This course provides an overview of Python programming. It covers setting up the Python environment, variables, data types, conditional and iterative statements, functions, strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, classes and objects, files, exceptions, and regular expressions. The course aims to help students develop foundational Python skills through hands-on coding exercises. It is intended to be a short, bite-sized introduction to the Python language.



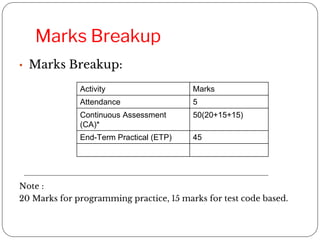


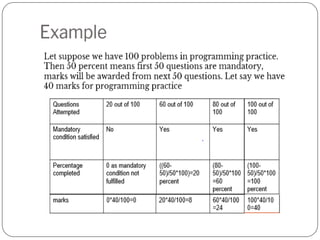

![Performance in best 2 Code based
test[x]
Weightage of programming practice
x>=81 percent 100 percent marks of programming
practice
71<=x<=80 70 percent marks of programming
practice
51<=x<=70 50 percent marks of programming
practice
30<=x<=50 30 percent marks of programming
practice
X<30 No marks will be awarded in
programming practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int108l02-230903065347-6e8720cc/85/INT108L0-2-pptx-9-320.jpg)