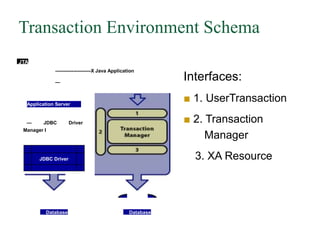
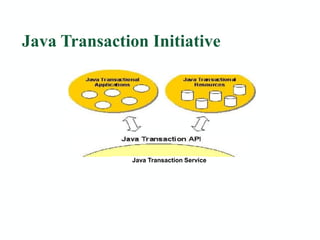
The Java Transaction API (JTA) provides a standard interface for managing transactions across multiple resources in Java applications. It specifies interfaces for a transaction manager and XA resource to enable distributed transactions between an application server, JDBC driver, and database. JTA transactions have ACID properties and allow the application developer to work with transactions without managing the underlying transaction coordination.