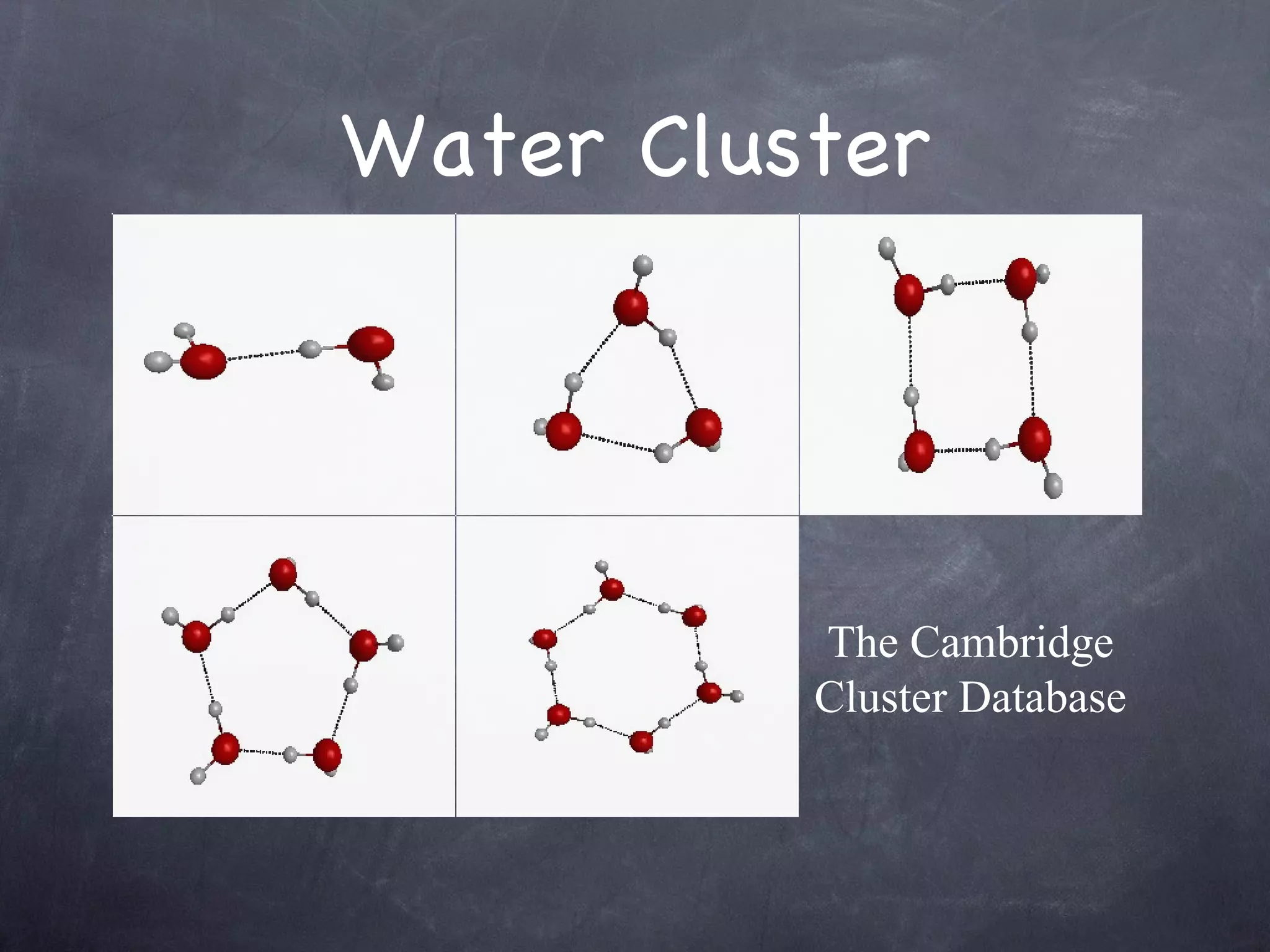
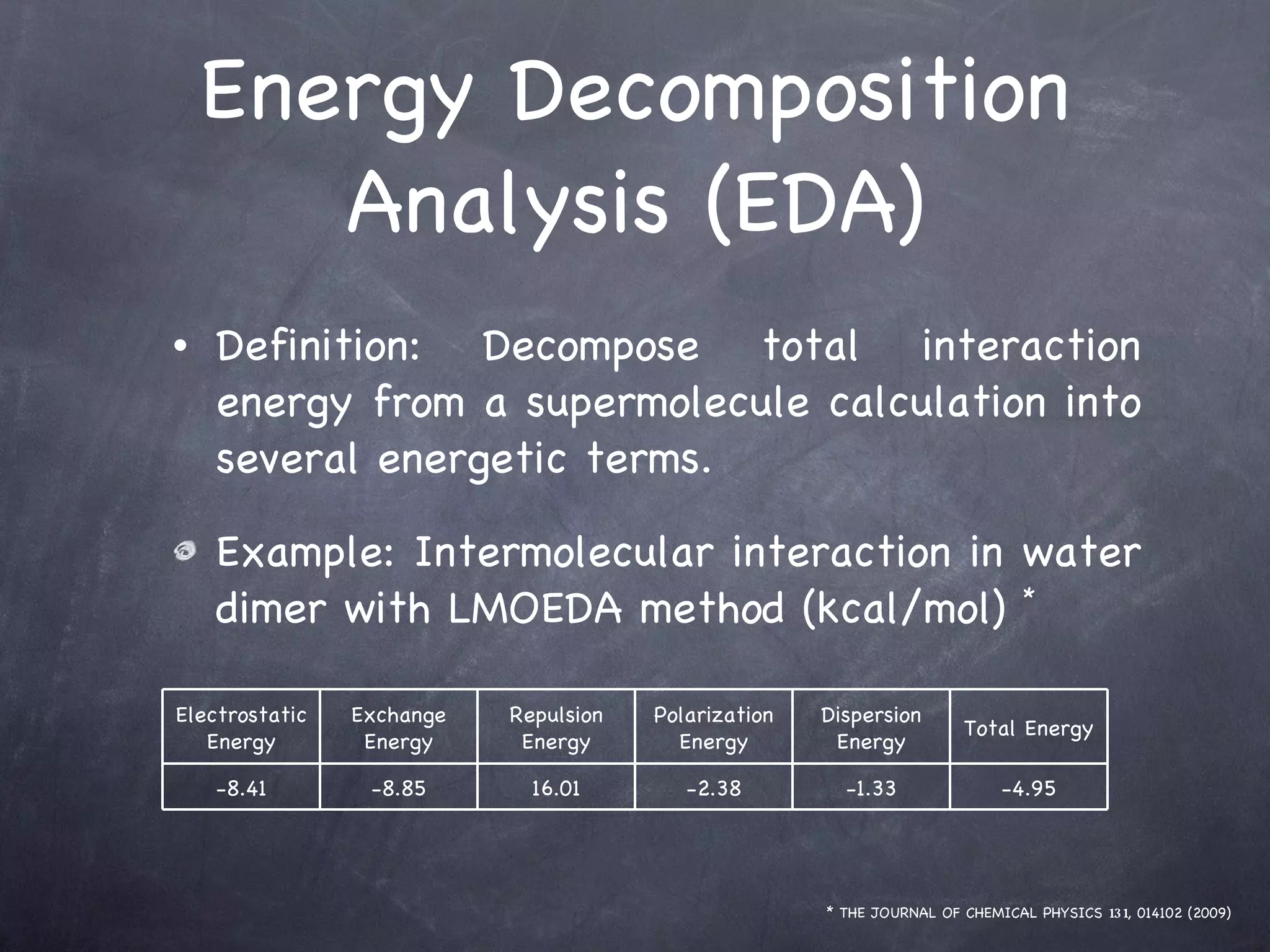
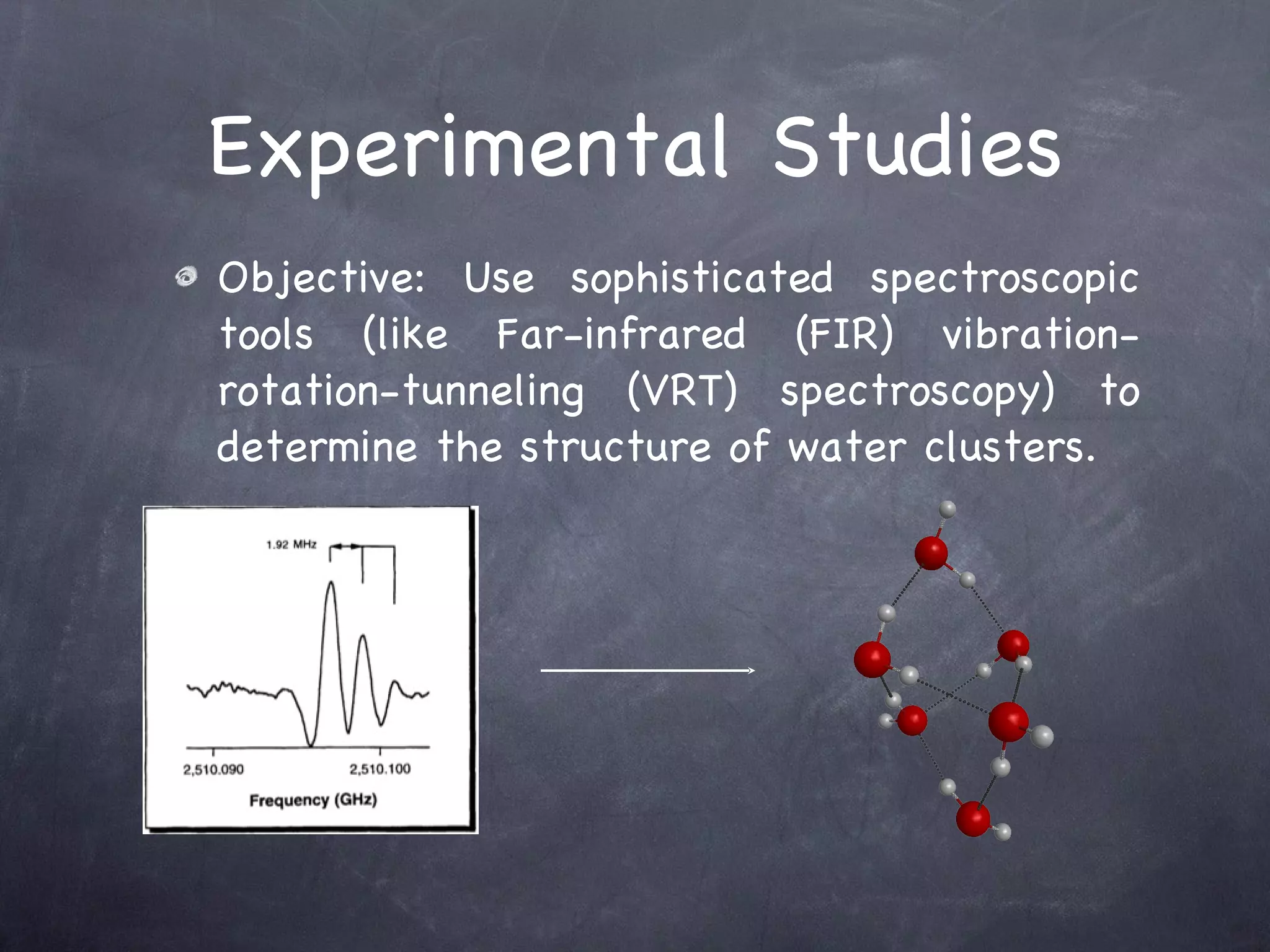
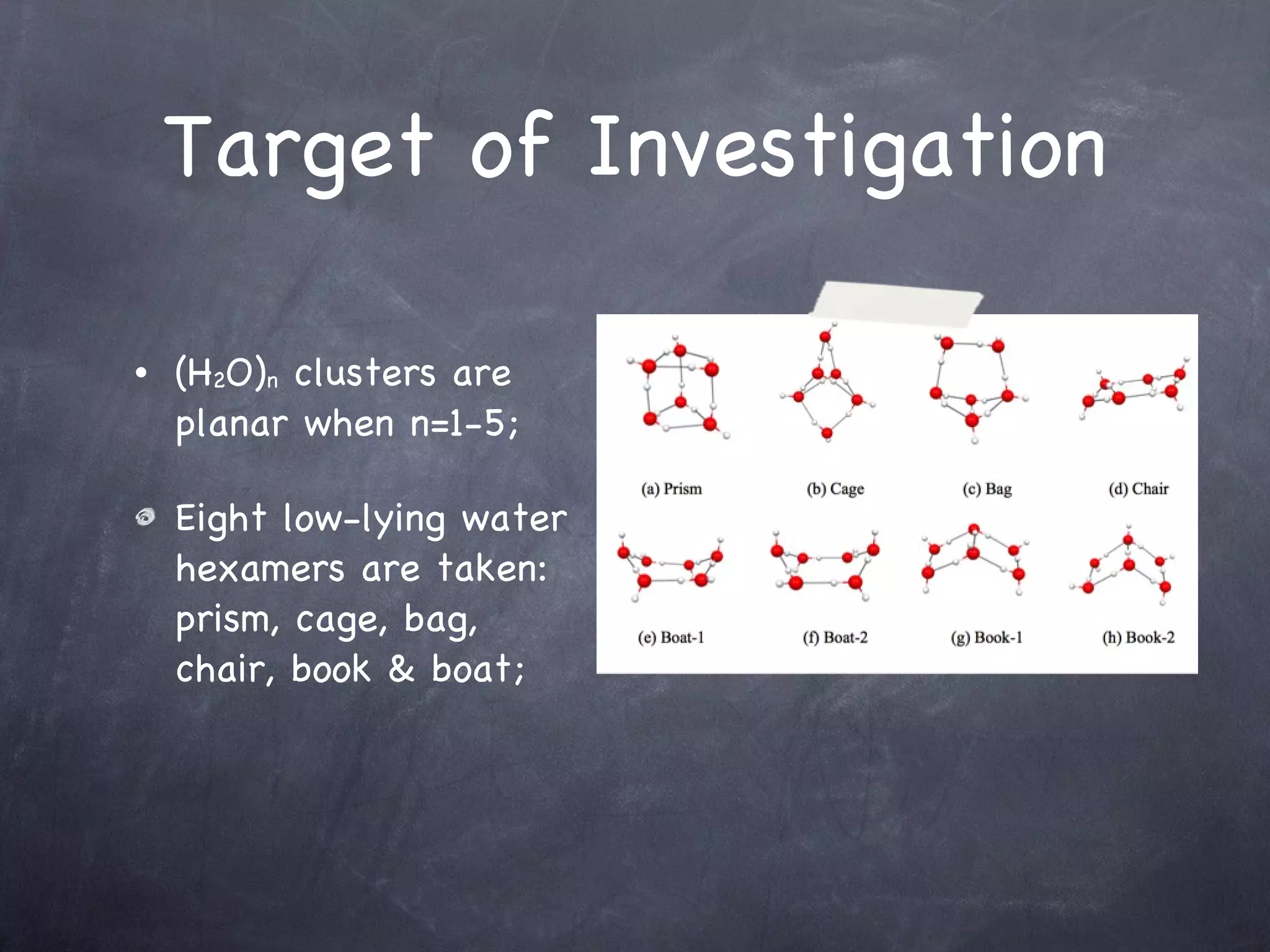
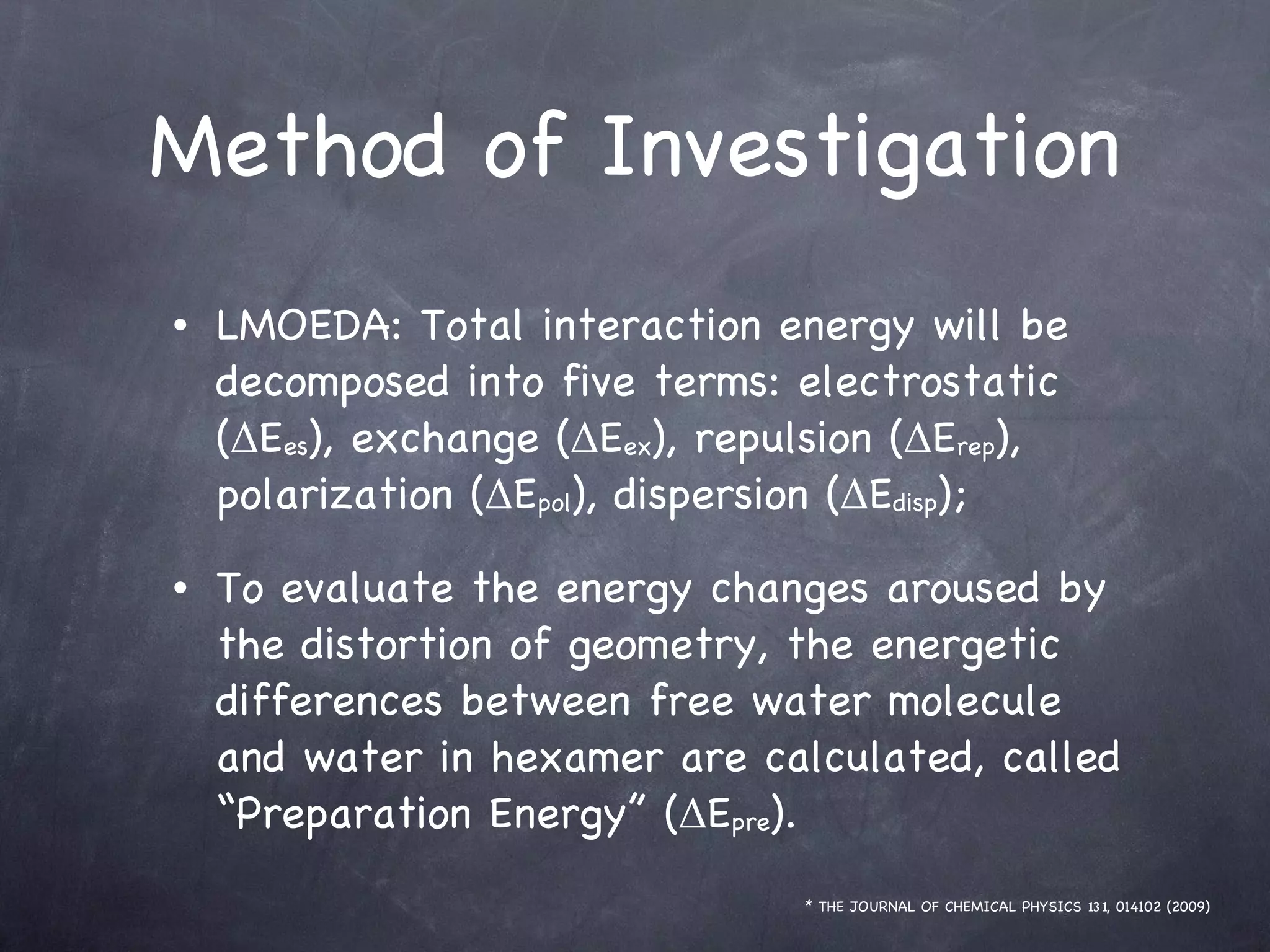
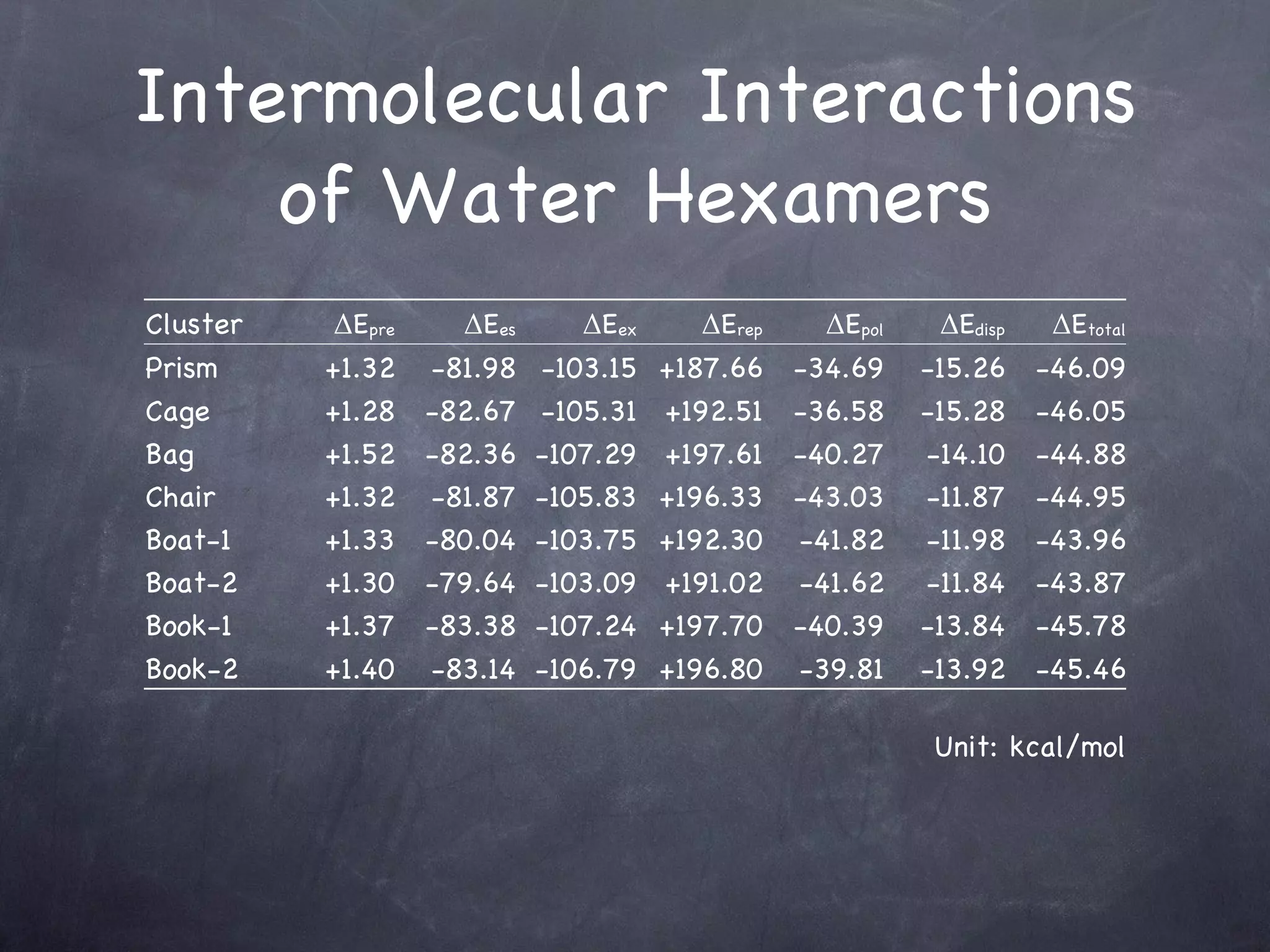
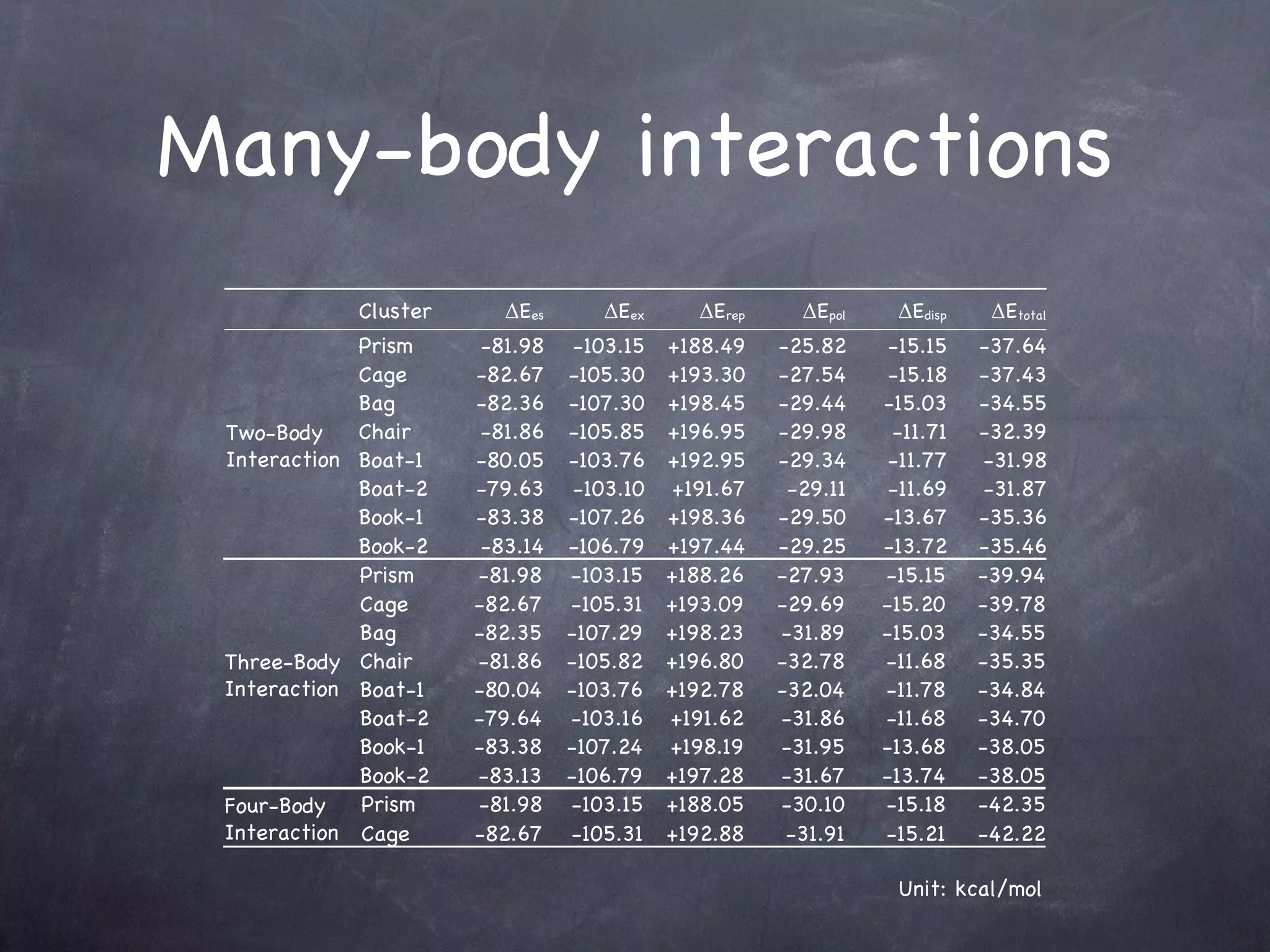
The document discusses intermolecular interactions in water hexamers using energy decomposition analysis. It analyzes eight low-lying structures of the water hexamer and decomposes the total interaction energy into electrostatic, exchange, repulsion, polarization, and dispersion terms. It finds the repulsion energy roughly equals the sum of electrostatic and exchange energies. It also examines the additivity of interaction energy terms between two-body, three-body, and four-body interactions and finds the electrostatic and exchange energies are strictly additive while repulsion and dispersion energies are roughly additive.