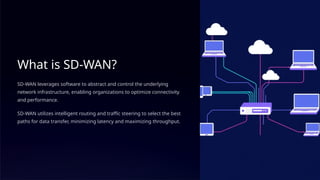
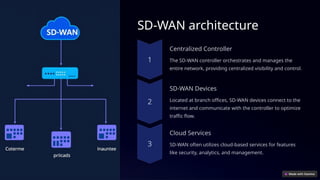
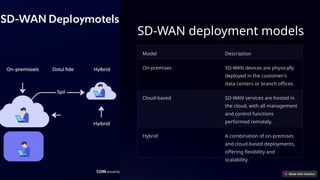
SD-WAN, or software-defined wide area network, revolutionizes traditional WANs by using software to optimize network traffic, offering improved flexibility and cost savings. It addresses the limitations of traditional WANs, such as limited bandwidth and high costs, by utilizing intelligent routing and centralized management. Key benefits include enhanced performance, significant cost savings, and simplified management, with future trends integrating AI, edge computing, and 5G technologies.