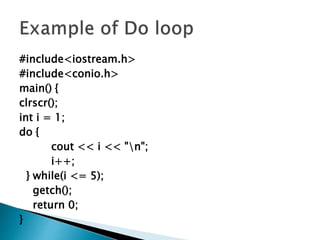
The document discusses different loop structures in Turbo C++ including for loops, while loops, and do-while loops. For loops allow code to be repeatedly executed and include an initialization, condition, and increment/decrement statement. While loops repeat code as long as a condition is true and check the condition before each iteration. Do-while loops are similar to while loops but check the condition after executing the loop code, so the code runs at least once.