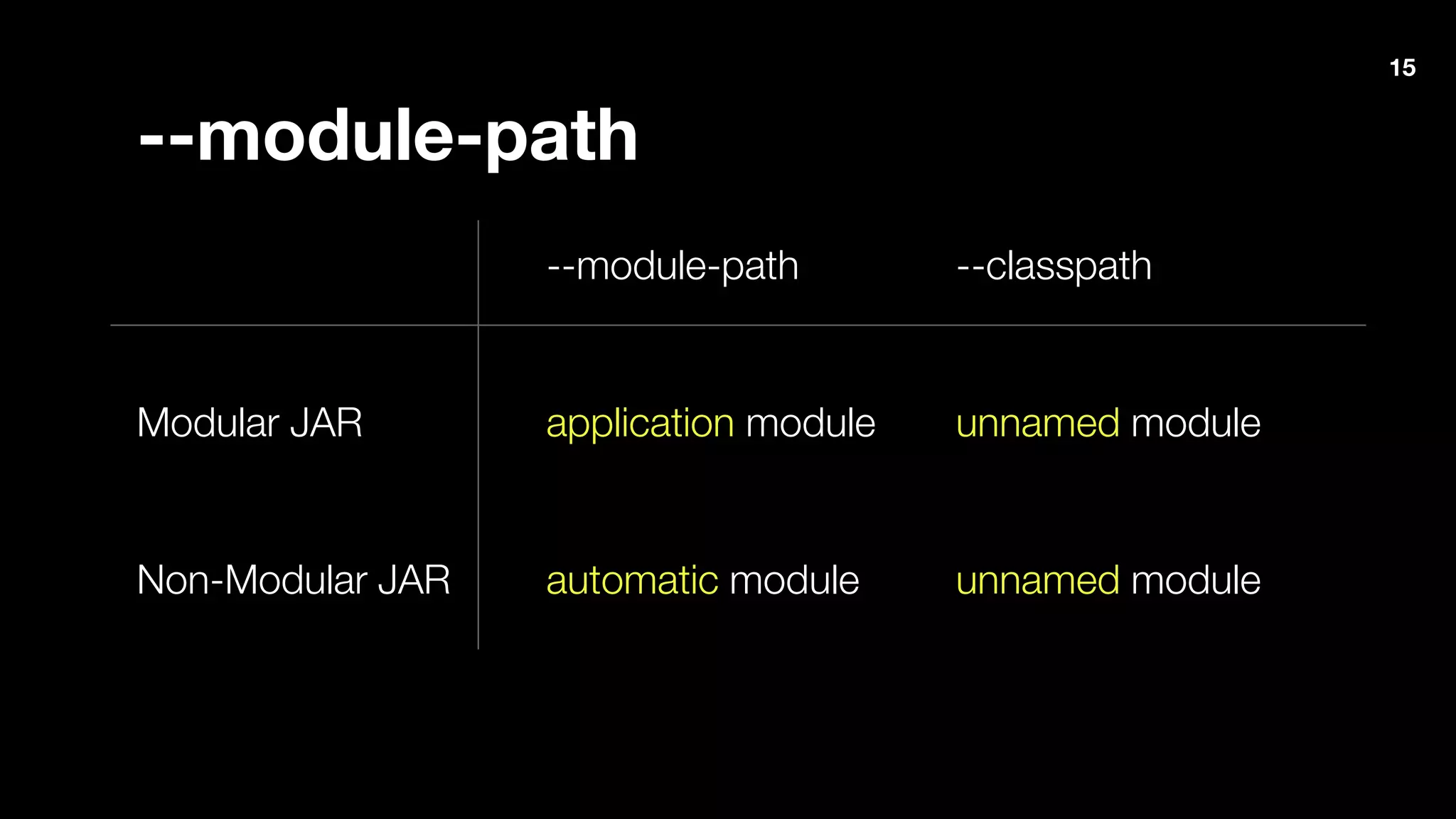
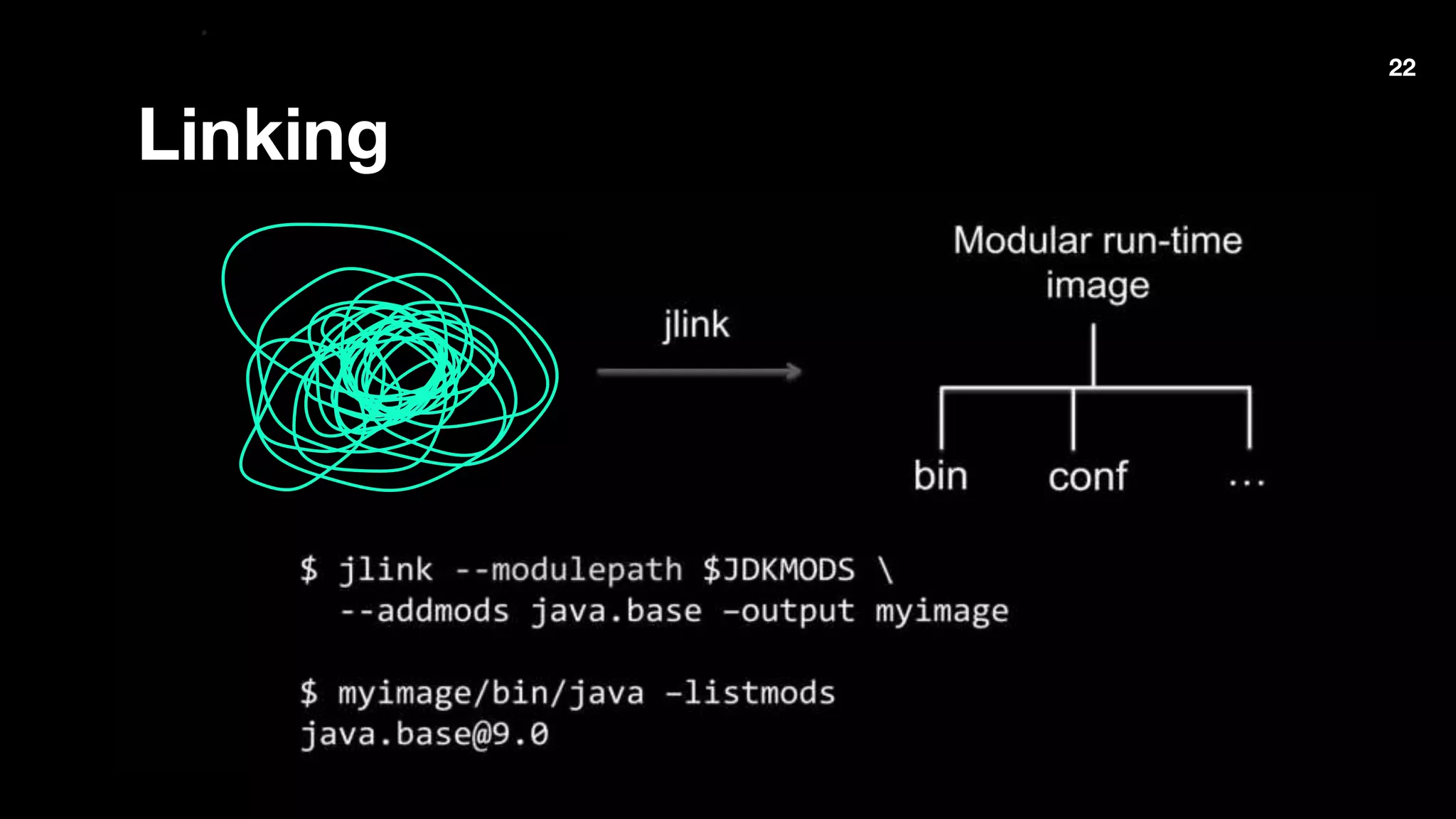
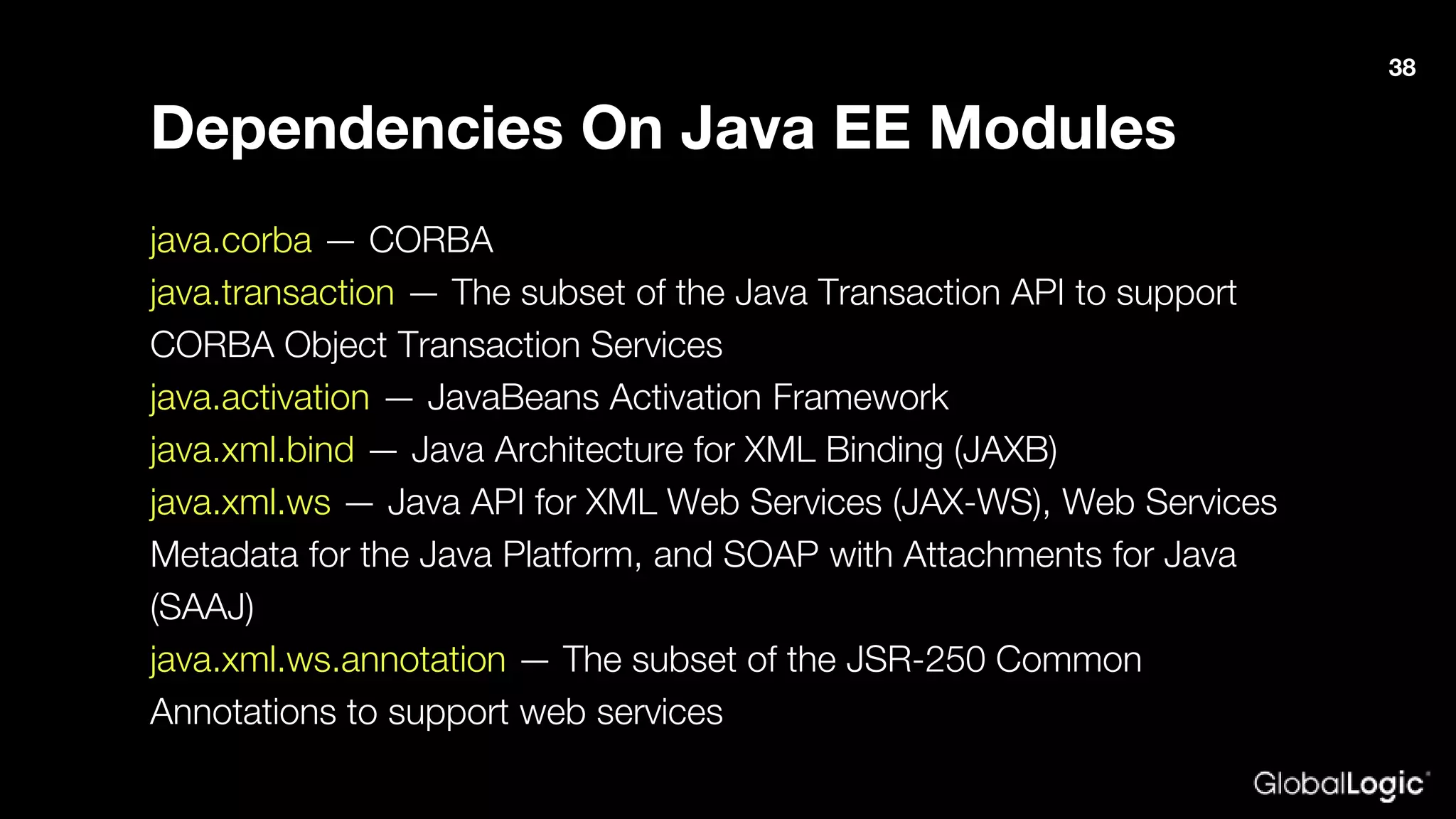
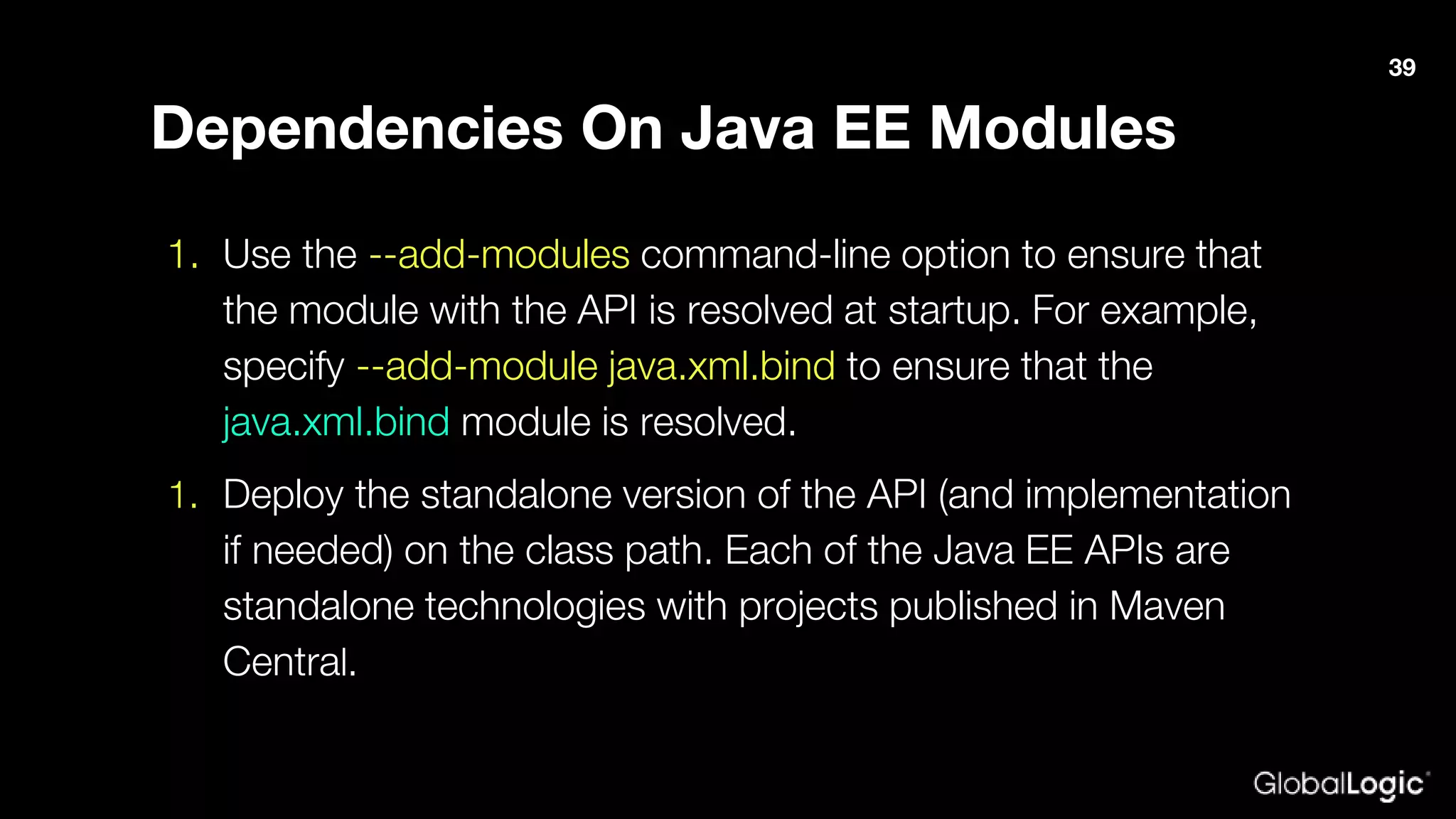
The document outlines Java 9 features, particularly focusing on Project Jigsaw which introduces modularity, discussing its benefits such as improved encapsulation, security, and maintenance. It addresses migration issues developers may encounter when transitioning from earlier Java versions to Java 9, detailing specific changes and APIs that have been removed or modified. Key directives for module management are provided, along with recommendations for resolving common migration challenges.