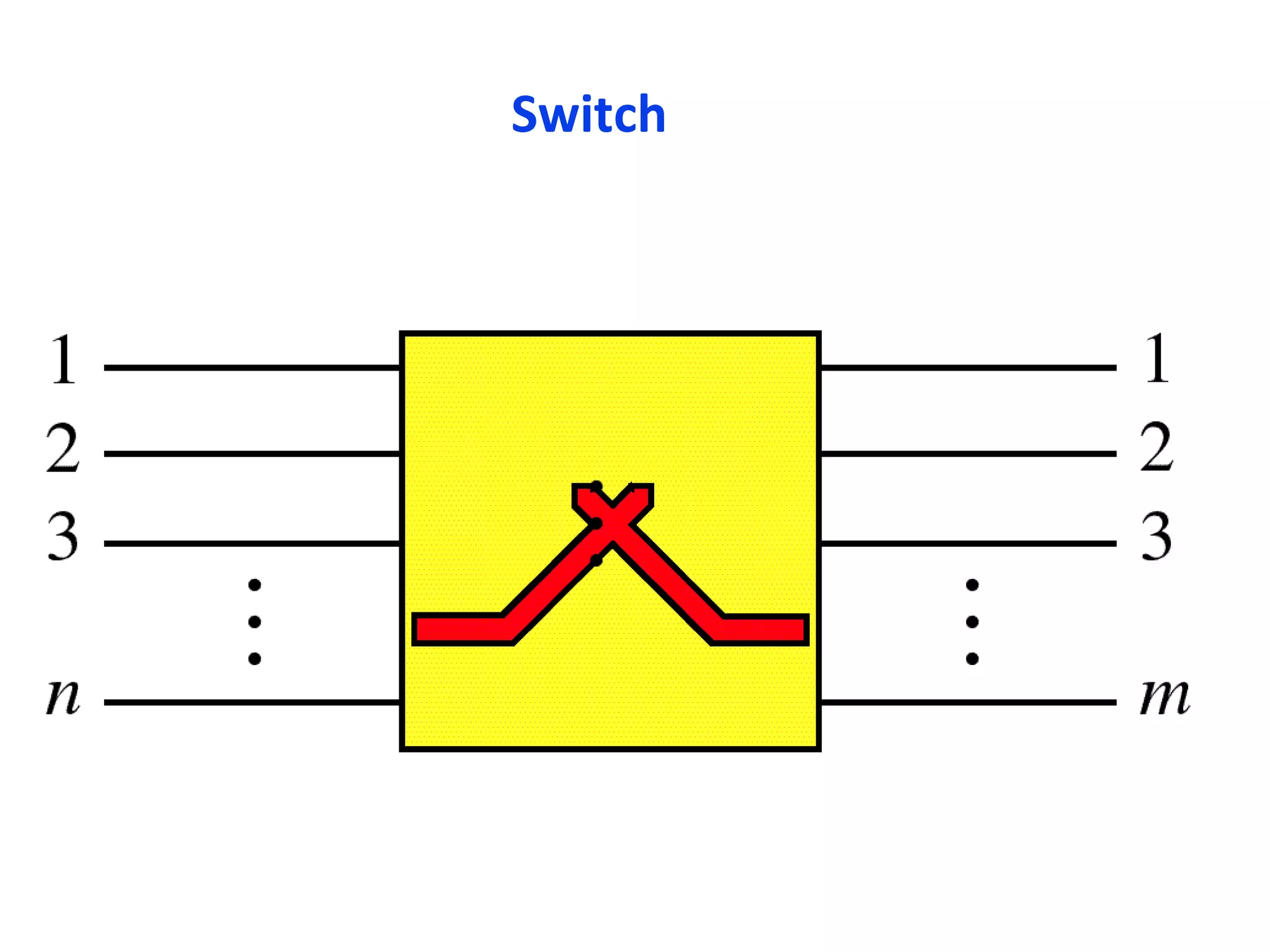
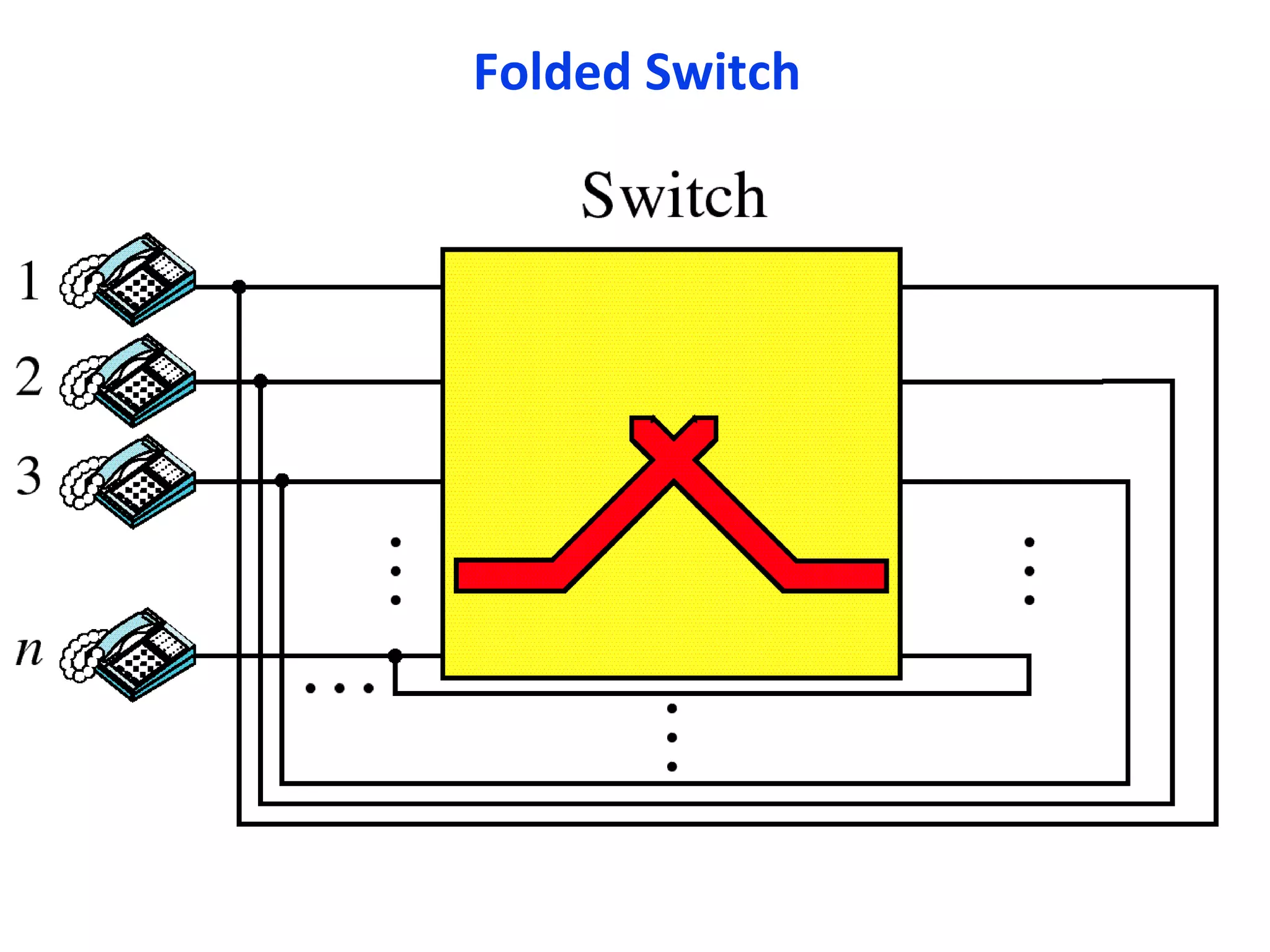
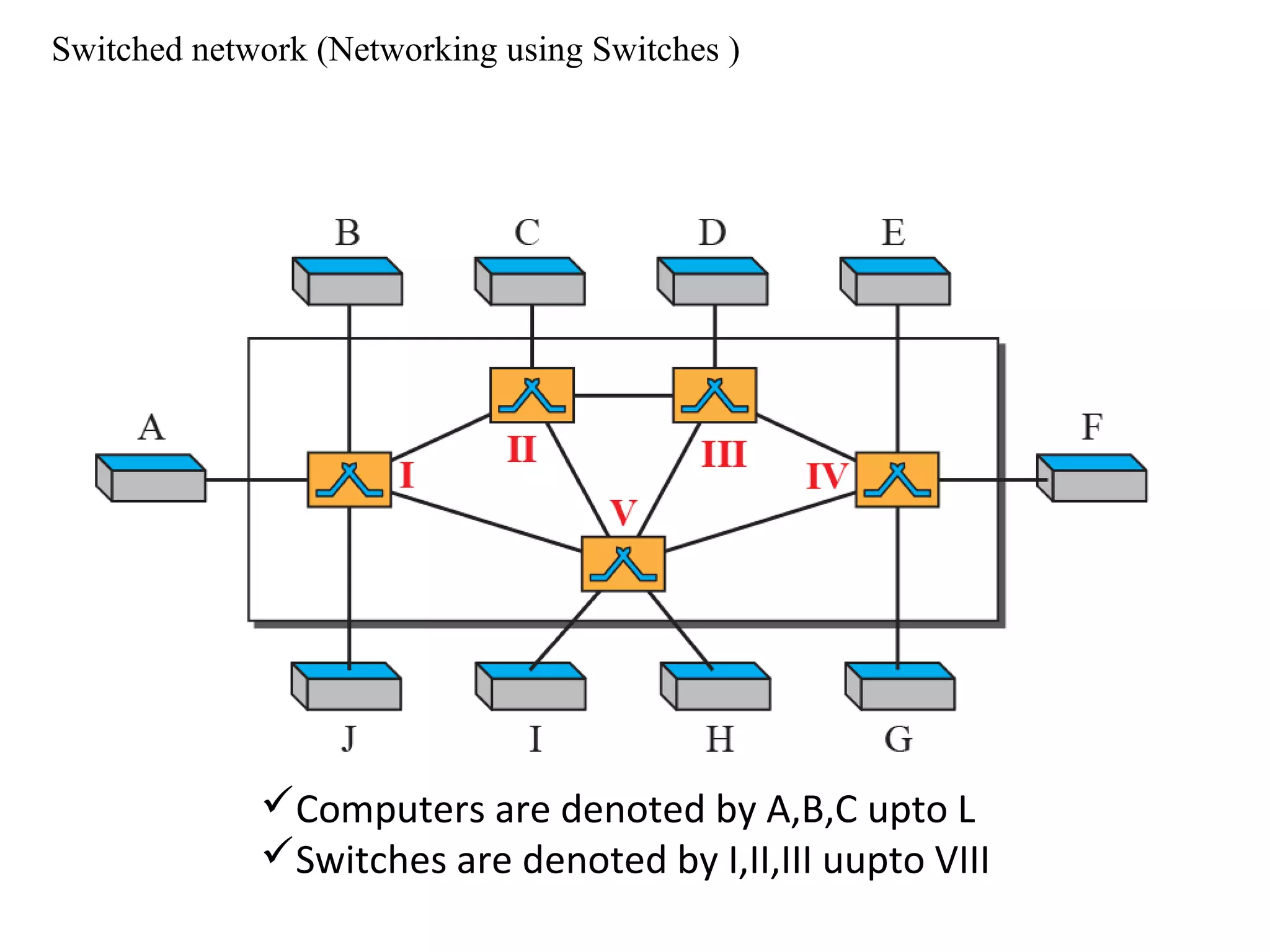
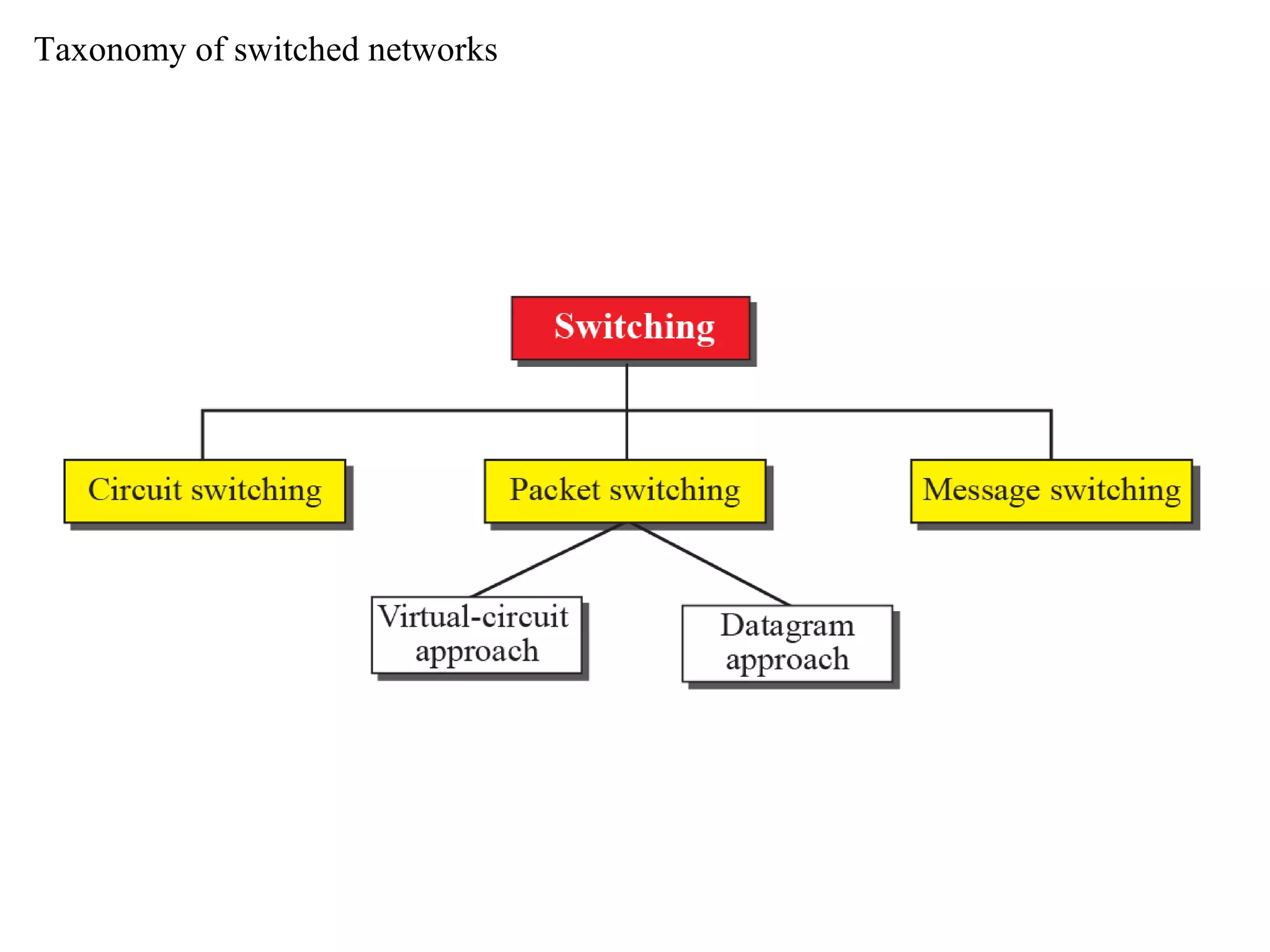
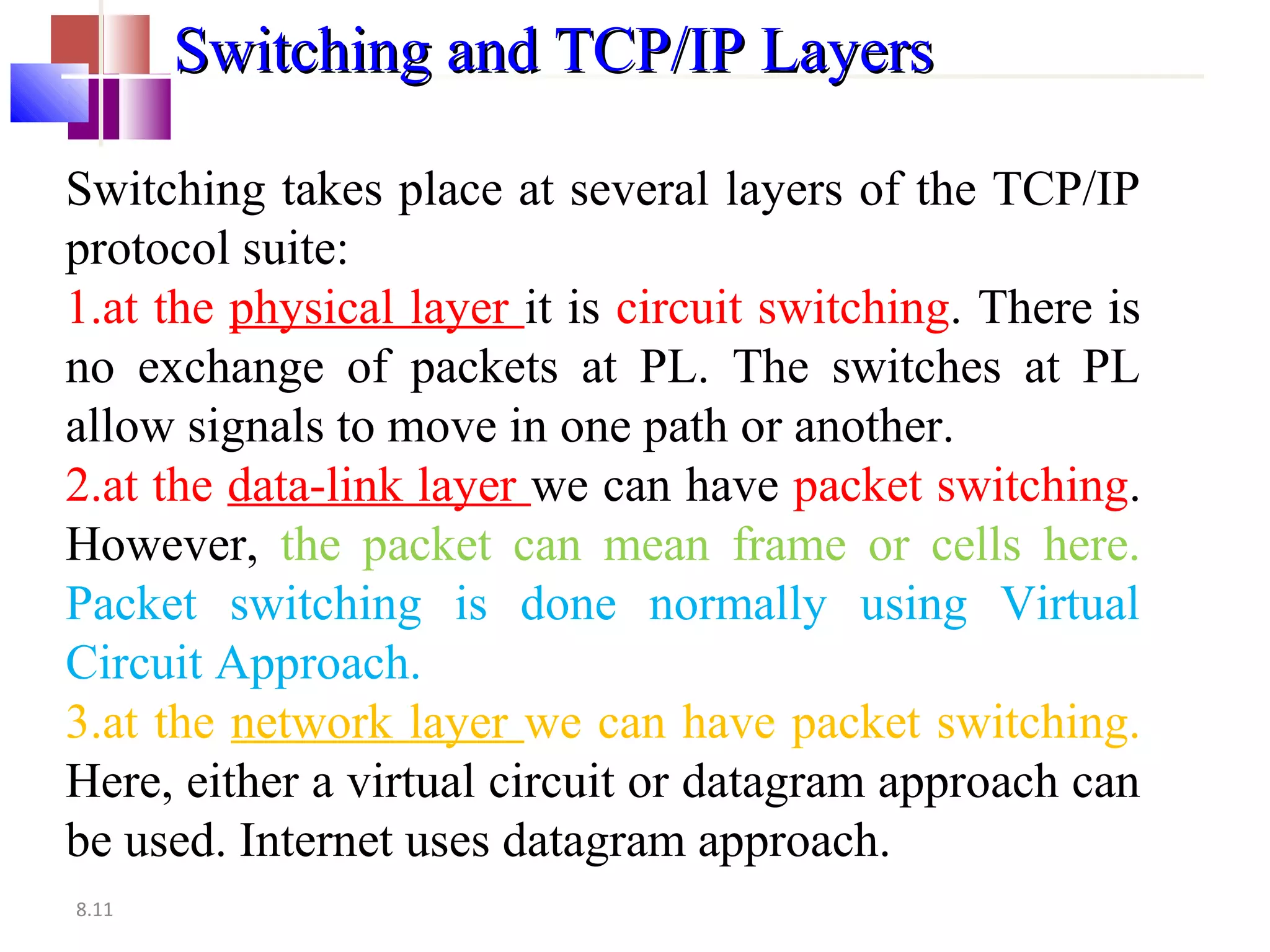
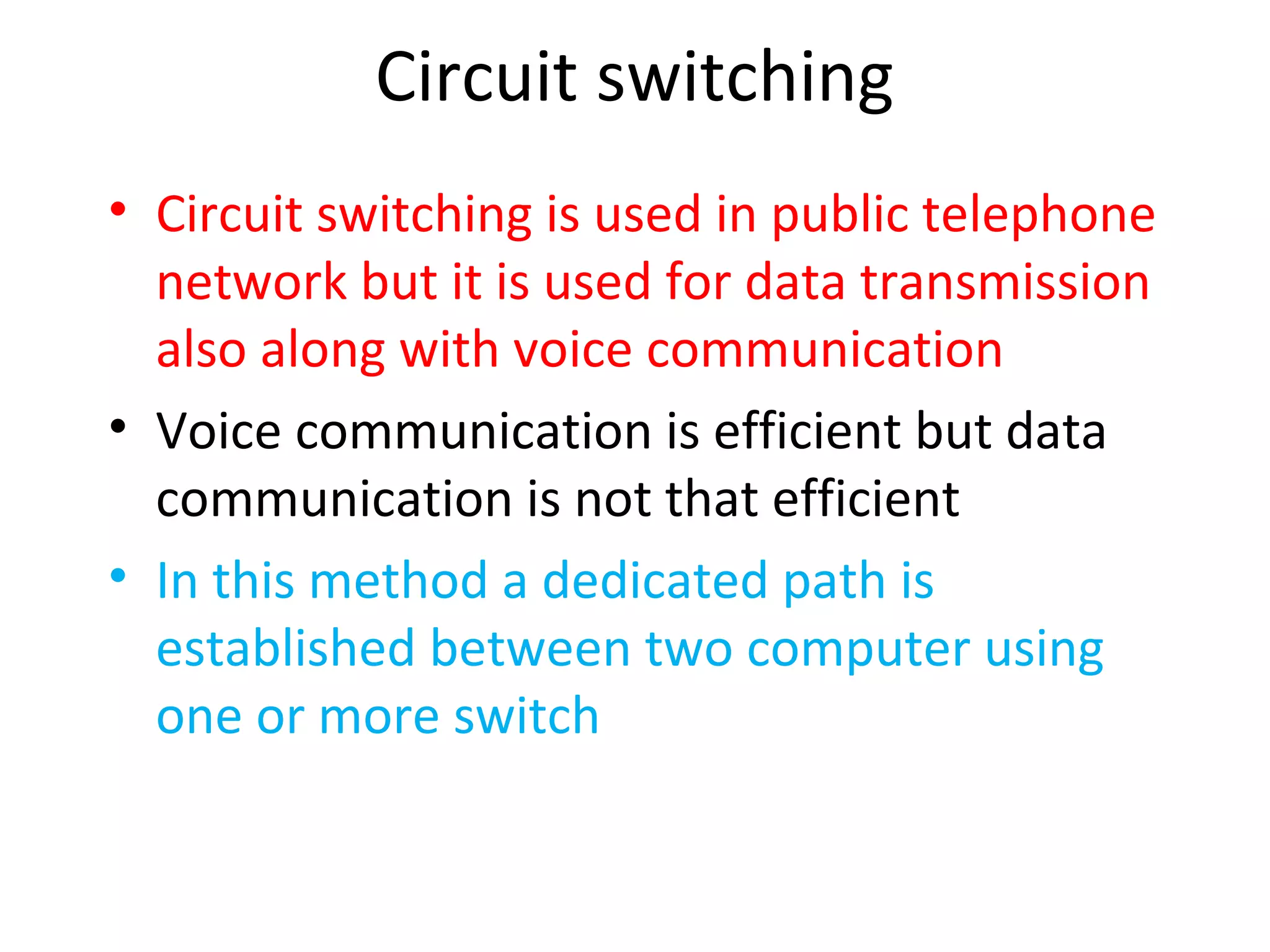
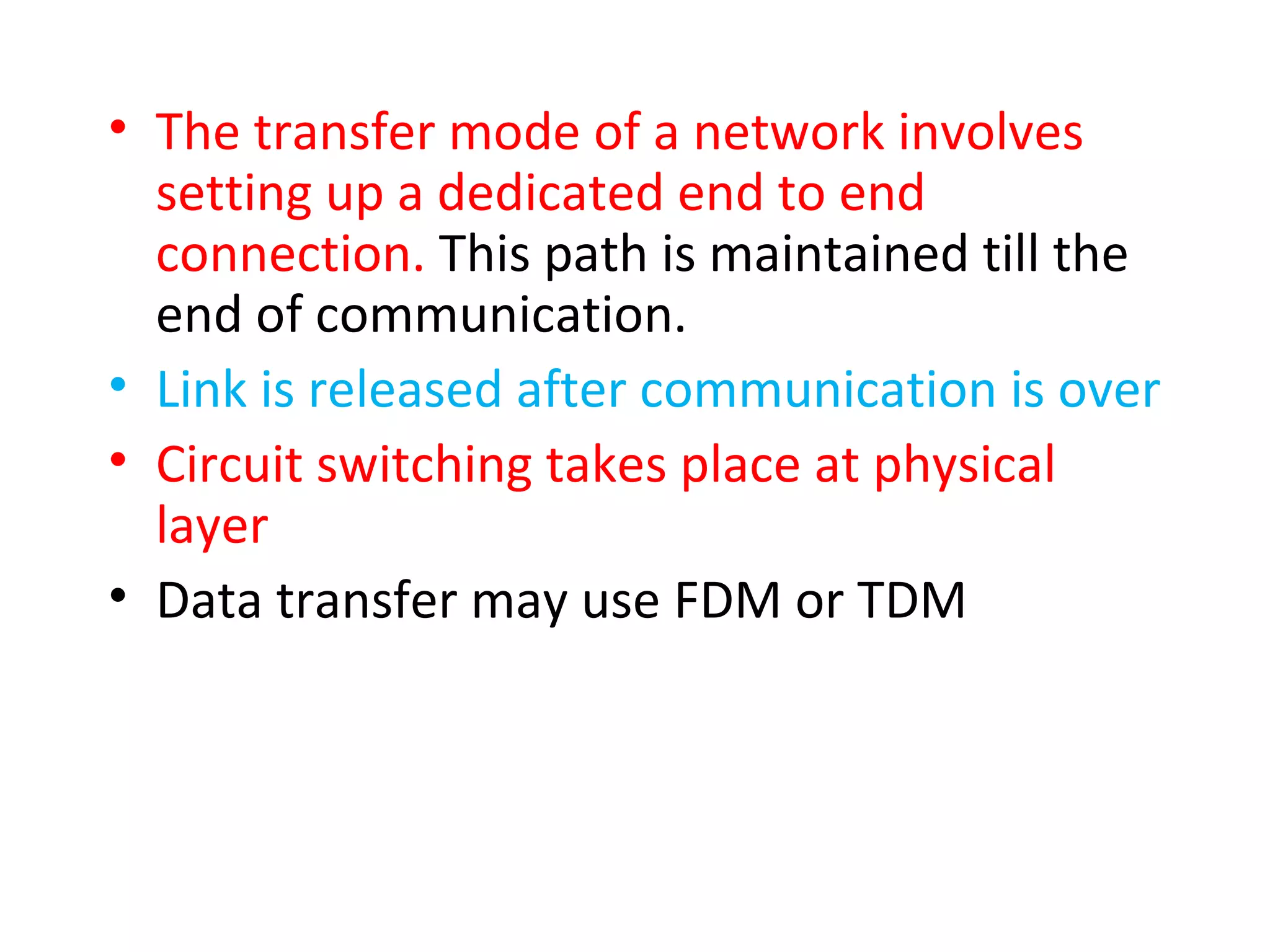
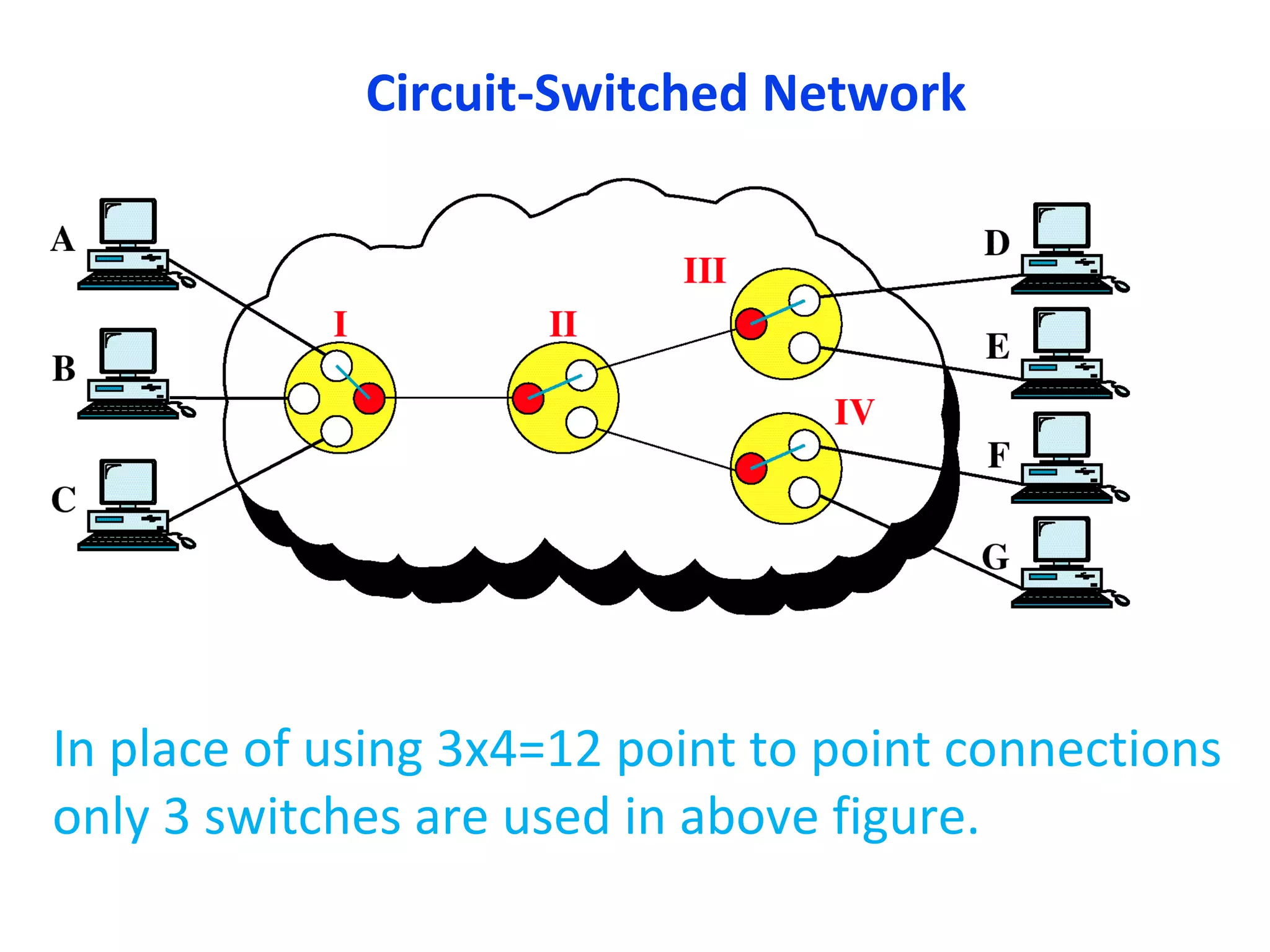
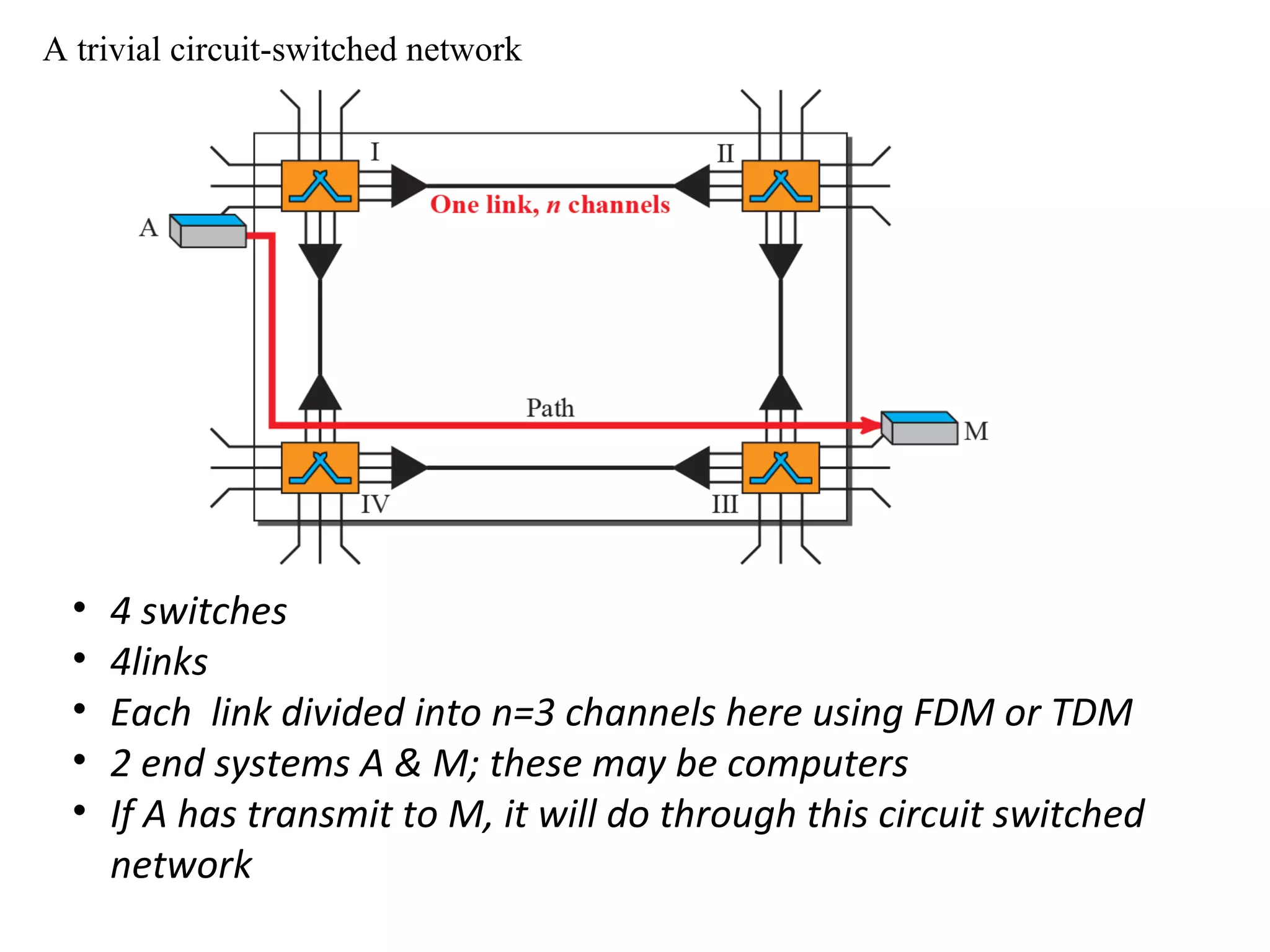
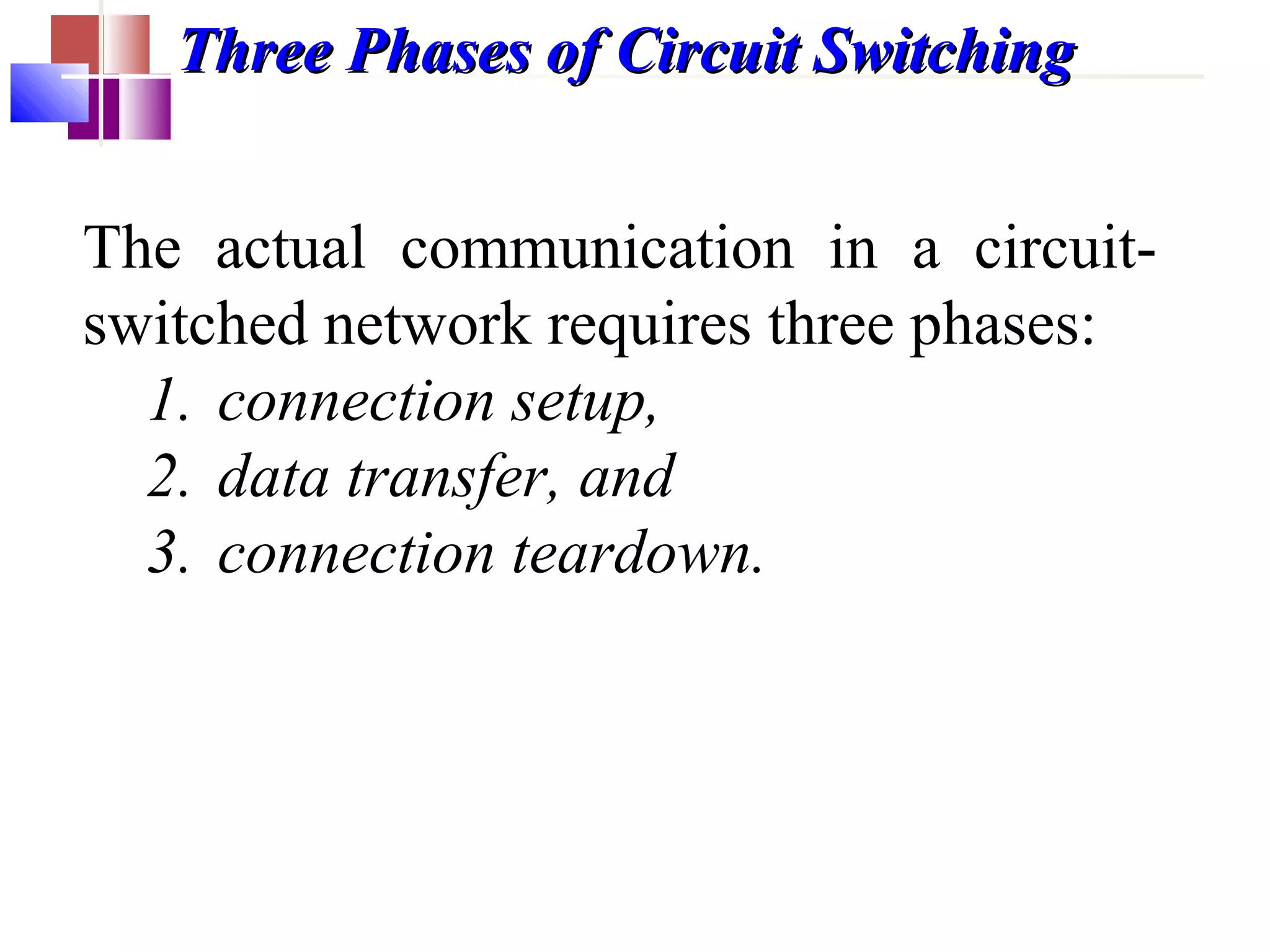
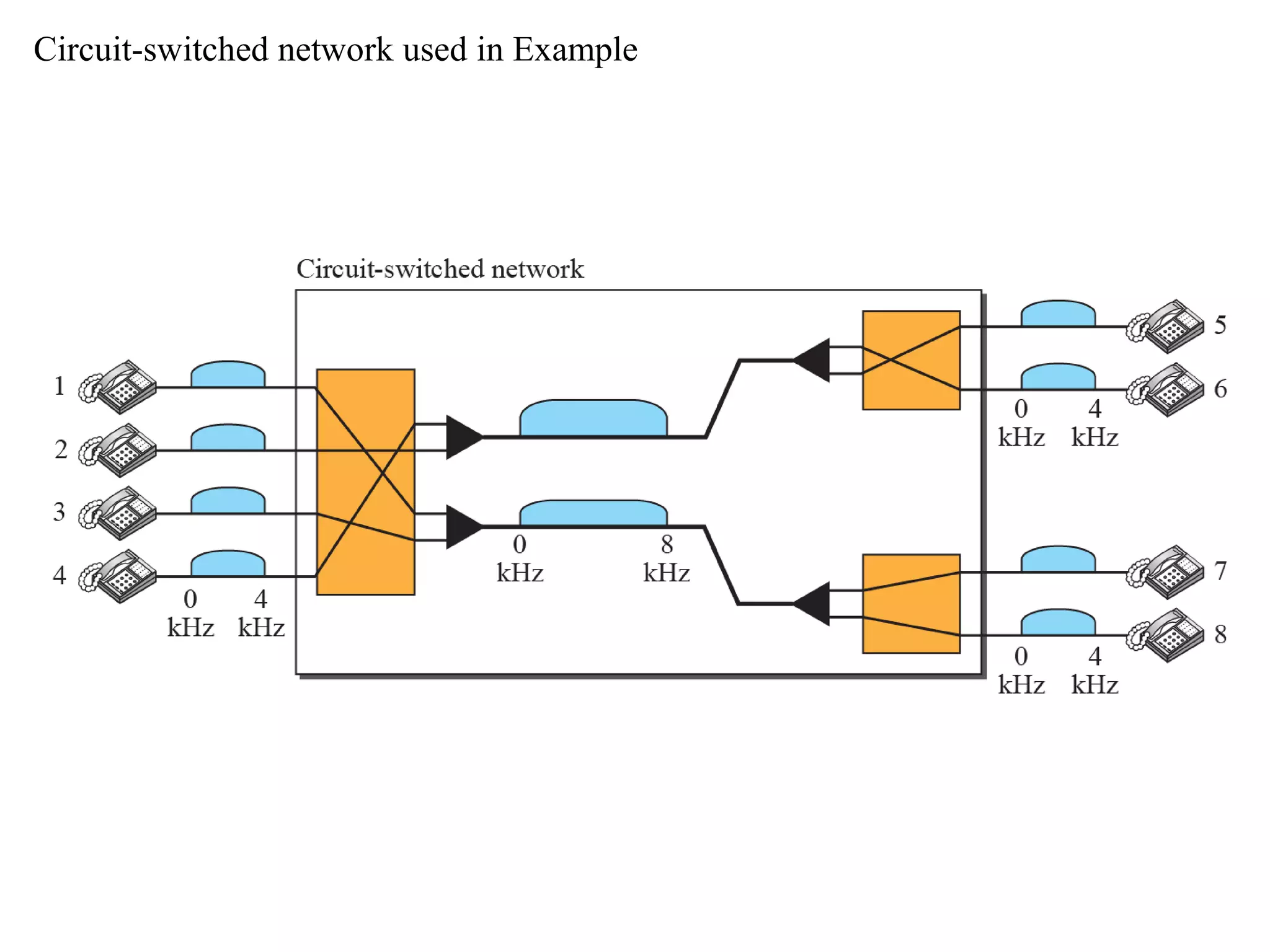
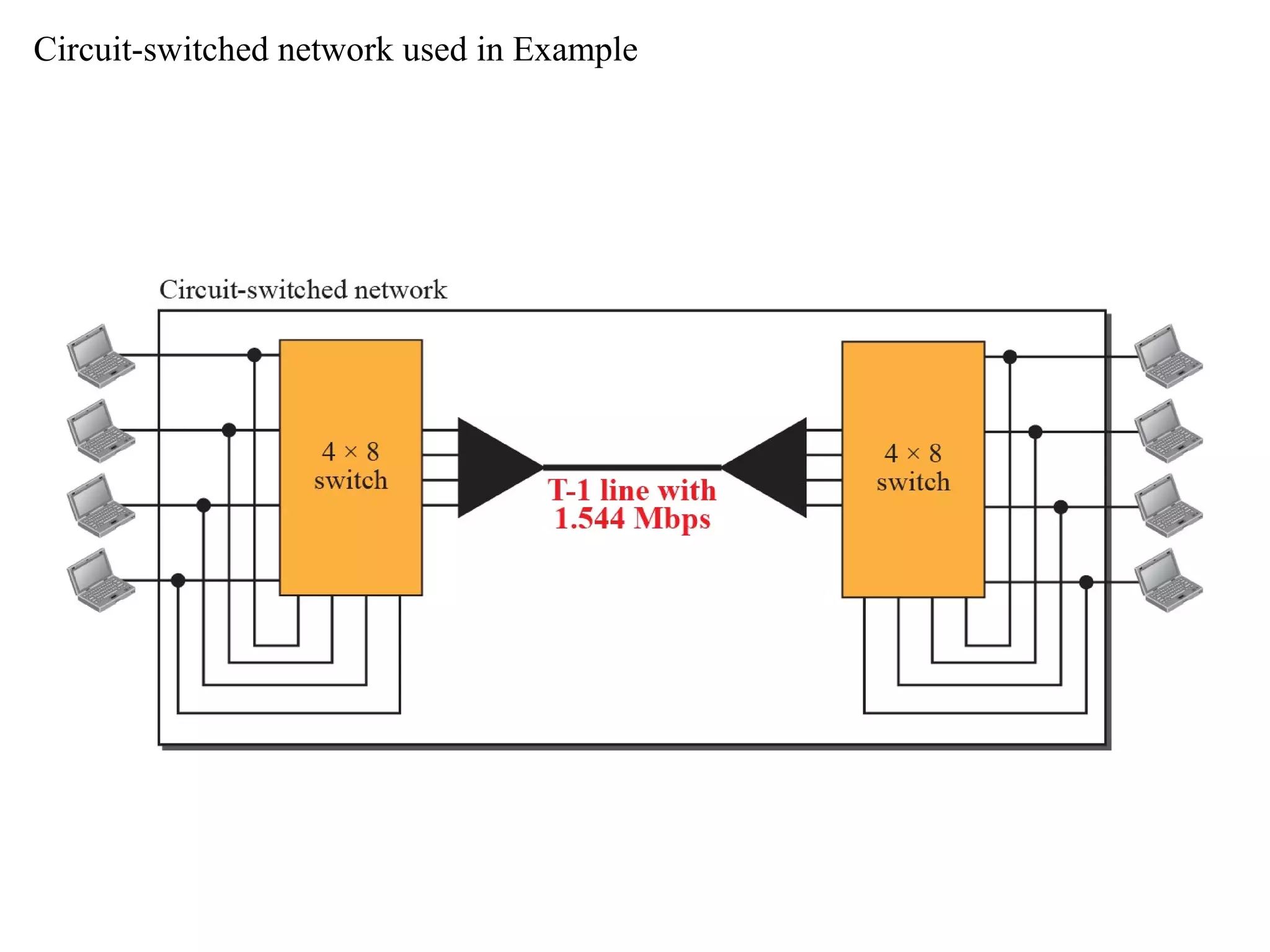
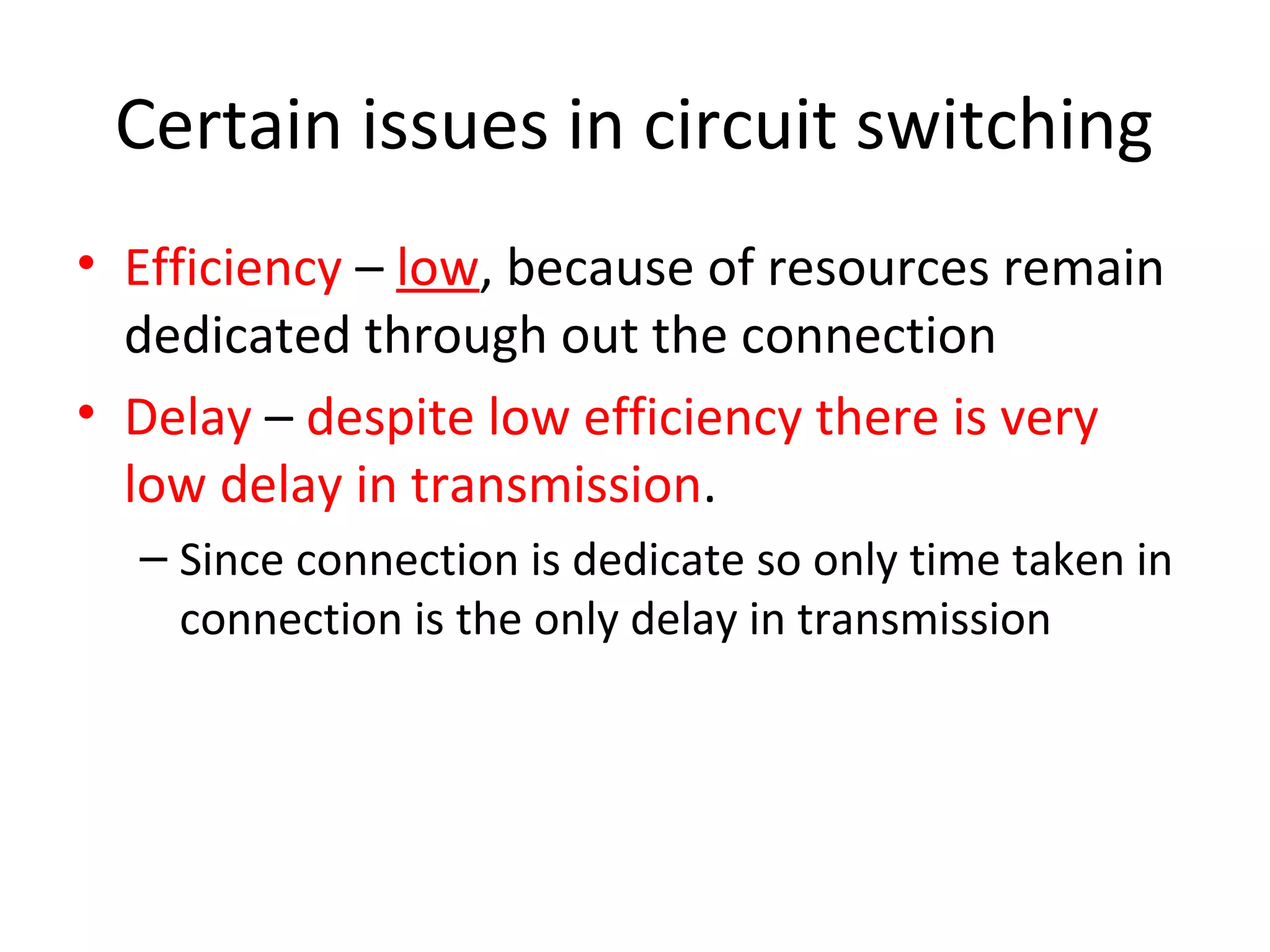
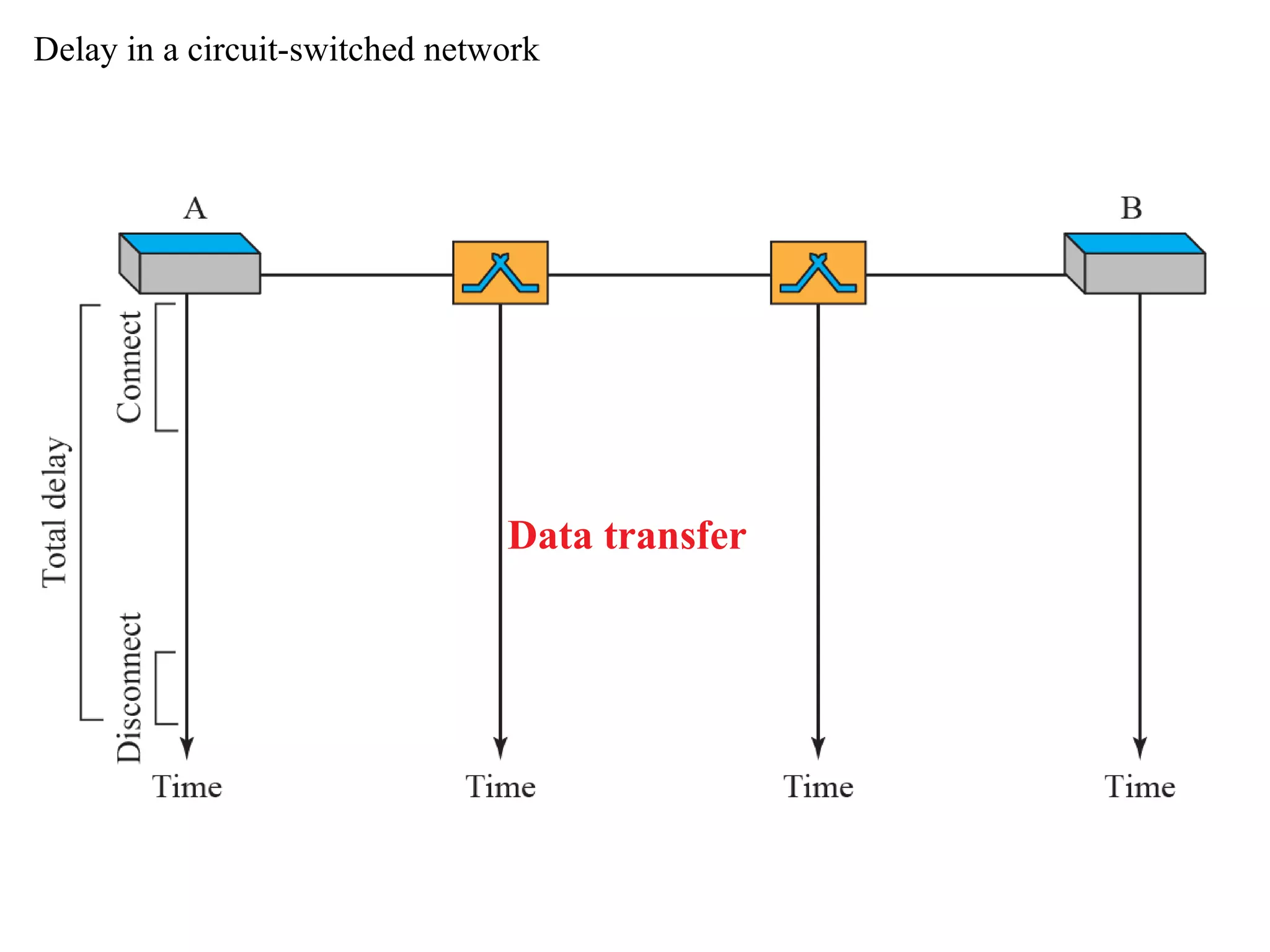
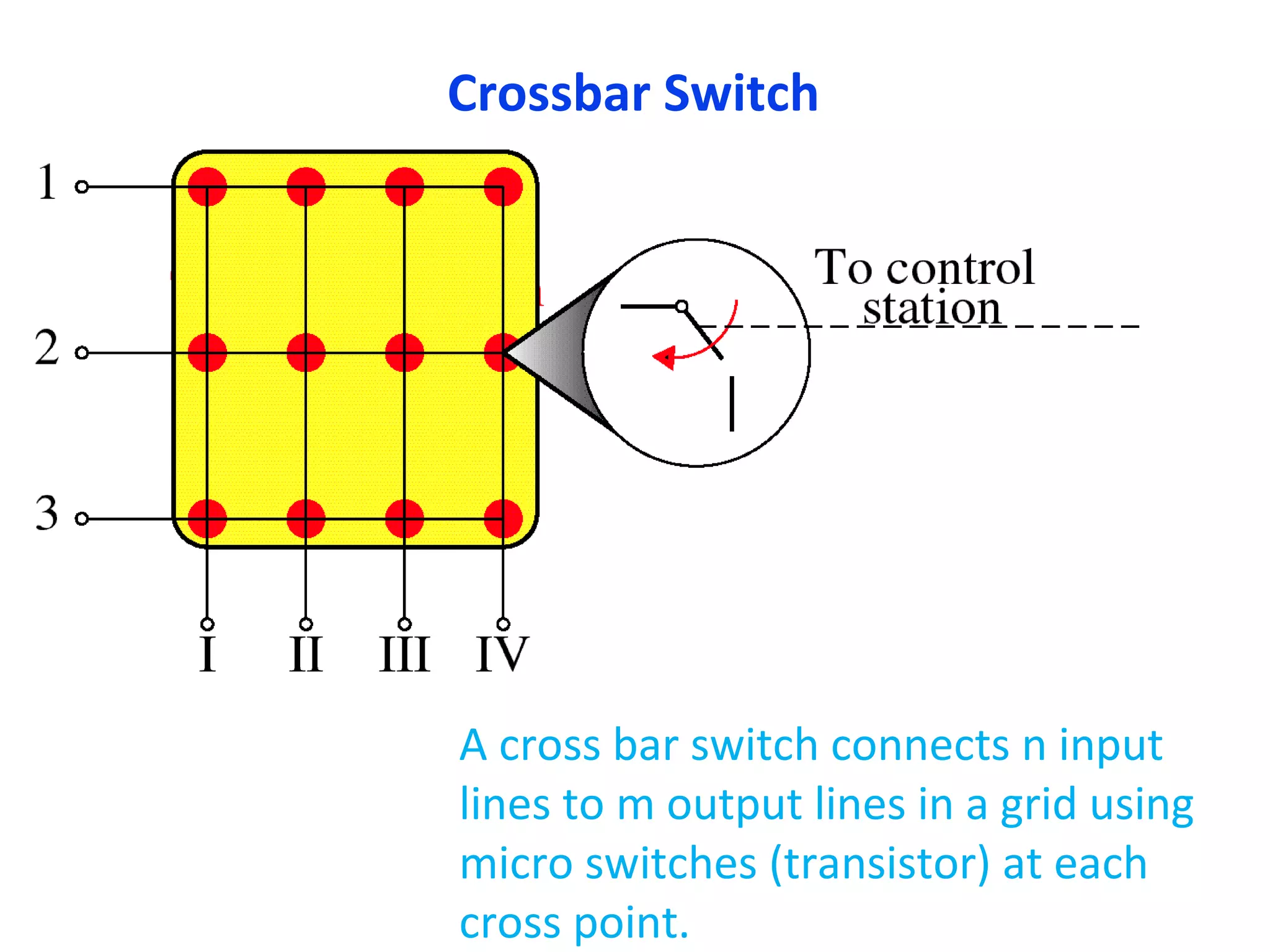
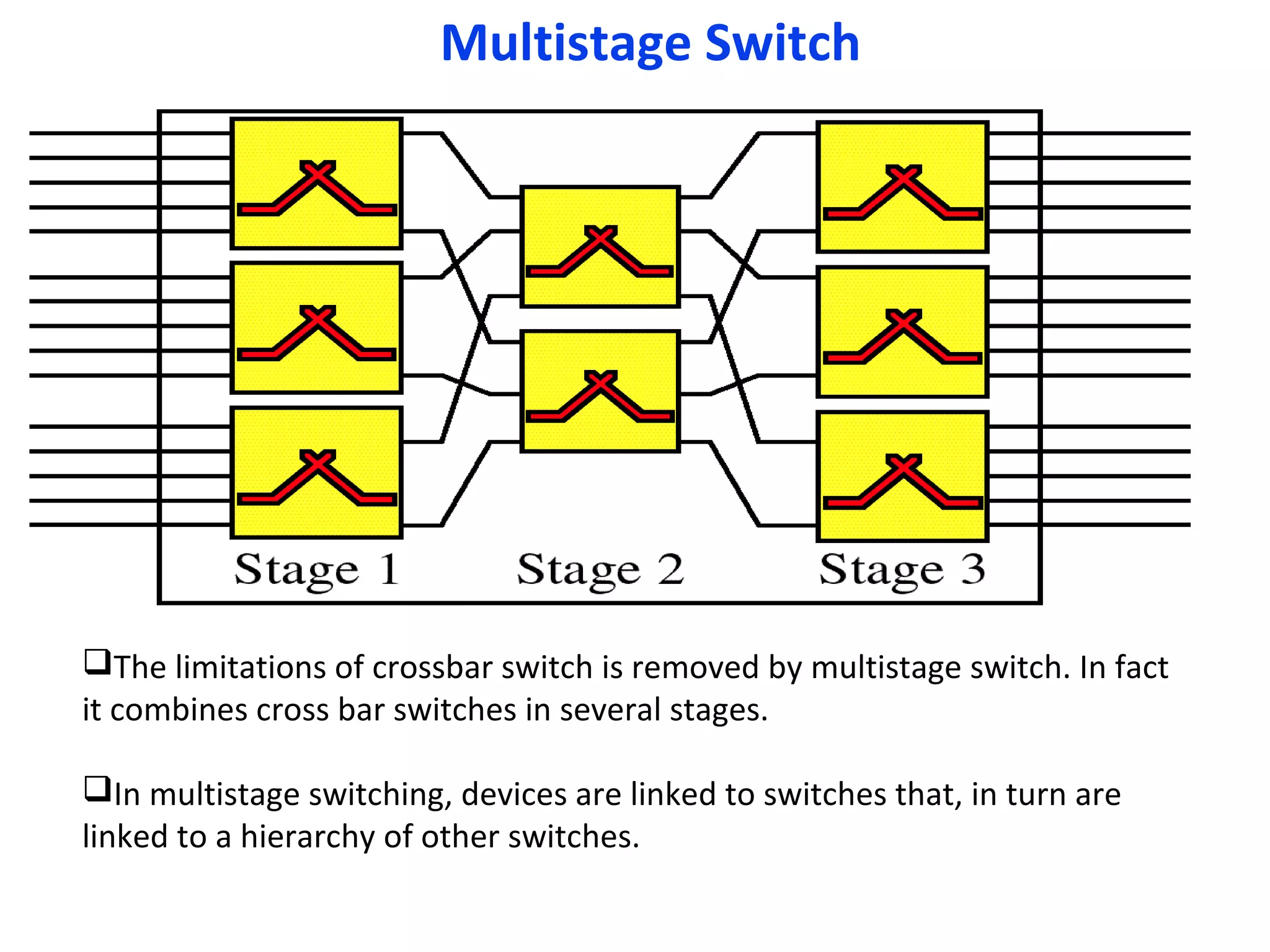
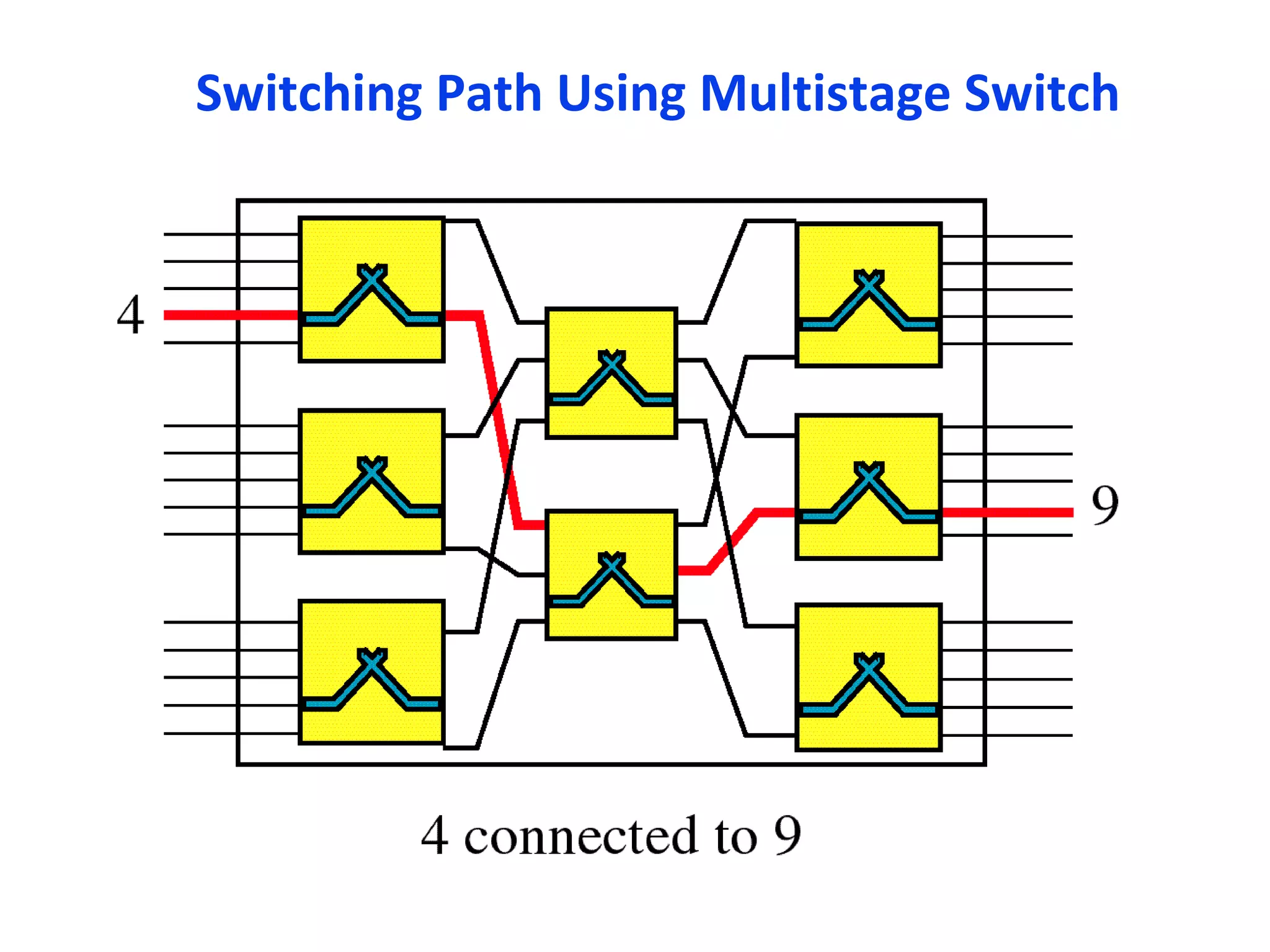
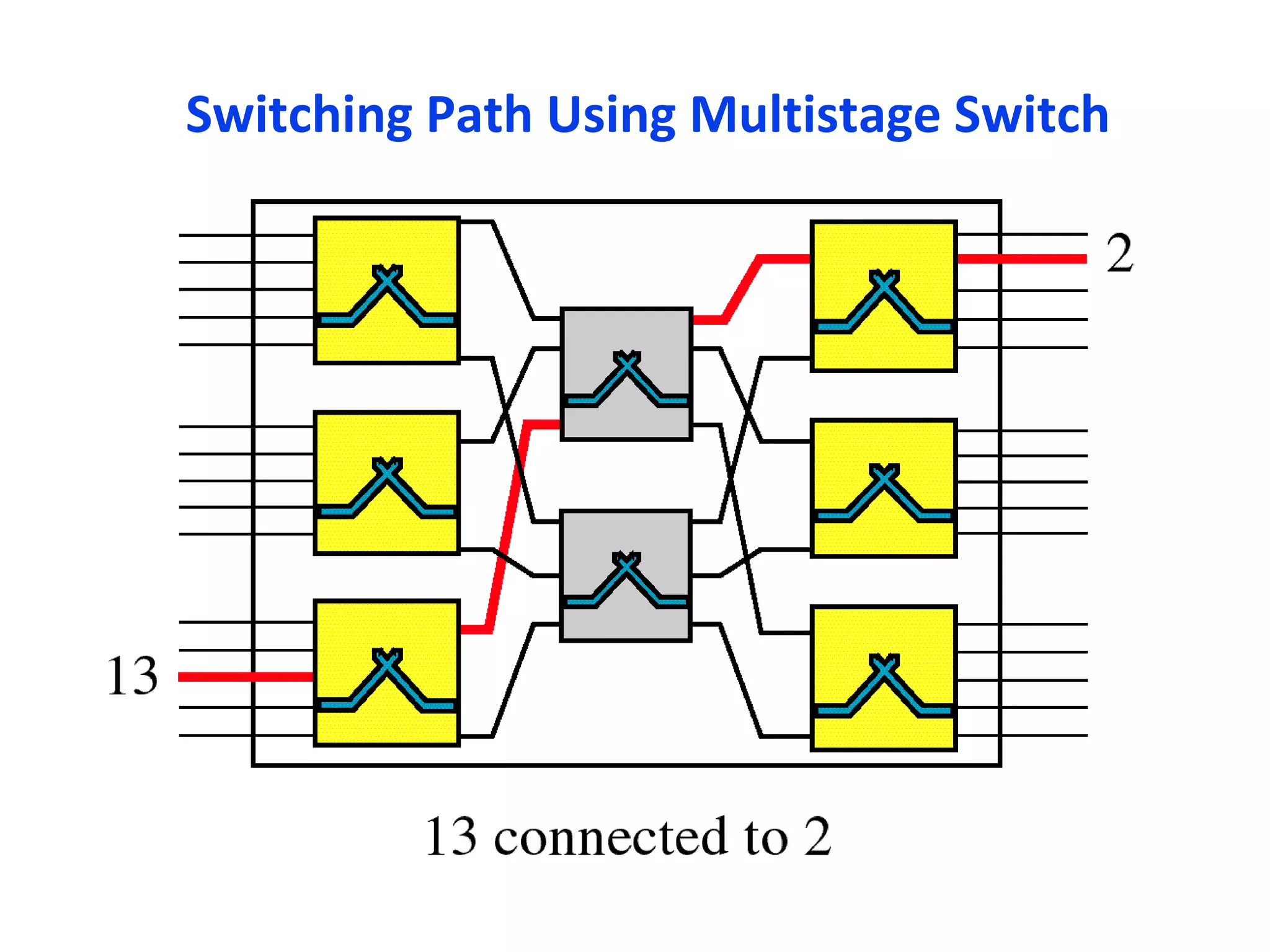
The document discusses circuit switching in data communication networks, describing circuit switching as a method of establishing a dedicated connection between devices using switches, which involves three phases of connection setup, data transfer, and connection teardown. Examples of circuit switched networks are provided, including the public switched telephone network and cellular data networks, and different types of switches used for circuit switching like crossbar and multistage switches are explained.