The document provides an overview of the Indian pharmaceutical market. It discusses key trends in the market including its size, growth drivers, segments and future scope. Some of the main points covered are:
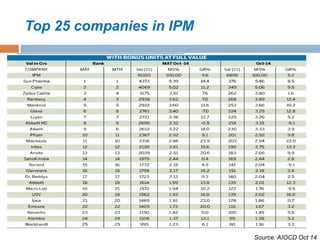
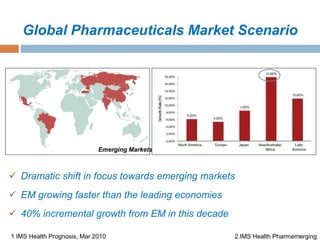
- The Indian pharma market is the 3rd largest by volume and 10th by value, with domestic sales of $6 billion and exports of $6.3 billion. It is expected to grow at 14% annually to $47 billion by 2018.
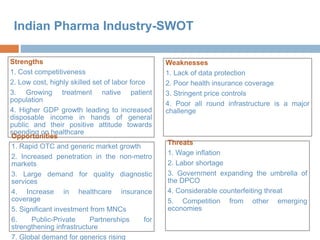
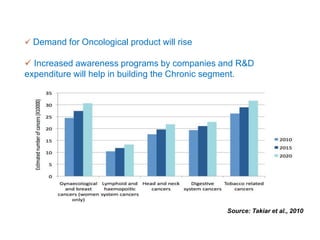
- Branded generics dominate at 90% of the market. Chronic therapies are growing faster than acute therapies. Rural markets represent 20% of the market currently and are seen as the next growth frontier.
- Key growth drivers include population expansion, a growing middle class