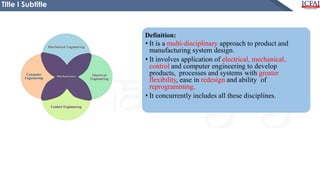
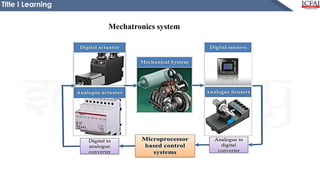
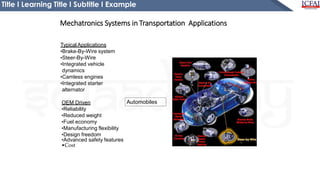
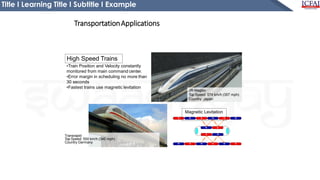
This document is a presentation on the introduction to mechatronics. It defines mechatronics as the application of electronics and computer technology to control mechanical systems. It discusses the importance of mechatronics in automation and provides examples of mechatronic systems in various applications like manufacturing, transportation, and daily life. The presentation aims to help students understand the basic concepts of mechatronics and how it integrates different engineering disciplines.