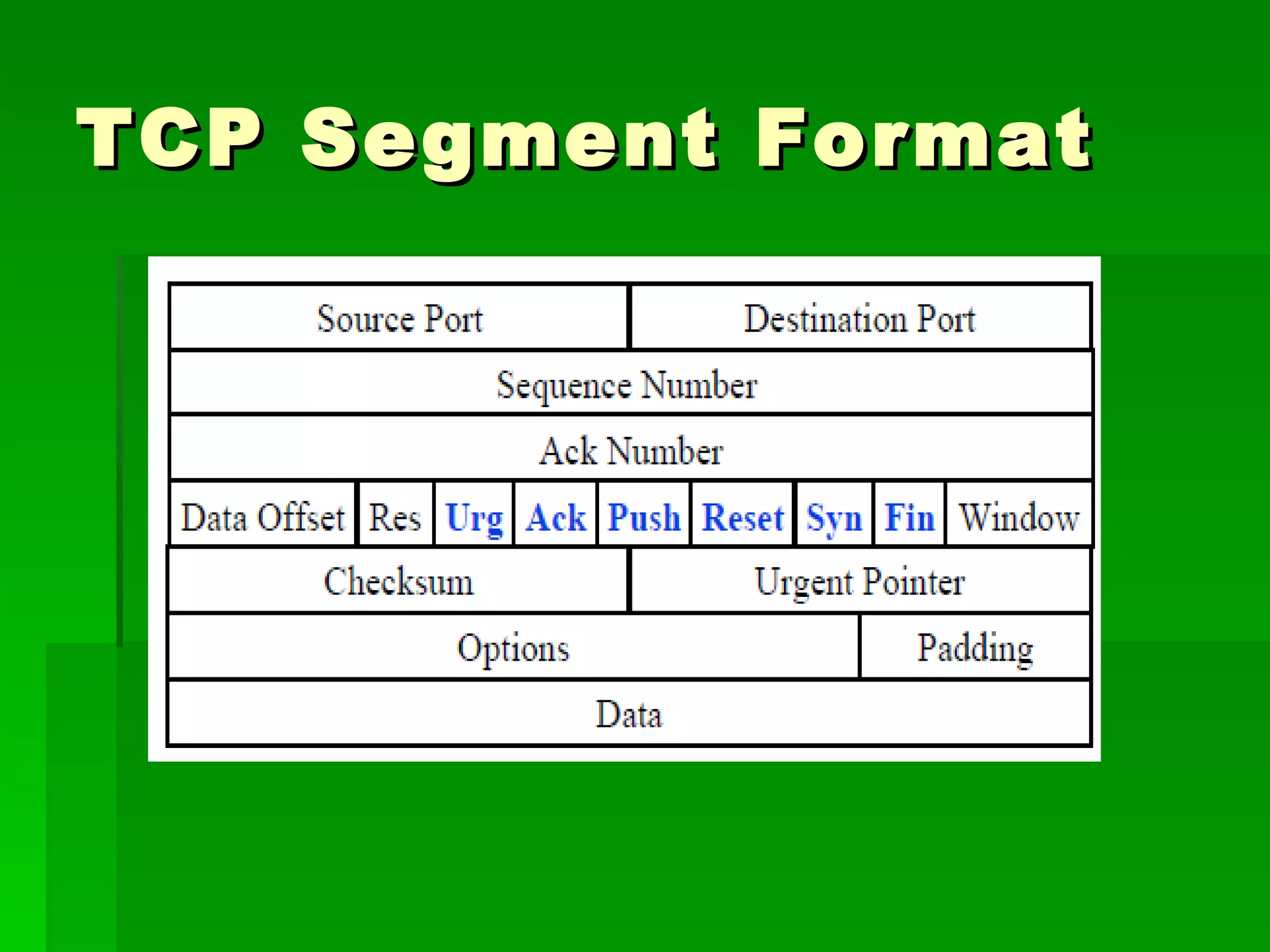
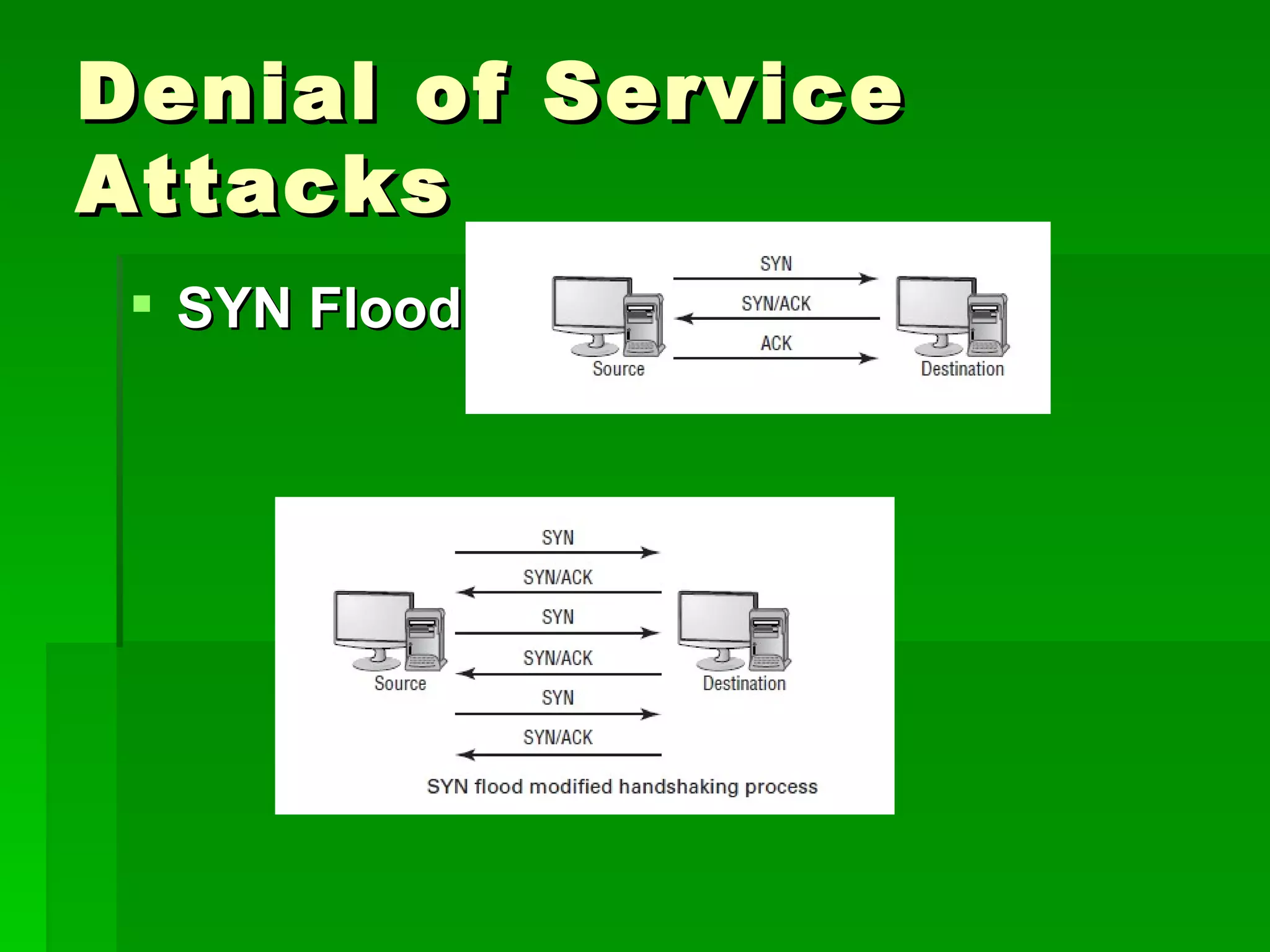
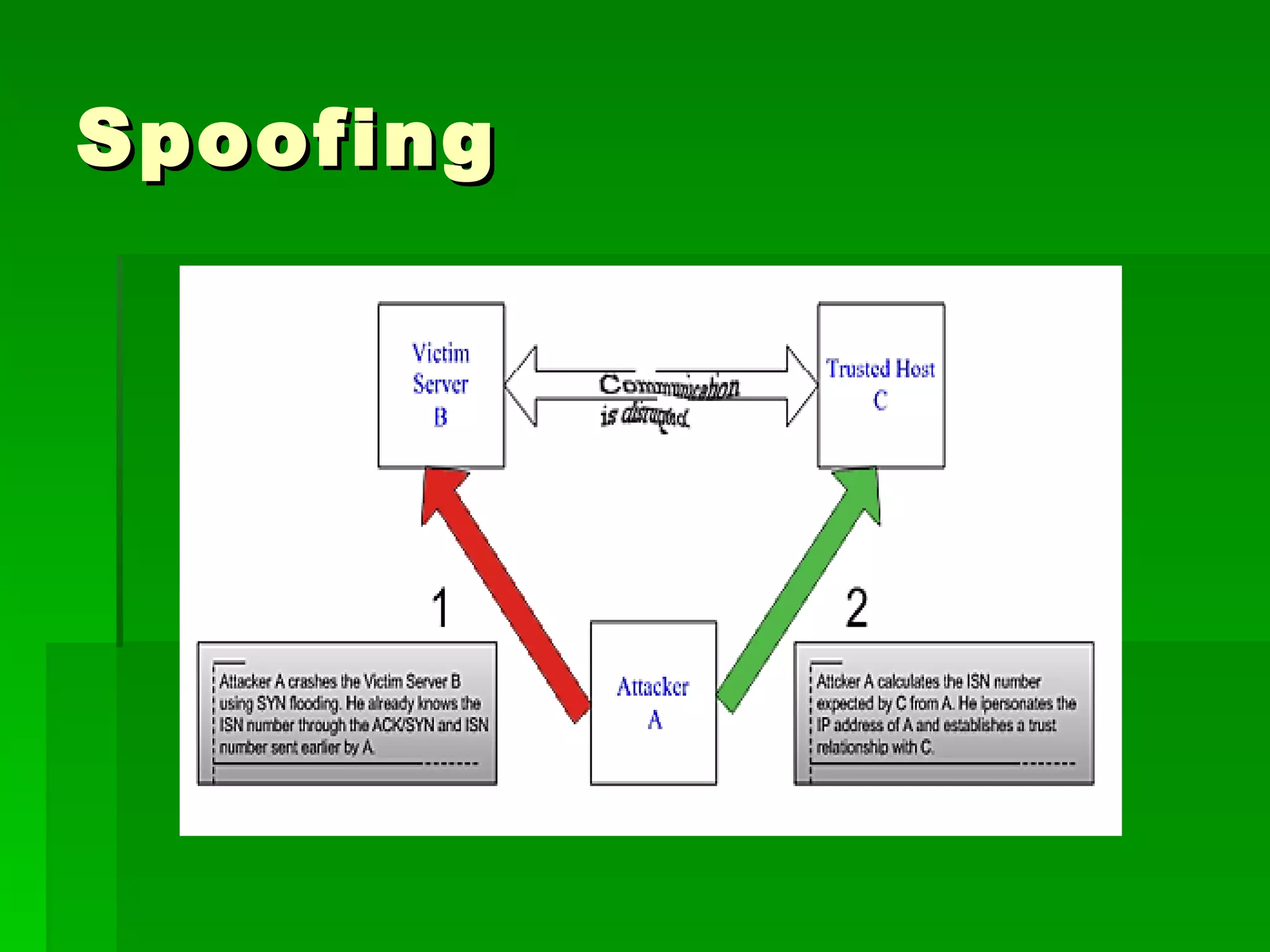
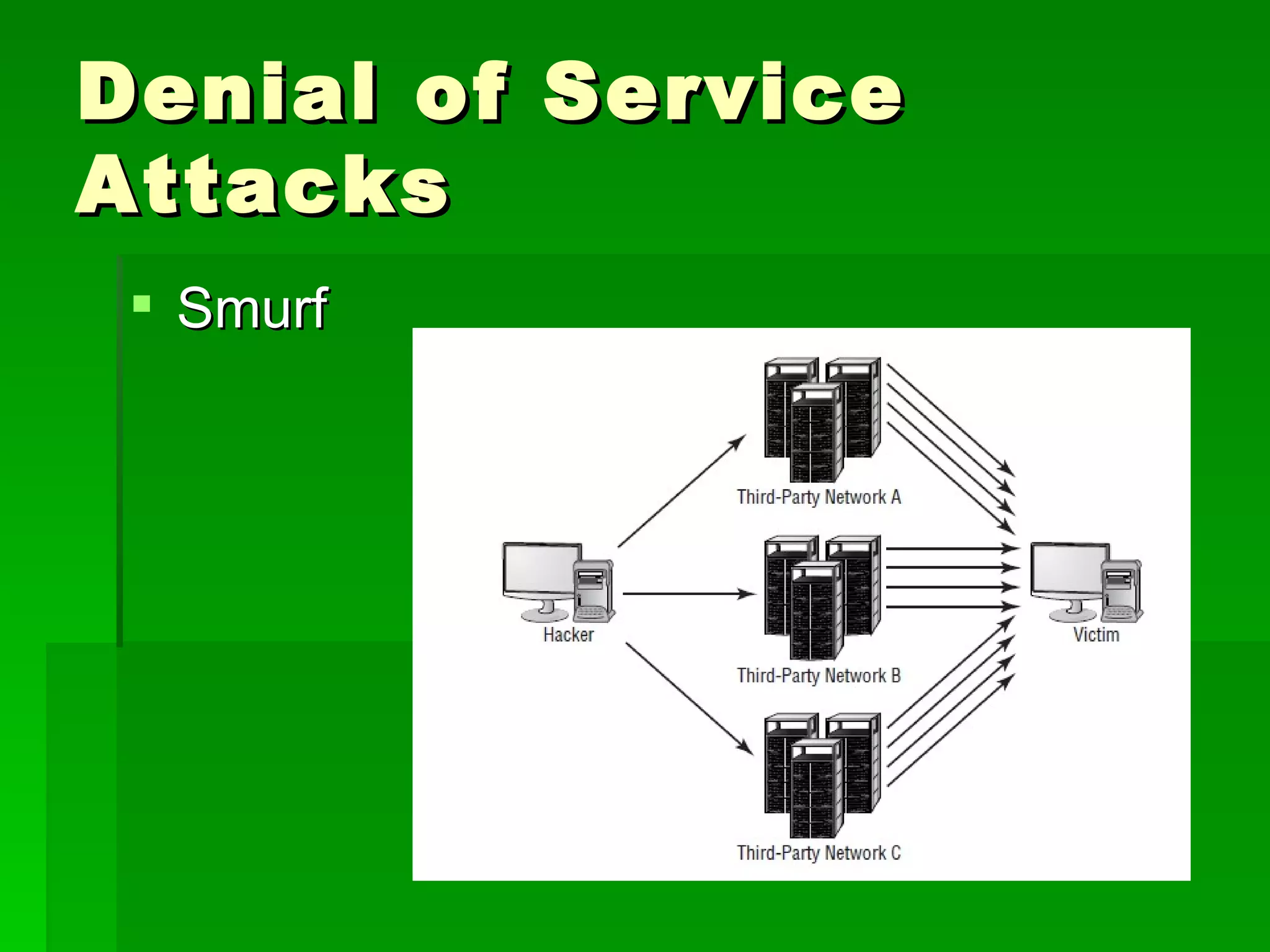
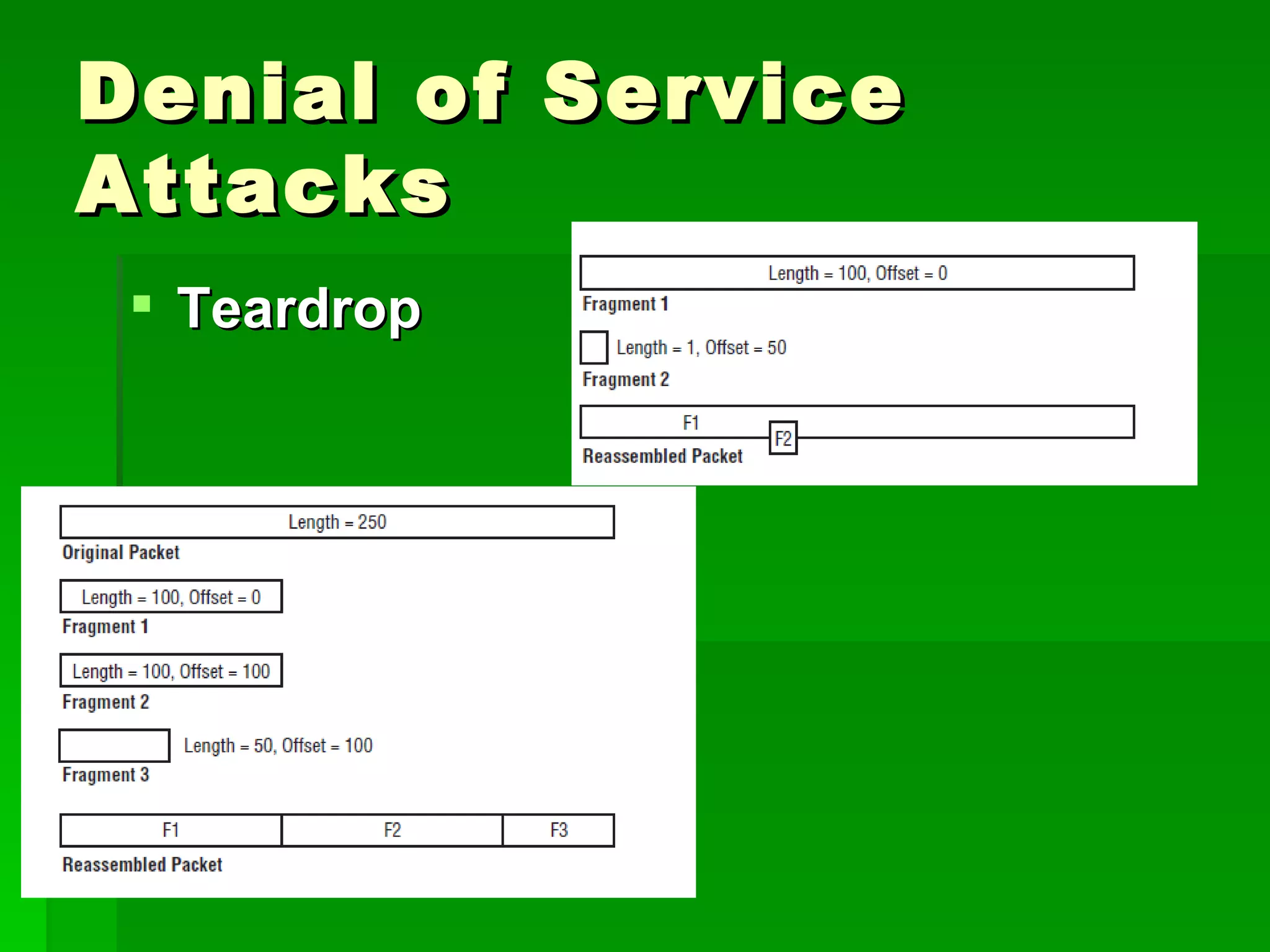
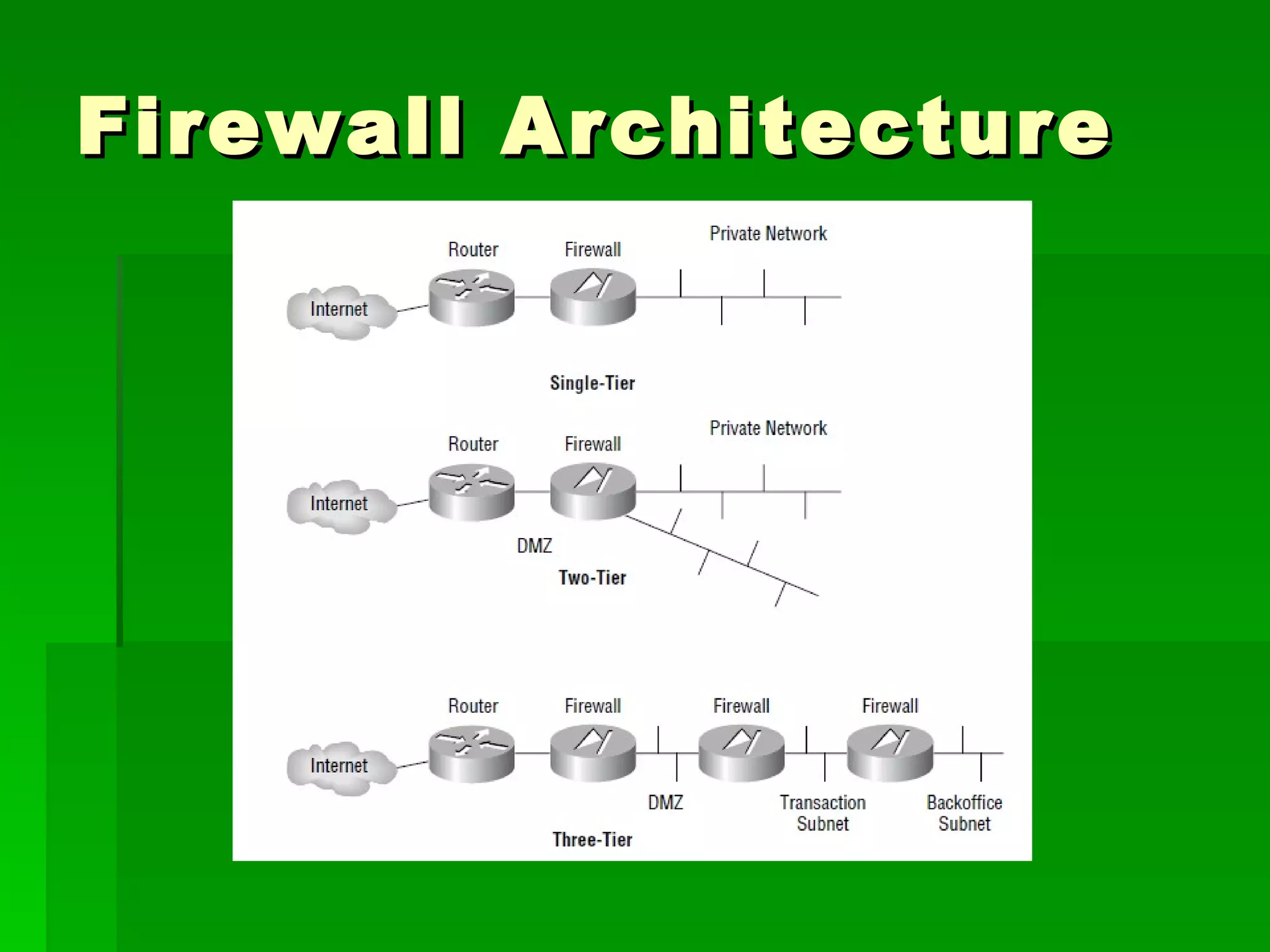
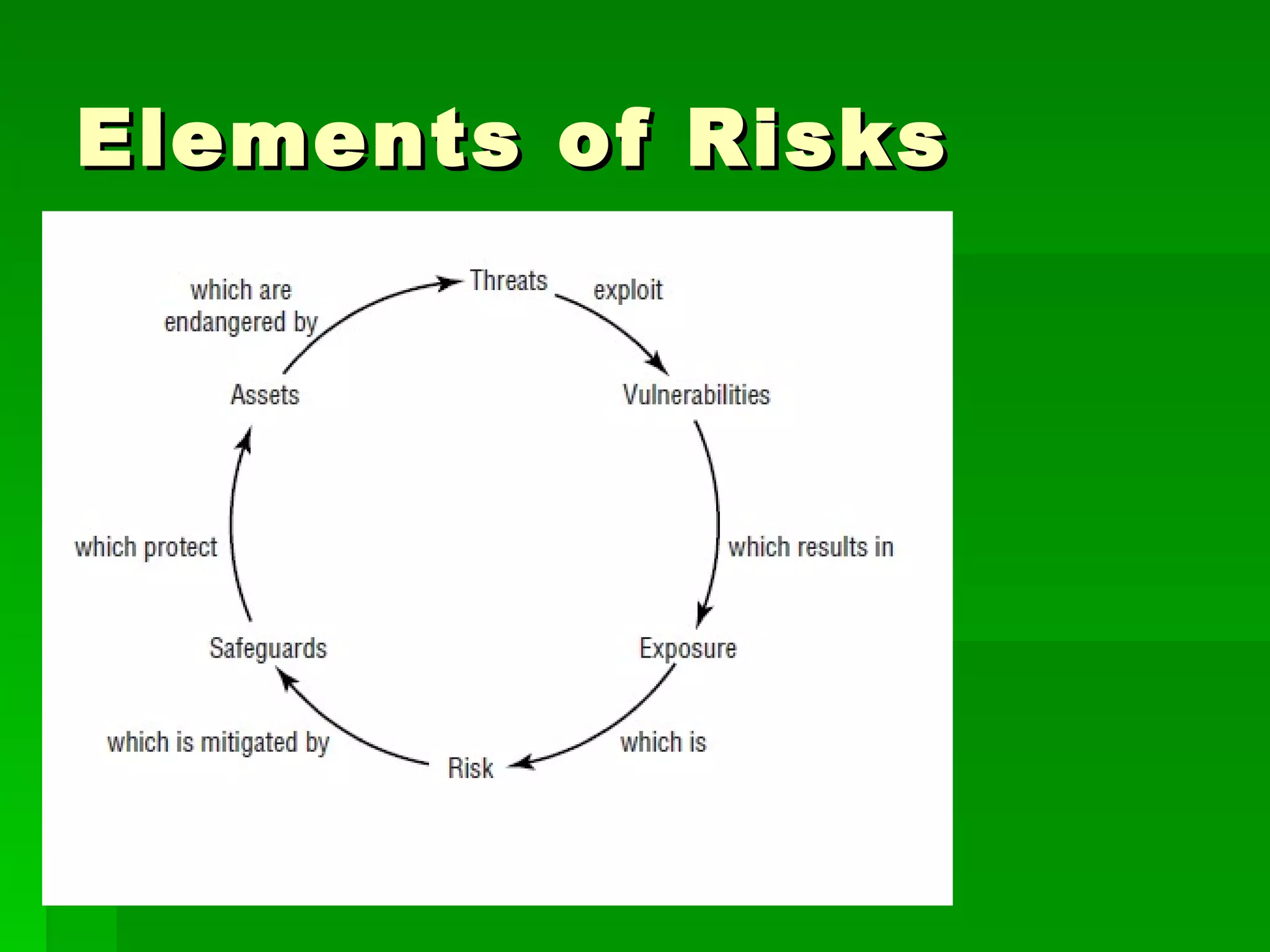
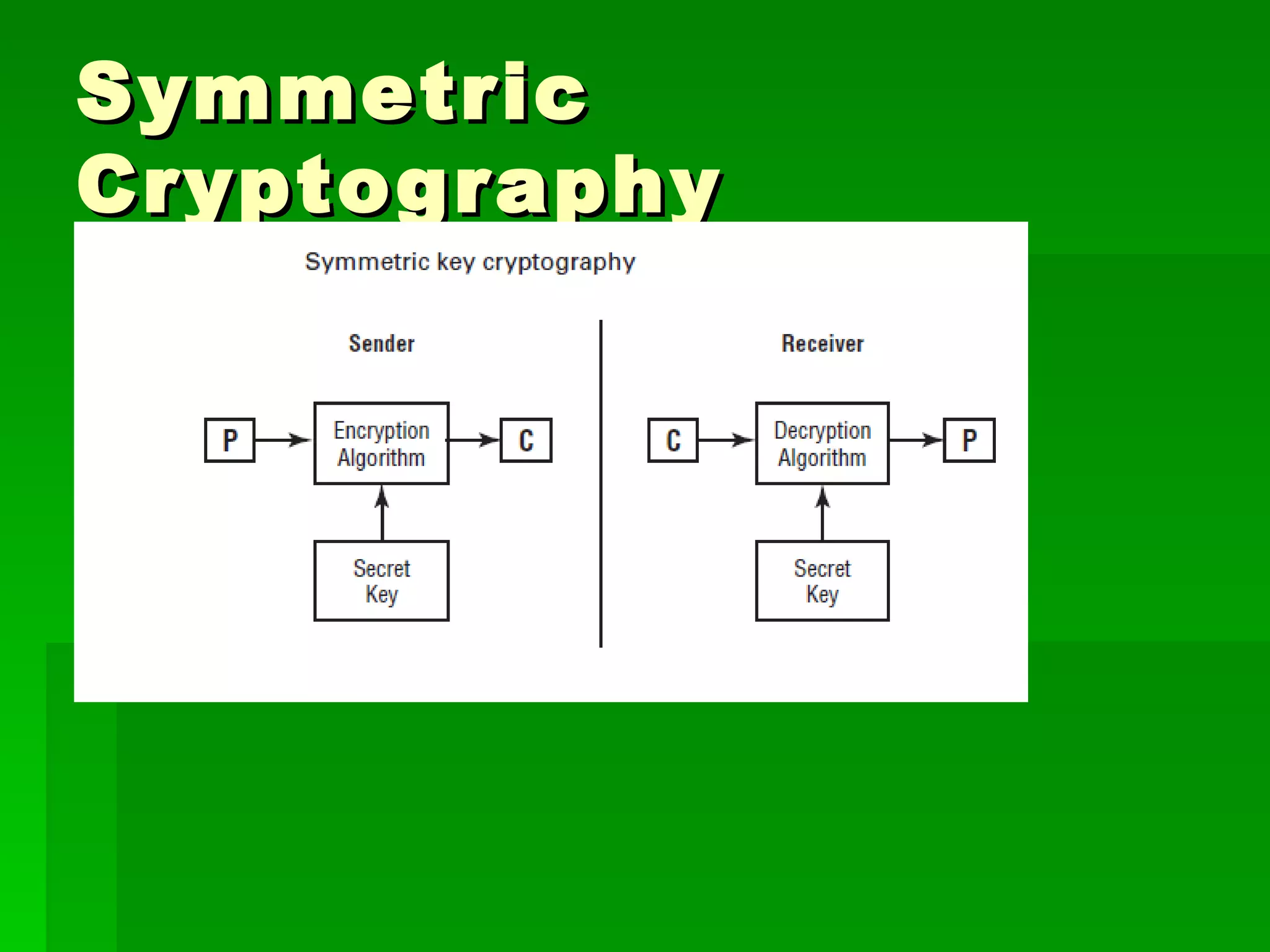
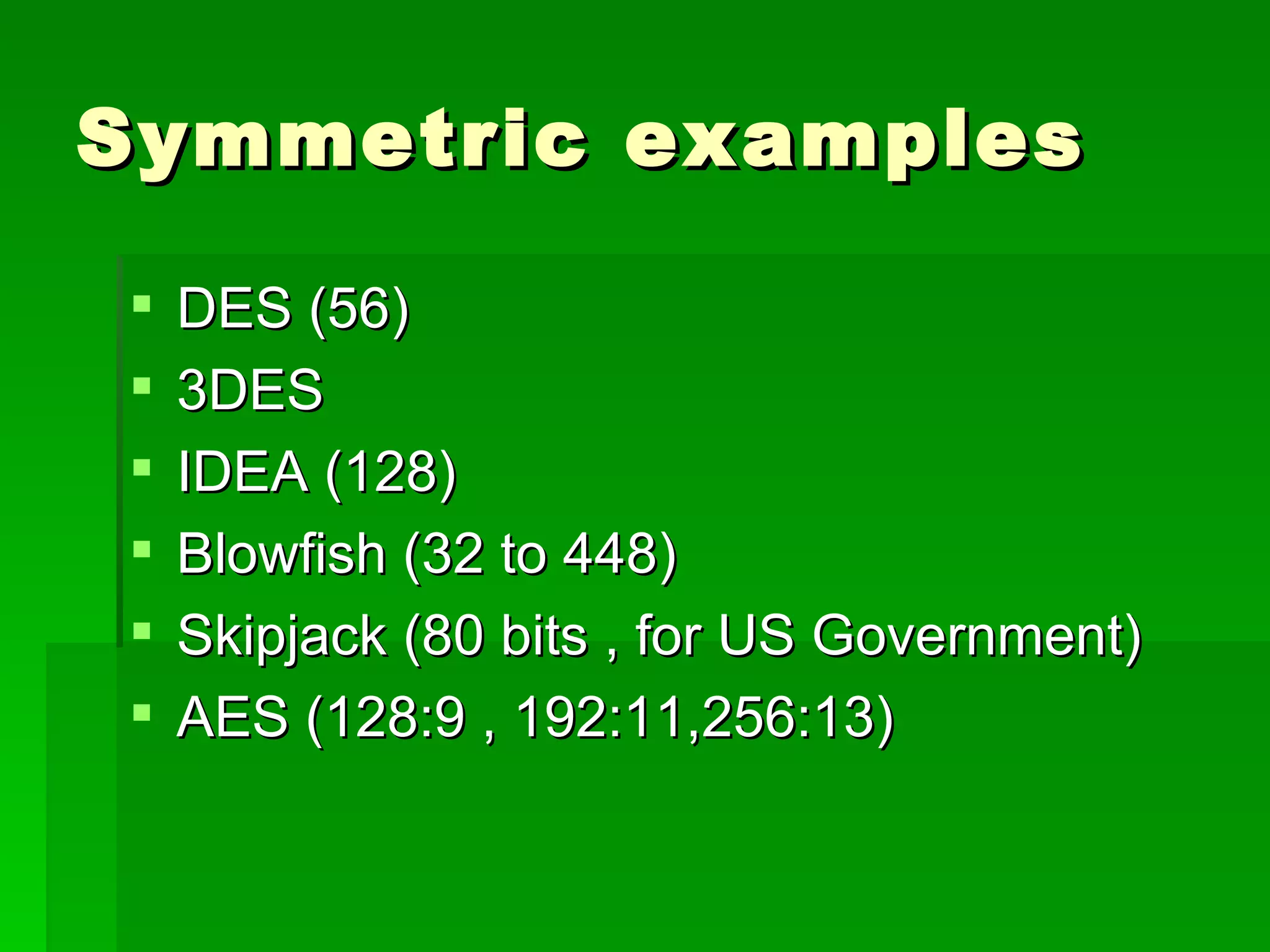
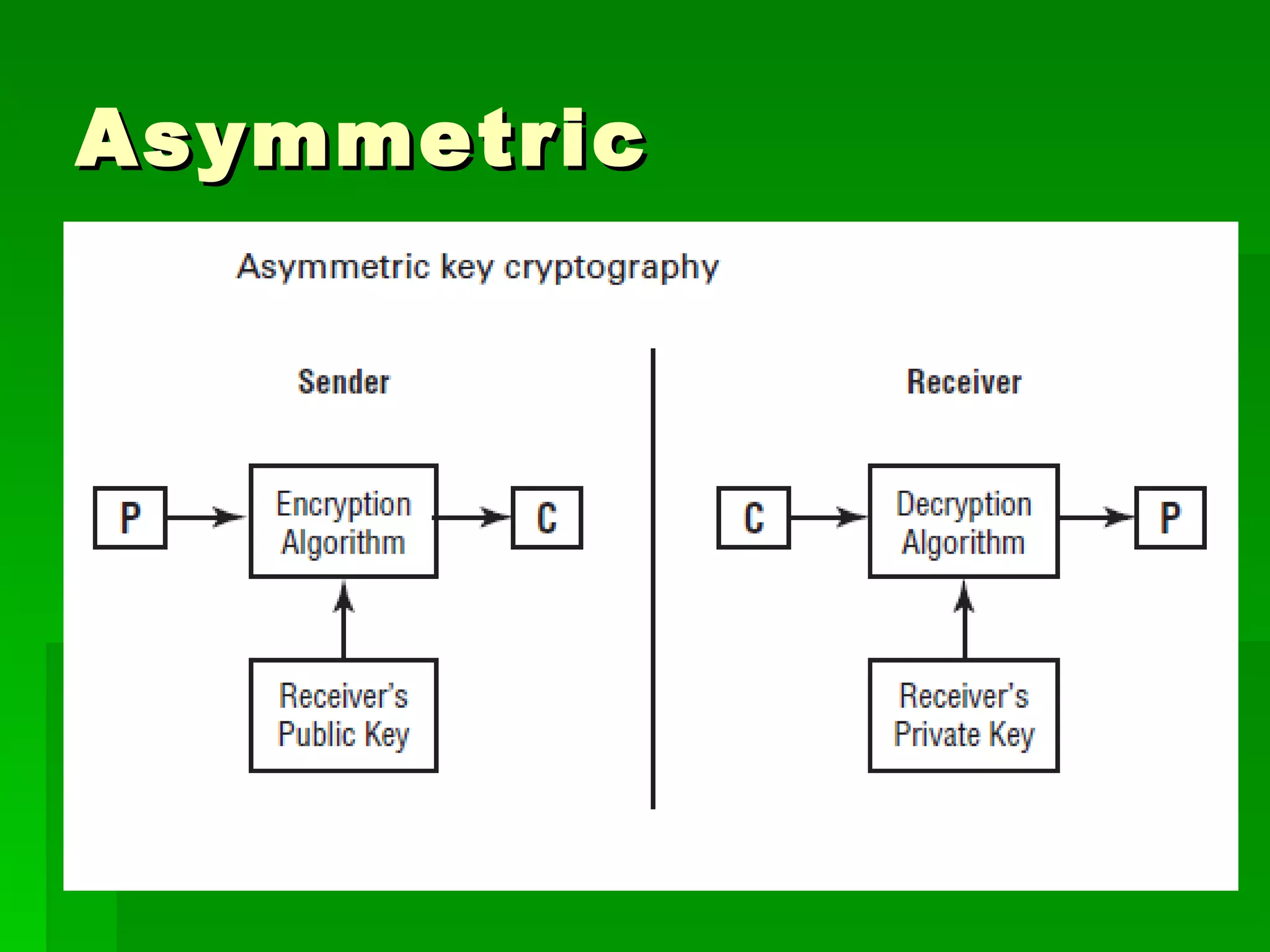
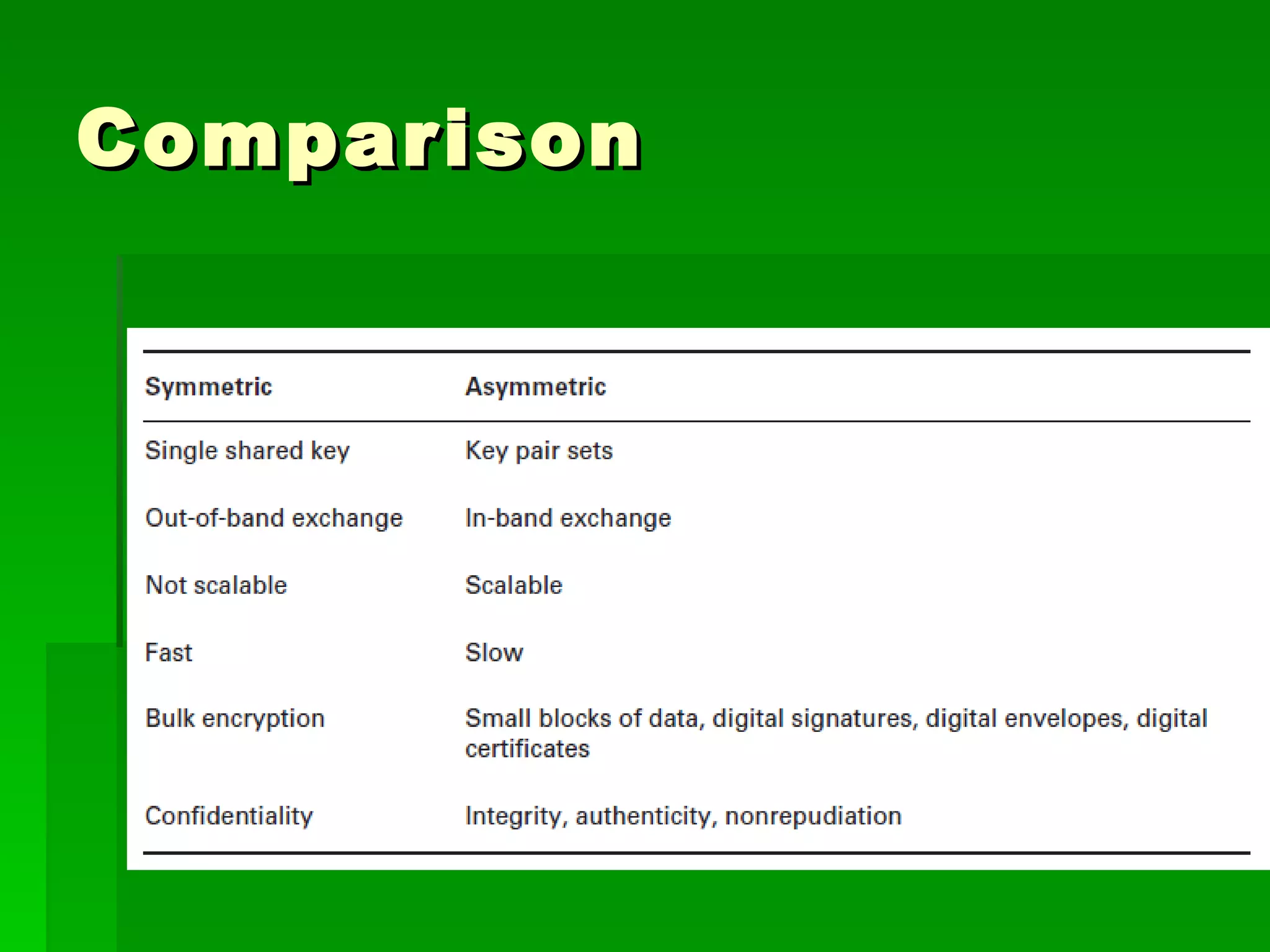
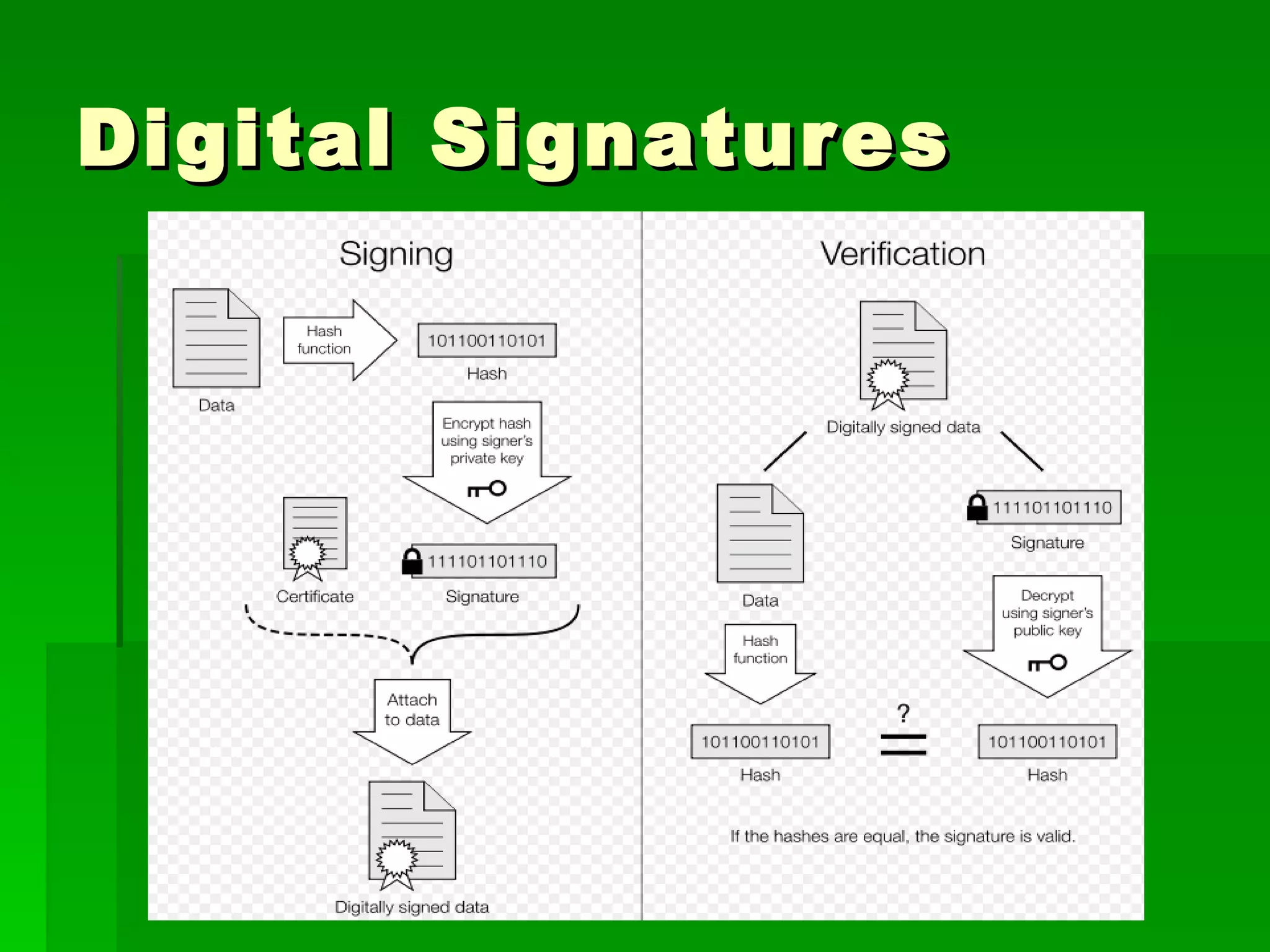
The document outlines fundamental concepts of information security, including historical cyber attacks, prevention strategies, and various types of security breaches such as phishing and denial of service attacks. It discusses the CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, availability), cryptography types, and various security protocols for systems and communications. Additionally, it covers incident responses, risk management practices, and the importance of maintaining up-to-date security measures.