This document provides an introduction and overview of .NET including:
1) It describes what .NET is, the .NET framework, advantages of .NET and the CLR, and Visual Studio 2005.
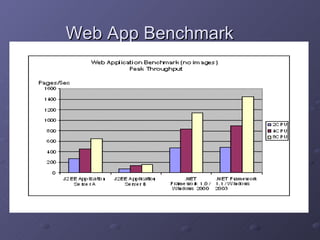
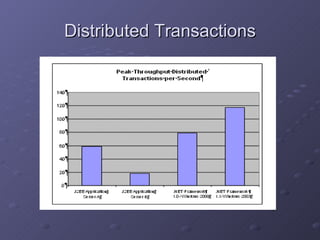
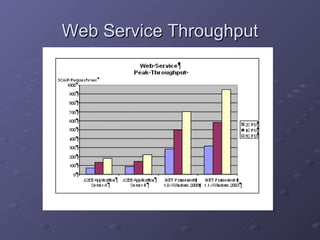
2) It outlines some of the main components of the .NET framework including namespaces, classes, and support for web standards.
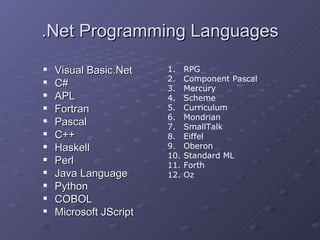
3) It compares C# and VB.NET programming languages and highlights some differences in syntax and features.











![C# vs. VB.Net C# class App { static void Main(string [ ] args) { int intCounter=0; foreach (string arg in args) { System.Console.WriteLine(“Counter:” + intCounter.ToString() + “=“ + arg); } //end of foreach } //end of Main() } //end of App{} VB.Net Class App Shared Sub Main(ByVal args as String( ) ) Dim arg as String Dim intCounter as Integer For Each arg in args System.Console.Writeline(“Counter: ” & intCounter & “=“ & arg) Next ‘For Each loop End Sub ‘end of Main() End Class ‘end of App{}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introdotnet-100802044905-phpapp01/85/Intro-dotnet-16-320.jpg)




