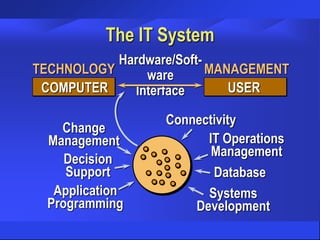
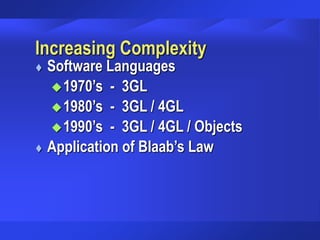
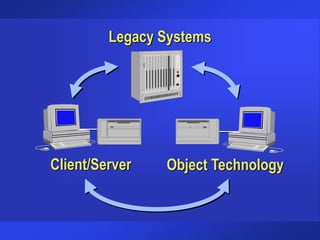
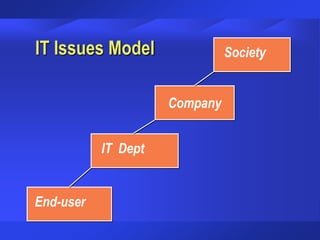
The document discusses trends and issues in information technology, highlighting the complexity of IT systems and the challenges they present. It covers the evolution of hardware, software, and data management, emphasizing the importance of effective management and user involvement. Additionally, it addresses the role of Chief Information Officers (CIOs) in shaping IT strategy within organizations.