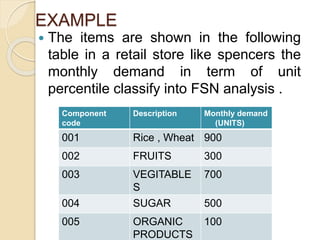
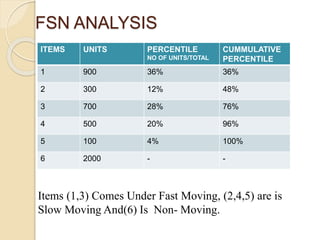
This document discusses various inventory control techniques, including ABC analysis, VED analysis, and FSN analysis. ABC analysis categorizes inventory into A, B, and C items based on their value and assigns different levels of control to each category. VED analysis classifies items as vital, essential, or desirable based on their importance to production. FSN analysis categorizes items based on their rate of consumption as fast, slow, or non-moving. The document provides examples and explanations of how to apply each technique.