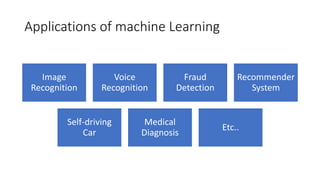
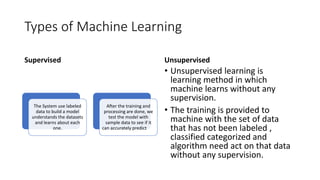
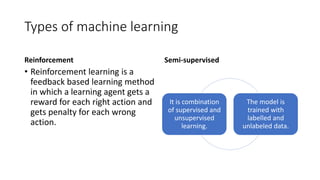
Machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, enables computers to mimic human behavior and has applications in areas such as image recognition and medical diagnosis. It encompasses various techniques like supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, with a life cycle that includes data gathering, preparation, model training, and deployment. The history of machine learning spans significant milestones from the conception of programmable devices in the 1830s to the rise of modern applications like self-driving cars and advanced AI systems.