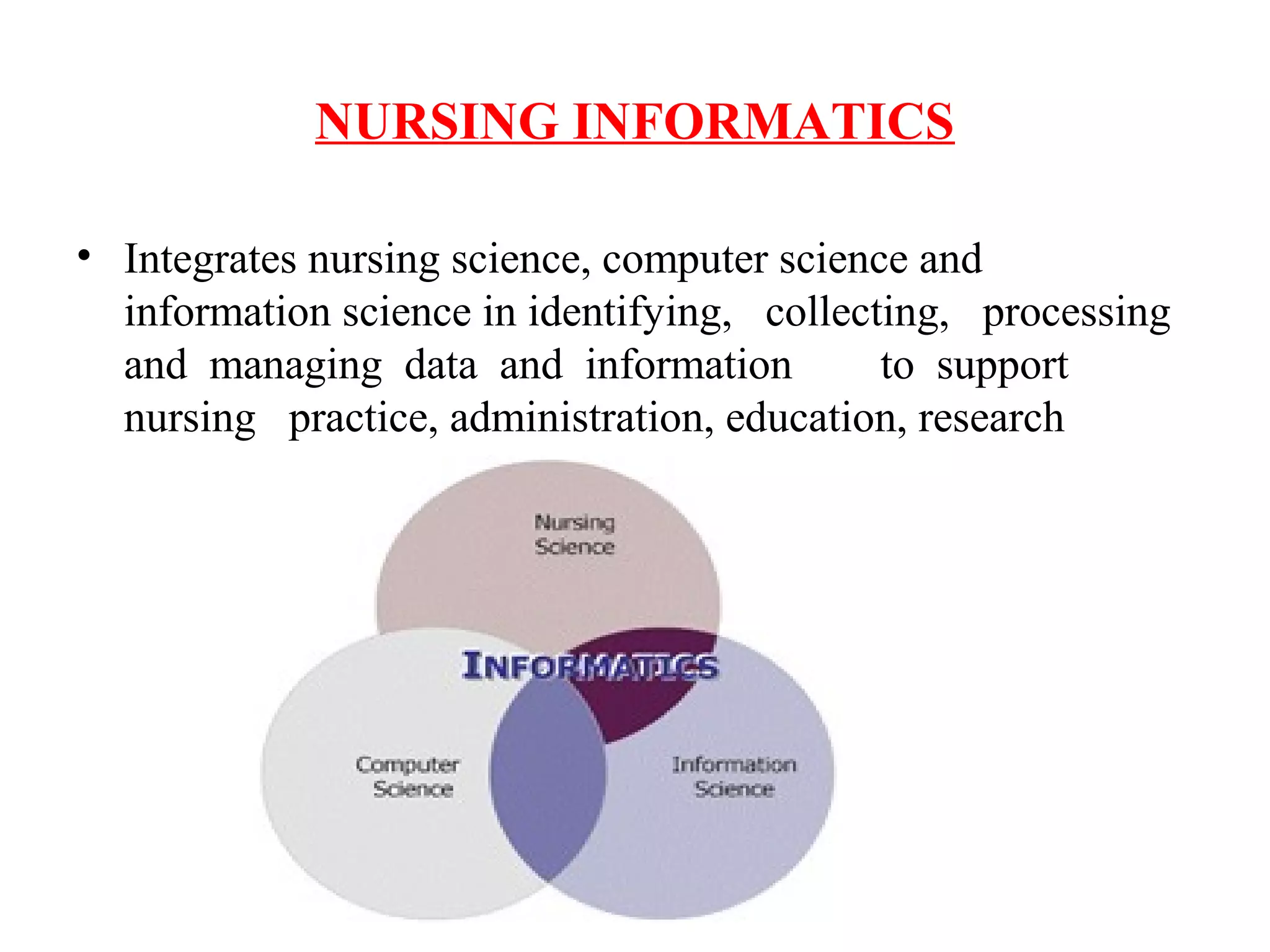
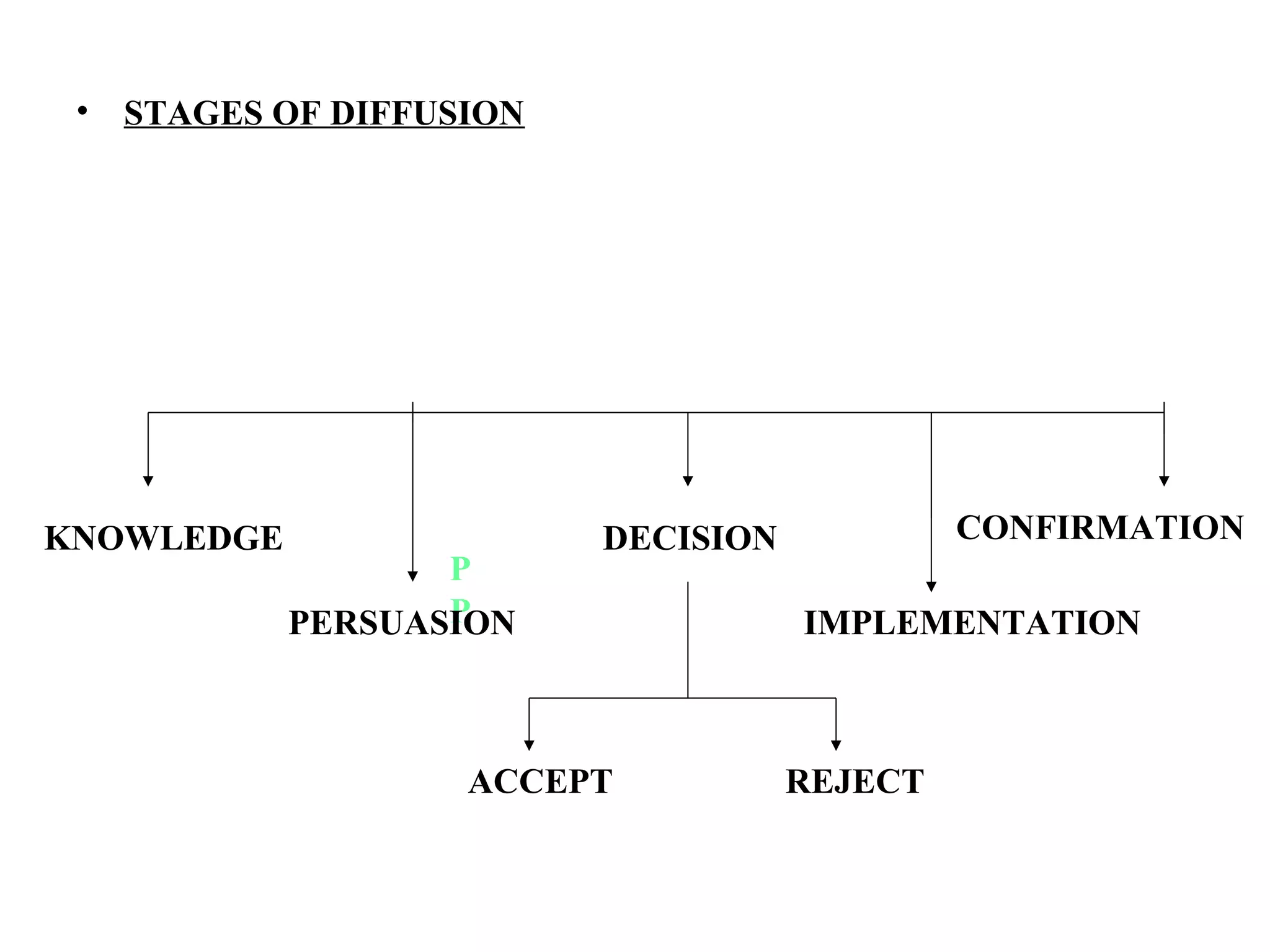
This document discusses innovation in nursing. It defines innovation as generating new ideas or applying existing ideas in new ways to improve organizations. The need for innovation in nursing is driven by demands for improved healthcare quality, growing healthcare needs, and workforce shortages. Characteristics that influence how innovations are adopted include relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability, and observability. The document then discusses various innovations in nursing education, clinical practice, administration/management, research, and primary/community healthcare. These innovations include technologies like e-learning, simulators, and electronic medical records as well as new nursing roles and programs.